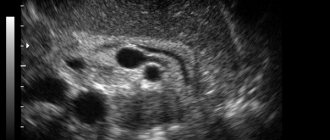
Often, for one reason or another, you have to visit an ultrasound room and in the conclusion you can find words such as “the echogenicity of the pancreas is increased.” What does this mean, is it dangerous or can this fact be ignored, we will try to figure it out in this article. First of all, it is necessary to understand that only a specialist should make a diagnosis, interpret the results of ultrasound and any other diagnostic method. There is absolutely no point in making conclusions, making diagnoses on the Internet and panicking.
Echogenicity: what is it?
The echogenicity of the organ, as noted earlier, is determined by ultrasound. First, let's look at the principle of operation of the device. When a certain stream of ultrasonic waves (usually above 20 thousand Hertz) is directed at an organ, its tissues are more or less capable of reflecting these waves. The extent to which waves are reflected depends on the density of the tissue.
If the tissues are dense, the wave transmission capacity is low. If the walls are not so dense, then, accordingly, sound waves penetrate into the organ more and are reflected less. It is this phenomenon that is called “echogenicity” or “echodensity”. The direction of the waves is reproduced using a special sensor directed by a specialist to the desired part of the body. The same sensor analyzes the waves that are reflected from the organ. Then, using a converter, the data is displayed on the screen.
Scientists have proven that, contrary to various opinions, ultrasonic waves do not pose any danger to the body.
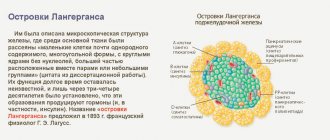
Experts, based on the level of absorption and reflection of ultrasonic waves, distinguish the following types of tissues:
- Hyperechoic tissues are those tissues that practically do not transmit waves due to their dense structure. In medical terms, they are characterized by high echogenicity or hyperechogenicity. These include bones, scar tissue, stones, if any;
- Normoechogenic tissues are those that reflect sounds at an average level. That is, their structure is less dense than that of bone tissue, for example, this category of organs includes the liver, kidneys, pancreas, heart, uterus, ovaries, prostate, mammary gland, thyroid gland, spleen. Experts classify all these organs as so-called parenchymal organs;
- Hypoechoic (anechoic, echo-negative) tissues are usually organs that are hollow inside or contain fluid. These include the stomach, intestines, lungs, and gall bladder. If we talk about pathological phenomena, such a picture can be observed in the presence of cysts, hematomas, and abscesses.
Those organs that have a hyperechoic property are displayed on the screen as a light image. Hypoechoic tissues are identified by a darker image. That is, the greater the degree of passage of ultrasonic waves of an organ, the darker colors it is displayed on the monitor.
Hypoechoic formation: causes of formation and possible risks
Using ultrasound diagnostics, the presence of a hypoechoic or hyperechoic neoplasm can be determined. In the first case listed, the patient has nodes that have a reduced level of density. Such a diagnosis can be either normal or a disease.
Only a doctor can determine why a hypoechoic formation occurred. It is impossible to do this on your own. The presence of a disorder can only be determined using an ultrasound machine. All tissues and organs have a certain level of echogenicity. Hypoechogenicity is characterized by a reduced level of density.
This can be clearly seen on the monitor during an ultrasound.
Hypoechoic and hyperechoic formations can be clearly seen on ultrasound
What is a hypoechoic formation?
Hypoechoic formation is a formation localized in any organ and having echogenicity below the normal level. This area weakly reflects ultrasonic rays. The monitor is darker than other areas.
A hypoechogenic formation contains water or a cavity. On the monitor, the area is visualized as gray or black spots. With hyperechogenicity, the zones are light or even completely white.
To decipher the picture, a special scale with 6 categories of gray shade is used. The diagnosis is made by specialist doctors. Often hypoechoic formations are cysts. In this case, the patient is additionally referred for a biopsy.
You can decipher the image using a special scale
The root causes of hypoechogenicity
The formation can have any localization. Formations also have different underlying causes of development and symptoms.
The root causes of hypoechogenicity, depending on the location of the formation, are listed in the table below.
| Liver and gallbladder | The causes of hypoechogenicity include: • polyps; • lymphoma; • angiosarcomas. |
| Bladder | The following factors provoking the lesion are identified: • fibroids; • transitional cell malignant process. |
| Abdomen and pelvis | Among the root causes that contribute to the finding of hypoechogenicity on ultrasound are: • hernia; • abdominal hematomas; • phlegmon; • inflammatory process in the lymph nodes; • spread of metastases; • carcinoma of the cecum: • testicular cancer in men. |
| Subclavian zone | The violation is a consequence of: • benign neoplasms; • cysts; • thymomas of the thymus. |
With all of the above factors, an ultrasound examination will diagnose a neoplasm with a reduced level of echogenicity. The current disorder does not always require any specialized treatment.
Similar formations can be found in different organs
Locations of formation localization
The clinical picture and the main diagnosis depend on the localization of the formation with a low density index. Pathological changes may affect:
- thyroid gland;
- uterus;
- mammary gland;
- spleen;
- ovaries;
- kidneys;
- pancreas;
- liver.
Hypoechogenicity is not a diagnosis, but only the result of an examination. That is why in an area with low density you should not worry ahead of time.
If the pathological process has affected the thyroid gland, then the presence of cysts and nodules can be suspected. Cancer is diagnosed in only 5 patients out of 100. An altered structure of the uterus indicates an inflammatory process, fibroids or miscarriage. Often the symptom indicates neoplasms of a benign or malignant nature.
Hypoechogenicity in the mammary glands may indicate various pathologies
Most often, hypoechogenicity is observed in the mammary glands. The symptom indicates:
- cancer;
- adenosis;
- the presence of cystic formations.
In the kidneys, an area of low density indicates either cancer or cystic formations. With a malignant tumor, the boundaries of hypoechogenicity are erased and the structure is uneven. Additionally, the patient may be recommended a biopsy.
Changes in the pancreas may be explained by:
- metastases;
- cysts;
- pancreatitis.
Hypoechogenicity can manifest itself in absolutely any human internal organ. Some of the underlying causes require drug therapy or urgent surgery. Ignoring any doctor’s orders is strictly prohibited. First of all, it is important to exclude the possible presence of a cancer process.
Such formations may indicate cancer and are observed in different organs
In some cases, hypoechogenicity does not cause any discomfort and does not provoke the appearance of negative symptoms. The reduced density will be discovered completely by accident.
Clinical picture
The clinical picture varies depending on the underlying cause and location of the deviation. The main danger signs include:
- difficulty swallowing and eating;
- respiratory dysfunction;
- feeling of a lump in the throat;
- pain and discomfort at or near the site of hypoechogenicity;
- hoarseness and hoarseness in the voice;
- unreasonable decrease or increase in body weight;
- improper functioning of the digestive organs;
- constant drowsiness and feeling of fatigue;
- sudden mood swings;
- change in body temperature;
- dullness of hair;
- brittleness of the nail plate.
Patients often complain of drowsiness and fatigue
All symptoms are common. The patient may have several symptoms or all at once. It all depends on the factor that provoked the decrease in density.
In the presence of serious illnesses, the patient’s well-being rapidly decreases. Every day a person has less and less strength. Usual things become a real test. The skin becomes drier.
Signs of general intoxication of the body appear. Aggression may occur without obvious reasons. High risk of underweight.
Diagnostic methods
The only way to detect a hypoechoic area is to resort to ultrasound diagnostics. In this case, the examination is carried out with a special device that emits ultrasonic waves.
Ultrasound is a painless and completely safe procedure
In contact with internal organs, ultrasonic waves are reflected and returned. Thanks to this, everything that happens is displayed on the monitor. Subsequently, the doctor deciphers the results obtained.
Ultrasound is harmless regardless of the patient's age. The method can be used during pregnancy and breastfeeding. The method does not require special preparation. An exception is abdominal ultrasound examination. In this case, sometimes you need to fill your bladder or follow a diet.
Before performing an ultrasound, an acoustic gel is applied to the area being examined. The product promotes better glide. Does not interfere with visualization and does not cause an allergic reaction.
After diagnosis, you need to remove the remaining gel. This can be done using dry wipes. The doctor will decipher the indicators and confirm or deny the likelihood of the presence of hypoechoic tissue.
From this video you can learn more about benign formations in the mammary gland:
Treatment measures
Treatment is selected by the doctor. Sometimes therapy is not necessary at all. Depending on the diagnosis, the patient may be recommended:
- vitamin therapy;
- physiotherapy;
- traditional therapy;
- homeopathic treatment;
- surgical intervention;
- taking medications.
There is no single treatment therapy. Self-medication is strictly contraindicated, since hypoechogenicity can be provoked by various provoking factors.
Possible risks
The most serious cause of hypoechogenicity is malignancy. Some tumors cannot be excised. The patient's condition is constantly deteriorating. Body weight rapidly decreases and appetite disappears.
Cancer is a serious disease, without treatment it always leads to death.
With cancer, the functioning of the body as a whole is disrupted. If left untreated, the patient may experience spontaneous death. Every day will begin with unbearable torment.
In order to avoid serious complications, preventive diagnosis is preferred. An ultrasound should be performed annually.
Did the article help? Rate it ( 4 votes, average: 4.00 5) Loading…
Source: https://infouzi.ru/ultrazvukovoe-issledovanie/o-procedure/gipojehogennoe-obrazovanie.html
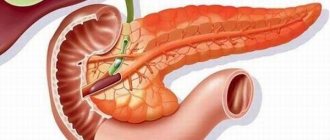
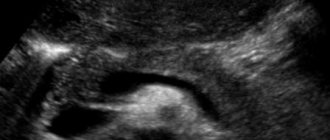
Normal echogenicity of the pancreas
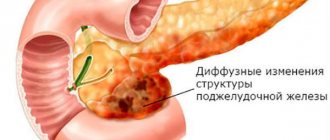
As mentioned above, the pancreas belongs to the category of organs that has normoechoic properties. If, according to the results of an ultrasound, it is revealed that the echogenicity of the pancreas has changed, then this indicates some kind of pathology. The pancreas contains glandular cells, which are mainly composed of fluid. Because of this, this organ absorbs some of the ultrasonic waves. When the echogenicity of an organ increases, this indicates that due to one reason or another there are fewer glandular cells. The echogenic pattern can be either local or diffuse.
The standard for comparison is the liver, since many organs containing glandular tissue are similar in structure to this organ.
During an ultrasound examination, the pancreas normally, in its echo structure, should be similar to the liver, having a uniform, homogeneous, fine-grained structure. It is acceptable that it may be slightly lighter. Only the gland duct is released. It is visible on the monitor in the form of a hypoechoic shadow, having an oblong shape. In medical terminology, when echogenicity is normal, the term “isoechoicity” is used.
Only a doctor can analyze the ultrasound results and make a final diagnosis.
Each ultrasound machine has its own comparative scale for the degree of echogenicity. A doctor with extensive experience can even determine the existing pathology in a person even without this scale.
Treatment
If the pancreas has increased echogenicity, the patient must undergo additional examination and undergo blood, urine and stool tests. Diagnosis and treatment are carried out by a gastroenterologist. The basic principle of treatment for acute pancreatitis is the rule: “cold, hunger and rest.” In the first days of the disease, the patient must remain in bed and refuse any food.
Treatment tactics may differ significantly depending on the patient’s condition, the prevalence and intensity of the pathological process. Some forms of the disease require surgery.
To relieve pain, analgesics and antispasmodics are prescribed, as well as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - Diclofenac, Ketoprofen, Papaverine, No-shpa, Drotaverine.
Since acute pancreatitis sharply increases the production of enzymes, agents are used to suppress pancreatic activity (Somatostatin). Antibiotics are needed to prevent bacterial infection.
If a diagnosis of lipomatosis is made, then it can be treated with therapeutic methods only if the fatty inclusions are small. In the case of large accumulations, fat islands compress the pancreatic ducts and disrupt the functioning of the pancreas. Then lipomas are eliminated surgically.
Treatment for lipomatosis involves dieting and weight loss. Medicines do not help get rid of fatty deposits, so all measures are aimed at preventing their further growth.
In case of enzyme deficiency, which accompanies chronic pancreatitis, tumor processes and a number of other diseases, enzyme replacement therapy is prescribed. The drugs are selected strictly individually, the most commonly used are Mezim, Pancreatin and Creon. During treatment, it is recommended to follow diet No. 5 and not drink alcohol.
It is important to remember that an increased echogenicity indicator is only a signal from the body about possible trouble. However, it cannot be ignored, and in any case you should consult a specialist.
The material was prepared by the authors of the project in accordance with the editorial policy of the site.
The echogenicity of the pancreas is increased; not everyone can understand what this is. If a doctor said this phrase during an ultrasound diagnosis, then this is a serious reason to think about your health.
Causes of increased echogenicity of the pancreas
Hyperechoic linear inclusions in the gland can indicate many pathologies. Let's look at them:
- Lipomatosis of the gland – pathology when glandular cells are partially or completely replaced by fat cells. Fat cells contain less fluid than glandular cells. Hence the result that these cells absorb less ultrasound waves, which is detected by ultrasound. Another sign of lipomatosis is that in the presence of increased echogenicity, the size of the pancreas remains normal;
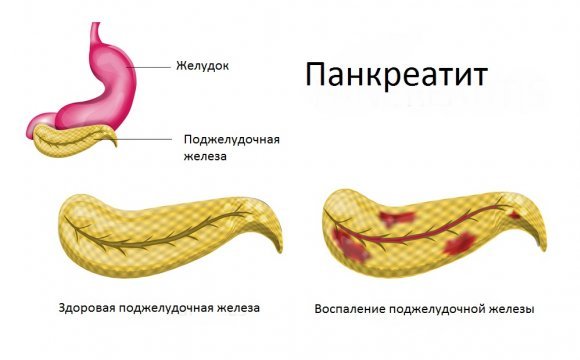
- Pancreatitis is an inflammatory process of the pancreas, which on ultrasound reveals itself as thickening of the gland tissue and heterogeneous structure;
- The presence of a tumor also leads to poor transmission of ultrasound waves. The device, in addition to changes in echogenicity, visualizes uneven and unclear contours of the pancreas. Usually, if the formation is malignant, it already has a clear clinical picture: the person is rapidly losing weight, digestive processes are disrupted, diarrhea is replaced by constipation;
- Pancreatic necrosis is a disease that leads to the death of pancreatic cells. On the monitor, during ultrasound diagnostics, an area with a light tint is visualized;
- Diabetes mellitus , a chronic disease that can lead to degeneration of organ tissue. The disease itself is not diagnosed by ultrasound, but leads to certain changes in tissues, which can be detected with this type of diagnosis;
- Parenchyma fibrosis is a disease when the glandular tissue of the pancreas is replaced by dense connective tissue;
Doctors can judge by the nature of the display of ultrasonic waves what kind of pancreatic disease a person has. It is believed that focal increases in organ density are a sign of the above pathologies. With the diffuse nature of echogenicity, the compaction of organs is temporary. Let's consider the reasons for the diffuse increase in density:
- Due to previous viral or bacterial infections (flu, pneumonia), the walls of the pancreas, as well as other organs, may become denser and appear on ultrasound with increased echogenicity;
- If a person has suffered food poisoning, or has changed their eating habits. I began to abuse fatty, spicy foods. This is an additional burden on the pancreas, since it has to produce large quantities of secretions for digestion, which can lead to compaction of the organ;
- Lifestyle changes and stress can also contribute to a temporary increase in the echogenicity of the organ;
- According to the observations of specialists, the echogenicity of some organs increases at certain times of the year. More often in spring and autumn;
- It is most often recommended to go to an ultrasound scan on an empty stomach, since eating, especially a large one, can distort the results and also show increased echogenicity.
Experts cannot confuse serious pathology with temporary changes in the echogenicity of the pancreas, since these changes are moderate and not as significant compared to the first ones.
Types of hyperechoic inclusions
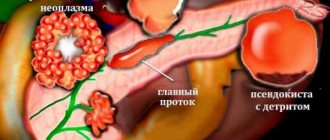
Hyperechoic inclusions in the parenchymal organ under study can be:
- pseudocyst, which is a liquid formation that occurs after elimination of an acute form of pancreatic lesion of the gland, is characterized by the formation of an uneven and jagged contour,
- as mentioned above, these can be calcifications or small pebbles,
- metastatic tumors,
- certain segments of fatty or connective tissues,
- cystic fibrous areas of gland tissue.
Reasons for decreased echogenicity of the pancreas
Diffuse and focal types are also characterized by reduced echogenicity of the organ. A diffuse decrease accompanies swelling of the stroma (supporting structures) and pancreatic capsules. The cause of fluid accumulation in the pancreas can be acute pancreatitis, allergies, and in general, swelling of the body. There are cases of reduced echogenicity of the gland due to the expansion of the pancreatic duct. Its dimensions can be increased so much that they can cover the entire gland. This picture is typical for advanced stages of chronic pancreatitis.
The presence of a cyst in the pancreas in most cases leads to a focal form of hypoechogenicity of the organ. But it all depends on the type of cyst. In true types of cysts, echogenicity is reduced. Multiple small cysts may be congenital and not manifest themselves in any way on ultrasound.
Also, some tumors can manifest themselves as either an increase in echogenicity or a decrease, depending on the type of tumor. There are cases when a tumor, especially a metastatic one, has mixed echogenicity. That is, during ultrasound, areas with both increased and decreased echogenicity are visualized. This picture is also typical for chronic pancreatitis, focal lipomatosis, and flatulence. Moreover, with subsequent ultrasound examination, the picture changes.
Enlarged
So, what does increased echogenicity of the pancreas mean? First of all, there is no need to panic; this term is not considered a disease. This is just a medical formulation used to describe ultrasound of the abdominal organs.
If the echogenicity of the pancreatic parenchyma is increased, this may also indicate that the pancreatic tissue is losing glandular cells containing a large amount of fluid.
Increased echogenicity manifests itself:
- Locally (focal). Indicates the development of tumors, metastases, fibrosis, stones, calcifications and fatty degeneration.
- Diffuse. It is temporary and most often occurs during the hot season of the year, after overeating or fasting, during infections and at elevated body temperatures.
If echogenicity is an episodic manifestation, then in this case it is moderate.
Factors provoking increased echogenicity
Increased echogenicity of the pancreas can be caused by the following pathological factors:
- Swelling of the pancreas.
- Salt deposits.
- Presence of stones.
- Pancreatic necrosis.
- Diabetes.
- Fibrosis.
In addition, hyperechogenicity of the pancreas can warn of the development of the following diseases:
- Malignant tumors.
- Pancreatitis (acute and chronic).
- Lipomatosis.
Symptoms of excessive echogenicity
It should be emphasized that in acute pancreatitis, the patient often experiences increased pressure in the pancreatic ducts, and the structure of the pancreas becomes heterogeneous.
Excessive echogenicity is manifested by the following symptoms:
- Vomit.
- Nausea.
- Low blood pressure.
- Rapid heartbeat (tachycardia).
- Intense pain in the left hypochondrium.
If increased echogenicity is observed in chronic pancreatitis, the following are added to the symptoms described above:
- Edema of the pancreas.
- Presence of hemorrhage.
- Enzyme deficiency.
- Decreased appetite.
- Difficulty with bowel movements.
- Feeling of a full stomach when in fact it is empty.
If problems with the pancreas began recently, then during an ultrasound examination the echogenicity of the pancreatic parenchyma will be at a normal level, and only after some time the symptoms of the disease will begin to intensify, in the form of abdominal pain and other unpleasant phenomena.
In addition, the likelihood of developing diabetes mellitus increases several times, and there is also a risk of lipomatosis (benign formations), in which glandular tissues are replaced by fat cells.
Features of therapy for increased echogenicity

Before starting treatment, the patient must undergo tests and an examination that will help determine the exact factor that provoked the increase in echogenicity. Based on the name of the disease that led to this phenomenon, appropriate medications and accompanying therapeutic measures will be prescribed. It is also worth paying attention to the fact that therapy is carried out under the strict supervision of a gastroenterologist. According to this:
- In acute pancreatitis, agents that reduce acid production and reduce the active production of pancreatic enzymes are recommended.
- Treatment of lipomatosis involves a strict diet, in which it is not recommended to consume foods with animal fats.
- If calcifications are present, it is also necessary to follow a diet, and if necessary, surgery is prescribed.
- To treat reactive pancreatitis, a specialist will prescribe the necessary medications and diet.
- If there is pain in the abdominal cavity, Ketotop or Diclofenac are prescribed to eliminate it.
- If the treatment does not give the desired effect, drugs with a stronger medicinal effect may be prescribed, for example, Morphine, Promedol.
- To relieve swelling and spasm, Platifillin and Nosh-pa are used.
- For enzyme deficiency, Atropine is recommended, as well as special enzyme and antioxidant agents.
When treating any of the above factors, you must quit smoking and alcohol. After a week of treatment, the patient must undergo an ultrasound; if the therapy was successful, then the echogenicity will be normal.
conclusions
From the above, we can conclude that a change in the echogenicity of an organ can indicate many diseases or may even be a temporary phenomenon. An increase or decrease in echogenicity is not a diagnosis, but only an indicator that pathology exists. If there is a suspicion of a particular disease due to impaired echogenicity, specialists prescribe additional types of diagnostics. So, if a tumor is suspected, blood tests are examined and other research methods are used, such as biopsy, computed tomography, etc. After determining the type of tumor, whether it is malignant or benign, the type of therapy is determined and treatment is carried out.
References: https://lekafarm.ru/stati/uzi-podzheludochnoy-zhelezy-pokazaniya-kak-delayut-normy-i-rezultaty.html medclic.ru/uzi/podzheludochnoj/ https://www.fundamental-research. ru/ru/article/view?id=33417 Notes from the author of the article, based on personal experience. This material is purely subjective and is not a guide to action. Only a qualified specialist can determine an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Last modified: 03/09/2020