The pancreas is an important organ of the human digestive system. Its task is to produce the enzymes and hormones necessary for digesting food. With systematic exposure to certain unfavorable factors, the structure of the gland tissue changes, which leads to a decrease in its functionality, and a disease such as pancreatic lipomatosis develops. As a result, the patient develops characteristic symptoms. The pathology requires timely treatment, which consists not only of taking medications prescribed by a doctor, but also of observing strict dietary restrictions.
Characteristics of the pathology
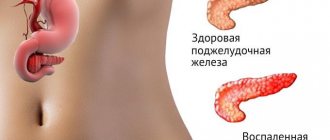
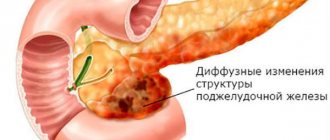
Pancreatic lipomatosis is a process in which the structure of the tissues of the organ changes. Its cells, which perform the necessary functions, are replaced by fat cells, which do not carry any functional load. This leads to disruption of the pancreas, as a result of which the entire digestive system of the body suffers.
The disease is characterized by gradual development and slow progression. For changes to occur, a number of unfavorable factors affecting the organ tissue are necessary. As pathology develops, the structure of the pancreas tissue gradually changes. The cells of the organ die, and lipomas (fat cells) form in their place.
Regarding treatment methods and diet, we recommend that you read the comments of the doctor at the Botkin Hospital on the patient’s specific diagnosis: https://health.mail.ru/consultation/2289709/.
Etiology of the disease
The main reason for the appearance of the pathological process has not been established as of 2020, however, there are unfavorable factors that significantly increase the risk of developing lipomatosis. These factors include:
- Inflammatory processes affecting pancreatic tissue (pancreatitis);
- Chronic diseases of the digestive system;
- Systematic drinking of alcohol;
- Compounded heredity (if the person’s closest relatives had similar problems);
- Pathologies of an endocrine nature (for example, diabetes mellitus);
- Chronic liver damage (hepatitis in one form or another);
- Hormonal imbalance (in particular, low levels of thyroid hormones).
Expert opinion
Shoshorin Yuri
General practitioner, site expert
These factors do not always lead to the development of lipomatosis. So, if a person has these problems, he does not always develop the disease. On the contrary, even in the absence of these reasons, fatty degeneration of the pancreas (lipomatosis) can develop.
Clinical course of the pathology
The clinical picture of the disease directly depends on the extent of organ damage, that is, on the stage of development of the pathology.
| Stages of development | Characteristic symptoms | Possible complications |
| Stage 1, in which no more than 30% of the pancreatic tissue is changed. | The pathology at this stage of development is often asymptomatic; the patient may feel only minor discomfort and heaviness after eating. In most cases, pathology is detected during a comprehensive examination. | In the absence of treatment, the pathological processes of replacement of pancreatic tissue continue, the disease enters the 2nd stage of its development. There are no other complications at this stage. |
| Stage 2, in which 30-60% of the organ tissue is damaged. | There are symptoms such as:
| At this stage of pathology development, various complications may occur. For example, if fatty tissues occupy large areas of the organ, the patient's body may not accept food entering the stomach. This only applies to heavy meals (for example, spicy, fatty, fried foods). As a result, a person experiences a significant deterioration in health, vomiting, and weakness after a meal. |
| Stage 3, characterized by almost complete replacement of organ tissue. | At this stage, the clinical manifestations of the pathology become more and more pronounced, symptoms such as:
| The main and most dangerous complication is the threat of dehydration, which, in the absence of proper treatment, can even lead to death. With the development of stage 3 lipomatosis, not only the digestive system, but also the endocrine system is affected. All this leads to a sharp deterioration in health and well-being. |
Diet
If you have lipomatosis, it is very important to follow the diet prescribed by your doctor. Depending on the stage and form of the disease, different products may be indicated and contraindicated for the patient.
In addition, it should be borne in mind that some foods that are beneficial for pancreatic diseases, for example, citrus fruits or red fruits, can be allergenic and cause other unpleasant reactions.
- The diet can only be effective if no more than 30% of the gland tissue is affected, that is, the development of the disease is at the first stage.
- For lipomatosis, table No. 5 is indicated, which is a categorical restriction on the intake of foods responsible for the formation of fat cells.
- The consumption of strong tea and coffee, fatty, fried and smoked meat, confectionery and sweets is prohibited.
- Spices and seasonings should be excluded,
- add salt in small quantities,
- All dishes should be consumed boiled or steamed.
Read about herbal remedies for pancreatitis of the pancreas here.
Diagnostic methods
It is quite difficult to identify pathology at an early stage, since there are no characteristic symptoms of the disorder. If the disease progresses to stage 2 or 3, to make a diagnosis it is necessary to assess the clinical manifestations, as well as collect an anamnesis (establishing the causes of the disease, assessing the patient’s eating habits, his lifestyle, studying the medical history and heredity).
To obtain a more detailed picture, additional diagnostic methods are used. This:
- Ultrasound of the digestive system to determine the location and size of fat deposits;
- A coprogram for determining the composition of feces (with the development of lipomatosis, fatty elements are found in it, the number of which can be used to judge the degree of damage);
- Blood test for hormone levels to detect damage to the pancreas and endocrine system organs.
Causes of lipomatosis
What is lipomatosis and what does the entry on the sick leave epicrisis mean - pancreatic lipomatosis? Such a diagnosis is made only when the development of fatty and pathogenic cells is detected in the internal organs of the body, which change the healthy environment of the pancreas and its cellular composition. This happens at a time when metabolism is disrupted, which leads to gland dystrophy.
The process of emergence will be generalized or regional. The nature of the development of changes that occur in the pancreas have their own forms of transformation:
- nodal transformation;
- developed diffuse;
- diffuse nodular compaction.
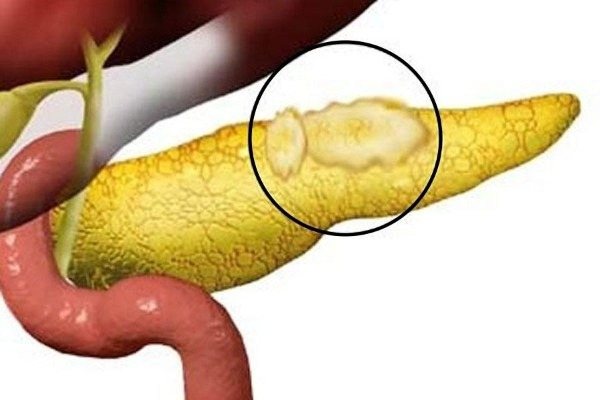
lipomatosis
In the first form of the pathology, nodes appear in the capsule. They have a group arrangement and a symmetrical state.
At the time of diffusion, the pathology progresses in the subcutaneous tissue with an abundant fat layer, and in the inner part of the pancreas. It may occur with a muscle lipoma, which grows in close proximity to muscle fibers and does not have clearly defined boundaries.
The diffuse nodular form of the pathology is characterized by two simultaneously progressive pathologies with the proliferation of adipose tissue. The development of lipomatosis, a pathology that has not yet been studied, and the reasons for its manifestation are associated with a malfunction in metabolism and the effects of catecholamines.
It is often observed that the occurrence of this pathology creates problems with the liver, pancreas, thyroid gland and is accompanied by a disorder of the pituitary gland.
In some cases, lipomatosis will manifest itself from heavy consumption of alcohol, diabetes, or congenital heredity. The disease also becomes a consequence of cancer and an increased level of urea in the blood of the affected person.
Each process in the human body does not occur independently. Therefore, no matter what pathologies there are in lipomatosis, they lead to consequences of their development and aggravation of the patient’s condition. Let's say that with pancreatitis, the main development occurs in diabetes mellitus, and this is the main disease of people who are overweight. This is reflected in the condition of the liver, which is revealed only by diagnosing the pancreas organ.
Fatty infiltration during inflammatory processes of the pancreas manifests itself in the following cases:
- violation of dietary norms;
- non-professional therapy of diseases.

poor nutrition
The consequences of the pathology of lipomatosis, leading to a complex course of the disease, are especially intensified with obesity of the pancreas and the occurrence of serious malfunctions in the digestive system.
A diffuse change in the pancreas, which occurs as a type of lipomatosis, involves the creation of focal fatty tumors over the entire area of the pancreas. This pathology does not make itself felt for quite a long time and does not cause damage to the tissues of the gland, and this does not create deviations in the functioning of the pancreas. This problem is detected randomly when diagnosing other diseases. Lipomatosis itself, as a disease, progresses slowly, sometimes accelerating, sometimes stopping in its development, and can remain in this mode for the rest of one’s life without threatening the health of the sick person.
There are reasons for the development of the disease – lipomatosis:
- chronic negative processes of the pancreas;
- trauma to the pancreas;
- developing diabetes;
- harmful abuse of habits (smoking, alcohol, medication abuse);
- heredity.
The disease lipomatosis is practically detected in childhood and does not progress, but is a risk for older people.
Treatment regimen
Therapy for pancreatic lipomatosis is complex. There are 3 types of therapeutic measures, such as:
- Changing diet and lifestyle correction;
- Drug treatment aimed at eliminating the causes and manifestations of pathology;
- A surgical operation, which is prescribed when an advanced form of the disease develops, when more than 60% of the organ is damaged, and conservative methods of therapy do not give the expected result.
Correction of diet and lifestyle
To eliminate the manifestations of pathology and normalize the functioning of the pancreas, it is necessary:
- Stop drinking alcohol;
- Adhere to the rules of fractional nutrition (5-6 meals in small portions);
- Eliminate foods that are difficult to digest from your diet. These are, for example, spicy and fried foods, pickles, foods rich in fat;
- Eating low-calorie foods.
Drug treatment
Depending on the symptoms present, the patient is prescribed the following medications:
- Painkillers;
- Drugs that facilitate the process of digesting food;
- Antidiarrheals;
- Medicines to relieve nausea;
- Antispasmodics.
Expert opinion
Shoshorin Yuri
General practitioner, site expert
These medications should only be taken as prescribed by a doctor, strictly following the recommended dosage and duration of treatment. Otherwise, there is a high risk of developing side effects that only worsen the course of the disease.
Surgery
With the rapid development of pathology, large-scale damage to the organ, surgery is necessary. Depending on the size and location, the degree of its fusion with the tissues of the organ, the following methods of removing adipose tissue are used:
- Husking, when the fatty tumor is carefully separated from the healthy tissue of the organ. This method is less invasive and has a more favorable prognosis for healing;
- Pancreatic resection. This method is used when the tumor is firmly fused with the organs. During the operation, the doctor removes not only pathological fatty tissue, but also partially pancreatic tissue. This operation is considered more complex and requires a longer recovery period.
Forms of the disease
The disease occurs in different species and class categories . Depending on the affected area, as well as the body’s adaptation to changes, several forms of the disease are distinguished.
Depending on the area of damage to the pancreas by adipose tissue, lipomatosis can be:
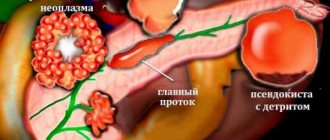
- Diffuse - the affected tissues are located throughout the organ and there is no clear outline of the neoplasm;
- Nodular - the location of the lesions is similar to tissue nodules and their sizes are clearly visible;
- Diffuse nodular is the most dangerous type of disease, in which it is very difficult to cure or remove all foci of inflammation.
Read more about how to treat diffuse changes in the pancreas here.
It is also worth noting that the disease may have:
- Focal , characterized by the development of a large number of fat cells in one place, is a direct indication for light surgical intervention.
- Regional type . Dangerous because a small number of unnecessary cells spread throughout the pancreas.
Characteristics of the medications used
A mandatory element in the treatment of lipomatosis is drug treatment, which involves taking drugs from various groups.
| Name | Description | Application | Price |
| Ibuprofen | The drug in tablet form helps eliminate pain and inflammation in the affected tissues. | The drug is taken orally, without chewing and with plenty of liquid. Children are recommended to take 1 tablet 3 times a day, adults - 2 tablets 3-4 times a day. Duration – about 5 days. | 35-45 rub. for 10 tablets. |
| Pancreatin | Available in various forms: hard-coated tablets, capsules, dragees. The drug contains active enzymes necessary for high-quality digestion of food. The action is aimed at replenishing missing enzymes and facilitating the digestion process. | The drug is taken orally, without violating the integrity of the tablet shell, with plenty of liquid. The dosage is selected individually, depending on the degree of damage to the digestive system, age and characteristics of the patient’s body (most often 2-4 tablets are prescribed per day). | 230-250 rub. |
| Loperamide | Available in the form of white tablets. The active substance is loperamide hydrochloride. The drug has an effect on the intestines, reducing its motility and relaxing the walls, which helps reduce the manifestations of diarrhea, eliminates bloating and discomfort. | Children are prescribed 0.5 tablets after each loose stool, adults 2 tablets per day, and 1 after bowel movements. The course of treatment is up to 5 days. | 15 rub. for 10 pcs. |
| Metoclopramide | Available in the form of small white tablets with flat edges. The drug helps to activate intestinal perilstatics, allowing you to quickly push through stagnant food. Due to this, nausea, heartburn and other unpleasant sensations associated with impaired food movement are reduced. | Chew the tablet thoroughly and then swallow it with water. The dosage is 20-60 MG. per day (this norm is divided into 3 doses). The duration of the course is determined individually. | 40 rub. for 10 pcs. |
Nutrition correction
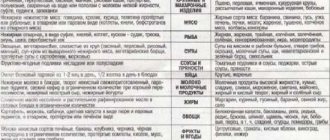
Diet is an important point in the treatment of lipomatosis. The patient will have to completely reconsider his diet, imposing strict restrictions on himself.
| Allowed | Forbidden |
|
|
Diet for lipid metabolism disorders

Along with drug treatment, diet is also extremely important. First, you need to understand which foods should be considered friends of the pancreas, and which ones should be classified as enemies. It is necessary to exclude all sour fruits from the diet: plums, pears, peaches, cherry plums, oranges, lemons.
Apples (if they are sweet) can be baked in the oven and eaten pureed. As for vegetables, you should avoid radishes, radishes, and white cabbage; it is undesirable to use sorrel and rhubarb. It is better to eat cucumbers without peeling, and bake tomatoes, like sweet apples, in the oven.
Alcohol, “heavy” foods such as pork, lard, fatty fish, smoked foods, spicy and salty foods, canned food, and fast foods can “kill” the damaged pancreas. Cakes, pastries, freshly baked bread, coffee, lemonades, strong brewed tea, sausages, fatty cheeses, sour cream are also classified as “difficult to digest”, and therefore harmful.
Among the “friends” should be considered low-fat cottage cheese, lean white meat (turkey, chicken, rabbit), pureed soups (preferably with weak meat broth or vegetable broth), mucous, porridge cooked in water with the addition of butter, boiled vegetables, white croutons or oven-dried bread.
Healthy drinks include jelly, dried fruit compote, green tea, rosehip decoction, and still mineral water.
There is a lot of controversy about milk: should you drink it or not? I will say this: if the body does not rebel after taking it, does not respond with diarrhea, pain, or unpleasant belching, then this is your product. If, on the contrary, you should pay attention to the percentage of fat content of milk and, if necessary, reduce it or abandon it altogether.
Other important rules in nutrition are to eat little by little, but often 5-6 times a day, monitor the temperature of the food you eat, adhering to the well-known principle “Food should not be too hot, not too cold”, chew it well, at least once every 7-10 days to arrange fasting days.