Pathogen
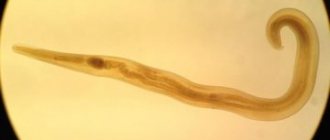
Hymenolepis nana (dwarf tapeworm) is a small cestode, 15-30 mm long, 0.55-0.7 mm wide, with a very small scolex equipped with four suckers. The flat body of the dwarf tapeworm is white, consists of a thin long neck and a large number (up to 200) of small tender segments - proglottids. The hermaphroditic segments have three rounded testes, a two-lobed narrow ovary and an unpaired vitelline. Mature segments, located in the final part of the body, contain a uterus in the form of a sac, which is filled with mature eggs. They are transparent, colorless, slightly opalescent, ellipsoidal, less often spherical in shape, equipped with a thin double-contour shell. Inside the egg there is an oncosphere with six hooks and a thin shell, from the poles of which so-called filaments extend - thin threads that sharply refract light, writhing between the shells of the egg and the oncosphere.
Humans are both intermediate and definitive hosts of the parasite.
Hymenolepiasis - what kind of disease is it?
The dwarf tapeworm, also known as Hymenolepis nana, colonizes the human intestine, leading to the development of the chronic disease hymenolepiasis. For such a disease, a dry and hot climate is favorable, where ascariasis is least common. This is due to the presence of relative antagonism in such worms, as well as specific intestinal microflora. Dwarf tapeworm is more often diagnosed in people with an urban lifestyle, especially when it comes to children of different ages (4-14 years). This category of the population also shows carelessness due to the peculiarities of the immune system.
Rat tapeworm can reach 30 cm in length, but is usually found in rodents. You can become infected with this parasite by eating underbaked bread, raw dough, or cereals. The dwarf tapeworm can reach sizes from 1 to 5 cm; its body consists of a scolex, a neck and small segments, inside of which, according to the maturation plan, a large number of eggs accumulate. Ways of infection are unwashed hands, use of contaminated household items, consumption of dirty and insufficiently heat-treated foods, ingestion of eggs with dust and water.
2 weeks after entering the body, tapeworms transform into adult sexually mature individuals, after which the mature segments with eggs are detached from the body. The offspring of the parasite exits through the intestines along with feces into the environment. Separated segments of the tapeworm can be seen in the stool, which most often occurs among infected people. Only a thorough diagnosis will allow you to identify the type of helminth and select a course of treatment.
Epidemiology
Hymenolepiasis is common mainly among children 3-12 years old. The main factor of transmission is the introduction of eggs through the hands into the mouth. Eggs most easily come into contact with objects contaminated with them, common pots and toilet seats, through the handles of doors and taps in restrooms, toys, etc. In a family, shared apartment, organized children's groups, if the sanitary regime is violated, conditions are created for the spread of hymenolepiasis and for the formation of its foci.
Water from reservoirs, vegetables, fruits, and soil play a minor role in the epidemiology of hymenolepiasis. Infective eggs of the dwarf tapeworm are found extremely rarely in synanthropic flies, but the possibility of them transferring eggs to food products cannot be ruled out.
In the external environment, parasite eggs are not persistent: they quickly die when dried out under the influence of high temperatures. At room temperature, the death of eggs upon drying occurs on the 3-4th day; at 55°C the eggs die within 30 minutes, at 60°C – very quickly. At 18-20°C in water, eggs remain viable for up to 25-35 days; in fecal slurry and waste water they die on the 19th day.
After irradiation with a mercury-quartz lamp for 10-20 minutes, all eggs die. When exposed to bleach and carbolic acid, eggs die within 5-30 minutes.
Pathogenesis and pathological anatomy
Dwarf tapeworms parasitize humans, often in significant numbers. The mechanical and chemical effects of parasites on intestinal tissue play a major role in the pathogenesis of hymenolepiasis. 2-3 days after infection, serous swelling of the mucous membrane of the small intestines occurs in the areas where cysticercoids are located, blood supply to the vessels increases, and hypersecretion of the liberkühn glands is noted. After another 3-5 days, there is a sharp increase in the villi, which contain cysticercoids, and their degenerative changes. Subsequently, the reactive inflammation subsides and atrophic necrosis of the affected villi develops, the connective tissue grows, and the epithelium proliferates.
Young tapeworms released from the villi attach to the intestinal wall, causing circulatory disorders at the site of fixation and subsequent necrotic changes in the mucous membrane, accompanied by the release of a significant amount of mucus into the intestinal lumen, sometimes mixed with blood.
The toxic and reflex effects of parasites on the body play a significant role. In this regard, the functions of the gastrointestinal tract are disrupted, painful symptoms of varying intensity develop, depending largely on the reactivity of the patient’s body.
Preparing for analysis
In order to unambiguously determine the type of parasite, it is necessary to undergo an appropriate analysis. To prescribe it, you must first consult a doctor.
To test for hymenolepiasis, 3 swabs of 50 grams each are taken from fresh feces. It must be taken in 3 stages - 3 times with a break of 5 days to several weeks. The duration of the break will have to be determined by the attending physician.
You need to properly prepare for submitting stool for analysis. For this:
- You should stop taking any antibiotics about a week before. If symptomatic treatment is used, such as anti-diarrhea medications or castor oil, this should also be stopped.
- Drinking alcohol is strictly prohibited.
- Stop using any rectal medications – suppositories and ointments – at least 3 days in advance.
- For at least 3 days, refrain from eating animal products - meat and fish, as well as tomatoes.
The method of taking this analysis is based on the cyclical release of helminth eggs from the human body. It allows you to determine the degree of infection with maximum accuracy.
Symptoms
Hymenolepiasis is sometimes asymptomatic, but most often patients complain of nausea, sometimes vomiting, drooling, heartburn, belching, changes in appetite, as well as aching, dull pain in the abdomen, mainly in the area of the small intestines. The pain can be in the form of daily attacks or appear at intervals of several days. The onset of pain is not related to the intake and quality of food; they last 1-2 hours or longer. A characteristic feature of the disease is unstable, loose and frequent stools mixed with mucus.
As a result of prolonged diarrhea and loss of appetite, the nutrition of patients is often disrupted, as a result of which they lose weight. The disease is accompanied by headaches, increased nervous excitability, irritability, and decreased performance. As a rule, in children the disease occurs in a more pronounced and severe form than in adults. There are often cases when the cause of long-term unstable stool in children is hymenolepiasis, and only after deworming does the stool become normal. In the presence of hymenolepiasis, the course of bacterial dysentery is delayed. When these two diseases are combined, the period of bacterial excretion is prolonged, exacerbations of the dysenteric process occur more often, and the general condition of the patients worsens.
The most characteristic of hymenolepiasis in adults is dyspeptic syndrome, the pathogenesis of which is based on functional, less often organic changes in the secretory and motor functions of the stomach. Often there are dyskinetic disorders of the duodenum. In this regard, hymenolepiasis can also occur with pain, and in these cases dyskinetic disorders of the biliary system may also occur. The disease often occurs with dysregulation of cardiovascular activity. Epileptiform seizures are observed in both children and adults.
There are usually no pronounced and characteristic changes in the blood. At times, mild anemia and a slight increase in the number of eosinophils in the blood are observed.
Dwarf tapeworms parasitize for a number of years, which depends on both repeated autosuperinfestations and repeated self-infections.
When is it necessary to collect stool for hymenolepiasis?
In order to fully pass the medical commission, it is necessary to do a stool test for hymenolepiasis. Obtaining results is required in the following cases:
- upon admission to kindergarten, school or other educational organizations;
- before employing any adult in a child care institution;
- before planned hospitalization in any hospital department;
- when taking tests for holidays in sanatoriums;
- when unpleasant symptoms from the gastrointestinal tract appear.

Since the dwarf tapeworm can be directly transmitted from person to person, to visit the pool you must have a certificate confirming the absence of helminths in the human body
Preventive measures are aimed not only at preventing the disease, but also at re-infection of those who have recovered from the disease. This is due to the fact that the immune system does not form a strong defense against hymenolepiasis.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made based on the detection of eggs in excrement during flotation studies. Hymenolepis nana eggs are transparent, colorless and easy to see under a dark microscope field. They are easily deformed and destroyed in the external environment, so they are more difficult to detect in feces that have been stored for a long time. More accurate results are obtained when examining fresh stool, no more than a day old. Eggs are released cyclically, so if the results are negative, the tests must be repeated.
Treatment
For deworming, preparations from the rhizome of the male fern are used - ethereal extract or filixan, akrikhin, pumpkin seeds, iomesan. Gentian violet, methylene blue, and yatrene are used as auxiliary agents. Diathermy and oxygen are used. It should be borne in mind that the listed anthelmintics affect only sexually mature dwarf tapeworms located in the intestinal lumen. The larvae, cysticercoids, located in the intestinal villi, remain viable and after some time emerge into the intestinal lumen, where they develop into sexually mature helminths. Therefore, for the successful treatment of hymenolepiasis, the most rational is cyclic treatment, repeated after a certain period.
Also, for the treatment of hymenolepiasis, a drug such as praziquantel is used, which is used in a single dose of 25 mg/kg. The drug is contraindicated for children under 4 years of age.
Prevention
It is necessary to carry out a set of sanitary and therapeutic measures according to a specially developed plan and adherence to the rules of personal hygiene (cleanliness of hands, body, clothing, home). It is especially important to monitor the cleanliness of the restrooms: toilet seats, floors and walls near the seats, door handles, washbasin taps should be treated with boiling water; You can also use disinfectants (bleach, etc.). Infected children should use individual towels and potties; the latter are treated with boiling water after each use. Control of flies and rodents is necessary. It is necessary to carry out active detection, timely deworming and subsequent clinical observation of infested hymenolepiasis, especially in children's groups.
The information presented in this article is intended for informational purposes only and cannot replace professional advice and qualified medical care. If you have the slightest suspicion that you have this disease, be sure to consult your doctor!
How and when to get tested
You can get tested for hymenolepiasis either with a referral from your attending physician or on your own.
When you consult a doctor and based on the results of the examination, a stool test may be prescribed. Then the examination will be carried out in the laboratory of the hospital where the patient went. Or - if it is impossible to carry out the study on site - the attending physician will refer the patient to the central hospital or to a larger city. There, local laboratories will take an analysis upon referral.
If there is no desire or opportunity to see a doctor, the test can be carried out in any paid laboratory. You don't need a referral for this. All you have to do is call and find out when you can pick up.
What needs to be done before taking the test:
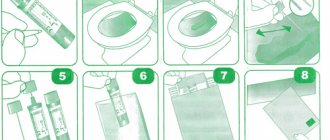
- Contact the laboratory or hospital in advance and find out whether the test is accepted in its own container, or whether it is necessary to take the test on site. If you can take the test in your own container, you need to take a small jar, preferably glass, dry and clean. Approximately two tablespoons of stool are needed, but care must be taken not to include any urine in the test.
- It is best to take an analysis from three different parts of the stool - top, inside and bottom.
- The jar must be labeled - stick a piece of paper with your full name, date of birth and date of analysis on tape. Cloth medical tape is also suitable for this purpose. The main thing is that the markings do not come off or get lost.
- The jar needs to be taken to the laboratory as soon as possible.
- If the test is taken directly in the laboratory, you need to get a free sterile container from the nurse and follow her recommendations.
- The results of laboratory tests in private laboratories are usually obtained quite quickly. They can be obtained in any way convenient for the patient, agreed upon in advance. This can be a message by email or in your personal account on the laboratory website.