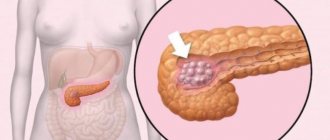
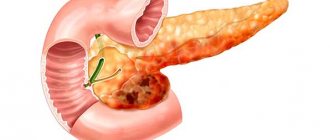
What is pancreatic parenchyma
Parenchyma is a homogeneous soft tissue of an organ that performs a specialized function. In addition to parenchyma, stroma is distinguished in body organs. Stroma is a connective tissue layer that performs supporting, formative, and supporting functions.
The pancreas is an organ of internal and external secretion:
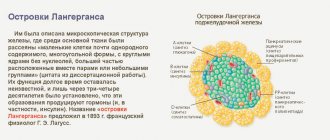
- One part of the parenchyma has cells aimed at the endocrine production of the hormones glucagon and insulin. Then they enter the bloodstream and participate in the regulation of carbohydrate and lipid metabolism.
- Exocrine activity is the production of the digestive enzymes amylase, lipase and trypsin, which are involved in the process of digestion of food in the duodenum.
Exocrine function is histologically provided by the pancreatic lobules. Lobules are areas of irregular, close to triangular shape, in which the synthesis of digestive enzymes occurs. Hormones are produced in the islets of Langerhans, a collection of glandular cells.
What does “diffuse changes” mean?
The term “diffuse changes” is used in ultrasound diagnostics. The very principle of this examination method is based on the difference in the density of body tissues. Ultrasound waves, having reached one or another organ, are reflected in different ways, as a result of which the corresponding picture is built on the device. The pancreas is normally a homogeneous organ, the edges of which are clearly visible during ultrasound examination, and the parenchyma is homogeneous (that is, homogeneous).
In the event of a pathological process occurring in the tissues of an organ (inflammation, necrosis, dystrophy), the density at the site of damage changes, as a result of which the focus of destruction can be clearly seen on the screen of an ultrasound diagnostic device.
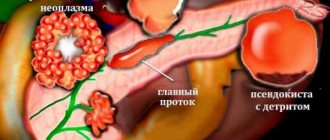
“Diffuse changes” in the pancreas A diffuse change is an area of the pancreas with a different density from the rest of the organ.
Diffuse changes in the pancreas
Ultrasound is an examination
using ultrasonic waves.
Ultrasound of the pancreas
determines the size, shape and contours of the organ, the homogeneity of the parenchyma, and the presence of any formations. But additional research will allow us to determine whether these are cysts, stones, tumors, or something else. Ultrasound is a necessary, but not sufficient examination in this case. In addition, gases in the intestines make the results difficult to interpret.
Read more about the study of the pancreas here >>
You must know:
- Diffuse changes in the pancreas are not a diagnosis, i.e. not a disease that needs to be treated. These are deviations from the norm in the gland caused by any factors or influences. This is information for the doctor.
- The doctor, having collected the patient’s complaints, ultrasound data - diffuse changes in the pancreas, the results of clinical and biochemical tests and other data, makes the correct diagnosis (for example, reactive pancreatitis or chronic pancreatitis) and gives recommendations for treatment, nutrition and lifestyle.
- Since we are talking about diffuse changes in the pancreas , I want to reassure you to some extent, this ultrasound conclusion suggests that there are diffuse, i.e. evenly distributed changes, but there are no most unpleasant things - tumors, stones, cysts.
More about this:
1. The pancreas performs an intrasecretory (endocrine) function, producing the enzyme insulin, which regulates blood sugar levels, and an exocrine (exocrine) function, producing the enzymes trypsin, lipase, amylase, lactase and other pancreatic enzymes that break down proteins, fats and carbohydrates in food.
If there are dysfunctions in the body, then during ultrasound diagnostics (ultrasound) diffuse changes in the pancreas (pancreatic parenchyma) will be observed.
Recommendations:
- If endocrine function is disrupted, this leads to the development of diabetes. The underlying disease, diabetes mellitus, is treated. Diffuse changes in the pancreas , in this case, are a consequence of the underlying disease.
- If exocrine function is impaired, then replacement therapy is used, treatment is prescribed by a gastroenterologist after examination.
2. Taste addictions to fatty, spicy, salty foods, and alcohol cause increased stress on the pancreas, liver, and gall bladder. As a result, the digestive organs malfunction and diffuse changes in the pancreas are observed.
Recommendations: Review your diet. Otherwise, such a diet can lead to inflammation of the pancreas, pancreatitis.
What are the symptoms of moderate changes?
Moderate changes in the pancreatic parenchyma occur as a result of a mild form of acute pancreatitis or edema of the organ. Moderate changes mean the initial stages of pancreatic cell replacement, which can occur:
- by type of fibrosis - when the parenchyma is replaced by connective tissue;
- according to the type of lipomatosis - when the parenchyma is replaced by adipose tissue.
Adipose and connective tissues have a different density and reflectivity from the pancreatic parenchyma, as a result of which they can be clearly seen on the screen of an ultrasound diagnostic device.
In this form, enzymatic deficiency is not detected, the function of the pancreas is completely preserved. Only a small part of the organ is affected, usually away from the excretory ducts.
Moderate diffuse changes are usually detected accidentally during ultrasound diagnostics during routine medical examinations and are not accompanied by any symptoms.
Signs of severe chronic changes
Severe chronic diffuse changes in the pancreatic parenchyma are associated with irreversible damage to the histological structure of the organ. This is caused by severe forms of acute or chronic pancreatitis in remission, as well as advanced forms of diabetes mellitus, which has remained untreated for a long time.
Ultrasound can reveal multiple violations of the histological structure of the organ, the normal size and shape changes. With this type of diffuse changes in the pancreas, enzymatic deficiency is observed.
Pronounced changes in the tissues of the pancreas are manifested by classic symptoms in the form of nausea and vomiting, pain in the epigastrium (in the center of the upper abdomen), which can radiate to the back or be girdling in nature, flatulence and other digestive disorders.
Possible reasons
Disturbances in the functioning of the digestive organs affect the condition of the pancreas. Chronic diseases are especially difficult to bear because they are protracted. The gland is affected by both pathological processes and side effects of medications.
Causes of diffuse changes in the pancreatic parenchyma:
- Inflammatory processes in the body. For example, pancreatitis ( acute and chronic ).
- Metabolic diseases. For example, diabetes mellitus, cystic fibrosis.
- Long-term use of toxic medications.
- Diseases of the liver and bile ducts.
- Chronic pathologies of the heart and blood vessels.
- Infections of internal organs.
- Inflammatory processes in the digestive system.
- Abuse of alcohol, fatty foods.
- Smoking not only cigarettes, but also hookah.
Also, in older people, age-related changes in the tissues of this organ and a decrease in its functions occur.
Echo signs of changes in organ structure
The echo signs of various pathologies in ultrasound diagnostics are different. In acute pancreatitis, the normal outflow of secreted fluid along with enzymes through the excretory ducts is disrupted. As a result, under the influence of its own digestive enzymes, pancreatic tissue is digested, and pronounced swelling of the organ is observed. As a result of this, ultrasound clearly shows a decrease in the density of the parenchyma and an increase in the size of the organ. Depending on various situations, the excretory ducts can be either partially or completely involved in the process with the discovery of stones in them, or remain completely intact.
During ultrasound examination during remission of chronic pancreatitis, the parenchyma of the organ is loosened due to the formation of foci of connective tissue. The swelling of the organ subsides, the size returns to normal. Excretory ducts on ultrasound showed no pathologies.
Diabetes mellitus is another serious pathology that changes the histological structure of the pancreas. With it, pancreatocytes - cells of the pancreatic parenchyma - due to a violation of fat metabolism in the body, begin to be replaced by adipocytes, adipose tissue cells. These cells are not able to perform the functions characteristic of the pancreas, as a result of which the production of hormones and digestive enzymes is disrupted. This process is called lipomatosis.
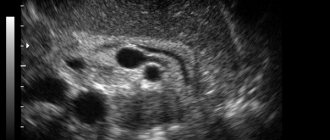
The echogenicity of the parenchyma is increased
Lipomatosis is common in older people. This is not a serious deviation and does not require special treatment; simple conservative supportive therapy is sufficient to stop the progression of the disease.
Symptoms indicating the presence of diffuse changes
Symptoms depend on what disease or pathological condition provoked the changes in the tissues. Most often, patients indicate the following general symptoms:
- Decreased appetite;
- Frequent constipation;
- Causeless diarrhea;
- Nausea;
- Feeling of discomfort and heaviness in the epigastric area.
What diffusion is and how it can manifest itself is best examined in specific measures.
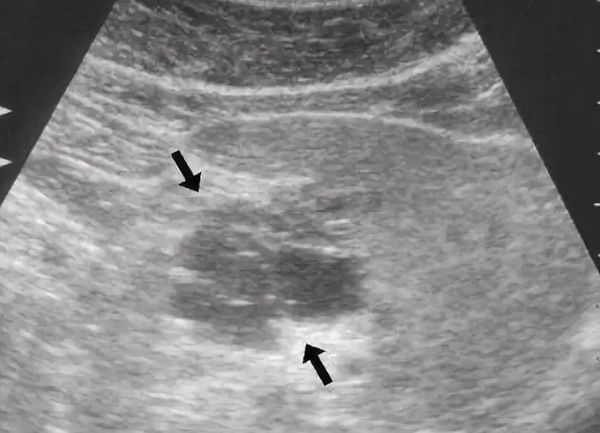
Diffuse changes in the pancreas parenchyma
Sonographic signs of diffuse changes indicate acute pancreatitis, as well as chronic forms of the disease. In diabetes mellitus, active replacement of glandular cells with fat is observed. The stronger and more acute the inflammatory process, the more fibrinoid tissue will be found in the organ.
Changes in organ structure
The structure of the organ can change evenly or unevenly. Depending on what diffuse changes in the pancreas were detected, treatment will be developed.
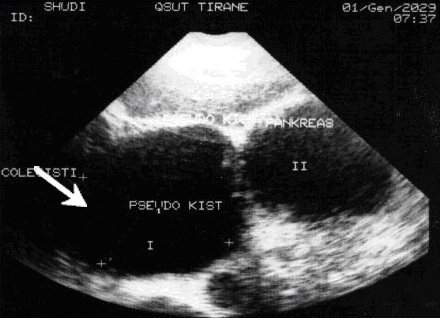
Diagnosticians can make an approximate conclusion directly during the diagnostic process. For example, local changes in structure indicate serious pathologies in a specific area. If signs of diffuse changes in the structure of the pancreas are expressed throughout the entire organ, it means that all tissues were susceptible to the pathological process.
Chronic organ diffusion
Chronic diffusion, as well as the pathology that caused the appearance of strong or moderate diffuse changes, may not manifest itself in any way. Chronic pancreatitis, age-related lipomatosis and fibrosis most often cause chronic tissue transformation.
Reactive Changes
Reactive diffusion is a common conclusion among diagnosticians. This means that reactions of secondary origin occurred against the background of concomitant diseases not directly related to the pancreas itself.
Most often, the cause was diseases of the digestive system. The closest connection is seen between pathologies of the liver and biliary tract. For example, a person may not have suffered from acute or chronic pancreatitis, but an ultrasound scan revealed pronounced diffuse changes in the pancreas. If the patient has a history of liver pathologies and other ailments, there is a high probability that the pancreas, being in a state of relative health, simply reacted to problems in the body.
We also recommend viewing: Severe pain in the pancreas: what to do and how to treat correctly
Minor diffuse changes such as reactive transformations usually indicate the health of the organ. However, there are situations when reactive reactions are the “first bells” signaling the development of secondary pancreatitis. In this case, the symptoms are carefully studied and a number of additional diagnostic measures are carried out.
Diffusion with elements of dystrophy
Pronounced diffuse changes may be accompanied by dystrophy of varying degrees. The process is irreversible; against the background of a deficiency of adipose tissue, the organ is greatly modified.
Partially normal cells die off and new elements do not take their place. To some extent, the destruction is leveled out due to the growth of the fat layer. This may mean that the organ will be able to retain its original appearance, but the new tissues will lack the functionality of the glandular structures. The hardware will not be able to fully fulfill its mission.
Symptoms will help to establish a more accurate diagnosis. The doctor’s further tactics will depend on many factors: the presence of acute pathological conditions, medical history, basic health, age and other nuances.
Treatment
There is no specific treatment with medications for diffuse changes in the pancreatic parenchyma. The replacement of pancreatocytes by adipose or connective tissue is irreversible, therefore the presence or absence of clinical symptoms, as well as correction of the patient’s lifestyle and nutrition, are of primary importance.
How to treat
The basis for stopping the progression of diffuse changes in the pancreas is diet therapy. It includes a complete rejection of:
- any dishes that can strongly irritate the gastrointestinal tract (fried, salty, spicy, spicy, pickled, sweet);
- consumption of alcoholic beverages and tobacco products;
- sweet carbonated drinks.
You should reconsider the frequency of meals and switch to 5-6 meals a day with a proportional reduction in portions. This allows you to reduce the one-time load on the pancreas.
In your diet, you should focus on eating vegetables, either boiled or steamed. When it comes to meat, choose chicken and turkey, preferably sirloin. Fatty meats can make the situation worse.
What medications are used
Several groups of medications are used to eliminate the symptoms of pancreatic damage.
The first group is aimed at eliminating enzyme deficiency. Pancreatin-based drugs are used, which reduces the load on the organ by introducing additional digestive enzymes. Common medications often used are Festal and Pancreatin.
To reduce pain in the abdominal area, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used. Recommended:
- nimesulide (Nise, Nimesil);
- paracetamol;
- ibuprofen (Nurofen);
- a combination of paracetamol and ibuprofen (Diclofenac).
You can use drugs based on paracetamol and ibuprofen for a long time without side effects. Nimesulide relieves pain better, but can cause various unwanted reactions from the body.
Do folk remedies help?
Traditional medicine can be a successful complement to conservative treatment. It is impossible to use treatment with folk remedies instead of pharmacological therapy, as this can lead to complications. Regarding each individual method, you should consult with your doctor to determine the feasibility and effectiveness of traditional treatment in a particular case.
Therapeutic measures
Treatment of diffuse changes in the pancreas can be conservative and surgical. The choice of treatment tactics depends on the nature of the disease, the severity of the general condition and the presence of concomitant diseases.
In most cases, echogenic signs do not undergo reverse development, as they develop over the years.
It is possible to restore the normal structure of the gland only in the case of an acute inflammatory process with adequate therapy.
In some cases, organ changes are caused by physiological processes such as aging and do not require treatment.
Author : Nikulina Natalya Viktorovna, especially for the site Zhkt.ru
Diffuse changes in a child
A child's body is constantly being rebuilt as it grows. The same is true for the pancreas. A child before reaching the age of 4-5 years may experience moderate diffuse changes in the parenchyma of the organ, which is one of the options for the normal development process. You should not pay attention to this in the absence of clinical symptoms. If any abnormalities occur in the feeding or behavior of a small child, you should immediately contact a specialist.
Signs of pronounced diffuse or focal changes in the pancreas are a pathology that requires medical intervention and complex therapy.
More specifically about the diffusion of ferruginous formations
Using ultrasound techniques, it is possible to qualitatively examine the abdominal organ, study the structure, shape, size, contours, homogeneity of parenchymal formations, and the presence of possible pathological neoplasms. This is a simple, safe, always informative way to study patients.
Echogenicity is the main sign that the pancreas is susceptible to diffuse phenomena. An increase or decrease in the echostructure indicates that the parenchyma of the organs in some areas does not correspond to the norm.
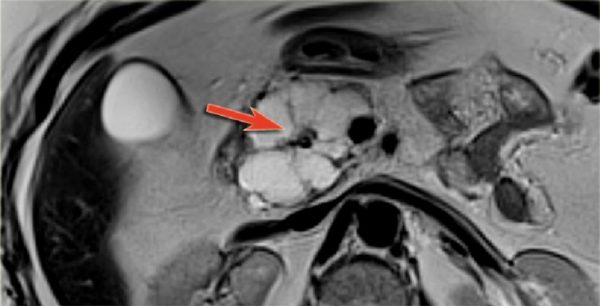
It is necessary to understand that moderate diffuse changes in the pancreas are not a specific diagnosis, but only the conclusion of the diagnostician who conducted the study. This phenomenon is not classified as a specific disease. Most often, this is a symptom that indicates acute or chronic pancreatitis or its consequences.
We also recommend viewing: Conducting and results of ultrasound of the pancreas
Prognosis for this disease
The conclusion “diffuse changes in the pancreas” from an ultrasound specialist is not a diagnosis. They can be found in almost any elderly person and are in many ways a demonstration of the lifestyle of the person being examined. In the presence of changes in the pancreatic parenchyma without the presence of clinical symptoms of serious damage to the organ, the prognosis is favorable.
In the presence of pronounced changes in the parenchyma of the pancreas, the prognosis for the patient is relatively favorable, but only if timely contact a specialist. Failure to treat enzyme deficiency conservatively can lead to severe complications, including death.
Ultrasound picture
The main method for diagnosing diffuse changes in the pancreas is ultrasound examination. With its help, you can evaluate such echo signs as the size and structure of the parenchyma, look at the contours, the presence of pathological formations, and the condition of the pancreatic ducts.
Each of the diseases that disrupts the normal structure of the gland has characteristic ultrasound signs. Using echography, you can determine the extent and extent of pathological changes in the organ. In 90% of cases they are caused by chronic inflammatory diseases.
The body of the pancreas consists of glandular tissue, so inflammation covers the entire organ at once, and ultrasound examination shows echographic signs of diffuse changes in the pancreas.