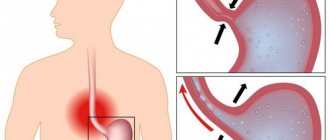
The cardia of the esophagus is its lower sphincter, the valve at the transition to the stomach. The main purpose of this physiological narrowing or muscle ring is to prevent the contents of the stomach from returning back into the esophagus. If for certain reasons the valve weakens and stops completely closing (closing), then this pathological condition is called cardia insufficiency. As a result, GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease) gradually develops.
Another variant of the pathology of the lower esophageal sphincter is achalasia. It is also called cardiospasm or megaesophagus. Occurs when there is a violation of esophageal peristalsis and its tone. Due to the fact that relaxation of the cardia does not occur at the moment of swallowing, food is untimely evacuated from the esophagus to the stomach. Doctors associate this condition with disorders of the parasympathetic nervous system, namely the Auerbach plexus.
The result of this disorder is that the esophageal valve opens only under the influence of the weight or hydrodynamic pressure of the food bolus. Because of this, the esophagus gradually expands, lengthens and becomes deformed. The mucous membrane becomes rough, and connective tissue may grow. The depth of the lesion depends on the duration of the course and the effect of achalasia on the esophageal tube.
What is cardia
The human body consists not only of organs, but also of many sphincters.
They ensure the transfer of contents from organ to organ. The role of the sphincter is played by the orbicularis muscle, the contraction of which causes narrowing and closure. In combination with vascular formations and folds of the mucous membrane, this muscle forms the sphincter apparatus. The cardia of the stomach is one of the sphincters. It functions as an inlet valve into the gastric section from the esophagus. If everything is functioning correctly, the cardiac sphincter remains closed when the person is not consuming food. During eating, the cardia opens, so food can pass into the stomach. In addition, the cardia blocks the return of food masses. This process is normal.
What is gastric cardia insufficiency? When the sphincter stops closing, the cardia is unable to prevent the internal contents, which provokes reflux. In simple words, there is a reflux of food, hydrochloric acid and gastric juice into the esophagus from the stomach.
This condition of the cardia is called chalazia. If symptoms of this disease are detected, it is recommended not to delay treatment. Useful articles on the topic - what is gastric metaplasia Treatment of cardia insufficiency
Prokinetics to increase the activity of the lower esophageal sphincter. These are Metoclopramide and Domperidone. They are prescribed 3-4 times a day before meals, sometimes the doctor may double the dose.
- Special medications to suppress reflux. Among them is “Propulsid” (“Cisapride”). Such products come in the form of tablets, suspensions and suppositories.
- Medicines to suppress heartburn. These are “Smecta”, “Gaviscon”, “Almagel”, etc.
Folk remedies for the treatment of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract have long been successfully used along with officially recognized pharmaceutical drugs. But when choosing, you should definitely consult with your doctor, who will recommend the safest and most effective recipe depending on the characteristics of the body and the stage of the disease.
To get rid of pathologies of cardiac sphincter, medicinal herbs are recognized as the most effective recipes. This is plantain juice, a decoction of calamus roots, an infusion of dandelions, etc.
Prevention
Humans are designed in such a way that preventing disease is not about them. Most often, you have to first treat the disease, and even in an advanced form, and then think about prevention. Diseases of the esophagus and the entire gastrointestinal tract are easy to prevent with the help of proper, moderate nutrition, normal drinking regimen, active lifestyle, giving up bad habits, and timely, regular medical examination. But from theory to practice in matters of such prevention there is an abyss.
I read somewhere that the fear of not having enough to eat and eating for future use is a genetically embedded fear in the subconscious of the descendants of those generations who experienced long times of famine. And, nevertheless, when it comes to health and quality of life, it is worth making an effort and gradually correcting eating behavior by reducing portions and giving up unhealthy foods. It is even more difficult to avoid frequent stress and maintain emotional calm. But these are important factors in maintaining the health of many organs and systems of the human body. This means that issues of strengthening mental health and the nervous system also need to be given constant attention.
We recommend: What is distal esophagitis, its degrees and how to treat
Non-drug treatment of the disease
If a person is diagnosed with gastric cardia insufficiency, treatment should begin as early as possible. And first of all, it will begin with the following measures:
The diet consists not only in the fact that the patient begins to eat properly at certain hours, but also in the fact that he will not overeat and eat at night. You should not lie down after eating for at least 2 hours. You need to include more pureed soups and cereals in your diet.
It is necessary to exclude from the diet foods that are irritating:
- chips;
- all products during the preparation of which chemical preservatives and flavor enhancers were added;
- tea (strong);
- coffee;
- fatty and fried foods;
- tangerines, grapefruits;
- food containing a large amount of spices, salt, spices, as well as all smoked foods;
- homemade pickles and marinades.
You should have dinner approximately 3 hours before bedtime. It is not allowed to eat immediately before going to bed.
Other restrictions in the patient’s life are also shown:
- you need to give up clothes that squeeze your stomach;
- for the same reason, it is necessary to limit the wearing of tight belts;
- you need to sleep on a bed with a raised headboard;
- you don’t need to bend down often and you shouldn’t work very long and hard;
- if a person’s activity involves the need to work hard and often bend over, then it is advisable for him to change jobs.
Insufficiency of the lower esophageal sphincter - achalasia cardia
Do you suffer endlessly from heartburn and belching? Do you have a bitter taste and unpleasant odor in your mouth? It is necessary to immediately consult a doctor; this may be achalasia of the esophageal cardia. The first mention of pathology can be found in medical works in 1672. However, to this day the exact cause of the disease has not been clarified.
Terminology
Achalasia cardia is a disease of neuromuscular etiology and belongs to the chronic form. The disease is characterized by the absence or partial opening of the cardia when swallowing food. Against this background, the patency of the esophagus is disrupted, and chaotic contraction of the smooth muscles of almost all parts of the esophagus develops.
The cardia is a valve, or, in other words, the sphincter of the esophagus. The location of this organ is on the border between the esophagus and the stomach. The main purpose of the sphincter is to regulate food and feces as they move between parts of the body.
If the functioning of the valve is disrupted, then this pathology is called cardia insufficiency, or reflux.
Development mechanism
When the disease occurs, the lower esophageal sphincter stops relaxing during meals. If pressure on the inferior valve increases, the valve narrows further and the esophagus re-expands. As a result, undigested food accumulates.
Most often, the disease develops against the background of pathological changes in the nerve cells located between the walls of the esophagus and the muscle layers.
The development of malignant neoplasms and diabetes mellitus can also cause the disease.
A possible cause may be dystrophic changes in both muscle fibers and the plexuses of the esophagus, or Chagas syndrome after bedbug bites.
The pathology of achalasia cardia develops quite slowly. The diagnosis can only be made by X-ray examination or endoscopy.
Causes
Gastric cardia insufficiency can occur in any person and at any age. And most often it is not even possible to establish the exact cause of the pathology. And some factors that lead to illness cannot be eliminated from your life. However, there is a certain list of factors that most often lead to achalasia cardia:
- alcohol and tobacco abuse;
- food with a lot of salt;
- excess weight, especially against the backdrop of a sedentary lifestyle;
- irregular meals, snacks before bedtime and “heavy” foods;
- some medicines;
- nervous shocks;
- very rarely the disease can develop during pregnancy.
Diseases that can cause the development of achalasia cardia:
- attacks of suffocation and disturbances in metabolic processes;
- obesity;
- anatomical abnormalities;
- prostration;
- chronic gastrointestinal diseases;
- problems with connective tissues.
Stages
Today, there are several stages of pathology development:
- Stage 1. Temporary decrease in sphincter tone, no expansion of the lumen yet.
- Stage 2. The condition is almost the same as at stage 1, but a mild degree of dilatation is gradually developing.
- Stage 3. At this stage of the disease, a stable expansion of the esophagus is already observed with simultaneous suprawall narrowing of the lower part of the esophagus. Scar changes form.
- Stage 4. Achalasia of the cardia at this stage progresses, complicated by fibrous mediastinitis, esophagitis or periesophagitis.
Individual signs
If gastric cardia insufficiency is diagnosed, doctors distinguish several syndromes:
- Dysphagia syndrome. Clinical manifestations in this case are as follows: a feeling as if there is a “lump” in the chest;
- hard to swallow;
- The patient constantly chokes while eating.
It is easier for the patient to eat solid than liquid food. This is due to the fact that solid foods put a lot of pressure on the pyloric sphincter and promote its opening. Simply put, there is a violation of the passage of food. These symptoms are very important for a correct diagnosis; for example, in the presence of cancer or stenosis, the clinical picture is the opposite, and it is difficult for the patient to eat solid food.
If the cardiac sphincter loses its functionality, then in addition to the syndromes described above, the patient also experiences other symptoms:
- unpleasant odor from the mouth due to changes in the diameter of the valve and the constant retention of food particles in the esophagus. Over time, this can cause erosions and ulcers on the mucous membrane;
- heartburn, the patient feels that the pain is burning and moves from bottom to top;
- some patients even feel how food moves through a valve that does not close, leaving behind a sour taste;
- belching with a sour taste;
- excessive salivation;
- hoarseness in the throat;
- problems with teeth and gums, caries;
- increased heart rate.
This pathology is a progressive condition, so exhaustion and deterioration are increasing.
Possible complications
Most often, if sphincter insufficiency is present, gastroesophageal reflux and esophageal stricture subsequently develop.
Lack of treatment can lead to the development of cancer, the statistics in this case are disappointing - from 2% to 7%.
It is also possible as a complication the appearance of megaesophagus, that is, a dramatic increase in the width of the size of the esophagus. This diagnosis is made in approximately 20% of patients.
Interesting! Chronic reflux esophagitis grade A - Barrett's esophagus
Diagnosis methods
The main goal of diagnosis is not only to confirm or refute cardiac spasm, but also to exclude the presence of cancer in the stomach.
As a rule, laboratory tests do not provide any information at all, which is why they are used to determine concomitant pathology.
To determine how the upper and lower esophageal sphincters work, first of all, X-ray examination is used.
Diagnosis is carried out with a barium element, which is injected into the stomach on an empty stomach to determine whether the lower valve is closed, which is typical for this type of pathology. The shape of the esophagus may take on something similar to a "bird's beak".
The lower esophageal sphincter is usually unchanged in size, and fluid accumulation can be seen above it. At an advanced stage, the esophagus takes on an S-shape.
To clarify the diagnosis of esophageal achalasia and identify the degree of damage to the mucous membrane, and to refute or confirm cancer, esophagoscopy is used. This study is also a preparatory stage in preparation for surgery.
Manometry is designed to assess the degree of contractile activity and the development of achalasia of the cardia, the work of peristalsis.
Treatment
To reduce the severity of symptoms and eliminate any obstacles that may occur during the passage of food, 3 treatment methods are used:
- treatment with pharmaceuticals;
- non-drug therapy;
- surgical intervention.
Conservative
The main criterion for the effectiveness of drug treatment is the elimination of symptoms. To determine the effect experimentally, an X-ray examination is carried out with parallel administration of barium. If barium suspensions pass normally through the esophagus, then the treatment has helped.
The following are used in therapy:
- nitrates and calcium channel blockers, which reduce lower esophageal sphincter pressure;
- sedatives.
Psychotherapy is usually recommended to patients along with medications.
Non-drug and surgical
The effect of such treatment is possible mainly in the first stage of the disease. In this case, diet therapy is used, which requires eating in small portions, chewing food thoroughly. After a meal, be sure to drink water, which should wash away food debris from the esophagus. Food should be cooked gently and be neutral in temperature.
Pneumatic cardiodilation for esophageal achalasia consists of dilation of the inferior valve while simultaneously delivering air or fluid under high pressure.
In practice, it looks like this: a balloon is inserted into the esophagus under fluoroscopic control. Once the balloon reaches the diaphragm, it is inflated.
The treatment method is effective in 75% of cases, but there is a high risk of a side effect in the form of GERD.
Endoscopic cardiodilation is recommended for significant curvature of the esophagus. However, the technique also has a side effect - gastric perforation, which occurs in 5% of cases.
If the patient is not recommended for expansion of the esophageal valve, surgery, or the patient is elderly, then chemical denervation is performed. The effect is achieved in approximately 80% of cases and can last up to 12 months. The essence of the technique is that ethanolamine oleate or botulinum toxin is injected into the esophageal sphincter using an endoscopic needle.
Cardiomyatomy is used if previous procedures to widen the valve have not helped. But there is a huge risk that reflux or strictures will appear - this happens in 15% of cases.
The essence of the technique is that after the introduction of anesthesia, local or general, a gradual expansion of the passage is carried out with cylinders of different diameters. The procedure is short-term, no more than 2 minutes.
Between procedures (on average 5-6 will be required) a minimum of 4 days should pass.
Interesting! Victory over ulcers and GERD with the help of the medicine Losek ????
The pathology of gastric cardia insufficiency can be treated using partial fundoplication. The procedure is also recommended for cicatricial changes on the walls of the esophagus.
Treatment consists of cutting the membrane near the junction from the stomach to the esophagus. After cutting, the edges of the incision are sutured to the fundus of the stomach.
The operation requires a recovery period of about 14 days, which will most likely have to be spent in the hospital, but in any case without going to work.
Good results can be achieved by using natural remedies. You can prepare a decoction of anise and fennel, which perfectly relieve inflammatory processes occurring on the mucous membrane.
To get rid of heartburn and pain, you can use raspberry leaves or make chamomile or mint tea.
However, it should be remembered that before using folk remedies, it is better to consult a doctor so that he can help you select doses taking into account damage to the mucous membrane.
If none of the recommended and carried out methods produces results, then an operation is performed to remove the esophagus.
Methods for strengthening the lower valve
As a rule, patients are offered all treatment methods. In our country, alternative methods of strengthening the sphincter are not widely used, although world practice proves their high effectiveness.
There are breathing exercises for gastric cardia insufficiency that allow you to get rid of symptoms in the first stages of achalasia. Therapeutic exercises must be carried out on an empty stomach, using abdominal and chest breathing.
Restoration of the sphincter can be carried out with the help of physical therapy. Treatment is best carried out against the background of conservative therapy, even in the acute period. Electrophoresis and DDT are usually used. Naturally, it won’t work directly on the valve, but the phrenic nerve is stimulated with current. The procedures are carried out about 10 times, every other day.
The electrophoresis method is similar, but medications are applied to the cuff with electrodes. The therapy allows for improved blood supply and healing occurs much faster. Some patients note a slight decrease in pain.
Forecast
If the disease is at stage 1, then the prognosis is quite favorable. Especially if the patient strictly follows the doctor’s recommendations. Physiotherapy and breathing exercises will help restore the sphincter.
The second and third stages are no longer the best prognosis for the patient’s recovery. Most often it is not possible to do without surgical intervention. Patients at this stage after treatment will have to be regularly examined to avoid exacerbations.
If left untreated, esophageal achalasia leads to carcinoma in approximately 5% of cases, and aspiration pneumonia occurs in 10% of cases. Patients will have to give up irregular meals and heavy physical work.
Source: https://KogdaIzzhoga.com/gerb/ahalaziya-kardii
Causes and risk factors
Insufficiency of the gastric cardia can occur for a variety of reasons against the background of:
- poor nutrition, overeating;
- excess weight;
- gastritis or ulcerative lesions of the stomach and intestines;
- insufficient physical activity;
- pyloric spasms;
- increased pressure in the abdominal cavity, which is associated with pregnancy or ascites;
- increased intragastric pressure;
- surgical intervention on the sphincter area;
- heavy physical labor;
- grasping hernia (hiatal hernia);
- sedentary lifestyle.
Causes of the disease: organic factors
There are many reasons for the occurrence of cardiac insufficiency. It is customary to divide them into two large groups:
- organic causes;
- functional reasons.
Organic factors in the occurrence of the disease are those phenomena that are not directly related to disruption of the muscle ring. Organic factors cause negative operating conditions for the gastric valve, which is the impetus for their disruption. They are:
- compression deficiency resulting from improper diet, as a result of overeating or infrequent consumption of food, but in large portions;
- complete lack of physical activity;
- formation of a diaphragmatic hernia;
- the presence of chronic diseases of the digestive system such as gastritis, pancreatitis, etc.;
- consumption of food before going to bed in large quantities;
- excess weight.
In addition, an inflammatory disease of the walls of the esophagus - esophagitis - can provoke the appearance of cardiac sphincter. Cardia failure will develop as the underlying disease progresses.
But there is an important nuance. It is worth understanding that any disease of the digestive system can provoke cardia insufficiency: atrophic gastritis, ulcers, pancreatitis, etc.
The group of functional causes includes those factors that are directly related to disruption of the sphincter. These include:
- a significant increase in pressure inside the abdominal cavity;
- significant increase in pressure in the stomach;
- spasms of the valve connecting the stomach and duodenum.
In addition, the appearance and development of gastric cardia insufficiency may be associated with surgical interventions. For example, the operation intentionally or unintentionally affected this area.
Functions
The functional responsibilities of the stomach are quite numerous. The main ones among them are the following:
- Preservation of eaten food.
- Control of gastric juice production.
- Carrying out chemical processing of food.
- Promotion of food and timely cleansing of organ contents.
- Most of the absorption of various nutrients occurs in the stomach.
- Bactericidal effect.
- Protection from harmful effects.

During the digestive process, all residual metabolic products are eliminated. This also applies to substances that negatively affect the functioning of the endocrine glands.
Few people know where the cardiac part of the stomach is located.
Symptoms
The intensity of the symptoms of the disease directly depends on the degree of the disease. The symptoms manifest themselves most clearly at stage 3 of cardia failure. However, there are symptoms and signs, the manifestation of which makes it possible to diagnose the disease at the very beginning, in the early stages:
- weakness and frequent dizziness that appear after a period of vigorous activity or physical exertion;
- heartburn that appears regardless of food intake (considered by experts to be one of the main symptoms);
- burping is also one of the main signs;
- frequent attacks of nausea and vomiting (with the release of large amounts of bile);
- chest pain;
- rumbling;
- pain predominantly in the epigastric region.
As the disease progresses, the intensity of symptoms increases. Belching may include stomach contents. Often it is constant belching and heartburn that is a reason to suspect the presence of insufficiency of the gastric cardia.
Cardia failure - what is it? Symptoms and treatment of stomach disease
- September 23, 2018
- Gastroenterology
- Evdokimova Irina
The human digestive system is a complex multifunctional device. The work of all organs of the gastrointestinal tract is harmonious and interconnected.
Disruption of the functioning of one of the sections of digestion causes disruptions in the entire system. Many gastric diseases are not associated with either infection or tumor; these pathologies are caused exclusively by functional abnormalities.
One of these ailments is cardia insufficiency; what it is will be discussed further.
Symptoms
If the work of the cardiac sphincter is rarely disrupted, it is almost not accompanied by unpleasant symptoms. The severity of the patient’s condition depends on the causes of the pathology and the characteristics of its course. Typically, obvious signs appear only at stage 2, gradually worsening.
Attention: prolonged cardia failure always leads to damage to the esophageal mucosa. The condition of the stomach and the entire digestive system also worsens.
The development of this pathology is often indicated by the following symptoms:
- frequent belching of air or even undigested food;
- heartburn not associated with food intake;
- pain and discomfort in the stomach;
- burning sensation and pain in the esophagus or behind the sternum;
- nausea, vomiting, often mixed with bile;
- bloating, flatulence;
- weakness, decreased performance;
- headaches, dizziness;
- chronic cough, often developing into asthmatic bronchitis.
The main symptom of the pathology is frequent belching or heartburn
Each person has individual manifestations of the disease; they may not occur all at once, but only some. But the malaise usually worsens due to overeating, when taking a horizontal position or after physical activity. Moreover, the consumption of certain foods leads to a deterioration of the condition only in cases where the pathology is associated with stomach diseases.
Gastric cardia insufficiency: how to cure
Achalasia cardia is a disease of neuromuscular etiology and belongs to the chronic form.
The disease is characterized by the absence or partial opening of the cardia when swallowing food. Against this background, the patency of the esophagus is disrupted, and chaotic contraction of the smooth muscles of almost all parts of the esophagus develops. The cardia is a valve, or, in other words, the sphincter of the esophagus. The location of this organ is on the border between the esophagus and the stomach. The main purpose of the sphincter is to regulate food and feces as they move between parts of the body.
If the functioning of the valve is disrupted, then this pathology is called cardia insufficiency, or reflux.
Diagnosis of cardia failure
The disease is diagnosed based on the results of an X-ray of the stomach. Esophagoscopy will help determine the stage of the disease. The methylene blue test determines the presence of reflux esophagitis in cardiac insufficiency. What it is? During an endoscopic examination, a dye is injected into the patient's stomach. The substance colors only healthy areas; inflamed areas do not change color.
In addition, additional studies are prescribed:
- stomach acid test;
- ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs;
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy.
Based on all the studies, the doctor makes a diagnosis of “cardia insufficiency.” How to treat this pathology depends on the cause and stage of the disease.
To diagnose cardia deficiency, you need:
- X-ray of the upper part of the digestive system;
- endoscopy (examination of the inside of the esophagus);
- daily ambulatory pH-metry of the esophagus (test to determine the amount of acid in the esophagus);
- gastrofibroscopy (determines pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract);
- biopsy followed by histological examination;
- fibrogastroduadenoscopy (FGDS) - examination of the gastric mucosa.
Based on all the studies, the doctor makes a diagnosis of “cardia insufficiency.” How to treat this pathology depends on the cause and stage of the disease.
To establish the diagnosis and form of cardia disorder, it is necessary to obtain a conclusion from a gastroenterologist. At the appointment, gastric palpation is performed to determine the location of the pain. The following studies are prescribed:
- examination of the esophagus and stomach area, taking into account contraindications for the patient (FGDS, X-ray, CT, MRI);
- tests - gastroenterology package;
- Ultrasound examination of OBP.
Etiology
Cardiac failure is a polyetiological disease. There are many provoking factors that can cause this state of cardia. In some cases, valve failure occurs due to a complex of reasons.
- the presence of spasms in the pylorus;
- unhealthy diet, overeating;
- adynamia, swelling or high intra-abdominal pressure;
- overweight;
- hiatal hernia, chronic gastrointestinal diseases;
- eating too much before bed;
- operations associated with resection of the cardia.
- the presence of spasms in the pylorus;
- unhealthy diet, overeating;
- adynamia, swelling or high intra-abdominal pressure;
- overweight;
- hiatal hernia, chronic gastrointestinal diseases;
- eating too much before bed;
- operations associated with resection of the cardia.
Pathology can manifest itself even in those people who do not have stomach problems. The risk group includes people over thirty-five years of age. With age, the disease manifests itself more intensely. This is explained by atrophy of the abdominal muscles and low physical activity. According to medical data, stomach problems are less likely to occur in people with developed muscles and a toned abdomen. Malfunction of the sphincter can occur during pregnancy, which is explained by the location of the internal organs.
Pathology can manifest itself even in those people who do not have stomach problems. The risk group includes people over thirty-five years of age. With age, the disease manifests itself more intensely. This is explained by atrophy of the abdominal muscles and low motor activity.
According to medical data, stomach problems are less likely to occur in people with developed muscles and a toned stomach. Malfunction of the sphincter can occur during pregnancy, which is explained by the location of the internal organs. Useful articles on the topic - the etiology of gastric reflux.
Structural features
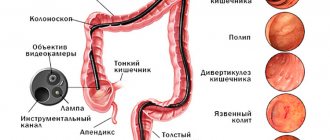
The esophagus has 2 valves:
- the lower one, connecting the esophagus and the section of the stomach located below, is also called cardiac;
- The pyloric sphincter of the stomach is also called the pylorus, which separates the duodenum and the pyloric region.
The fibers form the sphincter. When the muscles contract, the opening in the sphincter area closes (reduces in diameter). The organ has two sphincters:
- Pyloric sphincter or pylorus (superior). Separates the pyloric region of the stomach from the duodenum. Its functions include regulating the flow of stomach contents into the duodenum.
- Decreased tone. This pathology is characterized by the reflux of food particles or stomach contents into the upper esophageal region, sometimes into the pharynx. The socket begins to close insufficiently. Such disturbances in the functioning of the cardia can affect the lower esophageal sphincter or both sphincters simultaneously. Sometimes non-closure (when the sphincter does not close completely) and pressure provoke vomiting and nausea.
If the functioning of the cardia rosette is disrupted (insufficient), the esophageal sphincter does not completely close (does not close). During non-closure, gastric secretions, gastric enzymes, and food particles penetrate the esophagus, causing irritation, erosions, and ulcers. In medicine, the following main types of sphincter disorders are distinguished:
Symptoms
- Odor from the mouth.
Changes in the diameter of the esophageal sphincters provoke the appearance of such a symptom. This is due to a number of pathogenetic reasons, including the accumulation of food particles and gastric contents in the esophagus. If the upper and lower esophageal sphincter do not function correctly, the ingress of gastric contents can cause inflammation of the membranes, the formation of erosions, and various infections. - Painful sensations.
Pain can appear due to various disorders of the sphincters. Sometimes pain develops when swallowing; at rest, such sensations may be absent. The development of the symptom is triggered by irritation and damage to the membrane due to the regular ingestion of gastric contents. - gastrofibroscopy is considered the most informative type of research, as it allows for visualization of pathologies;
If suspicious signs appear, the patient should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
If necessary, the specialist will refer the patient for further examination. To examine patients suffering from this pathology, it is customary to use the following diagnostic methods:
Cardia insufficiency can be cured using several methods:
Source: https://gp195.ru/sustavy-drugoe/uprazhneniya-pri-nedostatochnosti-kardii-zheludka.html
Symptoms of pathology
Gastric cardia insufficiency is 95% an acquired disease and only 5% is a congenital defect. Valve non-closing has 3 degrees of violation:
Cardiac insufficiency of the 2nd degree can be cured comprehensively, but non-closure of the valve of the 3rd degree must be treated with surgery. Echosigns are poorly defined and resemble reflux esophagitis in nature. Valve deficiency is determined by the main symptoms:
PAY ATTENTION! Do not prolong gastritis or an ulcer until stomach cancer, it is better to be on the safe side, but this will be necessary. read the story of Galina Savina >>
- belching of air or acid;
- heartburn in the esophagus, throat and stomach;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- multiple stomatitis;
- vomiting bile;
- pain, bloating, distension behind the sternum;
- lump in throat;
- heavy salivation;
- weakness.
Operation methods
Treatment of polyposis involves surgical removal. There are several methods of performing the operation:

Compliance with diet and nutrition
Already at the first stage of the development of the problem, there is an urgent need to correct the nutrition system. Initially, the correct regimen is established - food is taken several times a day (4-5), in small portions. At the same time, meal times every day should coincide as much as possible. After the next meal, lying down is prohibited for 2 hours.
It is also important to remove the factor of mucosal irritation, that is, all foods that can provoke it are excluded from the diet. This is too hot or cold food, fried, spicy, smoked, highly salted, coarse, seasonings, alcoholic drinks, coffee, chocolate, etc.
The basis of the diet should be soups and delicate foods, steamed, boiled or baked. Before eating anything, the patient needs to drink a glass of clean water. The emphasis is on plant foods (vegetables and fruits). The last meal should be at least a couple of hours before bedtime.
Treatment and prevention
Sanatorium treatment brings good results
Treatment can go in several directions. First of all, it is necessary to treat the underlying disease that led to the pathology. It is advisable to follow a diet and engage in weight loss if you are obese. If the cause was ascites, one should try to reduce intra-abdominal pressure.
At the first stage, it needs properly organized nutrition. You need to eat regularly, several times a day. One portion should be small in volume. You need to eat according to a schedule; meal times should coincide from day to day. After eating, it is forbidden to lie down for two hours. Walking and sitting are allowed.
The diet is built preferably from soups, semi-liquid porridges, and homogenized products. In order not to further irritate the esophageal mucosa, exclude from food all foods that can have a thermal or chemically aggressive effect on the esophagus. Rough food is also not taken, so as not to mechanically damage the inflamed mucous membrane.
Cold and hot are completely prohibited. Before meals, drink plain water. Then you need to try to focus on vegetables and fruits in your diet. Chocolate is prohibited, you cannot drink alcohol, eat fried, fatty, pickled, salted, smoked foods. Seasonings are also excluded.
Have dinner at least 3 hours before bedtime. Even better if in 4 hours. Correction of the condition consists of following certain rules of behavior:
- do not wear tight, tight clothes;
- belts and belts are not tightened tightly;
- you need to bend down less often;
- physical activity is limited;
- sleep in an elevated position (so that the head and upper half of the body are higher than the lower part);
- if the work is physically difficult, chemically hazardous, or involves bending, it needs to be changed.
Heartburn as one of the symptoms of cardia insufficiency
The motor activity of the lower esophageal sphincter is regulated with the help of medications. Domperidone and metoclopramide show high effectiveness in correcting this condition. Preparations with the active ingredient metoclopramide:
- Cerucal;
- Raglan;
- Bimaral;
- Dimetpramide.
Read: What to eat when your stomach hurts: prohibited and permitted foods
These drugs are taken three times a day. Dose – 10 mg. In severe cases, take four times a day. If the drug is administered intramuscularly, the dose is 2 ml. 2 ml are also administered intravenously, this is done 2 times a day.
Domperidone has its own application characteristics. The standard dose is 0.01 g. Frequency is three times a day. Take it before meals; if the condition is severe, the dose is doubled.
Propulsid (cisapride) is a drug used to regulate gastroesophageal reflux. The dose of the drug is from 5 mg to 10 mg. Take it twice or three times a day. There is a form of suppositories that is also relevant for treating the disease. In this case, a dose of 30 mg per day is needed. It can be combined with other methods and methods of treatment. You can only take this remedy.
Treatment must be started promptly. This disease is very insidious. Severe consequences occur in the body, expressed in peptic ulcers, gastroesophageal bleeding.
Video material for the most curious - achalasia cardia:
Read along with this article:
- Insufficiency of the esophageal cardia: symptoms, diagnosis,…
- Sliding hiatal hernia: treatment and…
- Lower esophageal sphincter, or cardia of the stomach
- Pyloric stenosis - pyloric stenosis, symptoms of the disease
- Classification, treatment and symptoms of hiatal hernia. Types of therapy
- How to treat reflux esophagitis: drug treatment and…
- What does a symptom such as esophageal spasm indicate?
- Ranitidine, features of the drug use
- Is a sour taste in the mouth always a warning sign?
Degrees
There are 3 degrees of sphincter non-closure:
- 1st degree – the amount of incomplete closure of the cardia is about 1/3 of the diameter of the esophagus;
- 2nd degree – non-closure increases to half the diameter of the esophagus;
- Stage 3 – the valve stops closing completely.
As valve insufficiency develops and intensifies, the symptoms of GERD increase, esophagitis appears, and a serious complication may follow - degeneration of the esophageal mucosa: Barrett's esophagus.
The intensity of the symptoms of the disease increases as the functioning of the sphincter worsens. There are 3 degrees of cardia insufficiency, each of which has its own clinical signs and manifestations.
There are three degrees of the disease:
- I – has a functional character. Disturbances in the functioning of the valve are observed periodically, but changes in the mucous tube of the esophagus, as well as other morphological changes, are absent.
- II - the valve of the upper gastric section stops closing, closing its diameter only by half, as a result of which folds of the mucous membrane of the esophagus may fall out into the stomach.
- III – characterized by a complete cessation of the process of closing the walls of the sphincter. At this stage of the disease, gastric peristalsis is preserved, and the presence of pronounced inflammatory and erosive changes is noted in its mucous membrane.
How is the diagnosis done?
Usually the disease is diagnosed using endoscopic examination. In addition, X-ray examination may be used
Typically there are 3 degrees of deficiency:
- First degree. It is diagnosed if there is incomplete compression of the radius. In this case, the gaping of the esophagus is 1/3 during deep breathing. The patient has frequent belching of air;
- Second degree. This diagnosis is made if the cardia closes even worse. The gap of the esophagus is already ½ of its diameter. This is measured at the moment of deep breathing;
- Third degree. It is diagnosed when, during deep breathing, the cardia does not close at all. Again, there is frequent belching of air.
Disease severity
The stage of cardiac failure is established through instrumental diagnostics. According to the gastroentnrological classification, there are three stages of failure of the cardiac sphincter, and three forms of abnormal peristalsis (gastrointestinal motility).
Stages of valve dysfunction:
- Stage I – partial closure of the valve. The pulp closes partially (2/3 of the healthy state of the organ). Symptoms appear after eating or smoking.
- Stage II - The cardiac opening of the stomach closes only halfway. The gastric mucosa forms folds and moves towards the esophagus (prolapse is formed).
- Stage III - the cardiac sphincter ceases to function. Due to the constant aggression of acid, inflammation of the esophageal mucosa (esophagitis) develops.
Forms of peristalsis:
- hypermotility - intense functioning, not justified by the digestive load;
- hypomotility – decreased motor skills by half;
- amotility – lack of contractions to move food.
Determining the staging is necessary to select the correct treatment tactics and medications.
Photo gallery of prohibited products

Dishes with lots of spices

Smoked meats

Alcohol

Spicy dishes

Chocolate

Foods high in preservatives

Fried foods

Coffee
Photo gallery of drugs

Metoclopramide

Raglan

Cerucal
Diet price
Meals include regular foods, but increased protein content in the form of dairy dishes and cottage cheese, meat and fish should also be present daily. The estimated cost of weekly meals can range from 1400-1500 rubles.
The disease does not appear on its own. Gastric cardia insufficiency is a consequence of other disorders of the human digestive system. It is against the background of these diseases that this disease appears. Treatment of cardial insufficiency is aimed at eliminating the underlying disease, which served as a kind of impetus for the occurrence of cardiac sphincter.
Treatment is based on the principles of healthy nutrition. It is worth considering that if you are overweight, your doctor recommends trying to lose it.
The diet prescribed by a specialist includes fractional meals in small portions. It is not recommended to take a horizontal position for two to three hours. The best option would be a walk or minimal physical activity.
The diet must include:
- soups;
- semi-liquid cereals;
- vegetables;
- fruits.
It is strictly prohibited to consume foods that can cause irritation to the esophagus. It is necessary to exclude from the diet sweets, flour, smoked and semi-finished products, fried and fatty foods, marinades, and too hot seasonings (it is better to exclude them completely). Food should only be consumed warm. And immediately before eating you need to drink 200 ml (a glass) of water at room temperature. It is not recommended to drink tap water.
In addition, it is strictly prohibited:
- wear tight clothing that restricts movement and puts pressure on the abdominal cavity;
- bend over frequently and engage in heavy physical activity;
- lift weights.
In addition, experts recommend sleeping with the head of the bed slightly elevated.
Superficial gastritis: symptoms and treatment, diet
» Gastritis » Superficial gastritis: symptoms and treatment, diet
Superficial gastritis of the stomach is a “failure” in the human immune system. Insufficient attention to one's diet, frequent snacking, lack of hot liquid food, and hunger strikes are the main reasons for the development of gastritis in humans.
Superficial gastritis is considered a hereditary predisposition to the occurrence of the disease. So, what is it, how to treat it and what the consequences may be.
Causes of superficial gastritis
Superficial inflammation of the stomach walls is caused by concomitant pathologies:
- Anemia that impairs blood circulation.
- Initial superficial gastritis, cardia failure, if observed.
- Problems with the endocrine system (thyrotoxicosis, diabetes).
- Poisoning of an endogenous nature can be caused by problems in the kidneys.
- Infectious advanced diseases.
- Weak gastrointestinal valve apparatus.
- Frequent stress and strong feelings.
Children most often suffer from gastritis due to the irritant Helicobacter pylori, which was passed on from adults, as well as due to a disrupted nutritional system, especially for schoolchildren.
Food poisoning and poisoning, salmonella infection, rotaviruses, the presence of dysentery bacillus, and helminthic infestations can affect intestinal function.
Types of superficial gastritis
They are distinguished by distribution:
- focal superficial gastritis. Inflammation begins in individual areas of the gastric mucosa;
- diffuse superficial gastritis affects the entire lining or the entire area of the stomach.
According to localization, superficial gastritis is:
- superficial antrum gastritis;
- gastritis of the gastric body;
- gastritis of the gastric fundus;
- pangastritis, which affects only the surface of the organ.
Most often, gastritis is a primary inflammation, but can often exhibit secondary symptoms, depending on the pathologies of the body.
Also, superficial gastritis can show itself as reflux gastritis in case of impaired gastrointestinal tract functions - reflux of intestinal contents into the stomach.
Superficial gastritis has a complicated type - erosive, defects in the form of small ulcers form on the surface of the mucous membrane.
Healing occurs without scarring of connective tissue.
Symptoms of superficial gastritis
The causes of the disease can be various irritants. Remission lasts quite a long time.
The most common signs:
- In the epigastrium there is pressure, distension, burning;
- Pain is felt after eating, most often of the aching type;
- "Hungry" sensations;
- After eating junk food, heartburn appears;
- Decreased appetite, resulting in weight loss;
- Rotten taste from the mouth, unpleasant aroma;
- Pain on palpation.
At the stage of superficial inflammation of the stomach wall, individual signs of an increase or decrease in the acidity of gastric secretions appear.
At a young age, an increase in acidity is more common, which periodically leads to acute pain, sour belching, bowel problems (constipation, diarrhea), and dull pain in the epigastrium at night.
Gastritis with low acidity can turn into an atrophic form in a short time; this is typical from the age of 40 years.
With this form, there is poor appetite, weight loss, alternating constipation and diarrhea, and unpleasant belching.
Diagnosis of inflammation
Fibrogastroduodenoscopy (FGDS) is today the main method for diagnosing superficial gastritis. This check allows you to visually assess the condition of the mucous membrane of the stomach, esophagus, and duodenum as accurately as possible.
To demonstrate the presence of defects, differential diagnosis with a gastric ulcer is carried out. FGDS allows us to exclude oncopathology. Fibrogastroduodenoscopy makes it possible to take a small area of an organ for examination.
Diagnosis is carried out using a probe with a fiber optic cable, which is inserted through the esophagus. The process is unpleasant, but has no equal in terms of information content.
In addition to the above method for diagnosing the presence of superficial gastritis, there are a number of separate tests:
- Stool examination helps determine the level of acidity in the stomach; undigested particles, namely their quantity, determine the functionality of the intestinal tract. The analysis also excludes gastric bleeding and prevents helminthic infestation;
- Blood test (clinical) evaluates the level of red blood cells, hemoglobin, leukocytes, identifies and prevents signs of inflammation;
- Protein fractions of blood determine the functioning of a number of organs. Diagnostics allows you to prescribe other tests to identify Giardia and Trichomonas protozoa.
Clinical picture
- Painful shock (syndrome).
The cause of mucosal inflammation depends on the nature and intensity of the accompanying pain. There may not be any sensations. Frequent “hungry” cramping pains, as well as aching sensations. The pain appears after eating and lasts up to several hours. - Dyspeptic disorders: heaviness in the area, stomach belching, heartburn, vomiting appears in rare cases when there is no proper treatment.
Treatment of superficial gastritis
Before you begin full-fledged treatment of superficial gastritis, you should abandon the main pathogens of superficial gastritis so that there is no difficult relapse in the future:
- Quitting bad habits: alcohol, nicotine, NSAIDs, reduce the time spent around poisons and gases.
- Diet is an important stage in treatment. Following a diet helps normalize the condition of the patient’s body, thereby reducing treatment time. Superficial focal gastritis can only be managed with proper nutrition, without the use of drugs.
- In addition to the main treatment, if Helicobacter pylori is present in the body, antibacterial drugs are used.
Helicobacter pylori is most often destroyed using:
- Triple therapy: antibacterial, acid-increasing or decreasing vitamins are taken at the same time.
- Quad therapy. When four active drugs are used.
Increased pH acidity is reduced by taking antacids. They also envelop and soothe inflamed gastric walls if a diagnosis of superficial diffuse gastritis is established.
When diagnosed with superficial gastritis, the following drugs are used (complex treatment):
- Selective M-anticholinergic agents.
- Histamine H2 receptor blockers.
- Proton pump blockers.
- Enzymes.
- Eliminating dyspeptic disorders.
- Drugs that soothe inflamed mucous membranes.
- Vitamins.
A gastroenterologist determines dosages and prescribes a course of treatment to eliminate superficial gastritis; treatment depends on the nature of the disease, intensity and location of the lesion.
With this type of gastritis, the entire surface of the gastric mucosa is affected; in order for the pain to subside, do not take hot and solid foods, it is better to fast before undergoing diagnostics, inflammation will subside, since there will be no irritants.
Diet and nutrition
Proper nutrition is an integral part of the treatment of such a disease.
The diet goes through several stages, starting from strict and ending with softened ones.
Excluded on diet:
Intoxic is an anthelmintic that safely removes parasites from the body. Intoxic is better than antibiotics because: 1. It kills parasites in a short time and gently removes them from the body. 2. Does not cause side effects, restores organs and reliably protects the body. 3. Has a number of medical recommendations as a safe remedy.
4. Has a completely natural composition.
- Broths and soups are highly concentrated, too thick;
- Too many seasonings in food: spiciness, salt;
- Flavor enhancers, preservatives, dyes;
- Vegetables that contain a lot of fiber;
Can be eaten:
- Boiled meat, can be steamed. Chicken or rabbit meat is suitable. Recommended to be consumed in the form of soufflés or cutlets.
- Low-fat fish, steamed or boiled, also in the form of cutlets.
- Vegetables. At the beginning of the diet, use in ground form.
- Fruits also, if it is superficial diffuse gastritis, fruits in the form of juice or puree.
- Semolina, oatmeal in water, you can add a little butter.
- Low-fat dairy products.
You can get rid of superficial gastritis forever if you diagnose it in time.
Timely treatment of superficial gastritis of the stomach and keeping the body healthy will help speed up the treatment process.
Superficial gastritis is a disease that develops into more serious pathologies: ulcers and the development of tumors.
Source: https://nebolitzhivot.ru/poverhnostnyiy-gastrit.html