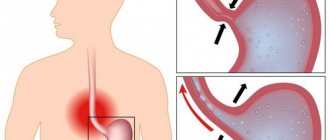
Anal sphincter spasm is defined as a syndrome that manifests itself as proctalgia (painful sensations with severe discomfort in the rectal area) caused by painful spasm of the anal sphincter muscles.
A similar clinical picture is typical for most proctological pathologies, but the diagnosis of “anal sphincter spasm” or “proctalgia syndrome” is justified in the absence of organic pathology of the anus and the identification of the true causes of pain (pain syndrome in the rectum of unknown etiology).
The disease in most cases lasts a long time, with the development of fear of defecation and the potty. Babies often forcibly retain feces, which only increases pain and discomfort and exhausts patients and their parents physically and psychologically. Therefore, diagnosis with determination of the causative factor and adequate treatment of this pathology are extremely important.
Rectal sphincter spasm symptoms
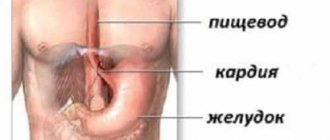
Proctalgia is a pathology of the anus, which is accompanied by a pain syndrome of various types in the rectum and/or anus, associated with transient or persistent spasm of the rectal sphincter.
Anal sphincter spasm syndrome is characterized by:
- acute pain of a paroxysmal nature with irradiation (“radiating”) to the perineum, tailbone or anterior abdominal wall, lower abdomen;
- pain syndrome can be associated with the act of defecation or occur independently, regardless of rectal emptying
- the pain is relieved or stops completely after taking a warm bath or after defecation;
- often the occurrence of spasms can be provoked by psycho-emotional experiences, chronic stress, neurological diseases, physical activity, especially in schoolchildren and adolescents.
Symptoms of stenosis
Acquired rectal stenosis
and can form in any part of the organ - from the anal ring to the transition zone to the sigmoid colon. The extent of the stricture may also vary. Acquired rectal stenosis is characterized by a slow development of symptoms. Several months or even years pass between the injury, operation or disease that caused the stenosis and the formation of a detailed clinical picture. Due to the slow progression of symptoms, patients with rectal stenosis have time to physically and psychologically adapt to the change in the act of defecation and often consult a doctor only after severe difficulties appear in the process of bowel movement. By this time, rectal stenosis, as a rule, has time to be complicated by secondary damage to the intestinal mucosa, and sometimes by fecal incontinence.
Patients complain of false urges, itching in the anus and difficulty in defecation. Feces pass out in the form of a thin ribbon; strong straining is necessary. In the stool of patients with rectal stenosis, impurities of blood, mucus and pus are often visible, caused by inflammation and ulceration of the intestinal mucosa at the site of its pathological narrowing. When examining the perianal zone, scars and areas of maceration are revealed. Traces of blood, pus and mucus may be found. The anus is narrowed or gaping. A digital examination reveals rectal stenosis and infiltration of the intestinal wall. When carrying out endoscopic and radiological studies, pathological expansion of the upper parts of the rectum is visible, caused by the accumulation of fecal matter over the area of narrowing.
Congenital rectal stenosis
, as a rule, is located in the area of the anal ring, less often - a little higher, very rarely - in other parts of the organ. The extent of the stricture is usually insignificant. Severe rectal stenosis is diagnosed in the first days of a newborn’s life. There is difficulty passing meconium. Subsequently, the feces are squeezed out of the anus with a narrow tape, “like paste from a tube.” With a sharp narrowing of the intestine, there may be no passage of feces, and a cloudy liquid is released from the anus. The volume of the abdomen gradually increases. A child suffering from rectal stenosis behaves restlessly, eats and sleeps poorly. With mild forms, recognition can be difficult; sometimes the diagnosis is made only several months or years after the patient’s birth.
Along with direct congenital rectal stenosis, narrowing of the lower intestine in young children can be caused by other malformations of this anatomical zone, for example, anal atresia with the formation of perineal, rectal-urethral and rectal-vaginal fistulas. Insufficient bowel movement with such defects causes the development of megacolon, causing inflammation and secondary narrowing of the lower parts of the rectum. Sometimes stenosis in children develops after surgery for anal atresia or rectal fistula.
Causes of rectal sphincter spasm
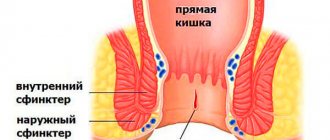
Spasm of the anal sphincter is caused by involuntary contraction of the smooth muscles located around the anus (external and/or internal anal sphincter), and along with them there is a contraction of blood vessels, nerves, nearby muscles and internal organs. Therefore, when smooth muscles contract, strong, sometimes pulsating pains (proctalgia) of varying duration and intensity always occur.
The basis of the treatment of this pathology is to determine the cause of the anal sphincter spasm.
Frequent spasms of this area in most cases are due to good innervation of the posterior wall of the rectum and its active vascularization. There is a reflexogenic zone here and any changes in the normal functioning of this area (prolonged constipation, inflammatory processes, violations of the integrity of the mucous membrane or varicose veins) are manifested by reflex spasms of smooth muscles and pain syndrome - secondary proctalgia.
In patients with an unstable psyche, pathology of the autonomic or central nervous system, spontaneous anal spasm develops, which only increases the emotional lability of patients and causes insomnia. True neurogenic spasms most often occur at night or early in the morning and provoke an increase in spasms and the development of cancerophobia if this symptom occurs in adolescence and in adult patients.
Often, spasm of the smooth muscles of the anus is caused by a spasm of the levator ani muscles, which are included in the definition of coccydynia. This syndrome combines pain syndrome that occurs in the anal-coccygeal region, which is often called “television viewer disease.” It is caused by disturbances of innervation as a result of injuries, operations on the pelvic organs, especially in the presence of extensive adhesions, after difficult childbirth, and injuries to the lumbococcygeal region.
Also, spasm of the anal sphincters can develop in emotionally unstable teenage girls and young women (with hysteria, neurasthenia, as a symptom of VSD such as viscero-vegetative disorders).
Sphincter weakness
This is exactly the opposite situation to the one we discussed above. If before this we discussed how to relax the sphincter of the rectum, normalize the passage of gases and feces and relieve pain, now we need to pay attention to what to do when loosening the same locking ring. A weak rectal sphincter leads to incontinence of gases, liquid or solid feces.
Treatment requires taking into account the individual characteristics of the person, as well as the disorders. As a rule, if the rectal sphincter is relaxed, a special diet, electrical stimulation and physical therapy are prescribed. Drug therapy in this case should be aimed at treating inflammatory diseases and dysbiosis.
If the sphincter is weakened due to organic reasons, surgical intervention is necessary, namely sphincteroplasty. After this operation, long-term rehabilitation treatment with mandatory diet is required.
Types of anal sphincter spasm
Depending on the duration of the attack, there are:
- rapidly passing (transient) spastic proctalgia;
- prolonged proctalgia.
According to the etiological factor, this pathology is classified:
- primary spasm of the anal sphincter (neurotic spasm of the muscles of the anus or coccygeus muscle);
- secondary proctalgia (manifests against the background of functional or organic pathology of the rectum: fissures, hemorrhoids, Crohn's disease or tumors localized in the anal canal).
Fleeting (passing) proctalgia manifests itself in the form of sharp pulling or stabbing pains in the anus that suddenly appear within a short period of time. The pain in most cases radiates (gives) to the tailbone, hip joints and is often accompanied by severe discomfort in the perineal area. Therefore, patients perceive this symptom as a pathology of the urinary or reproductive system (bladder, kidneys, urethra, uterus or its appendages).
Prolonged pain continues for a long period of time, and there is often no response to pain relief.
This disease has a wave-like course, and after a certain time the frequency of pain increases.
The factors that cause exacerbation and increase in pain are not completely defined and are more often associated with the emotional state (stress, physical and psychological overexertion).
All these problems require timely consultation with a specialist, diagnosis and treatment.
Causes
Most often, acquired rectal stenosis develops after traumatic injuries to the perineal area, surgical interventions for chronic paraproctitis, hemorrhoids, perineal rupture during childbirth, other diseases and pathological conditions of the rectum, perineum and perianal area. The cause of narrowing of the rectum can also be a tumor growing into the intestinal lumen, or a tumor of a nearby organ that compresses the rectum. In some patients, strictures occur due to inflammatory diseases, specific and nonspecific infections, including ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, paraproctitis and intestinal tuberculosis.
In some cases, rectal stenosis develops after the introduction of aggressive chemical compounds (usually during attempts at self-medication). Rarely are narrowings diagnosed as a result of chronic pectenosis (inflammation of the ridge localized at the base of the crypts in the transitional fold area), which occurs with anal fissure, perineal proctitis and chronic paraproctitis. Cases of the development of rectal stenosis due to sexually transmitted diseases have been described. Sometimes a stricture is detected in patients who have previously undergone radiation therapy for pelvic cancer. The cause of congenital narrowing of the rectum is developmental defects.
Diagnosis of sphincter spasm
When diagnosing anal sphincter spasm, collecting complaints and anamnesis of the disease plays an important role. Often past injuries, diseases of the rectum and genitourinary system, pathology of the nervous system or severe emotional lability are determined.
Primary proctalgia is often combined with spasms of smooth muscles of other organs and patients have previously turned to other specialists.
Diagnosis of “proctalgia syndrome” is carried out with a mandatory examination of the patient and determination of the presence of other diseases that may clinically manifest as spastic pain in the rectum.
Examination of patients includes:
- examination of the anus;
- digital examination of the anal canal (with primary proctalgia, this type of examination does not cause discomfort);
- an in-depth examination of the rectal wall is performed through sigmoidoscopy;
- If it is necessary to examine the colon, a colonoscopy or irrigoscopy is performed.
Diagnostics
The nonspecific clinic of sphincteritis requires a thorough diagnostic search. To confirm the disease, the following measures are necessary:
- Blood test. There may be signs of anemia (decrease in the number of red blood cells and hemoglobin) and/or inflammation (leukocytosis, increase in ESR);
- Coprogram;
- Digital examination of the rectum;
- Feces for eggs of worms and protozoa;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- Colonoscopy;
- Anoscopy;
- Irrigography when it is impossible to perform more informative research methods;
- CT/MRI.
During an endoscopic examination of the colon, it is possible to perform a biopsy - taking material, which is then sent for subsequent study by morphologists. This method is the “gold standard” for early diagnosis of cancer pathology.
Rectal sphincter spasm treatment
Treatment of the anal sphincter consists of three main areas:
- medicinal;
- surgical correction;
- folk remedies.
Drug treatment of anal sphincter spasm
The choice of treatment method for proctalgia syndrome and anal sphincter spasm depends on the general and psychological state of the person, the presence of complications of somatic diseases and pathological processes in the rectum, the duration of the disease and the degree of spastic contraction. But any method of therapy must be combined with compliance with the rules of hygiene and proper nutrition. The initial task of the specialist is to determine the causes of the development of spasm and eliminate all negative changes (inflammation or defects of the mucous membrane), reduce or completely eliminate sphincter spasm. For this purpose, antispasmodic and painkillers are prescribed, if necessary with antibacterial agents; for constipation, laxatives are prescribed. It is better to use the drugs in the form of rectal suppositories, creams and ointments, antispasmodics (No-spa) and warm sitz baths.
Relaxation of spasm is carried out by using:
- thermal procedures;
- physiotherapeutic methods of treatment - UHF currents, darsonvalization, diathermy;
- pain relief with antispasmodics and analgesic suppositories;
- electrosleep;
- compresses, lotions and ointments;
- microenemas with the addition of anti-inflammatory, antiseptic and oil agents;
- drugs to eliminate constipation, treatment of colitis and intestinal dysbiosis.
In this case, you need to pay attention to personal hygiene - wash the anus in the evening and in the morning, as well as after each act of defecation, so as not to injure and irritate the mucous membrane with toilet paper.
Diet
Proper diet is an important factor. Food should not irritate the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract, so it is better to minimize allergenic foods in the diet, as well as meat, fish, cottage cheese, eggs and spicy, salty dishes, smoked meats.
It is necessary to avoid fatty and fried foods, raw vegetables and fruits (strawberries, apples, plums, potatoes, cabbage and carrots).
How to relieve spasm of the rectal sphincter using folk remedies
Traditional medicine recommends treating anal sphincter spasms with warm baths with decoctions of medicinal herbs or a solution of potassium permanganate, enemas and microenemas, and tampons or suppositories.
Sitz baths
- Prepare a weak pink solution of potassium permanganate and take a sitz bath for 15-20 minutes. After this, irrigate the anus with a solution of octeniderm (a long-acting alcohol antiseptic) or any of its analogues (Altsept, Aseptinol spray, Lokasept). The procedure must be repeated daily for 7 – 10 days;
- a bath with a decoction or infusion of medicinal plants that have an antispasmodic and pain-soothing effect (chamomile, St. John's wort, yarrow, oak bark, calendula);
- baths with herbal decoctions and olive oil (2 tablespoons of knotweed herb, 2-3 hop cones and olive oil), pour 2 cups of boiling water over the herbs and brew for 10-15 minutes and leave for two hours, add 1 tablespoon of oil. Pour the infusion with oil into a basin, take a bath for half an hour, lubricate the anal passage with olive or sea buckthorn oil or any antiseptic solution.
Enemas with herbal infusions
For microenemas, decoctions of medicinal plants (chamomile, calendula, yarrow) are used with the addition of an aqueous solution of octenisept (1:10) or 0.35% solution of collargol (50 ml per enema). Enemas are done daily for 7-10 days.
Herbal tampons or rectal suppositories
1) to prepare a tampon, you need to take 2 tablespoons of a mixture prepared from crushed water pepper grass, flax flowers and oak bark taken in equal proportions. Grind the collection of herbs well in a mortar and mix with 100 g. melted pork lard. The product is completely ready after 12 hours. It is used as tampons, inserted into the rectum for 3-4 hours, 1-2 times a day. Repeat the procedure for 7-10 days.
2) to prepare rectal suppositories, take 500 grams of unsalted lard, 4-5 tablespoons of crushed hop cones, 3/4 cup of St. John's wort herb. The herbs are brewed in 1 ½ cups of boiling water, the steep broth is steeped and strained, mixed with melted lard and allowed to stand for 12 hours. Candles are made from this composition with mandatory cooling in the freezer. Place the candles at night for 10-14 days. You can also use candles with sea buckthorn oil, which are sold in pharmacy chains.
If there is a rectal fissure, use Ratovnik ointment-balm with sea buckthorn oil, milk lipids and echinacea extract or Evdokimov balm.
If there is no effect from conservative treatment, more frequent attacks of spasmodic contraction of the anus, or severe complications occur, resort to surgical intervention - sphincterotomy. It involves partial excision of the anal sphincter muscles, which helps relax the smooth muscles of the muscle and significantly reduce pain.
pediatrician Sazonova Olga Ivanovna
Article read: 1,369
Treatment
Symptoms of rectal sphincter spasm are especially unpleasant because they are not relieved by pain relief. No pills, intravenous or intramuscular injections help, which is why you have to endure unpleasant sensations for a long time. The disease is characterized by wave attacks, the symptoms appear mild or acute. However, after a short respite, the pain invariably returns.
Even now, doctors continue to argue about what factors provoke spasm of the rectal sphincter, although its relationship with emotional stress has already been proven. The problem arises due to emotional or physical stress. It is possible to overcome spasms by eliminating their cause.
Signs of secondary proctalgia appear after inflammation of hemorrhoidal cones or the development of anal fissures. Usually, in the presence of such problems, rectal sphincter spasms are a symptom of the underlying disease. With hemorrhoids, the nerve endings are intensely irritated, the integrity of the surface of the mucous membranes is damaged, they become inflamed and swollen. Because of this, smooth muscles contract and nerve endings become deformed. Spasms appear, causing sharp and acute pain, radiating to different places. When a spasm accompanies hemorrhoids, defecation significantly increases the pain, which bothers the person for hours. An analgesic is unable to eliminate it, so it is necessary to use other methods to get rid of discomfort.