What is pancreatic lipofibrosis
Fibrolipomatosis or lipofibrosis of the pancreas is not a separate disease. This medical term refers to a degenerative process in the gland, leading to an uneven distribution of the connective and fatty component of the organ. As a result, there is an excessive replacement of normal tissues with fibro-fatty structures.
According to ICD-10, the disease is designated by code K86.8.
In addition, it is worth noting the following nuances:
- With lipofibrosis, obesity of the gland is observed, as indicated by the increased echogenicity of the organ, which was caused by prolonged inflammation or an incorrect metabolic process.
- Fibrosis is characterized by decreased echogenicity and increased density.
With this pathological process, damage occurs to tissues that try to compensate for their deficiency by actively growing, forming compactions and nodules.
In severe cases of fibrolipomatosis, numerous fibromas appear on the parenchyma of the gland.
Types and forms of painful manifestations
Lipofibrosis, as an inflammation of the pancreas, has several forms of manifestation:
| Forms of the disease | Characteristics |
| Nodal | The presence of nodes, which are characterized by a symmetrical arrangement, surrounded by a capsule. The nodular form appears on the body of the pancreas. |
| Diffuse | Manifests itself in the subcutaneous tissues of the gland. The presence of multiple fat cells actively spreading throughout muscle tissue. There are no restrictions in the form of capsules and other shells. |
| Diffuse nodular | Combines signs of nodular and diffuse forms. |
Medicine distinguishes three stages of development of lipofibrosis:
- The first is that 30% of the gland tissue is affected. The disease is asymptomatic.
- The second is that about 30-60% of the organ is affected by pathology. There are signs of indigestion.
- Third – more than 60% of the affected area of the pancreas is noted. Serious abnormalities throughout the body.
Depending on the stage of the pathology and the provoking cause, specialists select the optimal treatment option.
Symptoms and treatment of pancreatic lipomatosis
Pancreatic lipomatosis is a sluggish pathological process, which results in atrophy and degeneration of healthy cells of this organ into adipose tissue.
The disease is irreversible and leads to fatty degeneration of the pancreas with loss of vital functions. According to the international medical classification, this pathology is assigned the code ICD-10-D17.
The symptoms and causes of this disease, methods of treatment and prevention should be considered in detail.
Pancreatic lipomatosis is irreversible and leads to fatty degeneration of the pancreas with loss of vital functions.
Classification
Lipomatosis of the gland develops slowly and unnoticed by the patient.
The disease can be considered a protective reaction of the human body to any damage to the organ.
The gland tries to restore its integrity with the help of fat cells, but its functionality is lost forever.
Doctors distinguish several forms of growth of adipose tissue:
- diffuse;
- focal;
- mixed.
With diffuse changes in the pancreas, a chaotic arrangement of multiple fat cells without a clear sequence is observed. They often accumulate along the muscle fibers of this organ.
Focal (nodular) lipomatosis is characterized by the symmetrical formation of single large foci from an accumulation of fat cells with clear boundaries.
Mixed lipomatosis of the gland is rare, combining both forms of the disease.
Obesity stages
Medical scientists, depending on the severity and spread of the disease, distinguish 3 degrees of pancreatic lipomatosis, each of which is characterized by a long period of development.
If at the initial stage of the development of the disease the lipoma formed in the organ is invisible and does not have a noticeable effect on the person, then the 3rd degree of the disease is considered the most severe with all the negative manifestations.
1st degree
The initial stage of the disease is asymptomatic. A pathological change in an organ is almost always discovered by chance during a preventive medical examination. During this period, dystrophic changes cover only 1/3 of the pancreas. The functionality of the organ is fully compensated.
2nd degree
The replacement of healthy parenchyma cells with adipose tissue occupies half of the pancreas. The organ is unable to cope with its functions and stops producing digestive enzymes.
In this regard, the symptoms of lipomatosis increase and the digestion process is disrupted. At this stage, when the disease has developed a clinical picture, the patient seeks medical help.
3rd degree
We are talking about the 3rd degree of lipomatosis if more than 2/3 of the pancreas is replaced by adipose tissue. The functionality of the organ is impaired: the cells cannot produce the required hormones and enzymes.
During this period, due to insufficient insulin production, there is a risk of diabetes mellitus.
The clinical picture of the disease is very pronounced. Despite the fact that degenerated pancreatic tissue will not lead to involution, proper treatment at this stage of the disease will stop the pathological process and improve the patient’s condition.
The growth of adipose tissue is more often observed on the head and body of the organ than in its tail.
Causes
Pancreatic lipomatosis is directly dependent on prolonged inflammation of the organ, leading to damage to healthy cells and their replacement with adipocytes.
The causes of fatty degeneration of the pancreas should be considered:
- chronic alcoholism;
- smoking;
- drug intoxication;
- untreated organ injuries;
- hereditary predisposition;
- obesity;
- pancreatitis;
- concomitant diseases: hypothyroidism, diabetes mellitus, hepatitis, etc.;
- infectious lesions;
- oncology;
- metabolic disease;
- poor nutrition;
- the presence of lipomas in neighboring organs;
- old age.
Often, the patient’s condition can be improved by eliminating the cause of the disease: by achieving weight loss, getting rid of bad habits, starting to eat a healthy diet, etc.
Symptoms
Pancreatic steatosis develops asymptomatically for a long time.
Clinical signs begin to be clearly expressed upon reaching the 2nd stage of the disease.
Often these are dyspeptic manifestations, because the digestive function of the pancreas weakens. These include:
- nausea;
- discomfort in the stomach after eating a heavy meal;
- bloating;
- flatulence;
- diarrhea or constipation;
- belching;
- painful sensations in the left hypochondrium;
- general malaise.
Clinical signs begin to be clearly expressed upon reaching the 2nd stage of the disease; the patient experiences nausea and stomach discomfort after eating a heavy meal.
As the disease develops and areas of the organ with fibro-fatty inclusions expand, endocrine functions are suppressed, leading to a failure of carbohydrate metabolism and insulin deficiency. Now the symptoms of diabetes are added:
- strong thirst;
- formation of ulcers on the tongue and oral mucosa;
- dry skin;
- rapid weight gain;
- apathetic state;
- constant pain in the middle part of the abdomen;
- dysuric disorders.
To make an accurate diagnosis, a complete examination of the patient is carried out.
Diagnostics
A feature of the course of pancreatic lipomatosis is the manifestation of characteristic symptoms of the disease with advanced degeneration of the organ. Diagnosis of this disease includes:
- conversation with the patient about lifestyle;
- visual examination with palpation of the abdomen;
- laboratory testing of blood, urine, feces;
- Ultrasound;
- performing a biopsy of pancreatic tissue, which allows you to see the predominant content of fat cells.
Ultrasound examination of the pancreas is considered the main diagnostic method in making a diagnosis.
In some complex cases, additional examinations may be needed to clarify the degree of fatty hepatosis: CT, MRI, etc.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound examination of the pancreas is considered the main diagnostic method in making a diagnosis. In ultrasound images, a specialist can easily see a picture characteristic of lipomatosis of this organ.
You can see a slight increase in the size of the gland due to the growth of fat mass.
The growth of adipose tissue is more often observed on the head and body of the organ than in its tail.
There is increased echogenicity of the damaged gland, indicating a change in its structure. The occurrence of organ pathology is manifested by echo signals with uneven pulses.
Treatment
Fatty infiltration of the pancreas is treated using an integrated approach, including:
- drug therapy;
- special diet;
- traditional medicine;
- healthy lifestyle.
In severe cases, the doctor may resort to surgery.
The fatty infiltrate of the organ cannot be converted back into healthy tissue. The goal of treatment is to stop the progression of the disease and improve the patient’s well-being.
An effective way to combat pancreatic obesity is the regular use of infusions and decoctions of medicinal herbs prescribed by a doctor.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine is a powerful addition to traditional treatment for pancreatic lipomatosis.
Correct use of such products will help stop the formation of fat cells and improve the structure of the organ.
An effective way to combat pancreatic obesity is the regular use of infusions and decoctions of medicinal herbs:
- hemlock;
- chamomile;
- St. John's wort;
- wormwood, etc.
The use of folk remedies must be agreed with the attending physician, because it is necessary to calculate the course and dose of administration, to find out the absence of contraindications.
Fermented medicines such as Creon, Mezim Forte, Festal will help normalize digestion and replenish insulin deficiency.
Drug therapy
Conservative treatment of pancreatic steatosis is aimed at obtaining regression of the disease, eliminating symptoms and maintaining the secretory function of the organ.
The following medications are prescribed to relieve pain:
- Baralgin;
- Ibuprofen;
- Solpaflex et al.
Fermented medicines such as Creon, Mezim Forte, Festal will help normalize digestion and replenish insulin deficiency.
To eliminate diarrhea, medications are used:
- Imodium;
- Loperamide;
- Enterobene.
Baralgin is prescribed to relieve pain.
Antiemetic tablets are effective:
- Cerucal;
- Raglan;
- Emetizan.
Patients are often prescribed antispasmodic drugs that relieve spasms in the intestines. These should include:
- Duspatalin;
- Nyaspam;
- Mebeverine.
Along with this treatment, drug therapy for concomitant diseases is carried out.
Surgical methods
Surgery for pancreatic lipomatosis is performed in cases where other treatment methods have not brought the desired results.
Indications for surgery may include large areas of damage (over 60%), impaired functionality of the gland, or compression of neighboring organs.
Surgery involves excision of dystrophic areas of the pancreas, which helps stop the progression of the disease.
Patients are often prescribed antispasmodic drugs that relieve spasms in the intestines.
Diet
Special nutrition for pancreatic pathologies should be observed for life. The main goal of a therapeutic diet should be considered to be reducing the load on the damaged gland and stopping fatty growths. It is based on treatment table No. 5 according to Pevzner, which includes the following rules:
- frequent and split meals;
- exclusion of fatty, spicy, salty, fried foods;
- cooking methods - boiling, baking, stewing;
- Allowed foods are lean meat, fish, milk, vegetables, etc.
The diet strictly prohibits overeating and drinking alcohol.
Complications
With an advanced form of pancreatic lipomatosis or improper treatment, life-threatening complications can develop. These include:
- malignant or benign tumors;
- diabetes;
- functional insufficiency of the digestive organs, etc. Surgical intervention for pancreatic lipomatosis is carried out in cases where other treatment methods have not brought the desired results.
Source: https://podzhelud.info/bolezni/lipomatoz
Reasons for the development of lipofibrosis

Diffuse lipofibrosis of the pancreas develops as a result of necrosis of healthy glandular cells of the organ, after which the resulting voids begin to be actively filled with fatty and connective tissue.
According to statistics, this disease affects older people with acute or chronic pancreatitis. Among other provoking factors, doctors name:
- Diabetes.
- Endocrine disorders.
- Intoxication of the body.
- Cystic fibrosis.
- Nicotine addiction.
- Allergic reaction.
- Cholelithiasis.
- Infectious diseases.
- Taking certain medications.
- Obesity.
- Errors in nutrition.
- Hormonal imbalance.
- Excessive alcohol consumption.
- Cardiovascular defects.
- Injuries and mechanical damage to the pancreas.
People with the above diseases, as well as those leading an unhealthy lifestyle and those with a genetic predisposition to pancreatic diseases are at risk.
Causes
When the tissues of an organ are systematically exposed to unfavorable factors, it begins to deteriorate. As a result of this process, dead cells of the mucous membranes are replaced by empty or fatty tissues.
Such areas are not able to normally perform the necessary functions. The consequence of this is a metabolic disorder. Such processes lead to loss of organ performance.
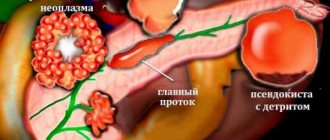
The key danger of fibrotic changes in the pancreas lies in the fact that the destroyed tissues cannot be completely restored. Even medications and surgery cannot cope with this problem. If the abnormal process is not stopped in time, there is a risk of tumor formation.
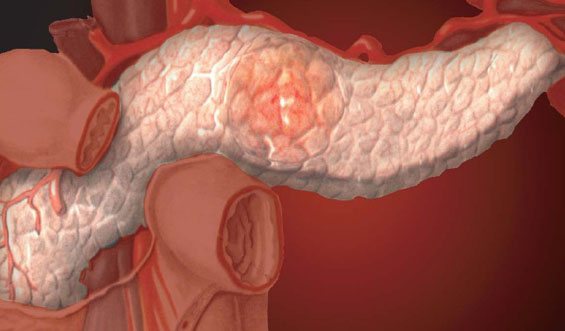
Often the appearance of fibrous tissue is a consequence of inflammation in the organ. This may be the result of chronic pancreatitis. Common factors that provoke the onset of the disease include the following:
- excess weight;
- drinking large amounts of alcohol;
- intoxication with various chemicals;
- smoking;
- long-term use of medications;
- disruption of the functioning of the biliary organs - this may be the development of cholelithiasis or inflammatory damage to the gallbladder;
- inflammation of the duodenum;
- infections;
- frequent stress;
- genetic predisposition;
- dietary disturbances;
- increased synthesis of thyroid hormones.
Acute inflammation of the pancreas leads to the development of necrosis, which affects an impressive part of the organ. This process leads to the rapid proliferation of fibro-fatty tissue.
With chronic inflammation, the anomaly does not develop so quickly and does not provoke discomfort. Therefore, many people are not even aware of the pathological processes in the body. Symptoms of the disease occur only during the period of exacerbation.
We also recommend viewing: The mechanism of formation of fibrolipomatosis and methods for its relief
Symptomatic features of pancreatic lipofibrosis

This pathological condition is characterized by mild clinical phenomena, so the disease is often detected randomly at the time of examination of the body.
Characteristic symptoms appear gradually as the disease worsens:
| Stages of the disease | Symptomatic signs |
| First | Intense thirst. Constant dry mouth. Development of stomatitis. |
| Second | Girdle pain in the peritoneum. Flatulence. Diarrhea. |
| Third | Feeling overwhelmed. Pain. Nausea. Vomit. Belching. Hyperthermia. Weight loss. |
Prognosis and prevention
The prognosis of the pathology depends on the volume of functioning tissue and compliance with the doctor’s recommendations. If you completely abstain from alcohol and use enzyme agents correctly, the disease can persist for a long time without noticeable progression. However, fibrosis cannot be completely eliminated.
To prevent the occurrence of the disease, you need to give up alcohol and promptly treat diseases that can cause fibrotic changes. If the disease does appear, a preventive examination should be carried out twice a year.
Fibrous lesions of the pancreas are considered a serious disorder that is irreversible. It will not be possible to completely cope with the pathology, however, medication and diet can significantly slow down the development of the anomaly.
What are the dangers of lipofibrosis and possible complications of the pathology?
Fibrolipomatosis, like other pathological phenomena in the pancreas, requires mandatory therapy, since its presence is an irreversible situation in which restoration of the affected pancreatic tissue is impossible.
Although this disease is not considered a critical deviation for the gland, its progression leads to a failure not only of the functions of the organ, but also to changes in the excretory ducts of the gland, which cannot be restored and often causes the formation of calcifications, cysts and tumors.
Such aggravation of lipofibrosis leads to the following negative consequences:
- Severe abnormalities in the digestive system.
- Significant weakening of the immune system.
- A pronounced change in carbohydrate metabolism.
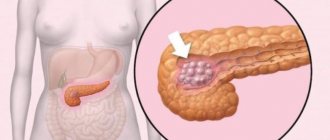
- Development of malignant neoplasms.
In addition, the disease often develops against the background of diabetes mellitus. The combination of these two pathological conditions can significantly worsen the well-being of diabetics.
Treatment of the disease
Many people are interested in the question: how to treat? This disease has no special treatment. Medicine has not come up with specific drugs that can restore the organ parenchyma from connective tissues. All treatment methods are aimed at improving the general condition of the patient. Treatment can be carried out either at home or in the hospital.
An important point in case of pancreatic fibrosis is a diet that alleviates the patient’s condition, since the functionality of the gland is impaired and digestion is difficult. Fatty foods, marinades, pickles, meat broths, smoked dishes, and hot seasonings should be excluded from your daily diet. Small and frequent meals are recommended, which will reduce the load on the pancreas. Diet is the most important method in treatment.
Drug treatment is primarily aimed at restoring the functionality of the gland. Enzyme replacement therapy is prescribed to compensate for the deficiency of pancreatic enzymes. It is also mandatory to take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and antioxidants. Sometimes in the process of cell breakdown, intoxication of the body can occur. In this case, the gastroenterologist can prescribe detoxification and antibacterial drugs to the patient.
Drug treatment of the disease consists of taking the following drugs:
- antispasmodics,
- digestive enzymes,
- anti-inflammatory drugs,
- antiemetic drugs.
The surgical method for treating fibrosis is used extremely rarely and in the case of tumor development. When the tumor grows rapidly, surgery is prescribed to remove it.
Options for diagnosing the disease
If any deviations in general health and signs indicating pancreatic dysfunction occur, you should contact a gastroenterologist. If this is required, you should additionally obtain advice from:
- Surgeon.
- Endocrinologist.
- Oncologist.
After a visual examination, the doctor will prescribe an examination, which includes laboratory and instrumental procedures.
Lab tests
Laboratory tests recommended:
- General blood analysis.
- Blood sugar test.
- Urine analysis for diastasis.
- Studying urine for sugar.
- Coprogram.
In addition, a biochemical study is prescribed to clarify the level of the following substances:
- Bilirubin.
- Diastasis.
- Total protein (and its fractions).
- Transaminases.
Hardware research
From hardware diagnostics for lipofibrosis of the pancreas, the following is used:
- Ultrasound.
- CT.
- MRI.
- Biopsy.
- Endoscopic ultrasonography.
Ultrasound
Using ultrasound, the condition of the organ is assessed:
- Form.
- Current size.
- Uniformity index.
- Location.
- Presence of pancreatic obesity.
- Degree of echogenicity.
Increased echogenicity indicates a disturbance in metabolic processes or an inflammatory focus in the tissues of the pancreas.
Endoscopic ultrasonography
Helps determine the condition of the gland according to the following parameters:
- Presence of heavy formations.
- The degree of tuberosity of the contours of the pancreas.
- Disturbances in the ductal system.
- Indicator of echogenicity of parenchyma.
MRI/CT
Magnetic resonance imaging, like computed tomography, allows you to study the pancreas in three-dimensional reflection, assess the severity of the pathology and the area of its distribution.
Biopsy
Performing a biopsy is practiced during differential diagnosis when there is a suspicion of the presence of a tumor in the tissues of the gland, or:
- Insufficiently clear information after undergoing non-invasive diagnostic procedures.
- Differentiation of abnormal processes in the pancreatic parenchyma is required.
- It is necessary to clarify information about focal or diffuse abnormalities in the gland.
As mentioned above, fibrolipomatosis is an undoubted companion to inflammation of the pancreas. Often this disease is present for life with long periods of calm and rare phases of exacerbation. As a result, the disease develops very slowly, which makes it difficult to detect it in a timely manner at the initial stage of formation.
Diagnostics
Since this pathology does not have specific symptoms, and its manifestations are the same as in many pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, in order to stop changes and prevent complications, it is recommended to undergo regular examination by a doctor. The presence of pancreatic fibrosis can only be detected by ultrasound. Tissue compaction is manifested on a sonogram by increased echogenicity.
Most often, fibrous changes in the pancreas are detected during ultrasound
Blood tests are also prescribed to detect the presence of enzymes. For example, low amylase activity indicates damage to a significant part of the gland cells. Enzyme deficiency can also be detected with coprogram. If stool tests contain undigested fiber, fats or proteins, this indicates a low level of enzymes produced by the gland. To confirm the diagnosis, a CT scan or biopsy may be prescribed, which can more accurately determine the location and type of altered tissue.
Prescribed treatment for pancreatic lipofibrosis
Fibrofatty changes in the pancreas are treated using the following methods:
- Conservative.
- Surgical.
In addition, several courses of radiation therapy are possible during the postoperative period.
Among the conservative methods used:
- Drug therapy.
- Folk recipes.
- Diet food.
Let's take a closer look at the treatment of pancreatic lipofibrosis.
Drug therapy
If the disease is in the dormant stage, then intensive drug intervention is not carried out. In the acute phase of the disease, medications of various groups are prescribed:
| Group | Example of drugs |
| Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs | Diclofenac, Paracetamol or Ibuprofen. |
| Enzymes | Creon, Mezim-Forte, Pangrol. |
| Antispasmodics | No-shpa, Papaverine. |
| Antiemetics | Metoclopramide. |
| Antienzymes | Octreotide, Rabeprozole. |
| Antibiotics | Cephalosporins, Penicillins. |
Along with medications, it is recommended to follow a gentle diet and maintain a correct lifestyle.
The use of folk recipes
The use of alternative medicine for pancreatic lipofibrosis is recommended only after consultation with your doctor. If the gastroenterologist approves of the feasibility of this technique, then you should pay attention to the following variations of herbal medicines:
| Means | Application |
| Hemlock tincture | Take the medicinal liquid according to the following scheme: 1st day – 1 drop of tincture, second day – 2 drops. Every day increase the dose by 1 drop. When 40 drops are reached during treatment, the medication is taken in the reverse order: daily reducing the dosage by 1 drop. |
| Herbal infusion (first option) | To prepare the medicine, you need to take in equal parts: nettle, valerian and St. John's wort. Mix the raw materials, measure out 1 tbsp. mixture and brew 200 ml of boiling water, leave. Strain the resulting liquid and take small sips throughout the day. The course of treatment is 3 weeks, after a 7-10 day break, repeat the treatment. |
| Herbal tea (second option) | You will need equal quantities of mint, immortelle, fennel, rose hips, yarrow, corn silk and valerian root. Mix everything, measure 2 tbsp. raw materials and pour 200 ml of boiling water, leave for half a day. Divide the resulting infusion into 3 parts and drink 3 times a day. The duration of treatment is 25-30 days. |
Features of dietary nutrition

A careful approach to nutrition will help a person reduce the intensity of the symptoms of fibrolipomatosis. With this disease, gastroenterologists advise adhering to diet No. 5, with the obligatory observance of a number of rules:
- Eat 5-6 times a day.
- Portions should be small.
- Food should only be warm.
- You cannot eat cold or hot food.
- The presence of salt in dishes should be minimized or eliminated altogether.
- I cook food by boiling or steaming without using fats (any kind).
It is necessary to pay attention to the category of products that are allowed for problem glands, which should be discarded, and which can be eaten in reasonable quantities:
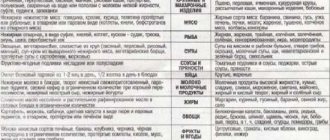
| Allowed | Prohibited | Limited |
| Biscuits. Crackers. Porridge. Milk. Vegetables. Omelette. Fruits. Casseroles. Lenten soups. Boiled eggs. Yesterday's bread. Dairy products. | Fatty meat and fish. Fried eggs. Offal. Mayonnaise. Sauces. Smoking. Conservation. Pickles. Ice cream. Baking. Fresh bread. Semi-finished products. Hard cheese. Sweets. Animal and vegetable fats. Fatty dairy products. | Honey. Nuts. Sugar. Spices. Mushrooms. Spices. |
A gastroenterologist or nutritionist will provide you with a more complete list of healthy and unhealthy foods.
With this anomaly, doctors insist on absolute abstinence from alcohol; even a small amount of alcohol often causes a sudden relapse of the disease, which leads to extensive death of pancreatic tissue.
Surgical method of treatment
Surgical intervention is practiced only in severe cases of lipofibrosis, when:
- Constant pain that is not relieved by medication.
- A pronounced increase in the volume of the connective and fatty component with the formation of a significant volume of cysts, tumors, nodes, etc., which compress the ducts, tissues and vessels of the gland.
- Compression of the small intestine due to an increase in the size of the head of the pancreas due to the development of abnormal processes in it. This situation is dangerous due to necrosis or internal bleeding.
Any surgical intervention in the pancreas is associated with a high risk of sudden bleeding.
Features of therapy
Since the consequences of pathogenesis cannot be eliminated, the destroyed areas of the cellular structure cannot be restored, the main goal of therapy is to stop the further development of the process and improve the patient’s condition. Depending on individual characteristics, the treatment regimen includes:
- quitting smoking and alcoholic beverages,
- careful control over the schedule,
- weight loss.
Proper nutrition and exercise play a key role in restoring pancreatic function and stopping transformation processes.
Proper nutrition
Dietary nutrition for any pathology of the pancreas involves a complete rejection of fried foods, fatty foods, abundantly seasoned with spices. Among those prohibited for use:
- excessively hot and cold,
- sour,
- drinks with excess caffeine and alcohol.
The daily menu must necessarily consist of vegetable soups with broth from lean chicken or beef, main courses with a side dish of cereals, pasta or potatoes, with boiled fish, pieces of meat or steamed cutlets. Recommended drinks include non-sour juices and compotes, jelly, and light tea. Food intake occurs at regular intervals up to six times a day, in small portions.
Physical exercise
In case of pathologies of the pancreas, excessive loads are prohibited, but they should be enough to keep the body in good shape. It is recommended to exclude pumping the abs and muscles from the list of regular exercises. Breathing exercises will be especially useful. The following have a positive effect on well-being:
- swimming,
- walking,
- daily walks.
For any physical activity, a moderate pace is recommended, without intense stress, which can affect the activity of the organ and accelerate scarring.
Medications
The use of medications is necessary to eliminate particularly disturbing symptoms in the event of concomitant, for example, infectious diseases. The specific composition depends on the patient’s condition and individual tolerance. The list may include:
- enzyme-containing preparations;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- antiemetic drugs;
- various options for painkillers.
If the listed medications are ineffective, a benign tumor forms, the size of which increases, and along with them the risks of oncology increase, a decision is made on surgical intervention.
Estimated forecast
Lipofibrosis of the pancreas is characterized by slow development, and the disease is benign in nature. With a timely, correct diagnosis, doctors predict a favorable outcome.
If the patient correctly follows drug therapy, diet and leads a healthy lifestyle, then nothing threatens his health - the disease goes into remission without further development.
Treatment methods
The main method of treating pancreatic fibrosis is replacement therapy. The choice of a specific agent and its volume depends on the severity of the pathology. If insufficient enzyme synthesis is observed, the use of enzyme complexes - amylase, lipase, trypsin - is indicated.
Symptomatic therapy involves the use of anti-diarrhea medications and medications that normalize intestinal motility. In the scleroderma form of the disorder, agents are used that stop the process of fibroformation.
If signs of diabetes mellitus appear, medications are prescribed to reduce blood sugar levels and insulin therapy is administered.
Any medications are used against the background of a strict diet. This allows you to relieve stress from the affected organ, cope with unpleasant symptoms and eliminate inflammation. To do this, you need to remove fried, fatty, coarse foods from your diet. Salting, smoked meats, sweets and spices are prohibited.
We also recommend viewing: Treatment of the pancreas with the most modern medications
You should not eat foods that increase the production of gastric juice. These include seasonings, marinades, and strong meat broths. This disease requires adherence to the principles of fractional nutrition. You should also drink plenty of water.
In difficult situations, surgical treatment is indicated. The operation is performed when large tumors form that compress neighboring organs. In other situations, the patient needs observation.