All causes of burping air and a lump in the throat, diagnosis and treatment options
A sore throat is a pathological condition in which an unpleasant pressing sensation occurs in the throat area; if it is accompanied by belching, it makes sense to pay close attention to your own health.
Almost always, the complex of symptoms described indicates a pathological process; what type and whether this is really the case (there are exceptions) should be shown by objective diagnosis. However, there is something the patient can do on his own - conduct an initial self-diagnosis. How to do it? We need to figure it out.
Wheezing in the throat: how it occurs, causes and diseases, symptoms, diagnosis, therapy
Wheezing in the throat is a noisy and whistling sound that occurs when breathing in people with diseases of the respiratory tract. They can be different: rough with a trumpet tone or high-pitched, like a whistle.
This is due to the localization of the lesion, the amount of sputum in the bronchopulmonary structures, and the degree of obstruction present. Hoarseness caused by diseases of the larynx and wheezing emanating from the bronchi are significantly different.
The sound characteristics of pathological noises are very important and are always taken into account when making a diagnosis. In each specific case, the throat may wheeze differently.
In healthy people, air enters the lungs freely. The only obstacle to the air flow is the place where the laryngeal ligaments attach to the laryngeal cartilages.
The main etiological factors of wheezing are narrowing of the bronchi, accumulation of mucous or purulent exudate, swelling of the epiglottis, tumors and foreign bodies blocking the airways.
Air passing through these structures causes intense vibration, which is accompanied by atypical sounds.
Wheezing in the throat is not the only symptom of the pathological process. They are usually accompanied by various unpleasant sensations: changes in speech, hoarseness, soreness and scratching in the throat, the feeling of a foreign object inside.
If the cause of hoarseness is laryngitis, then patients have to strain to make a sound. This causes the ligaments to spasm, which further aggravates the overall well-being. With prolonged closure of the ligaments in patients, the function of voice formation is impaired. They speak in whispers.
Extreme dysphonia is a complete loss of voice sonority.
Wheezing in the throat is not always a consequence of pathological processes. Sometimes they appear in completely healthy people. The causes of a hoarse throat are often addictions, mental stress, and anatomical and physiological characteristics of the respiratory system.
If you experience wheezing in your throat, you should contact a medical facility. Only an experienced specialist will be able to understand what underlies the process - pathology or a special condition. Therapeutic and diagnostic measures are carried out by ENT doctors, pulmonologists, phthisiatricians, oncologists, and allergists.
After a comprehensive diagnostic examination, they prescribe appropriate therapy. The sooner the cause of wheezing is determined, the more favorable the prognosis for recovery will be.
Any abnormal sounds that occur in the throat when breathing require special attention and adequate treatment.
Symptoms
Wheezing in the throat of pathological origin is one of the symptoms of the underlying disease that became its cause.
Usually this symptom is combined with manifestations of intoxication - fever, chills, myalgia, headache; pain syndrome - sore throat, aggravated by swallowing and talking; catarrhal symptoms - cough, rhinorrhea, hyperemia of the pharynx, hypertrophy of the tonsils, lacrimation, scleral injection.
- Laryngitis is an inflammation of the laryngeal mucosa, manifested by a barking cough, sore throat, and hoarseness. The cough is painful, barking, often paroxysmal. At first it is dry, and as the pathology progresses it becomes wet. Patients' voice changes. It “sits down”, acquiring some roughness and hoarseness. Painful sensations in the throat intensify when swallowing food and when talking. The doctor, examining the throat, notes hyperemia and swelling of the pharynx with minor hemorrhages on the mucous membrane. When the ligaments swell, the voice completely disappears.
laryngitis
- Patients with ARVI have a sore and dry throat, painful sensations when swallowing, and a runny nose. Against the background of elevated temperature and chills, aches throughout the body and cough appear. Wheezing in the throat is caused by swelling of the respiratory epithelium and hypersecretion of sputum, which vibrates during breathing.
- Quincke's edema develops when allergens enter the body. This extremely severe form of allergy is manifested by excessive accumulation of fluid in the soft tissues of the throat, narrowing its lumen. A person with laryngeal swelling may die from suffocation. He requires emergency medical attention.
- When a malignant tumor becomes the cause of wheezing in the throat, patients experience accompanying symptoms - incessant coughing, sore throat, foreign body sensation, severe discomfort when swallowing. These signs of hoarseness in the absence of pain should alert the patient and doctors. Pain syndrome appears much later - in the last stages of cancer, when it is no longer possible to save the person.
- With bronchial asthma, whistling and gurgling sounds in the larynx are accompanied by shortness of breath, heaviness in the chest and rapid breathing. Under the influence of allergens, infection or stress, an attack of suffocation occurs. The patient makes loud wheezing sounds that can be heard from a distance. Breathing becomes difficult when exhaling. As air passes through the narrowed bronchi, the throat begins to wheeze. To stop an attack, special inhalers are required. bronchial asthma
- Heart failure is manifested by wheezing in the throat, shortness of breath at rest, swelling of the legs and hepatomegaly.
Diagnostic measures
To get rid of wheezing in the throat, you need to find out its cause. To do this, you should consult a doctor and undergo a full medical examination.
Specialists collect complaints and anamnesis. They find out when wheezing appeared, what the patient associates with its occurrence, and how often they bother you. Examination of the mucous membrane of the pharynx and larynx is carried out using a pharyngoscope and laryngoscope.
These mandatory procedures are performed by an otolaryngologist. After a general examination and physical examination, a preliminary diagnosis is made.
To confirm it, the results of laboratory tests and instrumental procedures are required.
Laboratory diagnostics:
- Hemogram - signs of bacterial or viral inflammation, allergies;
- Microbiological examination of the throat discharge - isolation of the infectious agent and determination of its sensitivity to antibiotics;
- Blood for tumor markers - if laryngeal cancer is suspected;
- An immunogram is an assessment of the state of the patient’s immune system.
Hardware research methods:
- Spirometry – measurement of volume and speed parameters of breathing;
- X-rays of light;
- Bronchoscopy;
- Tomographic examination of the neck.
Medical complex
Treatment of wheezing in the throat is etiotropic, aimed at eliminating the causes of this problem. Experts recommend that patients remain calm and communicate in a whisper. Against a background of silence, drug therapy is carried out.
- Infectious inflammation can only be cured with antibiotics. Usually drugs from the group of macrolides are prescribed - Azithromycin, Klacid, penicillins - Amoxicillin, Augmentin, fluoroquinolones - Ciprofloxacin, Ofloxacin, cephalosporins - Cephalexin, Ceftazidime. Antibiotics must be taken together with pre- and probiotics - “Linex”, “Acipol”, “Bifiform”.
- Antiviral drugs - Ingavirin, Valtrex, Arbidol.
- Mucolytics help thin mucus, and expectorants help release it. The first include "Bromhexine", "Mukaltin", and the second - "ACC", "Ambroxol".
- Antitussive drugs are prescribed for dry cough - Codelac, Sinekod.
- Bronchodilators dilate the bronchi and make breathing easier - Berotek, Salbutamol. In the absence of a therapeutic effect, inhalations with corticosteroids are performed - Pulmicort, Beclazone.
- If the patient has a fever, antipyretic drugs are used - Paracetamol, Ibuprofen. These NSAID medications reduce pain and relieve inflammation.
- Antihistamines eliminate swelling and reduce the risk of developing allergies - Suprastinex, Erius.
- For laryngitis, to eliminate wheezing and pain, antiseptic sprays are widely used - Hexoral, Miramistin, as well as anti-inflammatory lozenges - Strepsils, Lizobakt.
Experts recommend that patients drink a lot. This is necessary to relieve intoxication during inflammation and soothe a sore throat. It is useful to drink herbal teas, berry fruit drinks, and still mineral water.
Nutrition should be high in calories, easily digestible, and balanced. Preference should be given to semi-liquid porridges, vegetable purees or stews, low-fat and warm soups, steamed chicken or minced fish cutlets.
To warm a sore throat, you need to wear a warm scarf or apply a compress with mashed potatoes and honey.
There are folk remedies that eliminate wheezing in the throat. Decoctions and infusions of medicinal herbs and herbal mixtures are used for rinsing a sore throat, inhalation, and oral use. Infusions of eucalyptus, chamomile, sage, and calendula are widely used. Eggnog and a mixture of honey and lemon soothe irritated ligaments.
Prevention
Measures to prevent the appearance of wheezing in the throat:
- Timely treatment of pathological processes,
- Breathing exercises, physical education, swimming,
- Correction of the daily routine,
- Proper nutrition,
- Strengthening immunity,
- Walks in the open air,
- Fighting bad habits
- Protecting the body from colds and contact with sick people.
Wheezing in the throat is an unpleasant phenomenon that occurs in most cases in people with serious respiratory diseases that need to be treated promptly. If wheezing is ignored and treatment is neglected, the underlying pathology will begin to progress. Only in the initial stages of the pathological process is it best to treat.
Opinions, advice and discussion:
Source: https://uhonos.ru/gorlo/simptomy-gorla/xripy-v-gor/
Physiological factors
Essentially there are two of them. The first option is a psychosomatic manifestation under intense stress. Everyone most likely knows the feeling of a lump in the throat during strong emotional experiences.
This is due to spasm of the esophagus and/or larynx. Belching in such a situation is an optional manifestation. It begins to make itself felt only in the case of aerophagia due to stress (when a person begins to literally swallow air).
This is the so-called nervous aerophagia. Air is an unnatural content for the stomach, so the body tries to get rid of the gas, and in this indelicate way solves the problem.
Another significant factor concerns the nature of nutrition. If a person eats quickly and does not chew food well, spasm of the esophagus occurs due to its mechanical irritation. On the other hand, the same phenomenon of aerophagia is observed, this time not due to nervousness, but during the consumption of food.
The consumption of carbonated drinks manifests itself in a similar way.
If these reasons cause belching and a lump in the throat, there is no reason to worry. You just need to adjust your lifestyle.
Pathological causes are more numerous.
They can be grouped into several categories:
- Endocrine pathologies. As a rule, the thyroid gland is affected.
- Diseases of the spinal column. They lead to disruption of the innervation of individual anatomical areas. Lead to spasms and secondary aerophagia (swallowing of air).
- Infectious and inflammatory pathological processes.
- Disorders of the gastrointestinal tract. Most common. A lump in the throat and belching of air are pathognomonic for many diseases of the digestive system.
- Oncopathology. Simply put, tumors of malignant and benign properties.
Now we should take a closer look at the presented groups.
Why do you hear clicks in your throat when swallowing?
Why does a clicking sound appear in the throat? It is believed that a healthy person does not hear the sounds that his body produces. There are few exceptions to this rule, one of them is episodic, quickly disappearing and not accompanied by pain crunching of joints (for example, limbs).
This does not cause concern and is perceived as a normal, physiological phenomenon, especially if a person has spent a long time remaining motionless. However, if there is a clicking sound in the throat when swallowing, there is cause for concern.
An unpleasant sound occurs suddenly and sometimes causes such significant discomfort that all the patient’s thoughts are focused only on finding the causes and a way to get rid of the obsessive clicking.
Eagle-Sterling syndrome
Eagle-Sterling syndrome, or stylohyoid syndrome, is quite multifaceted. It includes two main subtypes - stylopharyngeal and styloid-carotid syndromes. The development of pathology is due to:
- an increase in the size of the styloid process of the temporal bone;
- lengthening of the horns of the hyoid bone;
- calcification (deposition of calcium salts) in the stylohyoid ligament.
The symptoms are explained by the pressure of the listed structures on the anatomical areas of the oropharynx, the internal or external carotid artery. A clicking sound in the throat during a swallowing movement is not a necessary but probable manifestation.
One of the variants of pathological changes or a combination of them may be observed. Because Eagle-Sterling syndrome has many symptoms, it can be difficult to diagnose.
Sometimes patients spend months and even years searching for the true cause, turning to doctors of various specialties, but the treatment (for example, anti-inflammatory drugs) is unsuccessful.
The leading symptom of Eagle-Sterling syndrome is pain - in the throat, in the front of the neck, in the ear - usually one-sided.
In this case, the clicking sound appears sporadically, the patient’s attention is focused mainly on the pain syndrome, which can be constant, exhausting, and increasing in the evening.
Temporomandibular joint dysfunction
Temporomandibular joint dysfunction occurs due to:
- malocclusion;
- spasm, overload of masticatory muscles;
- overstrain of the masticatory muscles in a stressful situation;
- features of the anatomical structure of the joint and surrounding structures.
The disease can also be associated with infectious and non-infectious inflammatory processes. One of the forms of dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint is Costen's syndrome, which is characterized by vibrator noises of an objective nature (audible not only to the patient, but also to others).
The patient has a clicking sound in the throat - the appearance of the sound can be provoked by swallowing and is explained by the displacement of the articular disc due to increased muscle tone. Although its source is the temporomandibular joint, patients may feel that the “sound noise” is coming from the pharynx or larynx.
Fracture of the hyoid bone
A fracture of the hyoid bone occurs as a result of trauma to the cervical spine, larynx, and lower jaw and is accompanied by striking clinical manifestations - severe pain, difficulty swallowing (dysphagia), and a high probability of developing asphyxia (suffocation). When a fracture does not affect the bone body (the most massive area), but occurs in the area of the horns of the hyoid bone, the following occurs:
- Pain when opening the mouth.
- Pain when trying to stick out tongue.
- Frequent tongue retraction.
- Difficulty speaking.
- Difficulty swallowing.
An important sign is also the mobility and crepitus of bone fragments. This explains the presence of clicking and crunching - some patients feel it even long after the injury.
Clicking as normal
What does a clicking sound in the throat mean when swallowing normally? There is a concept of crepitation of the cartilage of the larynx - this is a crunching or clicking sound that occurs when the organ is displaced. The sound also appears when there is pressure on the thyroid cartilage, or Adam's apple. It does not indicate a disease; on the contrary, it is an expected phenomenon for a healthy person.
Clicking and crunching sounds in the throat when swallowing are not signs of a neoplasm.
Many patients, noticing crepitus of cartilage, begin to suspect a tumor. However, the neoplasm, on the contrary, is characterized by limited mobility of the larynx and the disappearance of the symptom of crepitus. Therefore, the “sound background” is a relatively favorable sign.
Endocrine diseases
The most common endocrine disease, which is manifested by belching and a feeling of a lump in the throat, is goiter.
A goiter is a growth of tissue of the thyroid gland of a different nature. It can be diffuse, when hypertrophy and hyperplasia of the entire organ or its individual parts is observed, or nodular.
In the second case, special protrusions are formed in the organ, which in their macroscopic structure are similar to nodules. In both cases, there is “squeezing” of the esophagus and larynx by overgrown tissues.
This leads to spasms, aerophagia and, as a result, constant odorless belching and coma in the throat. Of course, these are not the only symptoms of the problem. It is very problematic not to notice a goiter at the stage when it provokes such symptoms.
With hyperthyroidism, which is the cause of goiter quite often, a change in the relief of the neck, exophthalmos (bulging of the eyes), weight problems, hyperthermia, etc. occur. A competent endocrinologist recognizes “his” patient at first sight.
Due to the fact that the hormone TSH is synthesized by the pituitary gland, diseases of the chiasimal-sellar region and the region of the third ventricle are also possible. Including tumors, injuries.
What's bothering your throat?
A lump in the throat is a feeling of fullness or a foreign body in the front of the neck. This may make it difficult and unpleasant to swallow. It happens that wearing high-necked clothes or a scarf makes the situation even worse. If this symptom occurs regularly, you should definitely try to understand why it occurred, since the reasons can be varied.
Reasons why you feel a lump in your throat:
- pathologies of the thyroid gland;
- osteochondrosis or trauma to the cervical vertebrae with displacement;
- pharyngitis, tonsillitis, other viral diseases;
- neurosis and spasm of the throat muscles due to traumatic situations;
- long-term use of certain medications (NSAIDs, steroids);
- allergic reactions causing swelling of the larynx;
- diaphragmatic hernia;
- malignant formations in the larynx;
- diseases of the esophagus and underlying parts of the gastrointestinal tract.
As you can see, all of these are diverse diseases, therefore, in order to accurately determine why such a symptom as a lump in the throat appeared, you need to undergo an examination and begin treatment. A history and examination can help make the diagnosis. If, in addition to a feeling like a lump in the throat, there is constant belching, then the problem is most likely in the esophagus or stomach.
Pathologies of the spinal column
- First of all, similar symptoms are observed with osteochondrosis. The essence of this disease lies in degenerative-dystrophic damage to the spinal column, in particular at the level of the collar region (cervical spine). Compression of the nerve roots responsible for the innervation of the tongue, pharynx, etc. develops. which is the reason for the sensation of a lump in the throat and belching of air masses. Often additional companions for a spinal patient include neck pain, headaches (cephalalgia), impaired motor activity of the upper extremities and other symptoms (weakness of the arm muscles, tingling sensation, numbness).
- Another orthopedic disease is hernia of the cervical spine. Due to the high activity and mobility of this section of the column, hernias of this location are very common. They compress the nerve roots and spinal cord, causing unpleasant, unnatural sensations in the throat, limbs, etc. Partial paralysis and paresis are possible.
- Spinal column injuries. As a rule, the patient himself knows about them. Conditions that seem insignificant at first glance, such as subluxations, are especially dangerous.
- Instability, displacement of the spinal column at the level of the neck.
Treatment
The treatment plan consists of taking medications prescribed by the doctor - antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antiemetic, sedatives, and anti-spasm medications. Following a diet. Folk methods are considered auxiliary treatment - taking plant decoctions, sedative tinctures:
- valerian infusion;
- St. John's wort decoction;
- motherwort tincture;
- herbal teas of chamomile, mint, etc.;
- herbal preparations that have a sedative effect - Nervo-vit, Apitonus;
- herbal teas from motherwort, lemon balm, jasmine;
- aromatic baths with essential oils.
If swallowing difficulties appear due to problems in the cervical spine, physiotherapy will be effective: acupuncture, manual treatment, laser radiation.
It is important to remove the psychological burden from the patient - to alleviate tense, stressful situations, to eliminate neuroses. You need to rest more, take time for walks in the fresh air, strengthen the body’s immunity, and reduce working hours. Adequate sleep is important. In exceptionally severe cases, the psychotherapist prescribes sedatives and antidepressants.
If there is a tumor in the larynx, surgical intervention is necessary; after the operation, the doctor will prescribe drug therapy.
If the feeling of a coma occurs exclusively after eating due to poor nutrition, no medications are required. It is important to establish a rational eating regimen, eliminate harmful foods and carbonated drinks. Eat in a timely manner, slowly, chewing food thoroughly, and do not talk during this process. Try to eat foods that are easy to digest and avoid overeating.
When a lump in the throat is caused by diseases of the thyroid gland, in addition to taking medications, it is important to eliminate inflammation, replenish iodine deficiency in the body by including the following foods in the diet - any types of greens, seaweed, mussels, shrimp, squid, champignons. There is a high iodine content in beans, peas, chickpeas, and various types of cabbage (Brussels sprouts, cabbage, broccoli, cauliflower), but these products cause increased gas formation, they should be taken with caution, in moderation. For autoimmune thyroid diseases, the endocrinologist prescribes hormonal therapy.
Source: GastroTract.ru
Infectious and inflammatory pathological processes
Diseases of this profile cause irritation of the initial parts of the larynx (resulting in a feeling of a lump in the throat), coughing and instinctive swallowing of air after the next reflex attack (resulting in belching of air).
Among the most common infectious-inflammatory diseases are:
- Acute respiratory viral diseases. This is a heterogeneous group of pathologies provoked by viral agents (rotaviruses, adenoviruses, herpes agents and human papillomaviruses). This also includes the notorious flu. The main symptoms of diseases of this kind are sore throat, discharge of mucus from the nose, and the development of a paroxysmal cough (productive and dry).
- Throat abscesses. They develop as a result of an infectious or viral pathology. They compress the respiratory system, causing unpleasant symptoms. Large purulent structures are dangerous to health and life, as they can open and provoke secondary infection of surrounding tissues. Their melting is also possible.
- Sinusitis. They provoke the flow of mucous exudate into the throat. The result is a cough, a feeling of a lump in the throat and belching of air.
Pathologies of the digestive tract
There are two main diseases that can cause constant belching of air and a feeling of a lump in the throat:
- Gastritis with high acidity. Inflammation of the gastric mucosa. Characterized by pain and dyspeptic symptoms. Among them: heartburn (may feel like chest pain), sour taste in the mouth, heaviness in the stomach, belching with an unpleasant odor (rotten eggs, which is explained by excess production of hydrogen sulfide). Symptoms always intensify after eating, when the greatest amount of acids are released, and subside as the food is digested.
- Reflux esophagitis. Throwing stomach acid into the initial parts of the esophagus. Irritation of the throat explains the sensation of a lump, and belching of air and coughing are considered common symptoms of the disease. This process occurs due to a weak gastric sphincter; one of the reasons for the decrease in its tone is sleeping on the left side. However, gastric gases are not always belched. Aspiration of food or acid is possible, this can be dangerous especially during sleep, as a person may simply choke.
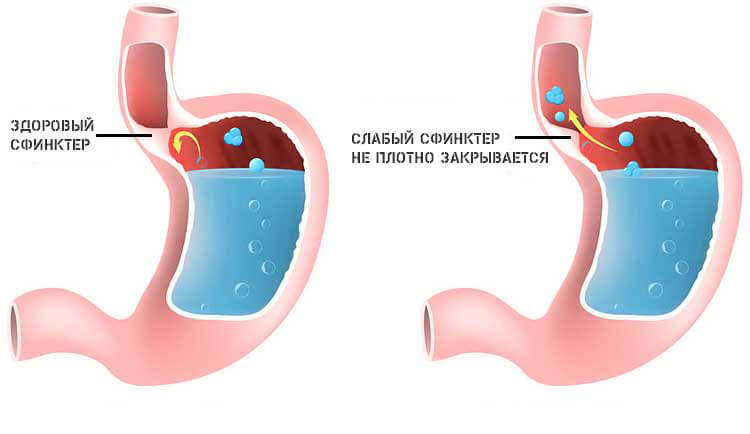
Somewhat less often we talk about a hiatal hernia. But a similar scenario with a lump and belching occurs only when the vagus nerve is compressed. In other cases, the patient may not even suspect that he is sick.
Each of the pathologies listed above can cause the symptoms in question. It is necessary to carry out differential diagnosis to identify the exact reason why this happens.
How to get rid of a rumbling throat
About a year ago, strange sensations appeared in the neck area, sometimes at the level of the thyroid gland, sometimes at the level of the Adam's apple, some rumbling in the throat after swallowing saliva.
At first, these symptoms appeared periodically, in recent weeks - almost daily. The sensations are painless, but nevertheless “intrusive” and depressing. At the same time, swallowing saliva, drinking and eating are painless, but when I swallow saliva, after 2-3 seconds some kind of rumbling occurs in the throat - again, not painful, but unpleasant, this phenomenon is not constant, sometimes it disappears altogether, with nothing I can’t connect, there are no belchings, no dysphagia. Gastroscopy – catarrhal gastrodoudenitis, signs of gallbladder dyskinesia (according to ultrasound, the inflection of the gallbladder neck) X-ray of the stomach with barium – without pathology (but it was done before the appearance of these symptoms, two years ago.)
The appetite is normal, as is the general condition.
I did an ultrasound of the thyroid gland - moderately pronounced diffuse changes in the gland, the size of the lobes was 50x19x19, the volume of the gland was 17.2 ml.
I have the following question. I understand that my symptoms may be a consequence of osteochondrosis or, as they say, “from nerves.” In person, the ENT specialist did not visually find any pathology, but in response to complaints of rumbling in the throat, he said that such a symptom was not familiar to medicine.
I didn’t find anything similar on the Internet either, maybe someone has come across this and knows something, I repeat that I don’t have any discomfort other than rumbling. Again, I can’t relate it to anything, the intensity changes, sometimes pronounced, sometimes barely noticeable. What needs to be investigated to establish the cause?? CT, MRI and what of the neck, esophagus, larynx, trachea.
I don’t even know which section to post it in, if it’s off topic, then please move it.
Male, 50 years old. height 175, weight 83.
Hello. As time passes, after opening the topic, I raise the question again. To date, the symptoms have not disappeared, the rumbling remains, only now sometimes without empty swallowing. sometimes even while eating.
I don’t experience any problems with the passage of solid food, but with liquid there is regurgitation, especially fizzy drinks; several times there were spasms with the inability to take a breath (a very unpleasant sensation). I did gastroscopy many times, but nothing other than erosions and gastritis were found.
The last gastroscopy was done under local anesthesia (for a better and objective examination) and it seemed like something began to clear up.
Esophagus: freely passable, the mucosa is smooth, shiny, pink, the vascular pattern is visible, on the mucosa, more in the middle third, there are focal whitish thickenings in a small amount of 1 mm - glycogen acanthosis.
But starting from 26 cm from the incisors, there is a permanent circular spasm of the esophagus, increased discoordinated (with elements of antiperistalsis) peristalsis, but there is no persistent expansion or narrowing of the lumen of the esophagus. Cardia: closes, but there is no stable spasm creating resistance for the device.
The dentate line is uniform at the level of the hiatal constriction. Stomach: contains a small amount of clear secretion. The folds of the body are of normal caliber and elastic. The mucosa is focally moderately hyperemic in the distal part of the stomach. In the antrum there are several flat-inflammatory and two hyperplastic erosions at the stage of exacerbation of the process, with signs of ongoing and/or ongoing bleeding. The gatekeeper closes. Bulb: without features.
Duodenum: the area of the large duodenal papilla without features.
Conclusion: Segmental distal esophagospasm. Erosive antral gastritis without complications.
There is also research from [Only registered and activated users can see links] ([Only registered and activated users can see links]) questions such as 1.
Are these studies enough to show that esophagospasm is not secondary? 2.what else needs to be done? CT, MRI? and what, the distal part of the esophagus, or surrounding organs, or an x-ray with barium? 3.
Is it possible to assume that the spasm is provoked by VSD? 4. Prognosis and treatment.
Thank you.
source
Constant belching of air and a lump in the throat - what to do?
If a person belches air and has a lump in the throat, the reasons for such symptoms can be varied. To identify the factors that provoked them, it is necessary to consult a doctor as early as possible and undergo all prescribed diagnostic measures.
Causes
The appearance of these symptoms is always associated with diseases that can be identified with a thorough examination.
Belching air and a lump in the throat may be signs of:
- pathological disorders of the thyroid gland;
- if a person has cervical osteochondrosis;
- pharyngitis;
- hernia in the area of the opening of the esophagus;
- injury or minor displacement in the vertebral area;
- stress;
- depression;
- insomnia;
- oncology of the nasopharynx;
- presence of goiter;
- insufficient iodine can cause lumps;
- diseases of the esophagus;
- alcohol abuse;
- a long history of smoking causes a feeling of coma;
- drug addict;
- disorders of the vegetative system;
- if a person has stomach problems;
- if increased acidity of gastric juice is detected;
- if there is frequent reflux of bile into the esophagus;
- bloating contributes to the appearance of a coma;
- if gastroesophageal reflux disease is diagnosed;
- with constant heartburn;
- in the presence of gastritis or stomach ulcers;
- with pathological contraction of the muscles of the larynx, a feeling of a lump appears in the mouth;
- if the patient takes a certain group of medications for a long time.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease
When the disease occurs, a person experiences inflammation of the esophageal mucosa and weakened functioning of the lower alimentary sphincter. As a result of this, food is requested into the esophagus, and its mucous membrane is affected and corroded by concentrated juice.
Therefore, after eating, belching and a lump in the throat often appear.
The following symptoms may also occur:
- constant pain in a person behind the sternum;
- it can be localized in the jaw area, in the shoulder or in the area of the shoulder blades;
- the patient has difficulty swallowing food due to a coma;
- a person coughs;
- burning and scratching sensation in the throat;
- there is pain in the stomach;
- belching after eating;
- nausea may occur;
- there is constant heartburn;
- a person experiences a feeling of lack of air, which makes it difficult to take a deep breath;
- possible appearance of weakness, depression, insomnia;
- Appetite disappears, and the person begins to lose weight sharply.
Source: https://ckiom.ru/gorlo/kak-izbavitsya-ot-urchaniya-v-gorle/
Which specialists carry out diagnostics?
The list of problems described is wide. Therefore, consultation with specialists in various fields may be required. First of all, it is recommended to consult a therapist. He acts as a kind of navigator in finding a specialized doctor. Conducts initial diagnostics using routine methods and refers the patient to the right doctor.
Such a specialist can become:
- Gastroenterologist. A doctor who specializes in treating the digestive tract. The primary diagnostic measure is palpation of the abdominal organs.
- Endocrinologist. Practices in the treatment of pathologies of secreting glands.
- Neurologist. Specialist in the treatment of pathologies with the central and peripheral nervous system.
- Neurosurgeon. A consultation with such a doctor may be required in two cases: there is compression of the spinal cord, or there are herniated vertebral discs. Both the neurologist and neurosurgeon perform a series of functional tests to identify problems with the innervation of tissues and structures.
- Infectious disease physician. It is addressed in case of severe bacterial or viral infection.
- Oncologist. A doctor who specializes in treating tumors.
At the initial appointment, any specialist interviews the patient about complaints, their duration, duration and nature. An anamnesis is collected (the doctor finds out what the person was or is sick with).
It is important to establish the following facts:
- A history of endocrine, orthopedic, gastroenterological, and other diseases.
- The presence of neck injuries or previous inflammatory diseases in the recent past.
What does a lump in the throat after eating indicate?
In order not to wind yourself up in vain, you first need to determine whether you have symptoms of this problem or not.
- Feeling of a lump in the throat after eating food or a stressful situation. However, the lump cannot be physically felt. It is only felt.
- If a symptom occurs, there may be a problem with breathing. The lump seems to block access to oxygen, and breathing becomes problematic.
- Sore throat.
- Sometimes there is a burning sensation in the throat.
- A feeling that there is an unpleasant aftertaste in the throat or chest.
If you identify one or more symptoms, you should think about the possible causes of their occurrence.
This problem occurs for two reasons: as a result of nervous tension or in the presence of somatic problems.
Nervous tension is the most common cause of this symptom. It appears as a result of stress, severe fear, excitement, and overexcitement.
However, these are not the only reasons for this problem.
Somatic disorders that cause a lump in the throat:
- inflammations in the throat (sore throat, tonsillitis, laryngitis, etc.), as well as adenoids. When inflammation occurs, the larynx swells and becomes compressed;
- pathology of the thyroid gland. Enlarged thyroid nodules put pressure on the throat and interfere with normal breathing and swallowing;
- pathologies in the spine in the neck area;
- gastrointestinal diseases. Often, with pathologies of the esophagus, heaviness in the throat appears after eating. An ulcer or gastritis often provokes discomfort in the larynx;
- the presence of a hiatal hernia;
- obesity;
- neoplasms in the larynx: benign and malignant;
- allergy;
- negative reaction to certain drugs;
- various injuries to the larynx or esophagus;
- parasites. Rarely, but sometimes parasites can lay eggs in the throat area, which are perceived as a foreign object;
- presence of a foreign object in the throat;
- problems with the heart or blood vessels are rare, but can also contribute to the formation of a lump in the throat.
What to do if heaviness occurs in the trachea?
First of all, you need to see a therapist. He will conduct a full examination and ask several leading questions regarding the problem that will help determine the cause of the disease.
Next you will be offered:
- take blood and urine tests;
- conduct thyroid examinations;
- examine the esophagus;
- take an x-ray of the spine in the neck area;
- undergo a full examination by an ENT doctor.
How to treat a lump in the throat due to a nervous disorder?
In this case, the patient is prescribed medication and consultation with a psychologist.
The patient may be prescribed the following medications:
- motherwort;
- Paleriana;
- herbal teas with a relaxing effect;
- St. John's wort-P;
- Nervo-Vit. This drug includes the herb blue cyanosis, which relaxes and calms the body;
- Apitonus-P. This is a complex of vitamins to increase stress resistance.
If it is difficult to breathe while squeezing the throat, then it is recommended to use breathing techniques that lead to relaxation.
It is advised to breathe with your stomach or inhale and exhale into the bag. This type of breathing leads to relaxation and calm.
How to treat a lump in the throat with somatic pathologies?
Depending on the identified causes, measures are prescribed to eliminate the disease. If the cause of heaviness in the trachea is problems with the thyroid gland, then the patient is prescribed medications containing iodine.
If there are problems with the neck, then special gymnastics are prescribed that will develop the neck. They also provide manual, laser and reflexology treatments.
To treat the esophagus, the patient is prescribed a special diet and appropriate medications. However, for a hiatal hernia, surgery is possible.
For inflammation of the respiratory tract, antibiotics or other medications are prescribed, depending on the cause of the inflammation. It is also recommended to gargle with soda, herbal infusions, and preparations containing iodine. In rare cases, warm compresses are prescribed.
For malignant or benign tumors of the throat, radiation or chemotherapy is given, and surgery is also possible. Depending on the situation, the events may be carried out all together, or only one will be selected.
Until you find out the cause of the unpleasant symptom and it causes you terrible discomfort, it is recommended to use folk tips that will help alleviate the symptoms:
- drink soothing tea;
- Pay great attention to your sleep. Try to get good sleep;
- do relaxing activities. This could be a relaxing bath, massage, breathing technique for relaxation;
- add foods high in iodine to your diet.
Differential diagnosis with various pathologies
Differential diagnosis requires a number of instrumental and laboratory studies.
- General blood analysis . Helps to identify an inflammatory process of an infectious nature. The concentration of leukocyte cells (white cells) increases, and the erythrocyte sedimentation rate increases. This is a direct indication of inflammation. Eosinophilia may indicate helminthic infestation or an allergic reaction (also, in some cases, it can cause a lump in the throat and belching).
- Biochemical blood test. Allows you to evaluate the biological composition of hematological fluid. Also indicates nonspecific inflammatory processes. Indirect determinants of oncopathology are possible.
- Hormonal tests. First of all, you need to determine the amount of T3, T4, TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormones, related to the work of the thyroid gland, produced by the gland itself and the pituitary gland).
- If there is a serious suspicion of a tumor, special tests for tumor markers are performed.
- X-ray of the cervical spine in several projections. Makes it possible to quickly identify pathologies of bone structures. Does not allow assessment of soft tissues. Therefore, it is rarely used in isolation. Insufficiently informative methodology.
- MRI diagnostics of the neck. Detects all changes in the spinal column.
- FGDS. Endoscopic examination of the stomach and esophagus. An unpleasant but informative way.
- Ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs.
Treatment and methods of elimination
If the factor causing the constant belching of air, the formation of a lump inside the throat, is a serious illness, you will not be able to get rid of the unpleasant symptoms on your own. Only professional treatment will help.
Therapeutic measures depend on the results of the examination and consist of drug treatment, the use of folk remedies, and the organization of a healthy lifestyle.
Taking medications
The doctor’s therapeutic actions are based on the diagnosis. For drug treatment, the following are prescribed:
- Antibacterial, anti-inflammatory drugs used for infectious diseases.
- Antacids, inhibitors that help with gastroenterological pathologies.
- Chondroprotectors are necessary to solve problems with the spinal column. Additionally, physiotherapeutic procedures and exercise therapy are prescribed.

Constant belching of air, the appearance of a lump in the throat, caused by endocrine diseases, are treated with products containing iodine. This helps to restore normal functioning of the thyroid gland.
When tumors are detected, surgical intervention is indispensable.
Folk recipes
If the reasons for the formation of a coma inside the throat and belching are physiological, treatment can be carried out with folk remedies. Decoctions and infusions of medicinal herbs and vegetable juices help eliminate unpleasant symptoms.
Effective remedies recommended by traditional medicine include:
- Mint - pour boiling water over fresh or dry leaves of the plant, leaving to infuse for 5-10 minutes.
- Herbal mixture - mix chamomile, lemon balm, St. John's wort, calamus, thyme, linden in equal quantities. Pour boiling water (1 cup) over the collection (1 tablespoon), leaving to steep for 30 minutes. Take the decoction throughout the day.
- Flax infusion - add flax seeds to the boiling water, reduce the heat, and leave to simmer for 2 hours. After cooling, drink 50 ml before meals.
- Vegetable juices - carrots, beets or potatoes, pass through a juicer. Drink 50 ml 30 minutes before meals.
- Goat's milk helps with aerophagia and flatulence. Drink at least 0.5 liters throughout the day.
- Apples – after meals, eat 1 apple, chewing thoroughly.
- Elecampane - pour boiling water over the root of the plant, leave to infuse for about 30 minutes, take throughout the day.
- Apple cider vinegar - to reduce acidity, mix boiled water (1 liter) with vinegar (2 tsp), drink about 10 ml of the composition during meals.

To restore the acid-base balance and normalize the functioning of the digestive tract, it is advisable to drink mineral water without gas.
Attention! Any of the folk remedies is used only after consultation with your doctor.
Minerals and vitamins contained in medicinal decoctions and infusions help strengthen the immune system, reduce the level of acidity in the stomach, and normalize intestinal function.
Treatment methods depending on the cause
Therapy depends solely on the underlying pathology. Unfortunately, there is no single option here.
- Endocrine diseases associated with disruption of the thyroid gland are treated with iodine preparations. In case of hyperthyroidism (excess of the hormones TSH, T3, T4), on the contrary, a diet low in this element is indicated.
- Infectious diseases can be cured by using a whole group of medications. Broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed (after analyzing sputum or mucus for sensitivity to antibacterial drugs), non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (used to relieve inflammation), steroid pharmaceuticals (corticosteroids, Prednisolone and Dexamethasone water).
- Pathologies according to the gastroenterologist are treated with the use of antacids and proton pump inhibitors.
- If there are diseases of the spinal column, anti-inflammatory and chondroprotectors are required. But pills alone won’t help matters. It is necessary to stabilize the spinal column. Exercise therapy and physiotherapy will come to the rescue.
- Tumors are almost always treated with surgery. In the same way, eggs of dangerous helminths (echinococci and others) are extracted.
As already mentioned, if the symptom is physiological, it is recommended to change your lifestyle: eat slowly and chew food thoroughly, avoid stress.
A lump in the throat combined with belching are nonspecific signs of various diseases. A whole group of options is possible. It’s difficult to figure it out on your own, so it’s better to work with a competent doctor. The therapist will tell you which one.
source
Treatment with drugs for belching
Any medications must be prescribed by a doctor, a gastroenterologist.

If the production of enzymes for digestion is impaired in the gastrointestinal tract, then drugs such as:
- Mezim - the active ingredient pancreatin, belongs to the group of digestive enzyme agents.
- Pangrol - also pancreatin is an active ingredient that helps ensure that proteins, fats and carbohydrates that come with food are broken down quickly enough, thereby eliminating discomfort.
- Creon - this drug fully compensates for the lack of enzymes and normalizes the general condition.
- Festal - helps in the digestion of all proteins, carbohydrates and fats. It also facilitates the absorption of vitamins A, E, K, and also helps reduce gas formation in the intestines.
- Digestal - replenishes the deficiency of pancreatic enzymes and bile, thereby improving the digestion process.
- Ferestal is prescribed to people whose digestion is generally normal, and is used in individual cases of consuming heavy foods (fatty foods, one large meal).
- Biofestal - this drug significantly improves the normal function of the gastrointestinal tract and restores the digestive process.
In order to restore the balance of intestinal microflora, medications containing lacto- and bifidobacteria are prescribed.
- Bifiform - this drug is used for the prevention and treatment of dysbacteriosis of various origins. The beneficial lactic bacteria it contains normalize the intestinal microflora.
- Enterozermina is a medicine that helps restore the quantity and quality of beneficial microbes.
- Lactofiltrum – regulates the balance of microflora in the intestines.
- Hilak Forte - eliminates the symptoms and cause of dysbiosis in the intestines.
- A – Bakterin is a universal effective drug that restores completely beneficial intestinal microflora.
- Linex is a drug that contains bacteria that enhance joint actions and normalize the general condition.
If the symptoms described above appear, it is recommended to undergo a thorough examination and identify the causes of belching with air and a lump in the throat, and then the attending physician will prescribe the necessary set of necessary treatment.
Symptoms such as belching air or a lump in the throat appear separately, together or in combination with other unpleasant phenomena. These complaints can often be heard in the office of a gastroenterologist or therapist. Why does this and that symptom occur, how are they connected, and what to do if these sensations interfere with your life? We will try to consider all possible reasons.
Description
Belching is the return of the contents of the esophagus into the mouth. This action is preceded by a feeling of fullness and heaviness due to excess pressure inside the stomach. To alleviate the condition, the body itself provokes the release of gases back into the esophagus with belching.
The appearance of rare odorless and tasteless belching is considered normal from a medical point of view. This happens when you involuntarily swallow air, which accumulates in a volume of 2 ml. To normalize the pressure in the gastrointestinal tract, the air itself comes out in small portions in the form of an imperceptible belch. If an involuntary release of air occurs outside of eating or drinking, it emits a pungent odor and unpleasant taste, then there is a risk of developing a functional indigestion (pneumatosis), accompanied by airbrushing and nervous belching. Consultation required.
Rumbling in the throat as in the stomach
About a year ago, strange sensations appeared in the neck area, sometimes at the level of the thyroid gland, sometimes at the level of the Adam's apple, some rumbling in the throat after swallowing saliva. At first, these symptoms appeared periodically, in recent weeks - almost daily. The sensations are painless, but nevertheless “intrusive” and depressing.
At the same time, swallowing saliva, drinking and eating are painless, but when I swallow saliva, after 2-3 seconds some kind of rumbling occurs in the throat - again, not painful, but unpleasant, this phenomenon is not constant, sometimes it disappears altogether, with nothing I can’t connect, there are no belchings, no dysphagia.
Gastroscopy – catarrhal gastrodoudenitis, signs of gallbladder dyskinesia (according to ultrasound, inflection of the gallbladder neck)
X-ray of the stomach with barium - without pathology (but I did it before these symptoms appeared, two years ago.)
The appetite is normal, as is the general condition.
I did an ultrasound of the thyroid gland - moderately pronounced diffuse changes in the gland, the size of the lobes was 50x19x19, the volume of the gland was 17.2 ml.
I have the following question.
I understand that my symptoms may be a consequence of osteochondrosis or, as they say, “from nerves.” In person, the ENT specialist did not visually find any pathology, but in response to complaints of rumbling in the throat, he said that such a symptom was not familiar to medicine.
I didn’t find anything similar on the Internet either, maybe someone has come across this and knows something, I repeat that I don’t have any discomfort other than rumbling. Again, I can’t relate it to anything, the intensity changes, sometimes pronounced, sometimes barely noticeable.
What needs to be investigated to establish the cause?? CT, MRI and what of the neck, esophagus, larynx, trachea. I don’t even know which section to post it in, if it’s off topic, then please move it.
Male, 50 years old. height 175, weight 83.
anonymous, Woman, 27 years old
I am 27 years old. Young woman. I take good care of my health; no violations have ever been identified. For a year or two I have been haunted by a loud rumbling in my throat. It is in the throat, not in the stomach, and not in the intestines. The upper part of the esophagus, closer to the throat... These “claps of thunder” are very similar to the sounds that other people have in the stomach.
But it comes up in my throat, like a burp... But there is no burp. Only rumbling. Not associated with food or drink. I never drink any soda. There are no problems with stool, no flatulence, no rumbling in the stomach. I’m already exhausted and I don’t know what it is... I can sit for hours and loudly involuntarily rumble in my throat.
What is this? help me please
I've been suffering for 2 months now. I took an x-ray with barium, everything is fine. I was treated for Helicobacter. I get up in the morning - burp, eat - burp. Loud! Where we have the collarbone, there is a feeling of fullness, a lump. Sometimes there is a feeling of heat in the throat, as if I had drunk strong alcohol. The doctor prescribed Gaviscon and Duspatalin.
But you won’t be drinking this forever! I did gastro a long time ago, about 3 years ago. I was diagnosed with reflux esophagitis. And now the x-ray has shown that everything is perfect there! And also, when I swallow saliva, there is a constant rumbling in the esophagus, closer to the throat.
I'm sick of all this! Who had something similar? What do you advise? Thank you.
Woman.ru experts
Find out the opinion of an expert on your topic
Fenina Ekaterina Arkadyevna
Psychologist. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Nevzorova Sofya Igorevna
Psychologist. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Fortunatova Oksana Vasilievna
Psychologist, Psychosomatologist. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Svetlana Chernyshova
Psychologist, Consultant. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Tropina Natalya Vladimirovna
Psychotherapist. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Natalya Maratovna Rozhnova
Psychologist. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Trukhina Natalya Vladimirovna
Psychologist, Psychologist coach. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Spiridonova Nadezhda Viktorovna
Psychologist. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Inna Kravtsova
Psychologist, Gestalt consultant. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Victoria Pedai
Psychologist. Specialist from the site b17.ru
Get a gastroscopy and pH-metry of the esophagus done in a good clinic, paid for. The symptoms are very contradictory. And certainly the wrong drugs were prescribed for your treatment.
Our women don't drink, unlike you
Source: https://limto.ru/urchanie-v-gorle-kak-v-zhivote/
Causes
- physiological, when belching air appears after a meal;
- pathological when the belching contains gases formed in the gastrointestinal tract.
Physiological
The air itself comes out in small quantities without a pungent odor. This phenomenon does not cause discomfort. Provoking factors:
1. eating in a hurry, as a result, air is swallowed and accumulates in the gastrointestinal tract, which then comes out; 2. conversations while eating; 3. overeating, due to which the stomach cannot cope with the volume of incoming food, it stagnates, ferments with the release of gases. 4. excessive consumption of soda; 5. physical activity after a meal, due to which food is not properly digested and poorly absorbed, stagnation and excessive gas formation appear; 6. frequent chewing of gum; 7. pregnancy in the 2nd trimester. At this stage, the uterus enlarges and begins to compress the diaphragm; 8. the first two months of a baby’s life, when air accumulates during sucking.
Pathological
During the process, a person experiences a sharp taste and smell. At the same time, the patient experiences other specific symptoms of gastrointestinal pathologies. In this case, the belching is permanent. Occurs against the background of the following conditions:
- destruction of the gastrointestinal tract, such as stenosis of the esophagus, narrowing of the stomach, kinks, tumors growing into the lumen of organs;
- gastrointestinal dysfunction caused by gastritis, ulcers, inflammation of various etiologies;
- pathologies of the liver and gall bladder;
- gastroesophageal reflux, accompanied by the release of food from the stomach into the digestive tract;
- cancerous tumors in the gastrointestinal tract;
- nerve dysfunction;
- problems with the heart and vascular system.
Causes of the unpleasant phenomenon
Heartburn appears for three main reasons - high or too low acidity of gastric juice, weakening of the sphincter muscles, difficulties with digesting food. Increased production of hydrochloric acid and increased acidity of gastric juice are provoked by acidic foods, medications, and bad habits.
At the same time, low gastric juice content makes it difficult to digest and break down food. This, in turn, also leads to the appearance of an unpleasant phenomenon.
A decrease in sphincter tone occurs due to nervous tension, spasm, pregnancy, and constant inflammatory process in the digestive organs.
All causes of the development of belching and a lump in the throat can be divided into natural (physiological) requiring only adjustment and pathological, requiring complex treatment.
Belching and pain in the stomach are a sign of a disorder in the digestive system. There are many factors influencing this process. This could be a poor diet, eating fruit, or even smoking after eating. These reasons are harmless and do not entail serious consequences. The situation is much more complicated if the cause of pain and belching is gastritis, ulcer or esophagitis. In this case, consultation with a specialist is necessary.
Main reasons
Symptoms
- sour belching with flatulence against the background of high acidity with gastritis, mucosal ulcers;
- rotten belching due to rotting processes, stagnation of products in the stomach with pyloric stenosis, cancer, gastritis;
- belching large volumes of air due to high gas formation in the gastrointestinal tract. Occurs after eating certain foods dry, having conversations, due to nasal congestion;
- bitter belching due to the backflow of bile into the contents of the stomach with cholecystitis, cholelithiasis.
Belching pain
The causative factor lies in the development of a disease that causes digestive disorders. Discomfort is felt due to improper nutrition and bad habits. Provoking factors:
- Smoking after the meal.
- Improper consumption of fruits. They should be eaten before or 1.5 hours after a meal. Otherwise, the organic matter in the fruit begins to interact with consumed but still undigested food, forming gases.
- Tea after the meal. The leaves of the drink contain enzymes. They make the process of protein digestion more difficult, which interferes with normal digestion.
- Bath procedures. Warm water increases blood flow in the extremities but decreases it in the stomach. Therefore, food is not completely digested, stagnation and fermentation occur. These processes cause belching with abdominal pain.
- Loose elastic band or belt. This action after eating sharply relaxes the abdominal muscles, the stomach begins to work worse, and belching occurs with pain.
- Addiction to cold drinks. Drinking after a meal is undesirable due to the risk of disrupting normal fermentation and absorption of lipids.
- Sleep after a meal. With general relaxation of the body, digestion is disrupted, which provokes not only discomfort, but also the development of gastroenterocolitis.
Return to contents
Why is pharyngeal heartburn dangerous?
If heartburn occurs occasionally, it does not pose any particular danger to the body. But if symptoms are observed regularly, then this is a cause for concern.
It may feel like there is a lump in the throat, as if the throat is being squeezed, and there is no way to take a normal breath.
Food, together with hydrochloric acid, being in the esophagus, causes tissue burns and discomfort.
The process of swallowing food becomes difficult, which leads to problems with appetite, sudden weight loss, or even bleeding in the esophagus.
Ulcers that appear in the stomach and esophagus are overgrown with connective tissue, which significantly narrows the lumen. If scarring occurs in the esophagus, it can even lead to death.
Heartburn can cause the development of caries, and in advanced cases, cause oncology.
For digestive dysfunction
Diseases of the digestive system often cause air belching.
Esophagitis
The pathology is characterized by inflammation of the walls and mucosa in the esophagus. Accompanied by:
- sensation of a lump, scratching in the throat;
- heartburn;
- aching, paroxysmal pain behind the sternum, in the jaw and shoulder, between the shoulder blades.
Simultaneously with inflammation, the functioning of the muscles of the esophagus is disrupted and peristalsis is reduced, which is often accompanied by regurgitation - the reflux of the contents of the digestive tract into the mouth.
Lump in throat with belching due to reflux
Gastroesophageal reflux is accompanied by esophagitis and weakening of the sphincter muscle. Due to inflammation of the stomach walls, digestive secretion increases. These phenomena cause heartburn, lump sensation and belching. At the same time, the patient experiences:
- pain behind the sternum, radiating to the left;
- nausea with occasional vomiting;
- mild cough;
- lack of air at night and in the morning;
- weakness;
- nervous disorders;
- sleep disturbance;
- sour taste in the mouth.
Return to contents
Prevention
At the first signs of heartburn, you should analyze your life over the past month to determine unfavorable factors. Heartburn, hiccups, is the first sign of impaired functioning of the digestive tract. With a timely reaction, you can get rid of an unpleasant condition quickly, easily, and prevent the development of serious gastrointestinal diseases. To avoid heartburn, you need to:
- Do not take a vertical position for 30 minutes after eating, do not lift heavy objects, or bend over for an hour.
- Dinner should be light and avoid overeating throughout the day.
- After spicy, fatty, salty dishes, it is recommended to drink non-carbonated mineral water, milk, low-fat kefir, homemade yogurt, fermented baked milk.
- Before a feast with alcoholic drinks, it is recommended to eat a piece of butter. The product will protect the walls of the stomach and esophagus from irritation and prevent heartburn.
- Monitor your diet, do not swallow on the go, chew thoroughly.
- Do not talk while eating. This allows air to enter the esophagus, causing hiccups, disrupting digestion, and heartburn follows.
It is almost impossible to avoid heartburn during pregnancy, but proper nutrition, an appropriate lifestyle, and a comfortable sleeping position will help you avoid too frequent attacks.
Compliance with the following rules will help prevent the appearance of belching and a lump in the throat:
- changes to eating less and avoiding unhealthy foods;
- slow absorption of food and lack of talking while eating;
- rejection of bad habits;
- prevention of stressful situations;
- giving up a sedentary lifestyle, increasing physical activity and walking after meals;
- correct and timely treatment of diseases of the digestive, endocrine and nervous systems, osteochondrosis.
People prone to belching and a lump in the throat are recommended to undergo a medical examination at least twice a year and promptly take medications prescribed by a doctor.
To avoid a lump in the throat and belching, it is important to observe the following measures:
- use fractional meals;
- chew food thoroughly;
- drink food with a small amount of liquid;
- avoid eating spicy foods;
- avoid stress;
- get enough sleep;
- to live an active lifestyle.