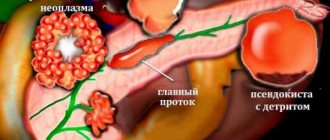
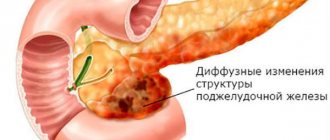
Pancreatic steatosis is when fat cells appear in place of healthy ones. This condition of the gland can be caused by abuse and diseases of neighboring organs. For a long time the disease does not manifest itself in any way and proceeds without symptoms.
Most often, this process leads to the fact that there are fewer and fewer healthy cells every day, and the patient does not undertake any therapy, since he is not aware of the disease. Diffuse is treated conservatively in most cases. Most often, this disease occurs in conjunction with liver steatosis.
Causes of steatosis of the liver and pancreas
The main reasons include:
- Alcohol abuse
- Poor nutrition associated with eating salted, smoked, fried, fatty foods in uncontrolled quantities
- Tobacco smoking
- Gallstones
- An inflammatory process in the pancreas, which led to the fact that diseased cells that died were replaced by fatty cells
- Diabetes
- Digestive system diseases
- Chronic cholecystitis
- Overweight or obesity
- Some medications, such as: hormones, cytostatics, painkillers, antibiotics
- Surgical interventions in the digestive tract
The most common cause of the disease is considered to be frequent consumption of alcoholic beverages together with fatty foods. Diffuse changes in the pancreas such as steatosis most often occur in people who suffer from diabetes with insulin deficiency.
Treatment of pancreatic steatosis
To determine the condition of the pancreas, a comprehensive examination is prescribed, which includes the following measures:
- Palpation, collection of information about disturbing symptoms.
- Blood analysis. General, biochemical, and, if necessary, tests for infections and viruses.
- Ultrasound. It is required, as it is one of the informative types of research. Ultrasound reveals pathological areas of various etiologies; it is possible to determine not only their location, but also their size, and suggest the structure based on the degree of echogenicity.
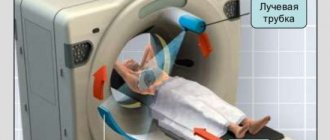
- Tomography, X-ray, CT. Hardware examinations are prescribed at the discretion of the doctor regarding the expected diagnosis and concomitant diseases.
- Biopsy. It is used as a last resort when there is a suspicion of developing oncological processes.
Based on the data obtained, the doctor chooses further therapeutic tactics.
Principles of treatment
It is not possible to completely restore pancreatic tissue; the goal of treatment is to preserve the remaining healthy cells and maintain the organ in its functionality. The following activities can be used for this:
- Drugs that facilitate the functioning of the pancreas and the digestive system as a whole, in particular enzymes, hepatoprotectors and others.
- Means to reduce the production of hydrochloric acid.
- Medicines that reduce or block the absorption of fats into the tissues and intestinal walls.
- Taking medications aimed at eliminating the root cause of steatosis, for example, normalizing blood glucose levels, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and others.
- Painkillers if there is increased pain.
- Diet.
Conservative treatment methods are used only in the initial stages of the disease, when the affected area does not exceed 40%, and the fat cells have not yet grown deep into the parenchyma. If a significant pathological area is already noted, then surgical intervention is prescribed.
A prerequisite for treatment is a change in diet. The diet is chosen to facilitate the work of the pancreas, to reduce fat cells in the body, as well as for general weight loss, since most patients are overweight.
When in a hospital, table No. 5 or No. 4 will be recommended; if a person has diabetes or other chronic diseases, then the diet can be further adjusted. It is important to limit the consumption of foods harmful to the pancreas not only during the treatment period, but also subsequently.
We suggest you read: How to treat a pancreatic polyp
It should be noted that it is impossible to completely eliminate steatosis of the pancreas and liver. However, modern adequate therapy can stop the development of the process and support the functioning of the organ.
The prescription of treatment is based on several factors: the localization of lipid stains, the stage of development of steatosis, the capabilities of the body and the age of the patient. If the parenchyma of the liver and pancreas is slightly affected, they are limited to prescribing medications.
Therapy for pancreatic and liver steatosis is based on relieving the condition that led to the disease. The following drugs are prescribed:
- biological catalysts that accelerate the process of biochemical reactions - aimed at maintaining the functioning of the organ;
- drugs that block the production of hydrochloric acid in the stomach;
- painkillers;
- fat blockers – limit the absorption of lipids in the gastrointestinal tract;
- antibacterial agents;
- vitamin complexes.
In case of diffuse damage to the parenchyma, the patient is indicated for surgical treatment. It consists of removing the necrotic area.
It is easier to treat this pathology, like most disorders in the life support systems of the human body, at the stages of the first manifestations. But for this you need to undergo a medical examination at least once a year.
Treatment by modern doctors is carried out mainly by conservative methods, that is, with the use of medications and diets. But do not delay, since complete obesity of the gland threatens its atrophy and cessation of the production of insulin and enzymes.
Drug treatment is aimed at stopping cell replacement. It is impossible to restore the affected areas with the help of medications, therefore it is necessary to recognize the disease at an early stage and take all measures to prevent it from spreading.
Pancreatic obesity is also treated with a special diet. Exclude from the daily menu all fried, salty, sour foods that burden the functioning of the gland. More attention is paid to low-fat foods that help remove fat from the body, these include cottage cheese, fish oil, beef, and chicken. Meals are carried out in small portions, but often, there should be at least 5 meals a day.
Treatment will be effective only when conservative methods are combined with diet. If the patient’s condition worsens, it is necessary to urgently seek help from specialists, since it is simply impossible to stop the development of the pathology at home.
First of all, it is necessary to remember that the basis of treatment for all diseases of the gastrointestinal tract is a rational diet. Since the digestive function of the body suffers, restricting food will help minimize the load on the pancreas and liver and speed up the recovery process.
Drug treatment of steatosis involves the use of the following groups of drugs:
- Enzymatic. The main goal is to replace the endogenous enzymes of the organ with artificial analogues.
- Antacids. They reduce the production of digestive juice by the stomach, which reduces chemical damage to the gastrointestinal mucosa.
- Metabolic. Improve microcirculation and all metabolic processes in the body.
In addition to diet, the issue of combating excess weight, quitting smoking and alcohol remains important. It will not be possible to completely heal the patient. The only thing that can be done is to slow down the progression of the pathology as much as possible and normalize the digestion of food.
Related Posts
Treatment of the disease can be carried out using two main methods: conservative and surgical. In addition, correction of nutrition and body weight are also important tasks.
Conservative
Drug therapy is prescribed in the following cases:
- if fat deposits are localized throughout the gland;
- the depth and scale of the damage is small;
- the exocrine ducts are not compressed by neoplasms.
Drugs prescribed for treatment:
- enzymes to support the functionality of the pancreas (Mezim, Festal, Pancreatin);
- lipid blockers that prevent the absorption of fats in the digestive system;
- antibiotics;
- antisecretory medications to maintain the balance of digestive juices;
- means for improving digestion;
- painkillers and antispasmodics.
Surgical
Used in cases of extensive organ damage. The operation involves removing fatty deposits and restoring the functioning of the ducts. Surgery is performed under general anesthesia.
After surgery, the patient needs to adhere to a rehabilitation regime, which involves proper rest, taking preventive medications, as well as a therapeutic diet.
Therapeutic nutrition is necessary to relieve the main burden on the digestive system, as well as correct body weight. A diet for diffuse steatosis of the liver and pancreas involves severely limiting carbohydrates and fats and increasing protein levels. At the same time, daily meals should be fractional and low-calorie.
You will need to exclude from the menu:
- roast;
- fat;
- salted, smoked and pickled;
- spicy foods and seasonings;
- semi-finished products and fast food;
- carbonated drinks and coffee;
- sour fruits and vegetables;
- sweets and confectionery;
- fatty dairy, meat and fish products.
The following are welcome in the daily diet:
- low-fat fish and meat products (boiled or baked);
- low-fat cottage cheese and kefir;
- vegetables (potatoes, radishes, melons, eggplants, tomatoes, cabbage);
- cereals (rolled oats, buckwheat, rice).
Allowed products should be used to prepare porridge, cereal and vegetable soups, casseroles, and steamed cutlets. Diffuse changes in steatosis corresponding to even the extensive type are corrected with a calorie deficit and a decrease in the load on the gastrointestinal tract.
ethnoscience
Non-traditional recipes can be a complement to basic therapeutic methods. Folk remedies help treat chronic problems and relieve inflammation. Herbs also improve well-being and digestion, help reduce body weight and alleviate pancreatic steatosis. Among the most effective and safe:
- Decoction of blueberry leaves. Grind a tablespoon of fresh leaves, dilute with a glass of hot water and simmer over low heat for ten minutes. Drink one hundred milliliters twice a day.
- Oatmeal broth. Pour one glass of grain into a liter of water and leave it like that for eight hours. After this, boil and keep on low heat for about half an hour. Remove and wrap in a towel, leave for twelve hours. Take one hundred and fifty milliliters of the drink every morning before meals.
- Herbal collection. Mix chamomile and immortelle herbs in equal proportions. Pour two tablespoons of herbal mixture into a cup of boiling water and leave for half an hour. Take one hundred milliliters three times a day twenty minutes before meals.
We invite you to read: Emergency care for diabetes mellitus and algorithm of actions
The pancreas is important for the body. It is entrusted with a large number of different functions, therefore, if there are deviations in the purpose of the gland, it will cause serious illnesses.
When patients are faced with the occurrence of steatosis, the question is often asked, is it possible to cure steatosis? Fatty infiltration cannot be eliminated; it is only possible to stop its formation and support the functioning of the pancreas with timely initiation of therapy.
Symptoms or signs
For a long time, the disease does not manifest itself in any way, so the person does not experience discomfort. The patient begins to notice that something is wrong in cases where adipose tissue has taken up thirty percent of the organ or has begun to interfere with the full functioning of the ducts. In these cases, a person notices the following:
- Stomach upsets such as diarrhea,
- Gas formation and, as a result, bloating,
- Heartburn and belching
- An allergic reaction to foods that were previously accepted adequately
- Girdle pain or pain in the left side, which is most often noticeable after eating,
- Nausea for no reason
- Loss of appetite,
- General weakness and decreased performance, apathy,
- Weakening of the immune system, which leads to very frequent illnesses,
- Itching and icteric color that appear on the skin.
Clinical symptoms
Steatosis does not have clinical manifestations for a long time, and the person does not know what is happening to his liver. As a rule, he has no complaints, so the disease is discovered during a random examination. When the changes reach a pronounced degree, the following symptoms appear:
- heaviness in the stomach;
- loss of appetite;
- constant nausea;
- increased fatigue;
- skin itching;
- icteric discoloration of the skin and mucous membranes.
The most pronounced symptoms are observed when cirrhosis of the liver or gross degeneration of pancreatic tissue develops:
- severe jaundice;
- ascites - accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity;
- redness of the palms;
- persistent diarrhea with discolored stool.
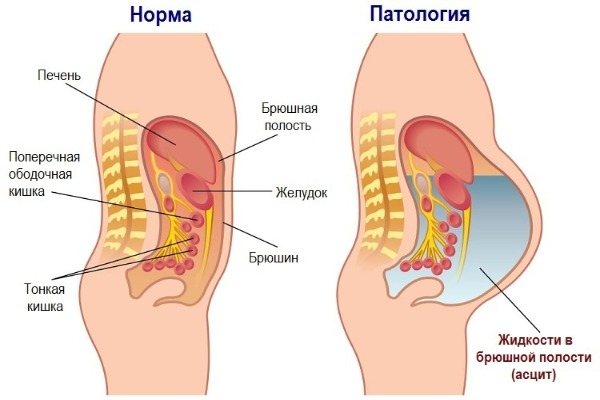
ascites
Diagnosis of the disease
- Ultrasound, which begins to display greater echogenicity,
- Blood and urine tests, in which, with steatosis, laboratory tests show a high level of alpha-amylase,
- MRI helps to distinguish adipose tissue from cancer with a high percentage of reliability,
- An endoscopy will help examine the pancreas more closely.
How is pancreatic steatosis diagnosed?
To examine the pancreas and make a correct diagnosis, the patient should contact a gastroenterologist. For diagnosis, a combination of instrumental and laboratory methods is used:
- Ultrasound of the pancreas: a non-traumatic, highly informative method that does not have strict contraindications, allows you to identify echogenic areas of the organ and areas with altered tissues;
- radiography with contrast: makes it possible to assess the condition of the ducts of the organ and their patency;
- MRI: allows you to see changed organ tissues and detect neoplasms in it;
- blood test: with steatosis, the alpha-amylase level will be higher than normal;
- biopsy: a sample of altered tissue is taken for examination.
We recommend learning how to choose probiotics for your gut.
Read: what is pneumatosis intestinalis.
Find out what symptoms indicate pancreatic necrosis.
How to treat
Treatment in this case is most often conservative. This type of treatment is used in the following cases:
- If adipose tissue does not take up much space on the organ,
- If fatty patches are observed throughout the pancreas,
- If the ducts are not damaged and there are no elements of compression on them.
Most often, the most important factor in treatment is strict adherence to diet. Treatment with the following drugs is also used:
- Medicines containing enzymes that are deficient in this disease.
- Drugs that make the secretion of hydrochloric acid much less.
- Products that help remove excess fat from the intestines.
The operation is prescribed if the ducts are compressed due to nodes. This process occurs using general anesthesia.
Some recommendations for the disease:
- It's worth following a diet
- It is advisable to get rid of bad habits
- Ibuprofen will help with pain
- To improve digestion, you can take pancreatin
- If you suffer from diarrhea, loperamide helps very well
- If you feel nauseous, you should take metoclopramide
- For cramps, you should take mebeverine
- Avoid stress and nervous tension
Diagnosis of the disease
signs of pancreatic disease symptoms and treatment
To diagnose steanosis, a number of popular methods are used:
A blood test that pays special attention to the level of amylase (alpha) in the serum.
MRI demonstrating the presence of tumors: malignant or benign.
Ultrasound showing echogenic zones.
Contrast x-ray designed to check the patency of the pancreatic ducts.
Based on the results of the analysis, the doctor assigns one of three degrees of the disease, in accordance with the volume of the affected areas of the gland:
From 0 to 30% - first.
From 31 to 60% - the second.
From 61 d 100% - third.
Diet
When treating pancreatic steatosis, it is very important to follow a diet and lead a healthy lifestyle, which should be quite active. If you are sick, you should adhere to the following rules:
- You need to eat fractionally, that is, often and in small portions
- You need to monitor the temperature of the food, you can’t eat hot or cold.
- It is best to grind food as much as possible, preferably to a mushy state.
- You need to cook it using regular cooking and steaming, you can also use stewing and baking in the oven.
For all types of steatosis, it is worth resorting to some exceptions, which include:
- Alcohol,
- Smoking,
- Everything is fatty, fried, smoked,
- Canned food and everything canned,
- Stress and all situations that can lead to nervous tension,
- It is necessary to exclude all very heavy physical activities,
- It is not advisable to overuse coffee and strong black tea,
- Binge eating,
- Poor nutrition
- Fast food,
- Carbonated drinks,
- Spicy and all foods with a lot of spices and seasonings, as well as containing vinegar,
- Chocolate and cocoa
- Baked goods and fresh bread,
- Products containing acid
- Solid food.
For pancreatic steatosis it is allowed to:
- All varieties of lean meat,
- Rose hip decoctions,
- Skinless poultry and lean fish,
- Vegetables and fruits in heat treatment. Vegetables are best steamed and chopped using a grater. Fruits can be used in the form of jams, pastilles, jellies, and apples can be baked,
- Day old bread,
- Marshmallow,
- You can add butter or vegetable oil to dishes in very small quantities,
- Fermented milk products with low fat content,
- Eggs are allowed only in the form of an omelet and without the yolk. And no more than one egg per day.
- It is very good to drink jelly and compotes, but without sugar and make sure that they are not sour.
- Cereals and porridges made from them with milk and water.
Can steatosis be cured?
Experts draw attention to the importance of early diagnosis of steatosis, since changes in organ tissue are irreversible. This means that therapy is not capable of completely restoring the affected organ. To reduce the likelihood of developing dangerous complications, it is necessary to identify pathology as early as possible, before it leads to significant disruption of the organ.

Treatment of steatosis should be comprehensive. It implies:
- taking medications to eliminate the symptoms of pathology and improve the digestion process;
- diet;
- rejection of bad habits;
- normalization of weight.
Medicines are prescribed to each patient individually, depending on the existing symptoms and concomitant diseases. Can be used:
- enzyme preparations;
- antibiotics;
- prokinetics;
- hepatoprotectors (for damage to liver tissue);
- antisecretory drugs.

Diet therapy
With pancreatic steatosis, a properly formulated diet plays an important role. Without following a diet, it is almost impossible to achieve a positive effect from treatment. The patient must avoid foods that place increased stress on the pancreas. These include:
- fried foods;
- high-fat foods containing refractory fats;
- canned food;
- fast food, semi-finished products;
- sweets;
- flour;
- coffee, cocoa, soda, energy drinks;
- alcohol.
Patients should adhere to the principles of fractional nutrition: eat up to 6 times a day, but in small portions. Overeating is dangerous! You can reduce your daily calorie intake only on the recommendation of a doctor to lose weight.
If conservative therapy is ineffective, surgery is performed. Damaged tissue is removed surgically. After this, the organ will not function fully, so the key goal of therapy is to avoid surgical intervention by slowing down the replacement of normal tissues with pathological ones. The speed of seeing a doctor plays a significant role in recovery.
Treatment with folk remedies
It is recommended to treat the pancreas using the following plants:

- Chicory,
- Dandelion,
- Blooming Sally,
- Plantain,
- Spiraea.
These herbs can be used in combination with rice water, this will improve the effect and give more noticeable results.
You can also use insulin-like plants, which will be very useful in treating the pancreas, these are:
- Elecampane,
- bean pods,
- Burdock,
- Nettle,
- Licorice,
- blueberry leaves,
- Corn silk,
- Dandelion.
All these herbs help lower blood sugar levels and improve gland and liver function.
Phytocollection
- Golden volodushka
- Corn silk
- Oat straw
- Fennel
- Burdock
- Anise
- Sagebrush
- Plantain
The herbs are finely chopped and poured with boiling water, half a liter per tablespoon of herbal mixture. The drink is infused for about an hour and filtered. Drink the infusion half an hour a day three times a day for two weeks.
Diagnostics
When clinical symptoms appear, it is necessary to confirm the diagnosis using tests and instrumental methods. To diagnose pathology the following are used:
- general clinical tests that determine increased fat content in the body, signs of inflammation of the liver and pancreas;
- ultrasound examination, which determines changes in the structure of the liver and an increase in its size;
- fibroscanning is a method that evaluates the ratio of normal liver tissue to fat.
Only a biopsy of the liver or pancreas can establish the diagnosis of steatosis with one hundred percent accuracy. But this method is labor-intensive and unsafe for the patient, so it is rarely used in practice.
Failure in work
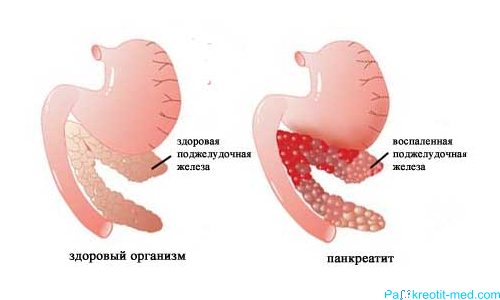
Sometimes all this activity begins to fail, and then fatty degeneration begins - pancreatic obesity, or lipomatosis.
What it is ? This is the name given to the process of replacing diseased or dead cells with adipose tissue. Cells damaged by the inflammatory process can no longer perform their functions, become weak, and die. And their place is taken by fat depots.
At the same time, outwardly these changes may not be noticeable for quite a long time and practically do not make themselves felt at all. At least until fat deposits begin to compress the tissue and interfere with the functioning of neighboring organs. Most often, the disease is detected by chance, during an ultrasound.
Misfortune never comes alone
The difficulty is that such a process of replacing healthy cells with fat is not isolated. Since our body is a single whole, the onset of a disease in one organ inevitably leads to problems in others. In this case, the liver most often suffers, which is also affected by the disease - fatty hepatosis - the degeneration of its cells into fatty deposits.
Symptoms and their absence
All these serious diseases may not manifest themselves for a long time. Only occasionally does slight fatigue, dry mouth appear, and small ulcers form on the oral mucosa.
But the stronger the disease, the more distinct its symptoms may be:
- vomiting, diarrhea, nausea
- flatulence
- pain in the right hypochondrium, often of a girdling nature
- in especially severe cases - weight loss
Looking for reasons
However, where and why does trouble come from? From metabolic disorders. But it is provoked by several reasons at once.

Lipomatosis is not a cause, but a consequence of pathological changes in this organ that occur in response to:
- pancreatitis, both acute and chronic
- alcohol abuse
- hepatosis (replacement of cells with fat) of the liver
- improper treatment of pancreatitis
- genetic predisposition
- the patient is overweight
Treatment
Effective treatment requires an integrated approach and includes:
p, blockquote 22,0,0,0,0 –>
- combination of traditional medicines with folk remedies;
- adjustment of life routine.
In severe cases, surgery is considered the optimal solution.
p, blockquote 23,0,0,0,0 –>
The duration of treatment is about two months. Upon completion, new tests are prescribed (blood biochemistry and ultrasound of the abdominal cavity) with the course repeated after six months.
p, blockquote 24,0,0,0,0 –>
Medications
p, blockquote 25,0,0,0,0 –>
Drug treatment is based on the use of drugs that correct the functioning of the pancreas and promote digestion processes.
p, blockquote 26,0,0,0,0 –>
- first of all, these are enzymes like Festal, Pancreatin, Mezim, which cope with heaviness in the stomach;
- Metoclopramide will help to cope with vomiting and nausea;
- antispasmodics (Platifilin, Ibuprofen, No-shpa) are prescribed as painkillers;
- stool disorders can be corrected with antidiarrheal drugs, for example Loperamide;
- Mebeverine calms intestinal spasms;
- Vitamin complexes have a general strengthening effect on the immune system.
If necessary, the doctor will also prescribe insulin therapy.
p, blockquote 27,0,0,0,0 –>
p, blockquote 28,0,0,0,0 –>
Additional Methods
p, blockquote 29,0,0,0,0 –>
What is pancreatic steatosis
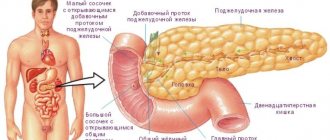
The pancreas is a glandular organ 7 cm long. It is located in the deep parts of the abdominal cavity. When food components enter the body, the body begins to synthesize a special enzyme that breaks down carbohydrates, proteins and fats - lipase. The pancreas also produces the hormone insulin, which is involved in the utilization of glucose in the body.

Official medicine claims that pancreatic obesity or pancreatic steatosis is a secondary disease and can occur as a consequence of pancreatitis, as well as against the background of diseases such as obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus and metabolic syndrome, which combines obesity, excess cholesterol in the blood and hypertension. Steatosis also occurs in the presence of a genetic factor.
Fatty degeneration of the pancreas develops if a lot of fat comes from food. This leads to the formation of large amounts of free fatty acids. Under their influence, inflammation of the tissue occurs, followed by the replacement of its cells with fatty elements. In this case, insulin secretion and sensitivity to it are disrupted, and insulin resistance appears.
Under strong pathogenic influence, the pancreas seeks to replace lost cells that have died due to abnormal transformations. As a result, fatty analogues appear in their place, unable to perform the direct functions of dead cells. Pancreatic lipomatosis, leading to abnormal changes in the structure of the organ, negatively affects the functional state of the organ and leads to irreversible processes.
Fatty degeneration of the pancreas often occurs against the background of obesity of the liver and other organs. The pathology is recorded in patients who regularly drink alcoholic beverages, as well as in people who have previously suffered from pancreatitis or suffered from its chronic form. Patients with excess body weight, chronic hepatitis, diabetes mellitus, deficiency of thyroid hormones, and also with a hereditary predisposition to diseases of the digestive system are more prone to pancreatic obesity.
Pancreatic steatosis is asymptomatic for a long time and is not accompanied by any special signs. The pathology is often diagnosed accidentally during an examination of the abdominal organs (ultrasound). It is permissible to talk about a characteristic clinical picture when 1/3 of the gland parenchyma is replaced by adipose tissue.