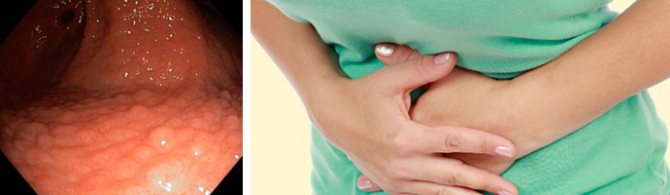
Hemorrhagic gastritis is an inflammatory disease of the mucous membrane of the stomach wall. The pathological process develops as a result of a violation of the secretory function of the stomach, as well as exposure to external factors. It manifests itself as pain in the epigastric region, signs of anemia and disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract. Diagnostics is carried out using laboratory and hardware research methods.
What kind of disease is this
Erosive gastritis is a common disease that is being recorded more and more often: WHO statistics indicate a tenfold increase in incidence over the past 10 years.
Inflammation develops against the background of impaired blood supply to the inner wall of the stomach. Blood from capillaries and larger vessels sweats into the thickness of the mucous membrane, forming hemorrhages and then ulcerations. Erosion appears only on the gastric mucosa, without damaging the muscle layer. With erosive-hemorrhagic gastritis, unlike gastric ulcers, scars do not form after the defect heals.
Acute hemorrhagic gastritis is more common in young and middle-aged patients, chronic - in older people.
Symptoms
Patient complaints are often related to food intake. After eating, there is discomfort or dull pain in the epigastric region, sour belching, heartburn, nausea, vomiting, and stool disorders may appear.
Sometimes the symptoms are smoothed out, and patients seek medical help only after obvious signs of gastrointestinal bleeding appear. Copious effusion of blood into the stomach cavity causes vomiting (hematemesis); vomit resembles coffee grounds. Due to the admixture of coagulated blood, the stool becomes tarry, almost black (in contrast to hemorrhoidal bleeding with scarlet streaks).
With minor but prolonged blood loss, signs of anemia increase:
- hypotension, headache;
- general weakness;
- dizziness, drowsiness;
- pallor of the skin and mucous membranes;
- nails and hair become dull and brittle.
Heavy gastric bleeding is accompanied by a sharp decrease in blood pressure, tachycardia, increased heart rate, and impaired consciousness.
An asymptomatic course is typical for drug-related gastric disease.
Classification
The disease can be primary (occurring in a healthy person) or secondary (associated with other gastrointestinal pathologies).
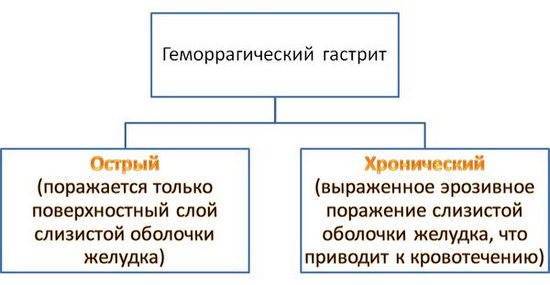
According to the duration of the course, hemorrhagic gastritis is divided into acute and chronic.
Based on the location of the lesions, erosions of the antrum, fundus and body of the stomach are distinguished.
Causes
The most common causes of the development of the pathological process are uncontrolled use of certain medications (analgesics, glucocorticoids, NSAIDs), as well as dietary errors. Irregular meals, hot and spicy foods, low-quality foods and alcohol trigger the formation of defects on the inner surface of the stomach.
Increased capillary permeability leads to a failure of metabolic processes. The consequence of this disorder is the leakage of plasma and blood elements into the lumen of the stomach.
Infectious agents can act as a provoking factor: Helicobacter pylori, salmonella or diphtheria bacilli.
Treatment of hemorrhagic gastritis
Depending on the stage of the disease, treatment is carried out both at home with an outpatient visit to a doctor, and in a hospital. The treatment method consists of relieving symptoms with medications and using diet therapy.
Diet for hemorrhagic gastritis
The diet for hemorrhagic gastritis is no different from the diet for any other type of disease. Allowed use:
- fatty boiled porridges with water or milk;
- soups with cereals and vegetables, also well boiled;
- Dairy products include cottage cheese, milk jelly, low-fat cream or milk;
- eggs in any form;
- lean fish and boiled meat;
- dried fruits (pre-steam well).
The list of prohibited products will include:
- fried, smoked, spicy foods;
- baking;
- sour milk;
- alcohol;
- sweets;
- salted vegetables.

Such rules will quickly remove aggravations and prevent them from arising in the future. Unfortunately, it must be admitted that even after the exacerbation is relieved, you will have to stick to the diet for the rest of your life with very rare relaxations on holidays.
Meals must be organized so that the patient eats little and often. It is difficult for the stomach to cope with digestion, so food should be consumed soft, boiled, ground or liquid. Bleeding is an indicator of eating refrigerated food, since low temperatures promote blood clotting.
Important ! Chilled does not mean icy. Too low a temperature also injures the stomach. Coffee, strong tea and fatty broths must be completely removed from the diet.
Traditional medicine to protect your health
Treatment with folk remedies can be very effective. The disease is not new, and for many centuries people have come up with various means to relieve pain symptoms and improve the functioning of the stomach. Only the most effective methods have survived to this day, which help relieve spasms, soothe proximal gastritis and improve food digestion.
Important ! Remember that traditional medicine is only an assistant. Discuss with your doctor the methods you want to use and never self-medicate. This can be dangerous and may make your condition worse instead of treating it.
- Green apples without peel, consumed by gastritis patients, improve acid levels. After eating one or two apples, you need to abstain from food for several hours.
- A more complex recipe: divide the sour milk into cottage cheese and whey. Boil the oats in the whey for three to four hours. Then use a sieve to separate the oats from the whey, add honey and a little alcohol to the liquid. Drink a tablespoon of the mixture before meals, after shaking, three times a day.
- You can drink half a glass of cabbage juice twice a day. Remember that juice that has stood for more than two days loses its medicinal properties.

- Various herbs: yarrow, plantain, nettle and others will help restore acidity. Consult an herbalist's reference book to find the right herbs for you.
- Red birch bark (spring), poured with boiling water, will perfectly help relieve pain. Drink half a glass three times a day.
- Freshly squeezed potato juice is a popular remedy for patients with gastritis. Drink one glass a day for two weeks in a row (it is best to do this in the morning, on an empty stomach).
Drug treatments
Acute hemorrhagic gastritis is usually accompanied by severe pain, which can sometimes be relieved only with medications. Pharmacotherapy can be treated only under the strict supervision of the attending physician.
- Treatment usually begins with correcting the acid balance of the stomach with drugs such as cimetidine, ranitidine, etc.
- To improve the environment, enveloping drugs, mucus-forming agents and reparants are used.
- Antibiotics are prescribed when a bacteria is identified as the causative agent of the disease.
- Your doctor may also recommend taking oils internally.
- In very rare cases, surgery may be performed.
The mortality rate of this disease is very high - up to 30%. Do not delay contacting a doctor, do not be negligent in following the recommendations after the attack is over - the risk of relapse is very high. When a doctor prescribes surgery, try to consult another experienced doctor for a more objective opinion. But if the experts insist, don’t contradict them.

The most important recommendation is to be attentive to your health. The earlier the disease is detected, the greater the chances of its successful treatment. An advanced disease will require long-term treatment with cautious prognosis, when at an early stage it may be possible to manage solely with diet therapy and lifestyle changes.
If you have your own story about how you were cured of hemorrhagic gastritis, be sure to share your experience in the comments. Save the article on social networks in order to re-read it if you forget something. Be healthy!
Diagnostics and necessary examinations
A gastroenterologist makes a diagnosis based on medical history, examination, clinical test data, and endoscopic examination.
An external examination reveals signs of anemia - pale skin, disruption of the structure of hair and nails. When palpating the stomach area, painful sensations are possible. A blood test reveals signs of iron deficiency anemia, and a stool test reveals occult blood.
The doctor receives detailed information when performing EGDS (esophagogastroduodenoscopy). The diagnostic procedure helps to establish the degree of damage to the mucous membrane, the localization of erosions and areas of hemorrhage. To exclude the oncological nature of mucosal defects, a targeted biopsy is performed in parallel.
The gastroenterologist may prescribe additional tests: PCR diagnostics or urease breath test to detect Helicobacter pylori, pH-metry to determine the level of acidity of gastric juice.
How can hemorrhagic gastropathy be cured?
Before starting treatment for the disease, it is necessary to make a diagnosis and undergo a series of mandatory tests.
The main research methods include the following:
- A detailed and biochemical blood test will determine the state of health, the presence of pathogens and the number of blood cells, which can be used to detect inflammation, suppuration and other pathological processes
- A urine test will determine the viruses and bacteria that are in the body
- stool analysis can “tell” about digestion and the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract
- gastroscopy with biopsy is a special method for studying the functioning of the stomach. A thin tube with a camera and a special spatula is inserted through the patient's mouth. On the screen you can see the condition of the esophagus and stomach from the inside. The spatula collects cells for further laboratory research. This method is not very pleasant, but it is difficult to call it painful
- Ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity allows you to determine the condition of the liver, spleen, and gall bladder. By the size, location and external signs of internal organs, the presence or absence of pathological processes can be determined
- Electrogastroenterography allows you to determine the contractile and digestive functions of the stomach, the secretion of gastric juice, and microflora
The results of gastroscopy will help confirm the diagnosis
Depending on the results of tests and other studies, the doctor prescribes treatment. It will be different for each patient, as individual characteristics, type of disease, stage of development and many other factors are taken into account.
Therapy includes the following drugs:
- antacids (Maalox)
- medications to correct acid balance (ranitidine)
- acid blockers (Pantoprazole)
- When the gastrointestinal tract is damaged by bacteria, it is necessary to take antibiotics, which eliminate the parasites. In addition, you need to drink probiotics and prebiotics in parallel so as not to completely destroy the microflora
- if there is bleeding or there is a risk of its development, then the hormone adrenaline and aminocaproic acid are prescribed
It is important to additionally check other organs in order to simultaneously provide them with treatment if necessary. That is, there is no point in treating the symptoms of pathology if you do not act on the underlying cause.
What complications and consequences can it cause?
If you organize treatment for gastritis in a timely manner, then you don’t have to worry about the consequences. Drug therapy in combination with proper nutrition and diets will quickly and effectively restore the condition.
If you ignore the symptoms and the condition withers, then you can provoke a number of other diseases resulting from gastritis:
- cholecystitis - inflammation of the gallbladder, the functioning of which can be impaired due to poor nutrition and the development of gastritis
- A stomach ulcer is a condition in which a wound appears on the mucous membrane
Most often, as a result of gastropathy, intestinal function is disrupted and problems arise with the pancreas. Sometimes this condition can result in death, so you cannot procrastinate with problems of the digestive tract.
Read: Preparation for MRI of the intestine, procedure and contraindications
Tips and tricks
Prevention of erosive-hemorrhagic gastritis lies in following the rules of a healthy lifestyle. It is necessary to give up bad habits - drinking alcohol, smoking, overeating. It is important to maintain a work-rest schedule, ensure proper sleep and proper nutrition.
You should try to avoid stressful situations.
You should regularly undergo preventive examinations and sanitize sources of infection (caries and other diseases of the oral cavity, rhinitis, tonsillitis).
When taking medications, you must strictly follow the manufacturer's instructions and the recommendations of your doctor.
Kinds
Hemorrhages are hemorrhages, which are divided into the following types depending on the causes of their occurrence:
- bleeding caused by violations of the integrity of the walls of a blood vessel due to exposure to an infection or a chemical substance;
- bleeding resulting from a decrease in the thickness of the walls of blood vessels;
- bleeding resulting from mechanical damage to blood vessels. This is how a bruise appears after an injection.
Depending on the location, types of hemorrhage can be:
- capillary (bleeding from small vessels);
- internal (hemorrhages into tissues and organs);
- venous (bleeding from damaged veins);
- external;
- arterial (intense bleeding from the arteries);
- parenchymal (bleeding of tissues that form organs).
Diet
In the treatment of hemorrhagic gastritis, an important place is given to dietary nutrition with the limitation of foods that irritate the mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines. Without proper nutrition, recovery processes are practically impossible, or will take a very long time even with drug therapy. The diet consists of the complete exclusion of fatty and spicy foods, as well as hard-to-digest foods. Dietary requirements include a complete abstinence from alcoholic beverages, spicy seasonings, marinades, artificial colors and flavors.
A special diet with properly selected dishes shortens the treatment time for the disease and prevents the occurrence of repeated exacerbations. It is recommended to eat frequently and in small portions; when cooking, use stewing, steaming or simply boiling foods. It is equally important to avoid long breaks between meals and feel hungry. Ready-made meals should be sufficiently liquid and at a comfortable temperature for the intestines, i.e. Not too hot and not too cold.
Medications
The use of medications is based on the individual characteristics of each patient and the nature of his disease. First of all, acidity correctors and drugs that eliminate inflammation are prescribed, as well as other drugs in accordance with generally accepted standards for the treatment of hemorrhagic gastritis. All drugs used in this case have certain pharmacological properties, namely:
- Antisecretory agents that reduce the acidity of gastric juice and normalize the secretion of hydrochloric acid. Omeprazole is most often prescribed for this purpose.
- Gastrocytoprotectors that protect the gastric mucosa from external adverse influences and from the negative effects of hydrochloric acid. In most cases, Almagel is used for this purpose.
- Medicines that have a hemostatic effect, such as Vikasol.
- Antisecretory drugs in the form of Mezim, Creon or Pancreatin are prescribed as means to promote the normal functioning of the stomach and facilitate the digestion of food.
- To eliminate the symptoms of the disease and increase the tone of the body, drugs in the form of Actovegin are used.
In case of prolonged bleeding, the patient is given a course of hemostatic therapy using a solution of aminocaproic acid with adrenaline or tranexamic acid. With the development of hemorrhagic shock associated with blood loss, the condition is normalized with blood products or blood substitutes with anti-shock action. Since gastritis poses a threat of developing severe complications in the form of stomach ulcers and many others, treatment of the disease should be carried out under the close supervision of the attending physician.
As measures to promote faster regeneration processes, anti-inflammatory agents are used in the form of natural oils from sea buckthorn, rose hips or carotene oil.
After eliminating the exacerbation phase, phytotherapeutic drugs will be useful during periods of remission. In cases that have exhausted all the possibilities of modern classical therapy, as well as endoscopic methods of treating this gastritis, have also not led to the expected result, they resort to surgical interventions of various volumes.
Main symptoms of internal bleeding
Manifestations of hemorrhage depend on the type of bleeding and its location. While external bleeding is fairly easy to detect, internal bleeding is often not noticeable. It can be identified by a number of specific symptoms, such as:
- general malaise;
- dizziness and fainting;
- unnatural pale skin;
- apathy, drowsiness;
- tachycardia;
- decrease in blood pressure.
These are common symptoms of internal bleeding. There are also a number of specific signs characteristic of certain types of hemorrhages.
Why are hemorrhages dangerous?
Hemorrhages are a rather insidious phenomenon. Its severity directly depends on the area of the damaged area and the intensity of bleeding. And although such minor injuries, as a rule, resolve on their own, there are cases when the site of hemorrhage festeres, which requires surgical intervention. Sometimes hemorrhages can destroy tissue, which can also lead to serious consequences. In this case, hemorrhages in the brain, lungs and heart are very dangerous.