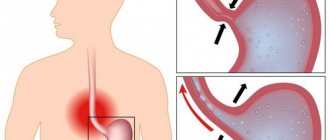
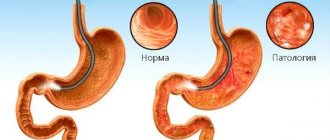
Chronic bulbitis is an inflammatory process that develops in the duodenum. However, very often one hears the diagnosis of chronic gastric bulbitis. This name is not erroneous, since in most cases this disease is directly related to gastritis.
Not knowing exactly what bulbitis is, many people confuse the disease with chronic pulpitis, the treatment of which involves turning to specialists of a completely different profile.
However, such diseases have little in common, because with chronic pulpitis the symptoms affect the oral cavity, and bulbitis is localized in the internal digestive organs.
Causes of chronic bulbitis
Very often this pathological process is accompanied by gastritis, which usually has similar symptoms.
There are many reasons for the occurrence of chronic bulbitis, but the main ones include: long-term use of certain medications, alcohol abuse, smoking.
The reasons why chronic bulbitis develops are quite varied and do not always indicate pathological changes in the body.
The main factors provoking the disease:
- long-term use of certain medications, especially in large quantities;
- mechanical damage of a domestic nature or work injuries and burns;
- alcohol abuse;
- smoking;
- consequences of surgical intervention in the abdominal cavity;
- disturbances in the structure or activity of certain internal organs (especially the liver, kidneys and cardiovascular system);
- decreased protective functions of the body.
The main reasons for the superficial form of bulbite:
- unhealthy diet, regular consumption of food with a lot of hot seasonings and sauces;
- prolonged exposure to stressful situations and depression;
- gastritis and peptic ulcers;
- infectious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- negative influence of pathogenic microorganisms.
Rarer causes include hereditary predisposition and congenital disorder of the structure of the duodenum.
Symptoms of chronic bulbitis

Chronic bulbitis has a number of specific symptoms. The main signs of chronic bulbitis are nausea and the urge to vomit while eating.
As a rule, this pathological process is accompanied by pain of varying severity, ulcerative lesions, hemorrhages and disruption of the gastrointestinal tract.
The disease may be:
- superficial;
- erosive;
- catarrhal
The chronic form of erosive bulbitis has a more severe course.
This pathology often causes the development of duodenal ulcer.
In this case, a through form of damage to the bulb is observed. The main symptom of the disease is the formation of erosions and hemorrhages.
The pathological process has the most vivid clinical picture.
The acute form of the disease is characterized by the presence of nausea and vomiting, pronounced pain. The patient may feel a bitter taste in the mouth, especially in the morning.
If the pathological process becomes chronic, there are aching pains, which are usually localized in the solar plexus area. Sometimes mild nausea may appear, but there is no vomiting.
This form of the disease can last for several years, periodically manifesting itself in the form of seasonal exacerbations.
The main signs of the erosive form of bulbite include:
- feeling of weakness throughout the body;
- increased irritability;
- nausea and vomiting while eating;
- dizziness and headaches of varying intensity.
Particular attention should be paid to the superficial type of disease, which is less dangerous since it affects only the outer area of the duodenal mucosa.
Such a disease can have a latent course without showing any symptoms.
The main danger of the pathological process is that, against the background of latent symptoms, a sharp exacerbation may begin. As a result, the disease becomes erosive in nature.
To prevent the development of complications, it is necessary to undergo regular examinations with a doctor and pay attention to any changes in the functioning of the body.
The main difference between the chronic course of the disease is less severe symptoms.
In this case, the patient pays attention to the presence of discomfort and nagging pain in the epigastric region. Most often, this symptom appears at night.
Sometimes there may be a feeling of heaviness in the stomach regardless of food intake.
If vomiting occurs, the patient's condition may improve for a while, since a certain percentage of the load is removed from the duodenal bulb.
With chronic bulbitis, a person experiences constant weakness, periodic dizziness and headaches.
In some cases, digestive problems such as constipation or diarrhea may occur.
In this case, there are painful sensations of aching nature. Heartburn medications or milk can help eliminate these symptoms for a short time.
If complications such as Crohn's disease develop, sudden weight loss may occur.
Prevention measures
To maintain health for many years and avoid such a debilitating disease, it is enough to follow a small list of simple rules:
- observe moderation in food and monitor your diet and daily routine;
- it is necessary to keep the body in good shape and do light exercise;
- include more dairy products in your diet;
- enjoy life more and avoid stress and neuroses.
Health-improving gymnastics
All diseases arise due to disturbances in the functioning of the autonomic nervous system. Constant anxiety and fear cause contractions of the muscles of the stomach and bulbous isthmus, disrupting the normal rhythm of work and secretion. Typically, bulbitis appears and causes unpleasant sensations when it is already in a fairly advanced state. Therefore, do not forget to monitor the condition of your body and consult a doctor on time!
Diagnostics
In order to make an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to carry out a comprehensive examination, which will include laboratory and instrumental methods.
Diagnosis and treatment for diseases of this nature are carried out by a gastroenterologist.
Establishing a diagnosis involves diagnostic procedures:
- A complete blood count can reveal the presence of anemia, which often occurs as a result of internal bleeding.
- Blood chemistry. In this case, decreased levels of protein and iron may be detected.
- FGDS is the most effective because it allows you to examine the entire duodenal bulb and determine the extent of damage. This will help the doctor determine the form of the disease. The examination is carried out using an endoscope.
- X-ray examination - this diagnostic method is the most ineffective, since it does not allow assessing the condition of the mucous membrane. X-rays are used only if there are any contraindications to endoscopic examination.
The following methods are used as additional diagnostics:
- external examination of the patient and determination of the intensity of symptoms;
- laboratory tests of gastric juice;
- breath test system (helps detect the presence of pathogenic microorganisms).
After the results of all examinations are received, the doctor prescribes appropriate treatment.
Treatment of chronic bulbitis with medication

It is necessary to treat the chronic form of bulbitis using complex therapy.
In this case, both medicinal and non-medicinal means, as well as traditional medicine methods, are used.
The choice of medications for this disease directly depends on the factor that provoked the pathological process.
When treating Helicobacter pylori infection, the doctor prescribes eradication therapy, which involves eliminating the Helicobacter pylori bacterium.
In this case, antibiotics and drugs that reduce the level of acidity in the stomach are used.
The duration of treatment and dosage of certain drugs is determined by the attending physician.
In most cases, anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed to help restore the normal state of the mucous membrane.
To eliminate pain, it is strictly forbidden to use non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, since they have a damaging effect on the mucous membrane.
As painkillers, the doctor may prescribe antispasmodic drugs such as Duspatolin and Trimedat.
To reduce acidity, antacid drugs are used, for example Maalox, Reni, Almagel.
Of the non-drug methods, physical therapy is considered the most effective.
Army and bulbit
To enlarge the picture, click on it.
In Article 59 of the “Regulations on Military Medical Examination”, which presents a complete list of diseases that exclude military service, there is no specific mention of bulbitis. However, it mentions duodenitis, a type of which is bulbitis.
Here you should refer to paragraph “b”, which mentions the following pathologies that imply the impossibility of entering military service:
- gastritis, occurring in a chronic form;
- gastroduodenitis, accompanied by significant impairment of secretory and acid-forming functions with frequent exacerbations and nutritional disorders, which require repeated and prolonged hospitalization in case of unsuccessful treatment in a hospital.
In case of rare exacerbations of the disease, the conscript is examined. Thus, you can only take a bulbit into the army with the B-3 fitness category.
Treatment of chronic bulbitis with folk remedies

In folk medicine there are a large number of recipes for the treatment of bulbitis.
The most popular of them are the following:
- Fresh potato juice. The product should be used 1 tbsp no more than 3 times a day.
- Oatmeal jelly. It is prepared by infusing a small amount of oats in 500 ml of boiled water. Used several times a day instead of tea.
- A decoction of chamomile and St. John's wort should be taken 1 glass twice a day.
If correct and timely treatment is carried out, chronic bulbitis will be in remission for quite a long time, without causing any discomfort to the person.
Diet
There are several important aspects in the treatment of bulbitis:
- strict adherence to the diet;
- giving up alcohol;
- to give up smoking;
- eliminating the cause of the disease;
- normalization of nutrition and adherence to the regime.

Therefore, therapy should begin with giving up inappropriate habits and maintaining a healthy diet. The diet for bulbitis must be followed with particular strictness during the period of exacerbation of the disease. This diet includes:
- slimy porridge;
- dairy products;
- chicken bouillon;
- jelly;
- oat cookies;
- crackers and refusal of fresh bread.
It is necessary to completely eliminate yeast products, hard fruits and vegetables, smoked foods and overly salty foods. You can eat meat, but only steamed or boiled. It is worth completely eliminating carbonated drinks, as they are incredibly harmful to the condition of the duodenal mucosa.
There are also a number of rules, following which you can improve the general condition of the body and get rid of symptoms related to peristalsis:
- you need to eat at least 5 times a day;
- portions should be of moderate size and not exceed 150 grams;
- food must be chewed thoroughly;
- it is important to eat slowly and in a cozy atmosphere;
- Under no circumstances should you eat on the go;
- you should not eat immediately before bedtime;
- The gaps between meals should be no more than 3-3.5 hours.
It is much easier to prevent the appearance of bulbitis than to waste nerves and energy fighting it. Preventive measures are an excellent alternative method to prevent many gastrointestinal diseases, in addition, this will improve the digestive system and reduce weight if you have extra pounds.