Unfortunately, current medical statistics regarding late detection of tumors in the pancreas are growing markedly. As a percentage, the increase in this disease during the year is 0.72%. To a large extent, this is due to the fact that the differentiation of cancer and pseudotumor pancreatitis is difficult. Simply put, patients whose ultrasound showed a mass formation in the pancreas should be examined in detail to confirm or refute the presence of a tumor.
Complications develop so frequently and are so severe, and the uncertainty of prognosis regarding the condition of a patient with such abnormalities is so high that it forces healthcare providers to use a sequential algorithm that can help make an accurate diagnosis of a patient with a mass lesion of the pancreas. The principle of waiting in this case can lead to irreversible changes in the organ. That is why patients with such formations should be examined not by the attending physician, but in an oncology hospital, where all the equipment necessary for such an examination is available, in order to avoid the possibility of missing a malignant tumor.
Quite often, in patients with acute pancreatitis, ultrasound reveals a focal formation of the pancreas. It should be noted that such changes are typical for the acute inflammatory process occurring in this case, but these same formations may indicate the presence of stones in the pancreas, a pseudocyst, and, unfortunately, a malignant tumor of the organ. The doctor should pay special attention to a patient who has a focal or any other formation, if in the past he was treated for a malignant tumor of any location. In this case, formations identified during examination of the pancreas can serve as a sign of the appearance of metastases, and the timing of treatment does not play a role, even if several years have passed.
Thus, any deviation from the norm, even if it may be perceived as a symptom of any other disease, including acute or chronic pancreatitis, is a reason for a complete examination of the patient in order to exclude more serious diseases.
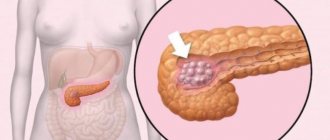
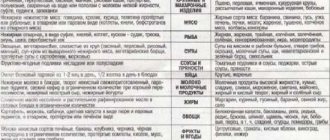
Formations in the pancreas
Focal formation of the head of the pancreas can contribute to complete closure of the bile duct. As a result, bile flowing from the liver into the duodenum accumulates. This leads to the following manifestations:
- the skin and whites of the eyes turn yellowish;
- darkening of urine occurs;
- the stool becomes discolored.
Any formation in the gland prevents this organ from functioning normally. The patient experiences dyspeptic disorders and pain. Histological classification of neoplasms:
- Neoplasms of mixed type.
- Non-epithelial in nature.
- Lymphoid and hematopoietic formations.
- Tumors with metastases.
- Unclassifiable tumors.
- Benign neoplasms.
- Malignant pathologies.
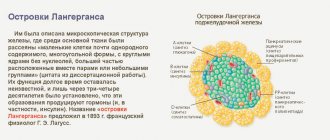
- Pathology of pancreatic islets.
Malignant formations
Pancreatic cancer is a terrible cancer pathology. The disease is diagnosed in the later stages, usually when the tumor has already metastasized. The survival rate of patients who underwent surgery is no more than 3.0%. The life expectancy of such patients after surgery is no more than 3 years.
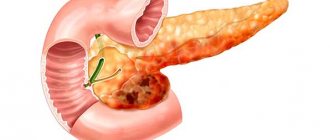
If the tail part of the pancreas is affected, the formation can affect the vessels of the spleen. With cancer, you can see focal changes that affect the entire organ.
A tumor of the head of the glandular tissues of an organ is difficult to recognize at an early stage.
She is difficult to treat. The development of the disease leads to obstruction of the bile duct and duodenum. If a tumor is observed in the body of the gland, then sometimes you can see its spread to other organs or to the wall of the stomach.
Late symptoms of pancreatic cancer include:
- the patient's appetite decreases;
- a person has an aversion to fatty foods and substances that cause poisoning to the body;
- there is pain in the abdominal cavity;
- there is general weakness;
- sleep disturbance occurs;
- Peripheral vein thrombosis is often diagnosed;
- weight loss occurs;
- obstructive jaundice occurs;
- there is an increase in the size of the spleen;
- upon palpation, an enlarged gallbladder can be detected;
- lack of enzymes causes disruption of the digestive process;
- a person begins to lose weight;
- stomach upset is common;
- if the disease progresses, then against the background of internal bleeding, vomiting occurs, the stool becomes black;
- after eating, heaviness occurs, the person suffers from belching;
- if the islets of the gland are destroyed, the patient is constantly thirsty, has a dry mouth, is often dizzy, and has itchy skin;
- if metastases affect the portal vein, then ascites is observed.
If you find yourself with most of the above symptoms, then it is better to get examined.
Research results
Results depend on the location and size of the tumor. With a single tumor, one focus is noticeable; with progression, a dense tumor conglomerate is visualized.
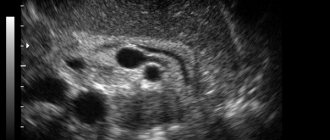
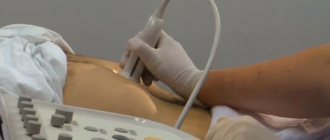
Signs of pancreatic cancer on ultrasound
An ultrasound will show oncology if the tumor size is more than 2 mm. Modern sensors visualize formations of smaller diameter, but are available only in research centers.
The tumor is visible on the ultrasound machine monitor in the form of a volumetric formation of irregular shape with uneven edges. Changed tissues of low echogenicity. The structure of education is heterogeneous.
It is often difficult to differentiate cancer from the pseudotumor form of pancreatitis. With this pathology, the Wirsung duct is significantly expanded, and with cancer, an uneven change in its lumen is observed.
During the study, the possibility of surgery is assessed. The location of the tumor between the pedicles of large arterial vessels is a contraindication to surgery.
Metastases are looked for in the liver, kidneys, and regional lymph nodes. They are visualized as weakly echogenic foci.
The most sensitive method is endosonography. Unlike a classic ultrasound sensor, a flexible video endoscope with an ultrasound element is used. The device is inserted into the intestine and brought directly to the formation. The method allows you to identify the early stage of the tumor. The monitor shows cancer with all its features. The condition of the vessels is assessed using a Doppler sensor. With a malignant neoplasm, the blood flow will become pathological. The vessels become fragile, and contact bleeding is also noted.
An ultrasound report is not a diagnosis. To confirm, a CT scan is performed and a tissue sample is taken. Only histological examination confirms cancer.
What other pathologies can be detected
As a rule, during an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, the condition of the liver and gallbladder, kidneys, and spleen is assessed. Ultrasound diagnostics can detect nephrolithiasis (kidney stones), which also causes pain. Cholestasis (stagnation of bile), associated with blockage of the bile ducts, causes yellowness of the skin. Also, dilation of the bile ducts causes dysfunction of the pancreas.
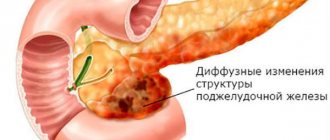
Diffuse enlargement of the organ indicates an acute inflammatory process. The presence of cysts indicates chronic pancreatic pathology. Cysts are often mistaken for cancer.
Benign tumors
Benign formations are divided into:
- neurogenic tumors – ganglioneurinomas and neuromas;
- changes in the epithelial tissue of the pancreas - cystadenoma and adenoma;
- tumors formed in connective tissue - lipomas and fibromas;
- lesions of muscle tissue - leiomyomas;
- tumors formed in the islets of the pancreas - insulinoma;
- formations that affected the vessels of the organ - lymphangiomas, hemangiomas.
Breast cancer has a number of distinctive features:
- the structure of the gland tissue does not undergo changes;
- the tumor slowly increases in size;
- metastases do not appear;
- there is no germination into neighboring organs.
Scientists cannot name the reason why benign formations occur. But they identified several factors that more often than others can contribute to the growth of formations:
- unbalanced diet;
- harmful addictions;
- in case of genetic predisposition;
- poor ecology in the place of residence.
If a person has a benign formation in the pancreas, this is accompanied by a number of symptoms:
- jaundice;
- nausea and vomiting;
- profuse sweating, confusion, weakness, fear;
- pain in the navel area, radiating to the left side of the body.
A benign tumor can degenerate into cancer and cause bile intoxication, chronic pancreatitis, and diseases of the endocrine system.
What are the most common pancreatic lesions?
The gland is oval in shape and small in size. According to statistics, it is this organ that most often suffers from focal lesions of various nature. Any formation on the pancreas first affects the epithelium and then continues its development on the head of the gland.
Such pathologies do not have a specific predisposition based on the patient’s age, but in 80% of cases people over 50 years of age suffer. Additionally at risk are:
- heavy smokers;
- alcohol abusers;
- lovers of spicy and salty foods;
- fond of seasonings when preparing dishes;
- patients with diabetes;
- patients with pancreatitis;
- patients with chronic diseases of the digestive system.
Focal formations of pancreatic tissue of both benign and malignant nature can occur on the head. If an ultrasound examination shows that there is a lesion, then a more in-depth diagnosis is necessary, which will indicate whether a tumor is present or the risk of its development.
Focal formations of the pancreas are divided into several types:
- epithelial formations, which can be benign or oncological in nature;
- pancreatic inclusions;
- mixed education;
- non-epithelial tumors;
- lymphoid formations;
- hematopoietic foci;
- metastatic tumors.
The most common are epithelial formations, but other groups of tumors are clearly characterized by their symptoms and are well identified using computer diagnostics.
Characteristics of epithelial neoplasms
A benign formation in the pancreas is characterized by the fact that it does not metastasize, does not change in size, but can be single or multiple. It is insidious in that it releases hormones into the blood that poison the body slowly but irrevocably.
Among benign formations, the most common are:
Their difference lies in their cellular composition:
- connective tissue;
- vascular structure;
- fat cells;
- muscle fibers;
- Schwann fabric, sharpened into a shell;
- nerve cells.
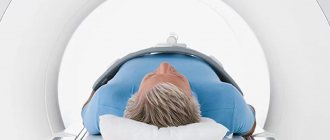
Malignant formations of the head of the pancreas are distinguished by the fact that they can grow very quickly, give metastases, and germinate into neighboring organs and tissues. They are quite difficult to treat, so timely diagnosis is important here. Magnetic resonance imaging will indicate what kind of formation the doctor is dealing with. Using a three-dimensional projection, you can easily see the boundaries and areas of the tumor, find out its nature and predict the further course of the disease.
Malignant tumors include:
- tumors that grow from the pancreatic epithelium;
- formations from lymphoid tissues;
- combined formations;
- tumors that cannot be differentiated (when there are signs of several tumors at once);
- metastasis.
Regardless of what type of tumor was diagnosed in the patient, the doctor prescribes preliminary treatment, takes the patient under control and subsequently decides whether surgical care is needed or whether medication can be used.
Reasons for the appearance of epithelial focal formations
It is impossible to determine whether the pathology of the pancreas in a person is benign or malignant. It is also impossible to make predictions about how the tumor will develop, but observations have shown that predisposing causes still exist. The main factors include:
- heredity;
- poor environmental conditions in the region of residence;
- inflammatory processes in the gland that have not been treated;
- patient self-medication;
- passion for alcohol;
- alcohol abuse;
- the use of traditional methods and recipes without the consent of a doctor;
- passion for foods containing large amounts of fat.
Knowing these risk factors, everyone can protect themselves with simple rules:
- undergo an annual medical examination;
- maintain a daily routine;
- give preference to proper nutrition;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- do not self-medicate;
- for pancreatitis, follow a diet and take the indicated medications.
Diagnosis of the disease and treatment
- Ultrasound helps to identify a mass formation in the pancreas. During an ultrasound, tumors larger than two centimeters are detected.
- MRI.
- A CT scan shows the position of the tumor, its size, shape, the presence of metastases and germinations.
- Positron emission tomography helps diagnose cancerous tumors.
- An x-ray of the abdominal cavity can show deformation of the internal organs.
- Angiography makes it possible to examine the vessels in the gland.
- With oral cholangiopancreatography and fibrogastroduodenoscopy, a biopsy of the affected area of the pancreas can be taken using an endoscope.
- The patient must also undergo a general blood test.
If a patient's ultrasound reveals a mass formation in the pancreas, then other types of examinations should be performed.
All pancreatic tumors are treated only through surgery. There are operations on the gland:
- aimed at removing the duodenum and the tumor located in the head of the gland - pancreaticoduodenectomy;
- surgeons often remove not the entire organ, but only part of it;
- removal of tumors only.
Laparoscopy is performed if the formations are located in the tail of the gland.
Rehabilitation of the patient after resection of space-occupying formations proceeds according to the following scheme:
- In the first months it is worth limiting physical activity.
- Strict adherence to the diet will help the patient quickly return to their previous lifestyle. It is worth removing flour, fatty, fried, spicy, salty foods from your diet;
- It is mandatory to take medications that contain enzymes;
- the patient must wear a bandage for 2-3 months;
- It is advisable to take advantage of a trip to the sanatorium.
Considering the difficulty of diagnosing cancer at the initial stage, in order to make a timely diagnosis, you should conduct an annual examination of the abdominal cavity, especially if you have already had this pathology in your family.
Information content of ultrasound diagnostics in pathology
It is difficult to judge the presence of oncology from one ultrasound report, and it is also impossible to determine its spread to neighboring organs and systems. In addition, it is impossible to distinguish small tumors from local inflammation of the pancreas using ultrasound.
According to research by some experts, the information content of this method for detecting cancer is about 90%. However, other data provide different figures: ultrasound - 83%, CT - 87%, sequential combination of ultrasound and CT - 98%.
Statistics from research centers say the following:
- an oncological process in the head of the pancreas is detected in 60% of cases;
- in the tail of the pancreas is found in 25% of cases;
- a tumor located in the body of the organ is detected in 13-15% of cases;
- with multiple localization, that is, total damage to several parts of the organ at the same time, the detection rate is 2%;
- in the uncinate process, this technique does not allow detecting a tumor in the early stages of development.
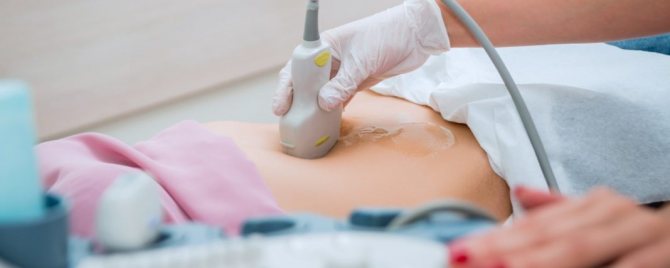
The above information indicates the high degree of efficiency of the ultrasound examination method.