Ultrasound of the pancreas preparation for examination of adults
The pancreas is the main organ of the gastrointestinal tract, responsible for the synthesis of digestive enzymes and hormones that control metabolic processes in the body.
With complete or partial dysfunction of this organ, serious digestive problems are observed. And in order to understand exactly what pathological processes occur in the pancreas tissues and what their extent is, doctors prescribe an examination, which includes an ultrasound examination. Preparing for an ultrasound of the pancreas is a very important undertaking.
If it is not carried out, incorrect data may be obtained during the study, which will be followed by incorrect treatment, further progression of the disease and the occurrence of complications against it.
Indications and contraindications
Ultrasound is prescribed to almost all patients who have disorders of the digestive system, accompanied by:
- aching or acute pain in the epigastric region or hypochondrium;
- diarrhea or chronic constipation;
- the presence of a large number of undigested pieces of food in the stool;
- increased fat content in stool (it becomes shiny, oily);
- nausea and vomiting;
- the occurrence of aversion to fatty foods and alcohol;
- symptoms of obstructive jaundice (yellowing of the skin, sclera of the eyes, etc.).
Ultrasound examination is also used if the doctor suspects, after examination and collection of anamnesis, the development of the following diseases:
- cholelithiasis;
- pancreatic cyst;
- gland hematoma;
- abscess in the pancreatic parenchyma;
- oncological diseases;
- pancreatitis;
- cholecystitis;
- papillitis;
- inflammation of the duodenum.
In addition, it is mandatory to conduct an ultrasound before surgery or after an abdominal injury to ensure that the integrity of the gland has not been compromised.
An ultrasound scan of the pancreas also checks the functionality of other organs of the digestive tract.
Carrying out an ultrasound makes it possible not only to assess the external condition of the gland (its dimensions - length and width), but also to detect the pathological processes that have arisen in it, as well as complications arising from them. For this reason, during an ultrasound scan of the pancreas, the doctor often also evaluates the condition of the gallbladder, kidneys and liver, since these are the organs that primarily suffer from malfunction of the gland.
Despite the fact that ultrasound is one of the most informative and safe diagnostic methods, in some cases it becomes impossible to carry out.
Ultrasound examination is contraindicated in the following cases:
- if the patient has an allergic reaction to the gel used (it is not possible to conduct an examination without his participation);
- conditions that threaten the patient’s life (for example, necrosis, abscess, etc.);
- high degree of obesity;
- pyoderma;
- viral skin lesions (herpes, molluscum contagiosum);
- infectious skin diseases (tuberculosis, leprosy, borreliosis);
- systemic diseases (lupus, syphilis, HIV);
- the presence of wounds in the abdominal area (cuts, abrasions, burns, etc.);
- fistulas in the upper abdomen.
Key points in preparing for the study
Talking about how to prepare for an ultrasound of the pancreas, it should be noted that the preparation itself is divided into 3 main stages. The first is carried out 2-3 days before the planned date of the examination, the second is carried out a day before it, the third - on the day of the ultrasound.
2-3 days before ultrasound
To eliminate the possibility of obtaining unreliable data during the study, pancreatic rest should be ensured several days before the procedure. And since its main task is the production of digestive enzymes, which are activated when food enters the stomach, you will need to follow a special diet.
During the examination, no acute processes should occur in the pancreas, as this will lead to incorrect data. Therefore, it is necessary to exclude the influence of all factors that may cause activation of pathological processes in the tissues of the gland.
You will need to eliminate foods from your diet whose consumption causes increased gas formation in the gastrointestinal tract. These are:
- legumes;
- fresh, boiled and steamed vegetables;
- greenery;
- grape;
- melon;
- milk and dairy products;
- carbonated drinks, including mineral waters;
- black bread;
- spices;
- fatty meats;
- fried foods;
- alcoholic drinks.
Also, while preparing for the procedure, you will need to stop eating foods that contain a lot of protein, as they also contribute to increased gas formation in the gastrointestinal tract (fish, cottage cheese, cheese, etc.).
When performing an ultrasound examination, the pancreas should be functioning at rest. These dietary restrictions contribute to this. But what then can you eat before an ultrasound? During this period you are allowed to consume:
- porridges made from cereals and oatmeal in water;
- lean meats - chicken, turkey, rabbit, etc. (the skin cannot be eaten);
- boiled eggs or steam omelettes (no more than 1 egg per day);
- water and herbal teas.
Herbal teas help improve the functioning of the pancreas and prevent exacerbation of pathological processes in it
In this case, it is necessary to eat food correctly:
- food should be warm (hot and cold dishes and drinks have a negative effect on the functioning of the pancreas);
- Food should be consumed in small quantities, but not less than 5 times a day;
- You should not eat 2-3 hours before bedtime.
Remember that lack of preparation for the examination reduces the accuracy of the examination by 60%! These are serious indicators. Therefore, in order to avoid an incorrect diagnosis and incorrect course of treatment, it is necessary to prepare for an ultrasound in advance.
One day before the ultrasound
The second stage of preparation for an ultrasound examination, starting a day before the procedure, is the most important.
During this period, it is recommended to take enterosorbents, especially if errors in nutrition were made during the previous stage of preparation.
These drugs help reduce gas formation in the digestive tract and provide more accurate information during the examination.
Such drugs include:
- activated carbon (dosage is calculated individually depending on the patient’s weight - 1 tablet per 10 kg);
- Espumisan;
- Enteros-gel, etc.
Enterosorbents help reduce gas formation in the gastrointestinal tract
The last meal should be 12–14 hours before the ultrasound. Bowel movement is also mandatory.
If bowel movements do not occur within 24 hours before the procedure, this may also cause unreliable results and an incorrect diagnosis, since fermentation processes may be activated in the gastrointestinal tract.
If defecation does not occur, the situation can be corrected with the help of special rectal preparations (suppositories, microenemas, etc.) or a cleansing enema.
Source: https://mr-gergebil.ru/uzi-podzheludochnoj-zhelezy-podgotovka-k-issledovaniju-vzroslyh/
Ultrasound for pancreatitis
Ultrasound for inflammation of the pancreas has a different picture depending on the stage of the disease. There are 3 forms of pancreatitis: total, focal and segmental.
- At the beginning of the pathology, it is noted: an increase in the size of the gland, blurred contours appear, and an expansion of the Wirsung duct.
- Changes may also affect nearby organs. There is an increase in their echogenicity (increase in density for ultrasound waves).
- Due to the increase in the size of the pancreas, the great vessels are compressed, which is clearly visible during duplex examination.
- When pancreatitis passes into the necrotic stage, pancreatic pseudocysts form.
- In advanced cases, abscesses form with a level of fluid in the abdominal cavity.
In a chronic inflammatory process, ultrasound can detect calcified areas (calcifications) in the pancreas. They are defined as areas of high density. With prolonged inflammation, glandular tissue is replaced by connective tissue, and scars form. Using ultrasound, you can detect the proliferation of adipose tissue in the pancreas - lipomatosis.
Preparation for ultrasound of the pancreas: contraindications and interpretation
The pancreas is involved in the digestive tract and is located in the abdominal cavity of the stomach. It produces enzymes that help break down and absorb nutrients and minerals.
If an organ malfunctions, the consequences can be negative for the entire organism. Ultrasound examination of the pancreas helps to quickly identify pathologies.
Ultrasound examination of the pancreas
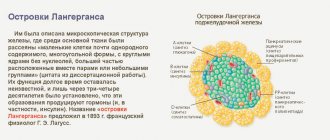
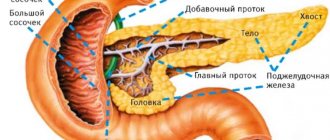
The pancreas is elongated (consists of a head, body and tail), and has a gray-pink color. Produces insulin (a hormone responsible for carbohydrate metabolism). The enzymes trypsin and chymotrypsin help the body process proteins, carbohydrates and fats. Performs functions in the digestion process. The gastrointestinal tract system is closely interconnected.
A person’s lifestyle, poor diet, and chronic diseases provoke disorders of the digestive system. To prevent the disease from progressing, the cause must be identified and treated. When patients complain of pain or discomfort in the gastrointestinal tract, the doctor must additionally examine the liver and do a kidney examination.
Ultrasound examination is one of the safe and informative methods for examining internal organs. Ultrasound rays are harmless, suitable even for a child and a pregnant woman, as they have no effect on the body.
If there are inflammatory processes in the pancreas, the disease can spread to neighboring organs. Therefore, if a disease is suspected, doctors prescribe an ultrasound examination of the pancreas and liver.
When is an ultrasound of the pancreas prescribed?
Examination of the pancreas alone to detect problems with the gastrointestinal (GI) tract is rarely prescribed. It is closely related to the work of the liver, stomach, bile ducts, etc. Therefore, a comprehensive examination of the abdominal cavity is used. An ultrasound examination is prescribed to a patient for the following symptoms:
- Systematic causeless nausea;
- You feel the urge to vomit, but after the eruption there is no relief;
- Feeling worse;
- Dizziness;
- Discomfort in the abdomen after eating;
- Stool disorder (diarrhea, constipation);
- Increased body temperature (37-37.5) in the absence of infection;
- The appearance of undigested food residues in the stool;
- Suspicion of a tumor process in the gastrointestinal tract;
- If a person has had a case of pancreatitis (relapse of the disease);
- Sharp pain in the upper abdomen;
- Bloating, increased gas formation (flatulence);
- For gastrointestinal diseases;
- A icteric color of the skin appears (jaundice);
- Sudden weight loss for no reason;
- Men are prescribed examinations for prostate disease;
- If a person has an inflamed gallbladder
- Increased tone of the anterior wall of the stomach;
- Diabetes;
- There are inflammatory processes in the liver.
If the listed signs are present, the patient is recommended to undergo a comprehensive medical examination. An ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity is performed to identify abnormalities and determine the cause of deterioration in health. Prescribed before surgery on the abdominal organs.
The ultrasound examination method is suitable for both adults and children.
Preparatory measures for ultrasound
For reliability and accurate results during a medical examination, it is necessary to prepare the body for the procedure and cleanse the stomach. Without following the recommendations, the quality of the study is reduced by 40-50%.
The patient needs to prepare for an ultrasound 2-4 days in advance. The doctor prescribes a special diet before the ultrasound. The goal of proper nutrition is to reduce the load on the gastrointestinal tract and remove toxins from the body (laxatives may be recommended). Dishes must be steamed or boiled. Can be used:
- Low-fat chicken broths;
- Fresh food (no seasoning, with minimal added salt);
- Herbal tea (decoction of chamomile, mint, rosehip);
- Rusks, unsweetened crackers;
- Hard varieties of low-fat cheese;
- Eggs;
- Porridge on the water;
- Dried fruits (dried apricots, raisins, prunes).
The following foods are prohibited before the procedure:
- Dairy and fermented milk products;
- Smoked meats;
- Pickled vegetables;
- Fatty foods;
- Hot, spicy food;
- Confectionery;
- Baked goods, bread;
- Legumes (beans, peas, lentils);
- Carbonated drinks;
- Strong tea or coffee;
- Alcohol;
- Grapes, apples.
The doctor who will conduct the ultrasound must explain to the patient how to prepare for the examination. You need to eat fractionally, in small portions. The day before the ultrasound, if possible, do not take medications. On the day of the ultrasound, you should not eat or drink. Preparatory measures before the examination will show an accurate picture of the internal organs.
Without preparation, ultrasound is performed in emergency situations. An experienced specialist will identify gross deviations from the norm.
Description of the ultrasound examination procedure
If dietary rules are followed, ultrasound examinations are more effective and the images are more accurate. This will help the doctor determine the cause of the disease and prescribe appropriate treatment.
The procedure is painless and not dangerous to health. An ultrasound examination is performed on an empty stomach (it is possible to carry out the procedure with a load on the stomach). The patient is placed on the couch, on his back.
A special gel is applied to the site where the ultrasound will be performed. The procedure lasts 15-20 minutes. The result is displayed on the screen in real time. The doctor can record the ultrasound and necessary pictures.
This is left in the patient’s medical record and helps to monitor the dynamics of the disease.
Purpose of ultrasound:
- Identify pathological processes.
- Determination of changes in shape and size (the structure and location relative to other internal organs are studied).
- Detection of congenital or acquired defects.
- Diagnosis of concomitant gastrointestinal diseases.
- Assessment of the condition of the pancreas.
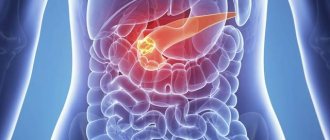
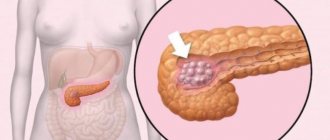
- Detection of neoplasms (benign or malignant tumors), seals, scars on the walls of the organ.
An ultrasound scan shows the abdominal cavity. During the procedure, the patient may be asked to turn to the left and right side to ensure clarity of the result. This allows the ultrasound specialist to examine the organ in three projections from different angles. The pancreas consists of a head, body and tail.
Interpretation of ultrasound of the pancreas
During an ultrasound scan of the pancreas, the doctor comments on the results displayed on the monitor. They are recorded separately on the card. Based on these indicators, a diagnosis is made.
- All parts should be clearly visible, without shadows or seals.
- The structure is noted (should be homogeneous) There is a predominance of small echo signals, evenly distributed throughout the pancreas.
- Study of the echostructure of the pancreas. There are significant changes and echo signs of diseases in the body. For example, an ultrasound examination of an organ in acute pancreatitis reveals a significant decrease in intensity and brightness. Changed echogenicity may cause swelling of the glands. In the chronic form of the disease, ultrasound shows heterogeneity of the echostructure and increased echogenicity. The organ will be marked by the development of scarring and fibrosis. Echo signs in women during pregnancy may deviate slightly from the norm.
- The shape of the pancreas in a healthy person is S-shaped. With pathology, a change in shape occurs: in the form of a spiral, a ring-shaped shape, the appearance of additional doubled parts of the organ. Defects of the pancreas indicate diseases.
- The size is estimated. The head length of a healthy organ is 25-30 mm, the body is 15-17 mm, the tail is 20 mm (normalized organ size indicators differ in adults and children). If there is swelling of the organ, increased size, then inflammatory processes may occur in the pancreas.
- Contours of the organ. In a healthy person they are smooth and clear. A blurred outline is a sign of pathology. Unevenness is caused by the formation of cysts, tumors, and stones. Each neoplasm has its own characteristics, and a qualified ultrasound physician can distinguish between them.
At the medical center, the doctor immediately interprets the examination results and makes a diagnosis based on the data obtained (it is possible to prescribe additional blood and urine tests).
Contraindications
The ultrasound method does not affect the body. Therefore, there are few contraindications for use. The procedure is performed with an ultrasonic sensor, which is moved over the surface of the skin. It is not recommended to conduct an examination using this method if:
- There is a large wound on the abdomen;
- At the time of examination, the person has a high body temperature;
- The patient has skin diseases in the abdominal area (lichen, itchy skin, purulent wounds, ulcers);
- Exacerbation of infectious diseases;
- It is prohibited to perform gastroscopy of the stomach (FGDS).
Ultrasound examination of the pancreas and other internal organs is an absolutely safe procedure that will help the doctor quickly make an accurate diagnosis. For prevention purposes, it is recommended that people who are elderly or have diseases of the gastrointestinal tract be examined.
Source: https://GastroTract.ru/obsledovanie/podgotovka-k-uzi-podzheludochnoj-zhelezy.html
Decoding indicators
Interpretation of the results of ultrasound of the pancreas is carried out according to a certain scheme. It should include information about the structure of the organ, its location, shape, echogenicity, contours, and dimensions. Normal ultrasound scan of the pancreas:
- S – shaped;
- the structure is homogeneous, single inclusions of 1.5 - 3 mm are acceptable;
- the echogenicity of the pancreas is close to the echogenicity of the liver and spleen;
- the contours of the organ are clear, the components of the pancreas (head, isthmus, body, tail) can be identified in the image;
- The dimensions of the pancreas according to ultrasound are normal in adults: head 32 mm, body 21 mm, tail 35 mm, duct diameter 2 mm.
The doctor draws up all this information in the form of an ultrasound report, which, together with the images, is then compiled into an outpatient card or medical history. Small deviations of indicators in one direction or another are acceptable.
Duplex scanning helps to see the condition of the vessels located close to the pancreas. Using this method, blood flow in the inferior vena cava, superior mesenteric artery and vein, celiac trunk and splenic vein can be assessed.
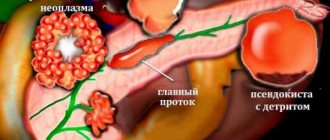
Of particular importance is the condition of the pancreatic duct (Wirsung's duct). If its patency is impaired, there is a suspicion of inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis), a tumor of the head of the pancreas.
Some diagnostic data may indicate diseases. A decrease in echogenicity means the acute stage of pancreatitis. The pancreas swells and the image becomes dim. A completely white gland on the monitor is a sign of an acute form of pancreatitis.
Tumors may not be visible on ultrasound; their presence is indicated by deviation of the tail of the organ. Echogenicity in malignant tumors or chronic pancreatitis is increased. You can see a change in color in some areas of the organ where neoplasms are possible.
A tumor is indicated by changes in the size of the liver and gallbladder. Taking material for histology helps determine whether a neoplasm is malignant or benign.
With pancreatic necrosis, the image shows extensive abscesses forming cavities with cloudy exudate. Inflammation of the pancreas is indicated by dilation of the Wirsung duct. The doctor visualizes stones and pancreatic abscesses.
Serious diseases of the pancreas can be asymptomatic at the initial stage and are detected as a result of a routine examination using ultrasound diagnostics. The interpretation of the results for each type of pancreatic pathology is individual.
Norm of indicators
Ultrasound examination of an organ rarely makes it possible to make an accurate diagnosis of pathology, but it is possible to assess the general condition - to determine whether the organ is healthy or has functional disorders. The following parameters are considered normal for men and women:
- The body of a healthy gland has a holistic, homogeneous structure similar to the structure of the liver. Small inclusions may be present.
- The echogenicity of the organ is average, but increases with a person’s age.
- The sections of the pancreas are clearly visible - tail, body, isthmus and head.
- The duct of Wirsung is not dilated, the diameter is from 1.5 to 2.5 mm.
- The vascular pattern is not deformed.
- The normal dimensions of the organ in adults are as follows: head from 18 to 28 mm, body 8-18 mm, tail 22-29 mm.
In a child, the normal size of the pancreas differs from the indications in an adult. For children from one to 5 years old, the following sizes are considered normal: head 17-20 mm, body 10-12 mm, tail 18-22. The normal size of an organ, determined by ultrasound, may have different indicators depending on the gender and age of the patient.
If according to ultrasound the contours of the pancreas are clear and even, this is normal.
If the patient has diagnosed diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, then the indicators are considered conditionally normal. It is important to take into account the patient’s weight and age when making a diagnosis. The parameters of the pancreas depend on the data.
Ultrasound of the pancreas is rarely performed separately; more often all organs of the abdominal cavity are examined. Since diseases of the pancreas are difficult to determine using ultrasound, by determining the pathologies of neighboring organs, one can judge the general condition of the contents of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space. If, as a result of the examination, it is possible to determine that the gland is not in order, the doctor may prescribe additional instrumental methods for examining the organ, such as magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography.
Ultrasound examination of the pancreas is an accessible, painless, safe diagnostic method that carries extensive information and is prescribed by a doctor at the first suspicion of pathology.
Preparing for an ultrasound of the pancreas: how to prepare for the procedure, indications for the study
The pancreas is located deep in the abdominal cavity behind the stomach. Therefore, visual methods or palpation are not suitable for examining her condition. Most often, ultrasound scanning is used to diagnose various pathologies.
This is a painless, non-invasive examination that allows you to see changes in the size and shape of the organ, the presence of stones or tumors. But in order for the result of an ultrasound scan to be reliable, proper preparation for the procedure is necessary.
Indications for use
An ultrasound scan of the pancreas allows you to see its shape, size, condition of soft tissues and blood vessels. As a result, it is possible to determine any structural changes in the organ, the presence of tumors, stones or areas of degenerated cells.
Ultrasound of the pancreas is used to diagnose the following pathologies:
- pancreatitis;
- formation of a cyst or pseudocyst;
- lipomatosis or fibrosis;
- deposition of calcium salts;
- tissue necrosis.
Typically, an ultrasound examination of the pancreas is performed in conjunction with an examination of the liver, spleen and gallbladder. After all, the pathologies of these organs are very related, so they often occur simultaneously.
An ultrasound is prescribed if a patient consults a doctor with complaints of pain in the upper abdomen or left hypochondrium, loss of appetite, slow digestion of food, nausea, increased gas formation, and frequent bowel movements.
It is necessary to conduct such an examination if there are any diseases of the kidneys, stomach, intestines, cholelithiasis, infections or abdominal injuries. An ultrasound is urgently prescribed in the presence of obstructive jaundice, sudden sudden weight loss, severe pain, and flatulence. This allows you to timely identify serious pathologies and prevent complications.
If pain or other discomfort occurs in the abdominal cavity, the doctor prescribes an ultrasound of the pancreas
Need for preparation
The pancreas is closely related to other organs of the gastrointestinal tract. It is located behind the stomach in the upper part of the abdominal cavity. This organ is in contact with the duodenum. Close to the gland are the liver and gall bladder.
And the bile ducts generally pass through it. Impaired functioning of any of these organs may affect the examination results.
The presence of food in the stomach and duodenum, as well as increased gas formation, makes it especially difficult to make a correct diagnosis.
Ultrasound is a painless examination method in which an image of organs appears on a screen due to the passage of ultrasound waves through tissue.
The device that the doctor moves over the patient’s body is both a source and receiver of these waves.
Their proper passage can be disrupted by the movements of the stomach that occur during the digestion of food, the processes of rotting and fermentation in the intestines, which cause increased gas formation, as well as the release of bile.
Fermentation processes in the intestines especially interfere with ultrasound scanning. They lead to increased gas formation, which makes clear visualization of the pancreas difficult and prevents reliable detection of its pathologies. In addition, the exact result of the study can only be obtained with an empty stomach. The presence of food in it distorts the ultrasonic waves.
When any of these processes occur, the reliability of the examination result may decrease by 50-70%. To prevent this from happening, proper preparation for an ultrasound of the pancreas is necessary. Usually this examination is prescribed by a doctor, who explains to the patient what he needs to do for this.
What should be done?
All preparatory activities should be aimed at increasing the accuracy and reliability of the ultrasound procedure.
Preparation for the examination should begin several days before it, especially if the patient suffers from flatulence or other digestive pathologies.
It consists of changing your diet, taking certain medications and giving up bad habits. These measures usually do not cause difficulties for patients; on the contrary, they lead to improved health.
In several days
It is necessary to prepare for an ultrasound examination 2-3 days before it is carried out. First of all, it is necessary to prevent the occurrence of gas formation and fermentation processes in the intestines.
To do this, the usual diet changes. It is necessary to exclude from it all products containing coarse fiber, fats, extractives and spices.
It is advisable to reduce the consumption of sweets, proteins and foods that are difficult to digest.
You must follow a diet for several days before the examination.
Usually the doctor gives the patient a list of foods that need to be excluded from the diet. It may depend on the functioning of its digestive organs and the presence of pathologies. But most often it is recommended to stop consuming the following foods 2-3 days before the ultrasound examination:
How to check the pancreas
- all legumes, especially peas and beans;
- vegetables containing coarse fiber - cabbage, cucumbers, asparagus, broccoli;
- spicy vegetables, as well as those that contain extractive substances - radishes, garlic, horseradish, radish;
- spices and herbs;
- fruits that can cause fermentation - melon, pear, grapes;
- animal proteins - eggs and any meat, as they take a long time to digest;
- fatty dairy products, whole milk;
- yeast bread, pastries;
- ice cream, sweets;
- sweet juices, carbonated and alcoholic drinks.
People who suffer from flatulence, slow digestion or metabolic pathologies are advised to make their diet even more strict for these 3 days. Often it is allowed to consume only porridge, pureed boiled vegetables, herbal decoctions, and still mineral water.
Per day
Sometimes this examination is prescribed urgently. It is especially important to learn how to prepare for an ultrasound of the pancreas. This can be done even the day before the procedure. This is the most important time during which it is necessary to cleanse the intestines and prevent the occurrence of flatulence. Often for this it is recommended to take special medications, do enemas, and follow a diet.
To prevent increased gas formation, you need to take activated charcoal the day before the procedure.
To cleanse the intestines you need to take enterosorbents. They will help prevent gas formation and reduce bloating. They are usually prescribed 2 times a day. It is best to take activated carbon in a dosage of 1 tablet per 10 kg of person’s weight. You can replace it with a more modern option - white coal or other enterosorbents.
Those patients who suffer from flatulence and increased gas formation are recommended to start taking Espumisan or similar simethicone-based drugs the day before the examination.
In addition, you need to take enzymes on the day before the ultrasound examination. They will help food digest faster and help empty the stomach.
Usually Festal, Mezim, Panzinorm or Pancreatin are prescribed.
The last meal should be at least 12 hours before the examination. Usually this is a light dinner in the evening no later than 19 hours. An ultrasound of the pancreas must be done on an empty stomach.
It is especially important to monitor this condition for obese people and those who have a slow metabolism.
They are recommended to do a cleansing enema the day before the procedure or use suppositories with a laxative effect.
On the day of the procedure
On the day of the ultrasound, the patient is not recommended to smoke or take medications in the morning. The only exceptions are people with chronic diseases for whom regular medication is vital.
It is very important to empty the intestines in the morning so that fermentation processes in it do not make it difficult to obtain a clear image of the pancreas.
If this causes difficulty, it is recommended to do an enema or use laxative suppositories.
On the day of the examination, you cannot eat anything; it is not even recommended to drink water 5-6 hours before the procedure. An exception can be made only for patients with diabetes mellitus, for whom long-term fasting is contraindicated. They can eat some carbohydrate food.
Preparing for the study also includes what you need to take with you to the office. There is no need to change clothes or use any equipment for an ultrasound.
But it is recommended to take a diaper to lie on, as well as a towel or napkin to wipe the gel used for better conduction of ultrasound pulses from the abdomen.
Timely ultrasound examination helps maintain the health of the pancreas. And proper preparation for this procedure will allow you to get a more accurate and reliable result.
Last updated: April 18, 2018
Source: https://sosudy.info/kak-podgotovitsya-uzi-podzheludochnoj-zhelezy
What should you do to properly prepare for the examination?
The most important thing is to follow a diet. To reduce gas formation, you should avoid:
- Carbonated drinks;
- Milk and dairy products;
- Raw vegetables;
- Sweet juices;
- Black bread;
- All legumes;
- Fatty meat;
- Spicy seasonings and excess salt.
Drinking alcohol is strictly prohibited.
Doctors recommend following this diet for 3 days before the procedure. You should definitely drink a lot of liquid these days: at least one and a half liters every day.
Instead of eating junk food, it is better for the patient to eat lean meat before the test, such as turkey, chicken breast, beef, boiled eggs, lean fish and cereals cooked in water. Such food does not irritate the stomach and does not complicate the work of the liver and pancreas, so the doctor will see the clearest possible picture on the ultrasound.
Ultrasound is usually performed in the morning, before 12 noon. You should have dinner before the procedure no later than 19:00 so that the food has time to be completely digested and empty the stomach and intestines. You can’t have breakfast before an ultrasound! It is also prohibited to drink water or any other drinks, smoke, or suck candy. Failure to comply with this rule will lead to stomach spasms, due to which the doctor may make an incorrect diagnosis.
An exception is made for people with diabetes. With this disease, the patient cannot fast and the examination is carried out after a light breakfast.
If there are problems with the intestines, for example, if the patient suffers from constipation, the doctor recommends that he take a laxative the day before the test, and if the patient has increased gas production, then he is recommended to drink activated charcoal or special pharmaceutical anti-flatulence medications for all three days. Sometimes, due to the location of the gland, it is not immediately visible on ultrasound. Then the doctor recommends that the patient drink a glass of water in small sips through a straw.
We recommend reading: Salbutamol: instructions for use for adults and children, composition and side effects
Be sure to tell your doctor about any medications you are taking, illnesses, or recent examinations, such as an X-ray examination of the abdominal organs or an endoscopic examination of the stomach. There is no need to stop taking medications before an ultrasound, but you should also inform your doctor about it.
How to prepare for an ultrasound of the pancreas
The pancreas is the main organ of the gastrointestinal tract, responsible for the synthesis of digestive enzymes and hormones that control metabolic processes in the body. With complete or partial dysfunction of this organ, serious digestive problems are observed.
And in order to understand exactly what pathological processes occur in the pancreas tissues and what their extent is, doctors prescribe an examination, which includes an ultrasound examination. Preparing for an ultrasound of the pancreas is a very important undertaking.
If it is not carried out, incorrect data may be obtained during the study, which will be followed by incorrect treatment, further progression of the disease and the occurrence of complications against it.
On the day of the ultrasound
This is the final stage of preparing the digestive tract organs for ultrasound. It begins 10–12 hours before the procedure. During this period you cannot drink or eat anything. An empty stomach is an important condition for everyone.
The only exceptions are persons suffering from diabetes mellitus or those with impaired glucose tolerance.
They are allowed to eat food at this stage of preparation, but only one that contains a lot of carbohydrates and little protein and fat.
In addition to the hunger strike, there are some other restrictions that all patients must adhere to 10–12 hours before the procedure - you cannot smoke or take any drugs orally (only intravenously, subcutaneously or intramuscularly).
Be sure to check with the clinic where the examination will be carried out to determine how developed their service is. If they don't provide disposable diapers and wipes, be sure to bring your own.
You can purchase these products at any pharmacy.
A disposable diaper will be needed to place on the couch, and napkins will be needed to remove any remaining gel, which is applied to the stomach before the diagnosis.
Ultrasound examination of the pancreas is a completely painless procedure. Before it is performed, the patient must take the desired body position - lie on the couch, straighten his legs and arms along the body.
During the examination, the doctor may ask the patient to change his body position. This is necessary for a more detailed examination of the pancreas, since there are other organs near it that may block access to it.
Ultrasound diagnosis of the pancreas is a valuable diagnostic method
After completion of the procedure, the patient can immediately return to their normal lifestyle. However, the “exit” from the diet that he followed for several days should be smooth. You should not immediately eat a lot of fatty and fried foods. All products should be introduced into the diet gradually.
The results of the examination are usually given to the patient immediately. With them, he needs to go to his attending physician, who, based on the data received, will make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment. A repeat ultrasound scan of the pancreas may be prescribed after 1–3 months to assess the effectiveness of the treatment. If it does not give positive results, therapy is adjusted.
Source: https://schsite.ru/diagnostika/kak-podgotovitsya-uzi
What is possible and what is not: preparing for an ultrasound of the pancreas and how it is done?
The pancreas plays an important role in the digestive system, performing a dual function: exocrine and endocrine. The first consists in the regular release of digestive juice , of which about 1 liter is released per day.
The second is the production of hormones and the regulation of metabolic processes in the body.
In light of the critical importance of the organ, preparation for an ultrasound scan of the pancreas in the event of such an appointment is an important element in making the correct diagnosis.
Ultrasound examination of the pancreas is included in the complex of general examination of the abdominal organs. However, there are a number of symptoms for which an ultrasound of the pancreas should be performed as an independent procedure and the organ examined separately.
Indications
The doctor is highly likely to prescribe an ultrasound examination of the pancreas if:
- the patient is bothered by dull pain in the upper abdomen;
- vomiting occurs;
- jaundice was diagnosed;
- there is a suspicion of a tumor or the patient is in the process of treating it;
- body temperature is elevated for unknown reasons;
- a diagnosis of pancreatitis, both acute and chronic, was made;
- there have been abdominal injuries;
- pathologies of the gallbladder or liver have been established;
- it is necessary to prepare for a planned operation;
- diseases of the duodenal zone or pancreatic necrosis were diagnosed.
The fragment presented below provides information about what are the indications for prescribing an ultrasound of the pancreas.
Preparation
Proper preparation for an ultrasound examination of the pancreas is the key to successful diagnosis of the organ’s condition.
Preparation for the examination differs slightly for men, women and children.
Reference! Excessive ultrasound exposure is not recommended for expectant mothers unless absolutely necessary.
A healthy pancreas should be examined no more often than once every six months. If the pregnancy is planned, then the woman is recommended to visit a diagnostician in advance to make sure that the internal organs are healthy and will successfully cope with the increased load that pregnancy will bring.
How can a child prepare?
Preparation for an ultrasound examination depends on the age of the child:
- If the baby is not even a year old, then the parents will have to skip one feeding so that the child does not eat for three hours before the procedure. You should not give water if there is less than an hour left before the ultrasound.
- If the child is 1-3 years old, then the last meal should be 4-5 hours before the ultrasound, drinking should be stopped 1-1.5 hours before the procedure.
- It is recommended not to feed children over three years old before the examination for 6-8 hours, that is, it is better to undergo an ultrasound in the morning, on an empty stomach. The intake of water or drinks should be stopped 1.5 hours before the test.
Can I drink and eat before the procedure?
If the ultrasound is performed in the morning, then dinner on the eve of the examination should be light and not late, and you will have to skip breakfast.
Important! The adult patient is prohibited from eating or drinking immediately before the procedure.
Drinking, even water or tea, is also prohibited. All this is necessary to avoid stomach cramps, which may interfere with the examination.
Diet
In order for the study to be as informative as possible, the patient is recommended to follow a diet. It begins three days before the procedure and consists of switching to food that prevents flatulence.
What you can do :
- lean meat, fish;
- porridge with water;
- vegetable broth soups;
- boiled egg (1 per day);
- tea, unsweetened compotes, water - no more than one and a half liters per day;
- low fat hard cheese.
What not to do :
- milk and products made from it, including fermented milk;
- grapes and any raw fruits;
- bread and baked goods containing yeast;
- kvass, beer and any alcoholic drinks;
- coffee, strong tea, spices (cinnamon, pepper, cumin);
- vegetables rich in polysaccharides (corn, potatoes, onions, cabbage, both raw and stewed);
- legumes and dishes with them, as well as mushrooms;
- carbonated drinks, including mineral water if it contains gas.
Before an ultrasound examination you should also not :
- smoke;
- sucking candy or lollipops, chewing gum;
- take medications (except for vital ones, which must be reported to the doctor before the ultrasound).
How do they do it?
To determine the echo structure of the pancreas, you need to free your stomach from clothes and lie down on the couch. After which the doctor will apply a conductive gel to the area under study and begin to examine the organ using a sensor.
Reference! To examine the tail of the gland, the patient will have to lie on his side, and may also have to take a semi-flexed position.
The entire examination takes from 15 minutes to half an hour, it is completely painless and non-invasive (that is, it takes place without damaging the skin).
Conclusion
Ultrasound of the pancreas has important diagnostic value and is a valuable method in the early detection of pathologies.
However, the examination requires careful preparation from both the adult and the child - otherwise it will be uninformative and simply useless. Diseases of the gland detected in time can be easily corrected.
And with proper nutrition and reasonable dietary restrictions, not only before an ultrasound, many problems can be avoided altogether.
What is possible and what is not: preparing for an ultrasound of the pancreas and how it is done? Link to main publication
Source: https://MediGid.com/uzi/organy/bryushnaya-polost/zhkt/podzheludochnaya-zheleza/podgotovka-i-kak-delayut-issledovaniye.html
Advantages
The survey has many significant advantages:
- If you compare ultrasound and x-ray, ultrasound, there is no radiation.
- Preserving the integrity of the skin. There is no need to cut anything, insert it inside, or inject anything.
- Complete absence of pain.
- The data received on the monitor does not require additional processing, which speeds up the process of obtaining results.
- Ultrasound is widely used. The devices are installed in most clinics, which indicates the accessibility of the examination.
- Another significant advantage is low cost.
- The study itself takes a short amount of time (about 20 minutes).
- frequent pain in the upper abdomen, tingling, prolonged aching sensations, discomfort;
- hematomas, neoplasms, purulent abscesses, suspicion of the presence of stones in the pancreas, cyst;
- changes in the loops of the duodenum, revealed by x-ray;
- confirmation of diagnosis is required;
- changes in the posterior wall of the stomach;
- frequent bouts of vomiting, nausea;
- abdominal bloating;
- diarrhea, stool disorders; incomplete digestion of food; feces are filled with large pieces of food;
- a blood test revealed a high sugar level in the patient;
- jaundice, frequent increase in body temperature (up to 38 degrees);
- abdominal injuries;
- planned operation.
How can a child prepare?
Preparation for an ultrasound examination depends on the age of the child:
- If the baby is not even a year old, then the parents will have to skip one feeding so that the child does not eat for three hours before the procedure. You should not give water if there is less than an hour left before the ultrasound.
- If the child is 1-3 years old, then the last meal should be 4-5 hours before the ultrasound, drinking should be stopped 1-1.5 hours before the procedure.
- It is recommended not to feed children over three years old before the examination for 6-8 hours, that is, it is better to undergo an ultrasound in the morning, on an empty stomach. The intake of water or drinks should be stopped 1.5 hours before the test.
We recommend reading: How to stop vomiting: what helps adults and children at home?