Reasons for the development of the pathological condition
Hyperemia of the gastric mucosa occurs in the following diseases.
A chronic disease of the esophagus, which is characterized by inflammation of its mucous membrane due to the constant reflux of stomach contents into it. Sometimes, when the disease occurs, the pain radiates to the sternum and resembles symptoms of heart disease.
Often, patients mistake pain for angina pectoris, without even thinking about digestive problems. The main signs of pathology include: belching of air or food, nausea, severe heartburn, sour taste in the mouth, regurgitation, prolonged hiccups. The chronic form of esophagitis is characterized by alternating periods of exacerbation and remission.
Inflammation of the gastric mucosa and its dystrophic changes. The form of the disease is determined by the location and nature of the redness and swelling: if the gastric mucosa is moderately hyperemic and there is a slight whitish coating, then we can talk about minor inflammation.
If the redness is severe, the mucous membrane is thinned and blood vessels are visible, then atrophic gastritis is diagnosed. Focal hyperemia is observed during purulent-inflammatory processes, characterizing the fibrous form. If the gastric mucosa is diffusely hyperemic, then perhaps we are talking about superficial gastritis.
The clinical picture of the disease includes the following symptoms: pain and a feeling of fullness in the epigastric region, nausea and vomiting, increased salivation, decreased or loss of appetite, frequent belching, bloating, weight loss. The chronic form of gastritis does not have pronounced symptoms, but is characterized by periodic exacerbations with disruption of the gastrointestinal tract.
A pathology characterized by damage to the gastric mucosa and the formation of ulcers in it. Signs of the disease can be different and are related to the size and location of the defects, pain threshold, stage of the disease, age of the patient, etc.: pain that can occur on an empty stomach and go away after eating, and vice versa, heartburn, belching sour or bitter, a feeling of heaviness in the stomach, rapid satiety, flatulence, decreased or loss of appetite.
Of all the pathologies of the stomach, peptic ulcer is the most insidious and can be accompanied by a number of complications. These include penetration, perforation, malignancy, pyloric stenosis and bleeding.
A disease in which there is redness and swelling of the mucous membrane of the bulbar part of the duodenum. The disease can be asymptomatic or have a pronounced acute period. The main signs of bulbitis are:
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- minor pain in the upper left abdomen;
- attacks of nausea and vomiting;
- often constipation.
In addition, other unpleasant symptoms may appear, such as a whitish coating on the tongue, increased gas formation, cramping abdominal pain on an empty stomach or after eating. If the pathology is not treated in any way, then there is a likely risk of developing gastrointestinal bleeding.
An inflammatory disease characterized by an inflammatory process in the duodenum. Often the disease is combined with gastritis, which most often affects the antrum of the stomach.
Characteristic signs of pathology are:
- epigastric pain that increases with palpation of the abdomen;
- constant nausea;
- rarely vomiting mixed with bile;
- rumbling in the stomach;
- flatulence;
- loss of appetite and weight loss.
When bile stagnates, yellowness of the skin and sclera of the eyes may appear. In elderly people, duodenitis is often asymptomatic and is diagnosed accidentally during an FGDS. But there are also factors due to which the gastric mucosa is hyperemic:
- mechanical damage to the digestive organ by any object;
- irrational and unhealthy diet;
- infectious diseases (measles, scarlet fever);
- bacterial infection (Helicobacter pylori);
- renal failure;
- prolonged exposure to stress and depression.
Diet for duodenitis: menu for the week
To achieve success in the treatment of any disease of the gastrointestinal tract, you need to eat right.
Thus, a proper diet for duodenitis will help the patient normalize the motility of the gastrointestinal tract, and give “rest” to the duodenal mucosa, exhausted by the inflammatory-erosive process.
The diet is rich in foods with enveloping properties, as well as dishes with a liquid and creamy consistency, which makes them easy to digest and assimilate.
Principles of nutrition
The main principle of the diet for duodenitis is the exclusion from the diet of all foods that can mechanically or chemically irritate the inflamed surface of the duodenal mucosa.
Throughout the course of active treatment, as well as during the recovery period from the disease. The patient must follow the following nutritional rules:
- Nutrition for duodenitis should be fractional: in small portions, 200–300 grams, every 3 hours. Under no circumstances should you overeat;
- Meals should be carried out according to a pre-planned schedule. This is necessary so that the body knows exactly at what time it is necessary to increase the secretion of juice, and at what time it is better to stop it;
- alcohol, cigarettes, fatty, spicy, rough foods are taboo. It is advisable to completely get rid of bad habits, and in addition to recovery from the disease, the patient will feel a general improvement in well-being and increased vitality;
- food must be properly prepared: boiling, steaming, baking;
- You can consume up to 12 g of salt per day, so it is advisable not to add it to food when cooking, but to add salt to ready-made dishes;
- Before eating foods of high and medium coarseness, they must first be crushed or ground to a puree. Eating food with abrasive particles injures the mucous membrane of the inflamed duodenum;
- When absorbing food, it must be chewed thoroughly. Moreover, the longer the food is in the mouth, the better it is processed by salivary enzymes;
- food should be consumed warm (from 20 to 45–50 degrees);
- You need to drink at least 1–1.5 liters of pure non-carbonated mineral water per day. By ignoring this rule, the patient complicates digestion and exposes the mucous membrane of the diseased organ to additional irritation;
- It is important to change the qualitative, not the quantitative, composition of food: increase the percentage of protein, and cut back on fats and carbohydrates. All sweets are also removed from the menu (at least for the period of exacerbations).
By observing all of the above principles, the patient significantly increases his chances of a speedy cure.
Allowed products on the menu for duodenitis
The diet for duodenitis consists almost half of cereals. A special place in their list is occupied by liquid oatmeal with water, or milk diluted 2 thirds with water. Corn porridge is also good.
Slimy oatmeal is an ideal option: it is easily digested, does not irritate the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum, and also gently envelops it, neutralizing the negative effects of hydrochloric acid.
You can eat up to 450–500 g of ready-made porridge per day. This amount is divided into 2-3 doses.
The finished porridge can be lightly salted (it is worth remembering that no more than 12 grams of salt is allowed per day) and flavored with a piece of butter. The butter must contain at least 82% fat; if a lower figure is indicated on the briquette, you should not buy it, because it is more of a milk-containing product rather than real butter made from heavy cream.
Diluted or low-fat, diet milk can be drunk for breakfast, added to porridge or tea.
For inflammation of the duodenum, it is useful to include non-acidic fruits and berries in the menu:
- In summer the choice is huge: strawberries, raspberries, blueberries, wild strawberries, sweet apples, cherries.
- In late summer and early autumn, you can eat pureed watermelon (you should never eat melon).
- In winter, patients often ask whether they can consume persimmon. The answer is definitely yes. It has a low level of acidity, so it does not harm the mucous membrane, and even, on the contrary, heals it: the fruit contains thiamine, a substance that normalizes the acidity of gastric juice. Persimmon is an antibacterial agent that slows down the development of pathogenic intestinal microflora.
- In the spring, when the choice of fresh fruit is small, you can enjoy a banana or pureed apple without skin (baked apples will be even healthier).
- Fruits should not be combined with milk. The berries can be mashed into a puree and added to milk. This homemade milk dessert will be a great summer afternoon snack.
For the first 12 days with duodenal inflammation, you should not eat meat. Only 2 weeks after the start of the course of treatment and diet, you can include in the menu boiled lean meat without skin and veins: chicken breast, veal. You can prepare steamed cutlets from lean fish (trout, pollock, pike perch) without bones and skin, and lean meat minced through a meat grinder.
The therapeutic diet welcomes a variety of puree soups, broths and pureed vegetable soups with boiled vegetables: carrots, pumpkin, cauliflower, zucchini and broccoli. Potatoes should not be consumed if you have duodenitis.
Dinner should be hearty and light. You can eat porridge, milk, oatmeal or berry non-sour jelly. You should not allow yourself to feel hungry: if it is already very late, you can drink a glass of kefir or natural yogurt without sugar.
Bread is not prohibited in the diet for duodenitis. The restrictions include wheat bran and fresh bread. As with gastritis, dried or toasted bread is acceptable here. Sandwiches made from white bread and low-fat cheese are allowed.
After each meal you need to replenish the water balance in the body. The patient can drink dried fruit compote, tea (green, mint, chamomile, meadowsweet, rosehip), jelly, low-fat kefir, milk, yogurt.
List of prohibited products
The diet for duodenitis prohibits the consumption of the following foods and dishes:
- factory-made sweets on a fat, biscuit and cream base, cakes, pastries, halva, any cookies, except long-lasting ones;
- salty and spicy foods, especially salted nuts, chips, crackers;
- semi-finished products: dumplings, sausages, ready-made frozen cutlets and pancakes;
- beans, lentils, chickpeas, peas;
- canned food, any homemade dressing and marinades;
- hot sauces, spices and seasonings for dishes: horseradish, ginger, mayonnaise, mustard, chili, red and black pepper, adjika, ketchup;
- sour soup dressings, tomato dishes;
- sauerkraut, lemon, vinegar (it is excluded both when adding to salads and when marinating meat or onion rings);
- salads from raw coarse vegetables (raw vegetables can only be chopped and during the period of remission);
- cold and hot smoked meat and fish (the second option is especially harmful);
- all alcoholic drinks;
- fried in oil and fatty foods.
In case of inflammation of the duodenum, all dishes and products that mechanically or chemically irritate the mucous membrane are prohibited.
Sample diet
An approximate menu for a week for inflammation of the duodenum can be compiled by combining these options.
Breakfast options:
- oatmeal with milk or water, banana, tea;
- low-fat cottage cheese with milk, toast with cheese and butter, a glass of green tea.
- rice puree, a piece of boiled meat or fish, yogurt;
- pumpkin puree with added butter, several long cookies, tea.
Afternoon snack options:
- yogurt and mashed banana;
- white bread and cheese, tea;
- cottage cheese casserole, jelly;
- apple pudding, tea;
- applesauce and bread and butter, tea.
Lunch options:
- vegetable puree soup of carrots, broccoli and onions, steamed chicken chop, thick oatmeal jelly;
- chicken breast broth soup, steamed fish, a slice of bread, dried fruit compote;
- a piece of oven-baked meat, vegetable puree, herbal tea;
- rice soup, boiled fish, sweet compote;
- vegetable casserole with sour cream, oatmeal jelly.
Dinner options:
- berry or oatmeal jelly;
- stewed vegetables, warm herbal tea;
- steamed beef cutlet and mashed apple with carrots;
- steamed lean meat, small vermicelli, tea.
As the patient recovers, he can enrich his diet menu with new dishes and products: raw vegetables, meat products, etc. It is important to do this gradually, following the same nutritional rules as the first days of the diet.
Source: https://gastrolekar.ru/duodenit/pravilnoe-pitanie.html
Diagnostics
Having looked at the statistics, we can conclude that almost 90% of people need consultation with a gastroenterologist. To make a correct diagnosis, a specialist prescribes an examination, which is divided into laboratory and instrumental diagnostics.
Laboratory methods include: studies of gastric juice, blood, urine and feces. With their help, you can determine the secretory function, bacterial composition of the gastrointestinal tract, enzyme activity and other important functions. But without instrumental methods, the analysis results are uninformative.
Instrumental methods include:
- gastroscopy or esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGDS) is a type of examination that is carried out using special equipment (gastroscope) with a flexible hose, equipped with viewing optics and a camera. Contraindications for manipulation are: heart disease, hypertension, mental disorders, severe respiratory failure. Before performing the procedure, the patient must refuse to eat food no earlier than 8 hours, and water 3 hours before, not take medications, smoke, or even brush their teeth;
- X-ray of the stomach with contrast agent. With its help, you can identify the condition of the gastric mucosa and diagnose improper functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. The procedure is contraindicated during pregnancy and lactation, intestinal obstruction, perforation of the stomach wall, or allergies to barium preparations. Before the procedure begins, the patient must take a contrast agent. A few days before the x-ray, completely abstain from legumes and dairy products; on the evening before the procedure, refrain from sweet products, raw vegetables and fruits;
- Ultrasound diagnostics or echography is a method that is based on the ability to reflect sound waves. This method is not very informative and is most often prescribed to young children. Using echography and ultrasound, you can determine the presence of tumors, ulcers, thickening of organ walls, etc.
An experienced and qualified specialist will immediately recognize a swollen and reddened mucous membrane, since normally the inner layer of the stomach should have a pale pink color and transparent mucus. If there are any deviations from this norm, then a preliminary diagnosis of hyperemia of the gastric mucosa is made.
Providing assistance with hyperemia of the gastric mucosa
If unpleasant symptoms appear in the stomach area due to hyperemia of its mucous membrane, it is necessary to contact a specialist as soon as possible to prescribe the correct treatment. But if you can’t see a doctor right away, you can temporarily use a few simple tips.
Ensure complete rest by taking a lying position. Drink a glass of clean, cool water. Take No-shpa or another antispasmodic drug. Apply a heating pad with ice to the epigastric area. Follow a strict diet by reviewing your diet.
There is an intermediate section between the stomach and intestines, which can often become infected. As a result, a disease such as duodenitis develops. This disease rarely occurs as an independent pathology; most often it occurs against the background of pancreatitis, cholecystitis, colitis, gastritis and other disorders.
Definition
The malaise is observed at least once in every tenth person and is an inflammation of the duodenal mucosa. It has no age restrictions, but is quite rare in children. Although gastroenterologists noted that duodenitis most often affects males.
Only a qualified specialist can make a correct diagnosis after a series of laboratory and instrumental studies have been carried out. Therapy directly depends on the course of the disease, but preference is given to conservative methods, which include following a gentle diet and taking medications. Surgery is required only in the most severe cases.
Causes
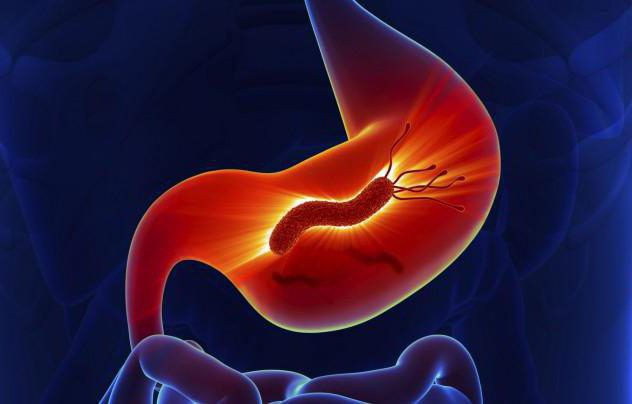
Most often, inflammation of the duodenum occurs as a concomitant disease. It usually appears against the background of another intestinal disorder, namely:
— dyspepsia – discomfort in the stomach after eating food; - cholecystitis - inflammation of the gallbladder; — acute hepatitis due to a viral infection; - peptic ulcer - damage to the lining of the small intestine and stomach; - Zollinger-Ellison syndrome - ulcerogenic pancreatic adenoma; - diarrhea - a chronic disorder; - gastritis - inflammation of the mucous membrane.
Significant stress, such as a serious infection or surgery, also contributes to the appearance of duodenitis. Non-steroidal drugs can often provoke inflammation of the duodenum.
The disease is classified according to several criteria:
1. Course of the disease:
- acute - occurs unexpectedly and does not last long, in this case all symptoms will be very acute;
- chronic - the disorder persists for a long period, most often does not manifest itself as pain syndromes, sometimes it can make itself felt with unpleasant, uncomfortable sensations.
2. Degree of damage:
- erosive – erosions and wounds appear at the base of the intestine;
- superficial - only inflammation is present.
3. Place of education:
- bulbar - the focus is located near the duodenal bulb;
- postbulbar - settles in depth.
Symptoms
In order for a person to independently diagnose that he has duodenitis, it is necessary to pay attention to certain signs:
- aching and prolonged pain in the upper abdomen, which most often occurs on an empty stomach;
- bloating and distension of the intestines;
- belching of food, usually immediately after a meal;
- nausea, sometimes vomiting mixed with bile;
- lack of appetite;
- heartburn.
If there is chronic inflammation of the duodenum, symptoms most often begin to appear after stressful situations, during an exacerbation and during errors in the diet.
Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum
Peptic ulcer disease occurs in people of any age, but more often at the age of 30-40 years; men get sick 6-7 times more often than women. The most characteristic manifestation of a peptic ulcer is pain in the upper abdomen, which often occurs on an empty stomach, i.e. between meals.
Pain may also occur at night, forcing the patient to wake up and eat. The pain usually subsides within the first 30 minutes after eating. Less specific, but common symptoms of peptic ulcer disease are nausea, heaviness after eating, a feeling of fullness in the stomach, vomiting, loss of appetite, loss of body weight, and heartburn.
Peptic ulcer is a chronic disease based on a recurrent ulcer of the stomach or duodenum. As a rule, an ulcer occurs against the background of gastritis (inflammation of the gastric mucosa) or duodenitis (inflammation of the duodenal mucosa) associated with Helicobacter pylori infection.
The patient’s main task is to adhere to the diet and carefully follow the doctor’s orders. The basis of the therapeutic diet is chemical, mechanical and thermal sparing of the affected organ. Avoid foods that increase gastric secretion (spicy, pickled, salted, fried, smoked foods, alcoholic drinks, coffee, tea, carbonated drinks, rich broths).
You should not eat very hot or cold food. Smokers are advised to stop smoking, since experts have convincingly proven that smoking not only complicates healing (extends treatment time), but also increases the risk of relapse (recurrence) of the ulcer. Also, patients with ulcers should avoid taking aspirin and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Instrumental studies

The most reliable method for diagnosing duodenitis is endoscopy. If there is superficial inflammation of the duodenum, then the monitor will show an unevenly swollen mucous membrane. Thus, it is possible to detect sharp hyperemia in the form of single spots. These zones protrude slightly above the rest of the surface.
With severe duodenitis, the mucous membrane takes on a diffusely edematous appearance. The patchy areas of hyperemia are much larger, often connecting into fields up to 2 cm in diameter. Small punctate hemorrhages are also present in such areas. The mucous membrane becomes easily wounded; a light yellow opalescent liquid and a large amount of mucus can be found in the lumen.
If there is pronounced inflammation of the duodenum, then the endoscopic picture will be even more vivid. With this disease, the phenomenon of semolina is noted. Ultrasound can lead to local pain under the sensor when pressing in the antrum, which helps differentiate unpleasant syndromes caused by the disease.
Therapy

Initially, the patient is required to adhere to a strict diet. How to remove inflammation of the duodenum? Treatment is carried out with medications taking into account the underlying cause of the disease.
1. Analgesics and enveloping agents are used for pain relief. 2. If an infection is detected, a course of antibacterial therapy will be required. 3. To reduce the acidity of gastric juice, specialized medications are needed. 4. To overcome enzyme deficiency, additional nutritional correction is needed. 5. General strengthening medications, antispasmodics and vitamins will be prescribed.
Sometimes therapy requires the use of immunocorrectors and sedatives. Physiotherapeutic methods have an excellent effect, namely magnetic therapy, electrophoresis and ozokerite, as they effectively remove inflammation of the duodenum. Symptoms and treatment of this disease may vary, so the patient is recommended to go through certain stages:
- stationary;
- outpatient;
- health resort
Then you can know for sure that all possibilities have been used to combat the disease.
Classification of the disease
There are several classifications of pathology; the manifestation of symptoms and treatment of duodenal gastritis will depend on the specified diagnostic indicators.
By degree of development:
- acute, it occurs with pronounced symptoms;
- chronic – the symptoms are erased and may not bother you until periods of exacerbation. More often they occur seasonally, or after overindulging in unhealthy foods.
Experts emphasize that the intestinal mucosa with gastritis in the chronic form is damaged more and more deeply than in the acute form.
According to the depth of tissue damage:
- superficial edematous,
- atrophic,
- erosive,
- interstitial.
By localization:
- bulbar,
- diffuse,
- local,
- postbulbar,
- papillitis
There is a specific duodenitis that occurs as a result of other diseases.
Pregnancy

During this period, treatment of duodenitis should be differentiated, comprehensive and strictly individual, and also be based on certain principles: drug therapy is carried out only at the time of exacerbation and if there is a lack of effect from following the diet, diet and antacids.
Astringent and enveloping preparations are often used (herbal origin is recommended - decoctions of St. John's wort, chamomile and yarrow flowers).
First of all, the following components are selected:
- anti-inflammatory (oak, plantain);
- antispasmodic (licorice, dill, mint, chamomile);
- antiseptic (St. John's wort, calendula);
- laxatives (rhubarb, zhoster, buckthorn).
Folk remedies

Despite the fact that most doctors now know how to treat inflammation of the duodenum using traditional methods, patients still trust centuries-old herbal complexes. The most commonly used medications are the following, which are easy to prepare:
1. Pour boiling water over 1 tsp. flaxseed, after which everything is left for 20 minutes. The prepared drink is consumed in small sips on an empty stomach. The medicine is taken for a month without interruption. 2. Chamomile, lemon balm, licorice and marshmallow root, buckthorn bark, lavender, and shepherd's purse are mixed in equal parts. Next 1 tsp. The prepared mixture is poured with a glass of boiling water and sent to a water bath. Strain and drink everything 30 minutes before eating. 3. Crush 0.5 kg of sea buckthorn and pour in 0.5 liters of sunflower oil. This composition is infused for a week in a closed container. Next, the mass is ground and taken, if inflammation of the duodenal bulb is observed, 1 tbsp. l. every day for a month. 4. An aqueous solution of St. John's wort is prepared and in moments of exacerbation, several sips are taken every day. 5. The juice is squeezed out of the leaves and stems of the large plantain, after which a little honey is added. The resulting mixture is drunk 1 tsp. before eating. 6. Rhubarb sprigs are soaked in clean and warm water, then they are applied as a compress in moments of inflammation on the stomach area.
Reviews and results
Basic Table No. 1 has been significantly expanded in terms of products and processing methods, making it varied and easily portable. It includes basic cereals, vegetables, meat, fish and dairy products. Contains the normal amount of protein and fat and can be prescribed for a long period. Reviews from patients note that dietary nutrition for duodenitis is carried out for up to 2.5 months, and then gradually expands. Everyone notes its positive effect on the gastrointestinal tract as a whole: heartburn and pain disappear, bloating and nausea go away.
- “... In case of exacerbation of duodenitis, I manage without hospitalization. I do a gastroscopy, the gastroenterologist prescribes treatment and diet. It helps me, although it causes additional trouble - you need to prepare pureed soups and steamed dishes separately. True, I only eat pureed ones for a week, and then I switch to the non-mashed diet diet. At this time I cook for everyone, and my family doesn’t mind. You can eat almost all known cereals, vegetable purees, or boiled and chopped vegetable supplements. I don’t add any spices, except for boiled twisted onions in the cutlets. Sometimes I have a desire to eat something fried and smoked, but I strictly resist for two months. I usually lose up to 4 kg on this diet”;
- “... For erosions in the duodenum, I was on this diet for 2.5 months, despite the fact that after 14 days the erosions healed. In the hospital I was on a strict pureed diet, but at home I switched to a less pureed diet and ate vegetables in the form of puree. I got used to making meat puddings and meat soufflé, cutlets for 2 days, and boiled various porridges with them. Dietary restrictions quickly affected my weight - as a result, I lost 6 kg in 2.5 months. This is understandable, since compared to the usual diet, I began to eat less in general; during this time, I began to eat less baked goods and cakes, fried foods, sweets, chocolate, and nuts. I think that we need to monitor our diet more carefully in the future - the doctor said that diet and frequent meals are important”;
- “... My frequent exacerbations of gastritis and duodenitis are associated with irregular nutrition, dry food and nerves. True, there are no severe exacerbations, so I manage without a hospital. I immediately begin treatment (it was prescribed by the doctor) and a gastric diet. I tolerate it well for the first month, but then I get tired of it. Since by this time there is nothing to worry about, all sorts of disturbances begin (smoked sausage, fried cutlets and potatoes), but little by little. I can’t eat spicy foods, spices and sauces, as pain immediately appears. Another bad thing from yeast baked goods is belching and bloating. So I gradually studied the body’s reaction and excluded them from the diet.”
Complications
Many people do not even suspect that they have inflammation of the duodenum. The symptoms of such a disease cannot always be diagnosed independently; for this reason, duodenitis is often neglected and treated late, thereby provoking the appearance of such complications:
- inflammation of the serous membrane of the organ;
- intestinal obstruction;
- extensive bleeding;
- ulcerative lesions and narrowing of the pylorus of the stomach;
- purulent inflammation of tissues;
- insufficiency of duodenal hormones.
But, despite the high probability of complications, the prognosis for duodenitis is favorable. If the disease is detected in the early stages, a complete recovery can be achieved.
There is no specific prevention as such. You just need to adhere to a healthy lifestyle, as well as promptly treat gastrointestinal disorders and follow recommendations regarding meals. Visit a gastroenterologist for preventive examinations several times a year.
Diet for gastritis and duodenal ulcers
Gastrointestinal diseases are very common among schoolchildren and older people. Gastritis and duodenal ulcers top the list in popularity among the population. The condition of patients with these diseases sometimes requires immediate intervention, as they suffer from severe pain in the epigastric region. Diet for gastritis of the duodenum is the first thing the patient should do. This will alleviate his condition and create favorable conditions for further treatment.
Diet for inflammation of the duodenum

Patients suffering from duodenitis need to adhere to the correct diet, which will promote recovery. First of all, you need to give up rough food, which injures the already damaged mucous membrane. Boiled, grated, stewed and steamed dishes are recommended for consumption.
You need to stop eating salty, spicy, sour and fried foods; marinades and smoked foods are also unacceptable. It is necessary to replace fresh baked goods with bread and crackers. Hot chocolate, alcoholic drinks, lemonade and coffee are completely contraindicated.
Enveloping and gentle foods should take precedence in the diet; these can be casseroles, porridges, purees, jelly, meatballs, cutlets, vegetable and cereal soups. It is very useful to consume low-fat fermented milk products. It is also necessary to observe the rule of fractional and regular diet. The water diet is not the least important: you need to drink at least 1.5 liters of liquid per day.
Prevention
To prevent duodenal disease from causing further complications and exacerbations, the following recommendations must be followed:
- get rid of bad habits (smoking, drugs, alcohol);
- strictly observe restrictions in medical nutrition;
- organize work and rest schedules;
- eliminate stress loads;
- promptly treat concomitant diseases;
- attend anti-relapse therapy courses.
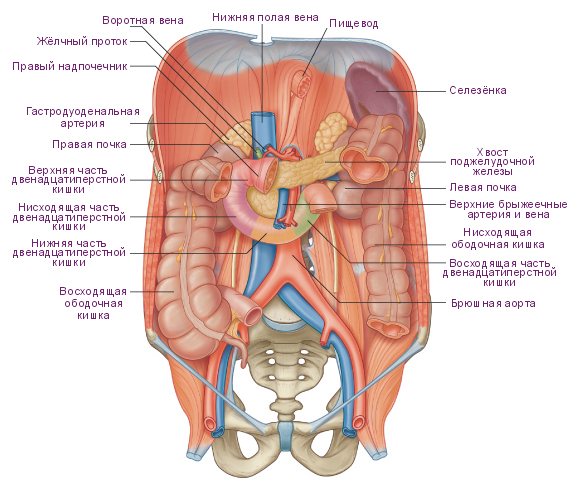
A section of the digestive tract such as the duodenal bulb has a special function.
It is located at the beginning of the organ that regulates the flow of food from the stomach into the intestines. In its shape, this bulb resembles a small sphere.
In some cases, it undergoes pathological changes: diverticulum, inflammation and deformation.
Treatment and prevention
The identified pathology requires complex therapy, selected individually and aimed at blocking symptoms, as well as restoring the motor function of the organ.
Nutrition changes. Meals are taken 4-6 times a day, in small amounts. Dishes should be easily digestible. Recommended cooking method: baking, steaming. The daily amount of fluid taken is up to 2 liters. Products containing fiber are excluded from the diet.
Fried, fatty foods, marinades, canned food, onions, garlic, hot seasonings, radishes, chocolate, alcohol, and semolina are also prohibited. Tea with sugar and dry biscuits should be consumed in small quantities.
Drug therapy consists of:
- drugs that normalize nerve conduction of cells;
- drugs that relieve spasms;
- sedatives and anticholinergic drugs.
In some situations, the patient is prescribed tranquilizers.
An effective treatment is considered to be washing the duodenum with mineral water (portion up to 350 ml) 3-4 days a day. It is recommended to perform the procedure no more than 2 times a week.
Exercise therapy and special massage help to consolidate the results obtained.
For duodenal dyskinesia, mud therapy, ozokerite therapy can be prescribed; pine and oxygen baths, acupuncture, and paraffin baths have a good effect.
After the exacerbation period is over, sanatorium treatment is recommended.
If there is no result from the use of conservative methods, surgical intervention is performed.
A healthy lifestyle is important to prevent the disease. It is necessary to adhere to a daily routine, a balanced diet, give up bad habits, try to avoid stress, adjust physical activity, and also promptly treat gastrointestinal diseases.
Intestinal spasm manifests itself as intense pain in the right upper abdomen and is accompanied by a feeling of heaviness and vomiting. Typically, such symptoms are associated with improper food intake and usually appear at night or on an empty stomach. Often the pain goes away after vomiting. Treatment of duodenal spasm is aimed primarily at relieving the pain syndrome, and only then at eliminating the main causes that caused the disease.
Therapeutic therapy for diverticulum
A diverticulum or protrusion of the wall of the duodenum mainly manifests itself at a late stage of the disease.
Patients do not immediately understand that their digestive organ, next to the stomach, is not in order, since at first the disease hardly makes itself felt.
The only thing that a person who has recently developed a duodenal diverticulum can feel is an aching pain in the abdomen that occurs periodically. However, it tends to disappear almost instantly.
But the disease in which duodenal diverticulum appears gradually progresses.
The bulging area of the tubular organ can become inflamed, causing various symptoms to appear:
- heavy bleeding from the anus;
- the appearance of blood clots in the stool;
- acute pain in the lower abdomen;
- persistent constipation or persistent diarrhea.
If a diverticulum appears in the duodenum and is affected by inflammation, then the patient’s body temperature will rise to 39 degrees.
This painful condition will be complemented by symptoms such as abdominal swelling, nausea and the constant release of gases accumulated in the intestines.
In order for these manifestations of the disease to stop disturbing and the diverticulum to disappear, the patient needs complex conservative treatment.
If the duodenal diverticulum causes complications, the patient is admitted to the hospital.
Lymphofollicular hyperplasia of the gastric and ileal mucosa
Endocrinologist of the highest category Anna Valerievna
28224
Update date: June 2020
Lymphofollicular hyperplasia (LFH) is a malignant or benign proliferation of lymphoid tissue of the mucous membrane. In most cases, lymphoid hyperplasia is caused by benign diseases.
Pathology can be detected in the organs of the endocrine system, but is more often found in the digestive tract (stomach, duodenum and ileum). The diagnosis is confirmed by histological examination of the removed lymphoid tissue.
Symptoms can vary significantly depending on the underlying disease.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=z3Tne5y7N3c
In the International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision (ICD-10), benign neoplasms of the digestive organs are designated by the code, and neoplasms of the stomach by D13.1.
What is lymphofollicular hyperplasia?
Generalized signs of lymphofollicular hyperplasia are considered to be an increase in temperature, a feeling of weakness, a quantitative increase in lymphocytes
Lymphoid hyperplasia of the gastrointestinal tract is divided into local (local) and diffuse (scattered). With local lymphoid hyperplasia of the colon, visible polyps are formed. Diffuse lymphoid hyperplasia is a scattered benign neoplasm; it is thought to be a general response of mucosal lymphoid cells to an unknown stimulus.
Nodular lymphoid hyperplasia of the duodenal bulb is characterized by multiple individual mucous nodules. The most common cause of malignant lymphofollicular hyperplasia of the intestine or stomach is extranodal B-cell lymphoma from marginal zone cells (maltoma, or MALT lymphoma).
Some studies show that maltoma is slightly more common in women than in men. No significant racial differences in disease prevalence were identified; Some studies suggest that lymphofollicular hyperplasia of the ileum is slightly more common in white people than in black people.
Classification
In medicine, benign and malignant forms of LFG are distinguished.
Less than 45% of lymphofollicular hyperplasias of the stomach are benign. In most cases, they are the result of past, long-term infection of the gastric mucosa by Helicobacter pylori.
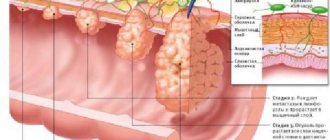
Determination of the stage of maltoma is carried out in accordance with the Ann Arbor classification adapted by the International Study Group of Extranodal Lymphomas. There are 4 main stages of maltoma development. At stages I and II, involvement of distant and nearby lymph nodes is observed. Stages III and IV are characterized by involvement of neighboring organs and tissues, as well as lymph nodes on both sides of the diaphragm.
Treatment
You should not try to cure the disease on your own; if you detect the first signals of an impending disease, you should consult a gastroenterologist for advice
Benign lymphofollicular hyperplasia does not require treatment.
If a malignant growth of gastric lymphoid tissue is diagnosed at an early stage, antibiotic therapy can help eliminate Helicobacter pylori.
Most lymphofollicular hyperplasia of the gastric antrum respond to modern treatment methods - radiotherapy and chemotherapy.
In later stages, surgery may help by removing only the affected part or the entire stomach. Complete removal of the stomach is called a gastrectomy.
Tumors that are limited to the inner layer of the stomach wall (mucosa) can be removed during gastroscopy. In this case, only part of the tumor and immediately adjacent tissue are removed.
For deep-seated tumors, part or all of the stomach, including surrounding lymph nodes, the spleen, and part of the pancreas, must be removed.
To restore the passage of food, the rest of the stomach, or the end of the esophagus, is connected to the small intestine.
Additional chemotherapy (given both before and after surgery) may improve the chances of survival for patients with locally advanced tumors that have an increased risk of recurrence.
If the tumor has spread to the abdomen (peritoneal carcinomatosis), the patient's life can be prolonged by surgical removal of the affected peritoneal membrane in combination with so-called hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy.
If the tumor cannot be completely removed, surgery is not performed. In this case, drug treatment (chemotherapy, possibly in combination with other medications) can relieve symptoms, prolong and improve quality of life.
If the stomach is severely compressed by a tumor, inserting a plastic or metal tube (called a stent) may help you eat normally.
Many patients suffer from digestive problems after surgery.
Forecast
The prognosis depends on the grade of the tumor; The 5-year survival rate for patients with early-stage indolent maltoma is 50%. In later stages, the prognosis is poor; The five-year survival rate is 25%.
Early treatment can significantly prolong the life of patients with lymphofollicular hyperplasia.
Patients are prohibited from self-medicating, since improper therapy can aggravate the disease. Traditional methods are allowed to be used only after consultation with a doctor, since some remedies can cause serious side effects and interact with chemotherapy drugs.
Source: https://limfouzel.ru/zabolevaniya/limfofollikulyarnaya-giperplaziya/
Actions to treat inflammation
A disease in which inflammation and damage to the duodenal bulb by surface defects occurs is called erosive bulbitis.
It is characterized by symptoms such as:
- painful sensations in the epigastric region, appearing an hour and a half after leaving the table and at night;
- frequent heartburn;
- belching, which causes a bitter or sour taste in the mouth due to the upward release of stomach contents;
- constipation that prevents you from going to the toilet for several days.
In addition, inflammation of the duodenal bulb manifests itself in vomiting and a constant feeling of nausea. What the patient vomits usually has a yellowish tint because it contains bile.
At the same time, when the bulb of the tubular organ below the stomach is inflamed, symptoms such as increased gas formation and a feeling that the stomach is bursting are also disturbing.
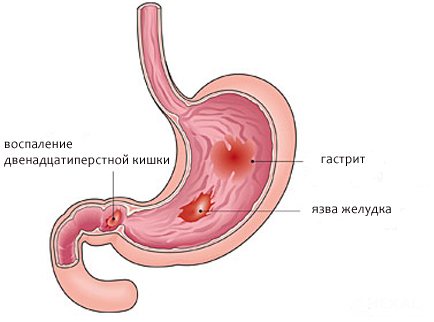
If the bulb, which is located between the stomach and intestines, is inflamed and hyperemic, then severe pain will be felt in the epigastric area.
They can radiate to the area under the left rib or spread to the area near the navel. Most often, such pain disappears or becomes less pronounced after eating a snack or drinking milk.
Vomiting can also reduce abdominal discomfort that accompanies inflammation of the bulb.
Considering the condition of the duodenum itself, we can say that during inflammation it swells and becomes filled with blood.
Due to the fact that its bulb is hyperemic, the folds of the mucous membrane of this tubular organ thicken.
All this is a natural consequence of an infection of the digestive system or an unhealthy lifestyle.
Treatment of the digestive organ that connects the stomach to the intestines is carried out using several medications.
If the duodenum is hyperemic, you will have to be treated with antacids, proton pump inhibitors, antibiotics and many other drugs.
For example, antibiotics are needed to destroy the Helicobacter bacterium, which usually causes erosion of the duodenal bulb, and antacids are needed to protect the mucous membrane of the digestive organs from the effects of hydrochloric acid.
In combination with drug therapy, treatment with folk remedies can be carried out. Inflammation will gradually subside, and erosion will be delayed if you use an infusion of oak bark.
To do this, you need to brew a teaspoon of dry ingredient with 200 ml of boiling water. The product is infused for 9 hours and taken a little before each meal.
Nutrition for inflammation of the duodenum
Diet for duodenitis is one of the elements of complex treatment. If you follow proper nutritional rules, the symptoms of the disease disappear faster and drug therapy becomes more effective.
Why do you need special nutrition for duodenitis?
With duodenitis, the mucous membrane lining the duodenum becomes inflamed. The pathological process most often begins due to irregular meals, abuse of spicy, too hot food and alcohol-containing drinks.
Removing inflammation from the mucous membrane is possible only through a healthy diet. During treatment, the patient must follow a special diet that includes sparing the duodenal mucosa. If all nutritional rules are followed, the progression of the inflammatory process stops. Gradual restoration of the mucous membrane begins.
Ignoring nutrition rules is fraught with:
- deterioration of health;
- increased symptoms of the disease;
- the occurrence of erosions and ulcers in the intestines;
- the appearance of dangerous complications - intestinal bleeding.
Types of duodenitis and required diets
Duodenitis is divided into acute and chronic. If the disease occurs in an acute form, then hunger and bed rest are indicated in the first 2 days. Subsequently, therapeutic diet No. 1 is prescribed.
Within its framework, patients are shown soups made with vegetable broths. It is allowed to add vermicelli, rice, and boiled egg to such dishes. You can improve the taste of soups with cream.
It is allowed to eat lean varieties of meat and fish.
For chronic duodenitis, it is recommended to follow diets No. 1a and No. 1b. The first is prescribed from the moment of exacerbation, and the second - during the weakening of the symptoms of the disease. Diet No. 1a is characterized by a reduced calorie content (from 1.9 thousand to 2 thousand kcal).
Food is prepared in liquid, puree or porridge form. The recommended food intake is 6-7 times a day in small portions. The diet for chronic duodenitis No. 1b is more varied and high in calories (from 2.5 thousand to 2.6 thousand kcal). Food may be prepared in liquid or porridge form.
The norm of food consumption is 5-6 times a day in small portions.
Nutrition rules
It is not enough to know what you can and cannot eat during a diet for duodenitis. It is also very important to follow nutritional rules.
Patients are advised not to overeat. You need to eat fractionally, that is, in small portions (200–300 g each). The intervals between meals should be no more than 3 hours, but not less than 2 hours. Eating too often is also harmful.
A diet for duodenitis and gastritis requires compliance with several more rules:
- Prepare food using methods such as steaming, boiling, baking. Fried foods are prohibited during the treatment period.
- Eat food warm (optimal temperature is 36–38 degrees). Hot food burns the mucous membrane, and cold food is poorly digested, causing bloating and constipation.
- Use only pureed foods. Food in this form is better digested and does not injure the inflamed mucous membrane.
- Do not overuse salt. This seasoning in large quantities enhances the secretion of digestive juice, which irritates the inflamed mucous membrane. It is allowed to add up to 8 g of salt to products.
- Avoid alcohol. Ethanol slows down the restoration of damaged mucous membranes, increases inflammation, because it provokes gastric secretion.
- Quit smoking. Cigarette smoke negatively affects not only the lungs, but also all other internal organs, including the stomach and intestines.
- Chew food thoroughly. In the oral cavity it is processed by the necessary enzymes. In addition, when chewing thoroughly, pieces of food do not enter the stomach, which could injure the inflamed mucous membrane.
It is also important to maintain a drinking regime. With a lack of fluid in the body, digestion processes slow down. The mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract is subject to additional irritation. The daily water intake is at least 1–1.5 liters.
Prohibited Products
The list of prohibited foods includes white cabbage. It should not be eaten if there are any pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract.
It is harmful in diseases due to the fact that it contains coarse fiber, which damages the inflamed mucous membrane. In patients, cabbage intensifies unpleasant symptoms.
After eating this product in its raw form, I suffer from pain and heartburn. There is a risk of bleeding and vomiting.
Coarse fiber is also found in mushrooms, so they are also prohibited for use if you have duodenitis. Mushrooms are also harmful for this disease because they are difficult for the body to digest. To break down all substances, the stomach requires large volumes of hydrochloric acid.
If you have duodenitis, you should not eat various pickles, smoked meats, and canned goods, both store-bought and home-made. Typically, these products contain many spices that are contraindicated for inflammation of the gastrointestinal mucosa.
Source: https://lift74.ru/pitanie-pri-vospalenii-dvenadcatiperstnoj-kishki/