Glucagon production and activity
Glucagon is a peptide substance that is produced by the islets of Langerhans and other cells of the pancreas. The parent of this hormone is preproglucagon.
Glucose obtained by the body from food has a direct effect on the synthesis of glucagon. Protein products taken by a person during meals also affect the synthesis of the hormone. They contain arginine and alanine, which increase the amount of the described substance in the body.
Glucagon synthesis is affected by physical work and sports. The greater the load, the greater the synthesis of the hormone. It also begins to be intensively produced during fasting. As a protective agent, the substance is produced during times of stress. Its surge is influenced by a rise in the level of adrenaline and norepinephrine.

Glucagon serves to form glucose from amino acids in proteins. Thus, it provides all organs of the human body with the energy necessary for functioning. The functions of glucagon include:
- the breakdown of glycogen in the liver and muscles, due to which the supply of glucose stored there is released into the blood and serves for energy metabolism;
- the breakdown of lipids (fats), which also leads to the energy supply of the body;
- formation of glucose from non-carbohydrate products;
- ensuring increased blood supply to the kidneys;
- increased blood pressure;
- increased heart rate;
- antispasmodic effect;
- increased content of catecholamines;
- stimulation of liver cell recovery;
- accelerating the process of removing sodium and phosphorus from the body;
- regulation of magnesium metabolism;
- increase in calcium content in cells;
- removal of insulin from cells.
It should be noted that in muscles, glucagon does not stimulate the production of glucose, since they do not have the necessary receptors that respond to the hormone. But from the list it is clear that the role of the substance in our body is quite large.
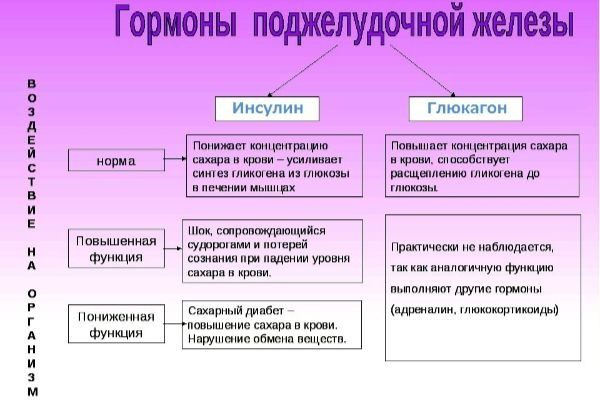
Glucagon and insulin are 2 opposing hormones. Insulin serves to store glucose in cells. It is produced when glucose levels are high, storing it in reserve. The mechanism of action of glucagon is that it releases glucose from cells and sends it to the organs of the body for energy metabolism. We must also take into account that some human organs absorb glucose, despite the functioning of insulin. These include the brain of the head, the intestines (some of its parts), the liver, and both kidneys. In order for the metabolism of sugar in the body to be balanced, other hormones are needed - this is cortisol, the fear hormone adrenaline, which affects the growth of bones and tissues, somatotropin.
How the pancreas works
The pancreas is conventionally divided into endocrine and exocrine parts, which perform certain functions in the body (production of gastric juice containing all the necessary enzymes).
The endocrine part of the pancreas consists of the so-called “islands of Langerhans” that are involved in the separation of the produced hormones necessary for the complete breakdown of food.
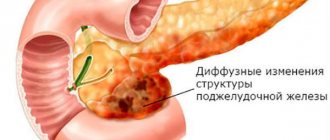
The general condition of the digestive system depends on the functioning of the pancreas, since with systematic disturbances in the body, serious diseases develop (pancreatitis, cirrhosis, gallstones).
Hormone norm and deviations from it
The level of the hormone glucagon depends on the age of the person. In adults, the spread between the lower and upper values is smaller. The table looks like this:
| Age (years) | Lower limit value (pg/ml) | Upper limit value (pg/ml) |
| 4-14 | 0 | 148 |
| Over 14 | 20 | 100 |
Deviation from the norm in the volume of the hormone may indicate pathology. Including, when determining a reduced amount of a substance, the following are possible:
- severe cystic fibrosis of the endocrine glands and respiratory organs;
- chronic inflammation of the pancreas;
- A decrease in glucagon levels occurs after operations to remove the pancreas.
The functions of glucagon are to eliminate some of the pathologies described above. An increased content of a substance indicates one of the situations:
- increased glucose due to type 1 diabetes mellitus;
- tumor lesion of the pancreas;
- acute inflammation of the pancreas;
- liver cirrhosis (degeneration of cells into tumor tissue);
- excessive production of glucocorticoids due to their generation by tumor cells;
- chronic kidney failure;
- excessive physical activity;
- psychological stress.
If the hormone is exceeded or decreased, the doctor prescribes other tests for an accurate diagnosis. Blood biochemistry is done to determine glucagon levels.
Action of somatostatin:
Somatostatin inhibits the secretion of somatotropin, gonadoliberin, thyroid-stimulating hormone, insulin, glucagon, gastrin, cholecystokenin, insulin-like growth factor-1, vasoactive intestinal peptide. From the gastrointestinal tract, somatostatin regulates the secretion of gastrointestinal hormones, preventing their increased formation; inhibits the motility of the stomach, intestines and their secretory processes; inhibits glucose absorption; inhibits the formation of enzymes in the stomach and pancreas; inhibits the production of hydrochloric acid and pancreatic juice in the stomach and pancreas, respectively.
From the nervous system: somatostatin is a neurotransmitter, participates in the regulation of sleep and has an antiepileptic effect. Somatostatin also has an antitumor effect, regulates retinal homeostasis and has a neuroprotective effect in it. With a deficiency or excess of the hormone, disturbances will appear in the organs regulated by it, and accordingly, the growth of tumor processes, acromegaly, the development of diabetes mellitus, calculous cholecystitis, steatorrhea, a decrease in the level of red blood cells and hemoglobin in the blood, and changes in the acid-base balance in the stomach are possible.
Glucagon-containing agents
Glucagon is synthesized from the hormone of animals, taking advantage of the fact that they have this substance of a similar structure. The medicine is available in the form of liquid for injection and in the form of tablets for oral administration. Injections are given intravenously or intramuscularly. The drug is prescribed in the following cases:
- diabetes mellitus with low glucose levels;
- additional treatment for depression;
- the need to relieve spasm of the intestines;
- to soothe and straighten smooth muscles;
- for diseases of the biliary tract;
- during radiological examination of the stomach.
The instructions describe that the dose of the injection, which is administered intravenously or, if it is impossible to inject a vein, intramuscularly, is 1 ml. After the injection, an increase in hormone levels, accompanied by an increase in the amount of glucose, is observed after 10 minutes.
The drug can be used to treat children. If the baby's weight is less than 20 kg, the dose should be no more than 0.5 ml. For heavier children, the dosage ranges from 0.5 to 1 ml. If the effect of the medication is insufficient, the injection is repeated after 12 minutes. You need to inject in a different place.
Treatment of children and pregnant women can only be carried out in a clinic under the supervision of a specialist. In preparation for radiation diagnostics, 0.25 mg to 2 mg of medication is injected. The dose, depending on the patient’s condition and weight, is calculated by the doctor. Taking the drug in any form without a doctor’s prescription is strictly prohibited.
If the medicine is being used as an emergency, after taking it, you should eat protein foods, drink a cup of warm, sweetened tea, and go to bed for 2 hours.
Contraindications to treatment with Glucagon
Glucagon should not be used for treatment in the following cases:
- tumor disease of the pancreas with the production of insulin by tumor cells;
- high sugar content;
- with a benign or malignant tumor (pheochromocytoma), the cells of which generate catecholamines;
- in case of individual intolerance to the drug.
Additional diagnostic procedures are required for early detection of contraindications to hormone treatment. Side effects from taking Glucagon may include nausea and vomiting. If the use of the medicine does not give the expected result, it is necessary to administer a glucose solution to the patient.
The drug can be used to treat pregnant women. It is retained by the placenta and does not reach the fetus. During the feeding period, the use of the drug is possible only under the strict supervision of a specialist.
Use of somatostatin for therapeutic purposes:
For therapeutic purposes, a synthetic analogue of the hormone somatostatin was created in the form of drugs such as octreotide (octra, sandostatin, octrestatin), lantreotide (somatulin), pasireotide (signifor).
These drugs are used to stop gastrointestinal bleeding (with varicose veins of the esophagus, ulcers, erosions, hemorrhagic gastritis); for prophylaxis after pancreatic surgery; for fistulas in the biliary tract, intestines and pancreas; to reduce the intensity of production of growth hormones, glucagon or insulin; with an increase in ketone bodies in plasma; with acromegaly; pituitary adenoma, gastrinoma, insulinoma.
If glucose is below normal, what to do?
Before the doctor arrives, you can increase your glucose level by eating certain foods. It's a good idea to eat 50 g of honey, which contains fructose, glucose and sucrose of natural origin. After all, only artificial fructose is harmful. And, if glucagon and glucose are not produced in sufficient quantities to supply us with glucose, it is necessary to take sugar in the form of food.
Tea with jam will help restore strength. After severe overload or nervous stress, it is useful to eat heavily with high-calorie foods. Their list includes seafood, nuts, apples, cheeses, pumpkin seeds, and vegetable oils. Rest in a ventilated room and sound sleep will bring benefits.
What hormones does the pancreas produce?
The main hormone produced by the pancreas is insulin, which controls blood sugar levels, since when the breakdown process is systematically disrupted, a disease such as diabetes mellitus occurs.
At the same time, the organ produces a number of other hormones:
- Somatostatin;
- Glucagon;
- Gastrin;
- Polypeptide;
- Amylin.
For a long time, C-peptide was considered a separate hormone, but recent studies have shown that it is a microparticle of insulin. Pancreatic tissue contains substances such as centropnein and vagotonin.
Functional features of hormones:
- Glucagon is produced by special alpha cells. This hormone is necessary to raise blood glucose levels;
- Insulin is produced by beta cells and is designed to control blood sugar levels;
- Somatostatin is represented by delta cells (about 10%). The hormone coordinates the exocrine and endocrine activities of the pancreas;
- The production of pancreatic polypeptide is carried out by PR cells. The hormone is responsible for the proper outflow of bile and participation in the process of protein metabolism;
- Gastrin is secreted by G-cells and is a regulator for the normal functioning of the stomach, as it affects the components of gastric juice (the interaction of regulating the volume of acid and pepsin).
Scientific resources annually disseminate material about what pancreatic hormones mean for the body. This allows us to identify new types, their effects and interactions.
The main hormone of the pancreas is insulin. Beta cells are responsible for its connection. In them, during the activity of proteolytic enzymes, the formation of insulin, its own preproinsulin, occurs. Its initiative accounts for 5% of the activity of insulin.
What hormones does the pancreas produce? Of the secrets involved in the exchange procedure, note:
- glucagon;
- somatostatin;
- gastrin;
- amylin;
- polypeptide.
main pancreatic hormones
Until a certain time, C-peptide was classified as an organ secretion. Then it was discovered that this substance is a microparticle of insulin that was torn off during synthesis. The designation of the element is retained when studying the volume of glucose in the bloodstream, since the amount is proportional to the main hormone. This is used in clinical diagnosis.
The main pancreatic mediators that regulate the functioning of the body are also synthesized by different types of endocrine cells.
- Glucagon is produced by alpha cells. This is about 20% of the total volume. Glucagon is necessary to increase the amount of glucose in the circulatory system.
- Insulin production is carried out by beta cells. Combines up to 80% of endocrine cells. Thanks to insulin, sugar is utilized and the optimal level in the blood is maintained.
- Somatostatin resources are represented by delta cells. There are about 10% of them. Regulation of somatostatin activity is capable of coordinating the exocrine and endocrine work of the organ.
- In a small number of PP cells. They produce pancreatic polypeptide, the action of which is aimed at regulating the secretion of bile and activity in the protein metabolism procedure.
- G-cells produce a small amount of gastrin, being a resource of the gastric mucosa. Gastrin affects the quality components of juice and helps regulate the volume of pepsin and acid.
What it is
The polypeptide hormone is formed in the pancreas during the process of transformation from preproglucagon. An insulin antagonist is necessary to control optimal glycemic levels in the body. The peptide hormone molecule consists of 29 amino acids.
Insulin and glucagon are interconnected: the second component suppresses the activity of the first. The optimal combination of regulators prevents both a sharp decrease and a significant increase in blood glucose concentration. Administration of an insulin antagonist quickly restores blood sugar levels during hypoglycemia.
Glucagon has another name - “hunger hormone”. The reason is the influence of several factors, under the influence of which the body signals a lack of energy. An important point is the receipt of signals in the brain to reduce glucose levels to activate the secretion of glucagon, which results in a feeling of hunger.
Against the background of heavy physical work, the level of the polypeptide hormone increases 5 times or more; with an increase in the concentration of alanine and arginine (amino acids), the levels also increase. In children born to a mother with diabetes mellitus, the secretion of insulin antagonist is often impaired, which can lead to the formation of neonatal hypoglycemia.
What is pituitary dwarfism and how to treat the lack of somatotropin production? We have the answer!
Read about how to take Siofor as maintenance therapy for type 2 diabetes in this article.
Reasons for deviations
Changes in pancreatic hormone secretion depend on many factors. In extreme situations, the level of not only adrenaline increases, but also glucagon. The values change with an unbalanced diet, excessive consumption of protein foods (more often by athletes or women when following certain types of diets). There are several pathologies that negatively affect the functioning of the pancreas and hormonal levels.
Glucagon is increased
Excessive secretion of the hormone has been noted against the background of the following diseases and conditions:
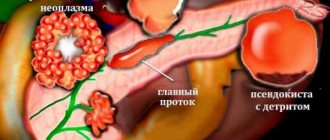
- malignant tumor in the pancreas;
- diabetes;
- development of hypoglycemia;
- Cushing's disease and syndrome;
- renal failure;
- glucagonoma – tumor of alpha cells of the islets of Langerhans;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- pancreatitis.
Hormone levels increase significantly in the period after surgery, against the background of injuries, burns, severe stress, and neuropsychic disorders. Another factor is excessive consumption of protein foods.
Decreased hormone levels
Causes of hormone deficiency:
- chronic pancreatitis;
- resection of the pancreas was performed;
- lack of the enzyme necessary for the synthesis of an insulin antagonist;
- cystic fibrosis.
Structure and functions
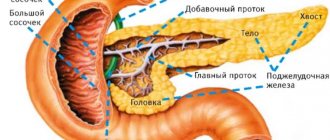
The pancreas is a digestive organ, so it is necessary to know its structure and functions. The head is the widest zone; it is surrounded by tissues of the duodenum. The body of the pancreas has an anterior, caudal, and lower edge. The elongated tail is directed posteriorly to the left. The length of the organ is from 16 to 23 cm.
The pancreas performs 2 functions for the body:
- External (exocrine) activity is responsible for the release of digestive juice. This area is formed by the connection of cells into the islets of Langerhans, where the main hormonal substances are released.
- Internal (endocrine) purpose - characterized by the activity of hormones required for the body, participates in the development of fats, carbohydrates, proteins.
An important phenomenon is that the pancreas produces hormones. Pancreatic hormones are responsible for connecting, enriching, and transporting sugar throughout the organs.
Functions in the body
The main role is to achieve a balance of pancreatic hormones and optimal glucose levels. The polypeptide hormone suppresses insulin secretion and prevents the development of hypo- and hyperglycemia.
Other functions of glucagon in the body:
- monitoring sodium levels, eliminating excess trace elements, normalizing the functioning of the heart and blood vessels;
- accelerating the breakdown of fats, reducing cholesterol concentrations, reducing the risk of atherosclerosis;
- stimulating effect on cells to remove insulin;
- accelerates the recovery of hepatocytes;
- activation of blood flow to natural filters. Poor blood supply to the kidneys is one of the reasons for damage to the nephrons, disruption of the concentration, filtration, endocrine and excretory functions of the bean-shaped organs.
The polypeptide hormone exhibits an effect similar to the effects of adrenaline. In extreme situations, when the body responds to stress, significant physical overload, the concentration of glucose increases almost instantly. The consequence is that the muscles quickly receive an additional portion of nutrition and energy for immediate action against the backdrop of a powerful surge of adrenaline.