Causes of fissures in the anus
The etiology of cracks is varied. There are several theories for the occurrence of cracks: mechanical, neuro-reflex, infectious. Proponents of the mechanical theory explain the occurrence of cracks due to damage to the anus by hard objects that are in the feces (husks of seeds, bones of fruits). The localization of cracks depends on the anatomical and physiological characteristics of the rectum, since it is located at an angle and has a very loose shell.
According to the neuro-reflex theory, the cause is anal neuritis. The infectious theory behind a fissure in the anus is that the anal glands become infected. The inflammatory process contributes to the occurrence of fibrosis in the surrounding glandular tissues, which leads to a decrease in its elasticity. The rupture of an abscess gives rise to an anal fissure.
Cracks rarely occur in completely healthy people. More often against the background of loosening and decreased elasticity of the mucous membrane of the anal passage with swelling of the hemorrhoidal veins.
Bloody discharge and other symptoms
With cracks in the anus, bloody discharge often appears. They usually occur after defecation. The blood has a light red tint. If there is a lot of blood, it may have a dark tint.
In this case, there is a high probability that large choroid plexuses were damaged. If there is heavy rectal bleeding, you should immediately consult a doctor, as blood loss can lead to the development of anemia.
What other symptoms appear with anal fissures? The most characteristic symptom is pain during bowel movements. Moreover, their intensity depends on the depth of the defect. In addition, with constipation, the pain syndrome is more pronounced. If the pathology has become chronic, then the pain is accompanied by spasm of the obturator muscle.
With an anal fissure, bleeding and pain are constantly accompanied by itching and burning in the anal canal. The intensity of these clinical manifestations also increases during the act of defecation.
If the above symptoms are present, a person should undergo a comprehensive diagnosis, since bleeding, itching and burning can be signs of hemorrhoids and even cancer.
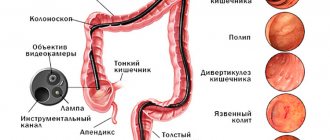
To make a diagnosis, you need to take a biochemical blood test and a stool test for the worm (this test will determine whether there is a parasite in the human body). Diagnosis also involves anoscopy and rectoscopy.
Based on the diagnostic results, the proctologist can make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment.
The main causes of anal fissures
- Stagnation of blood in the rectum - occurs in people who lead a sedentary lifestyle;
- Chronic diseases of the stomach and intestines, namely gastritis, peptic ulcer;
- Injuries to the anus that occur due to constipation, the presence of particles in the stool and when foreign bodies are inserted into the anus;
- Hemorrhoids are one of the important etiological factors in the occurrence of anal fissures. As hemorrhoids enlarge, the anus becomes weakened and injured during defecation;
- Against the background of impaired innervation of the intestine, sphincter spasm occurs.
Depending on the course, acute and chronic anal fissure are distinguished. Acute ones occur when the mucous membrane ruptures, for example, with constipation. Typically, acute cracks heal within three days without any treatment.
Chronic fissures occur as a result of new trauma to the rectal mucosa. The walls of the crack are dense and may not heal for many months or even several years.
The main causes of anal fissure
The development of this problem is facilitated by a whole range of different factors, but there are the main causes of anal fissures:
- Regular bowel irregularities – prolonged constipation or diarrhea;
- Failure to comply with personal hygiene rules. Cleansing procedures must be carried out after each trip to the toilet. Otherwise, diaper rash and inflammation appear on the intestinal mucosa, which lead to its rupture;
- Mechanical damage resulting from the use of rough and low-quality toilet paper and other similar products;
- Violation of normal sphincter spasms;
- Pregnancy and difficult childbirth - in this case, the development of an anal fissure is caused by strong pressure on the pelvis and compressed intestines;
- Anatomical features of the structure of the genital organs;
- Medical examinations (colonoscopy, rectoscopy, etc.) - most likely, we are talking about violations of the rules of the procedure and the unprofessionalism of doctors;
- Advanced hemorrhoids – very often causes symptoms of rectal fissure;
- Addiction to spicy food and alcohol;
- Lifting weights;
- Non-traditional sexual contacts (anal);
- Various pathologies of the central nervous system;
- Crohn's disease;
- Poor nutrition, which causes drying out of the intestinal contents;
- Disruption of natural blood flow in the pelvic area or blood stagnation can occur as a result of a sedentary lifestyle or characteristics of professional activity;
- Rapid or incorrect administration of the enema;
- Refusal of rectal suppositories and laxatives during the first stool after childbirth;
- Poor chewing of food - undigested pieces can damage the intestinal walls during bowel movements
- Inflammatory processes during proctitis - cause a decrease in the strength of the tissues of the anus and damage to them by feces;
- Excessive straining during bowel movements;
- Vascular disorders of the walls of the rectum;
- Frequent heavy physical activity;
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Symptoms of anal fissure
Signs and symptoms in the acute stage of the disease
The main symptom of an acute fissure is pain. The pain can be long-term or short-term, severe, cutting or prickly in nature. It can radiate to the genitals, perineum, bladder, which sometimes leads to urination problems in men. To reduce pain, patients seek a forced position - they pull their legs to their stomach or stretch them out on the bed, sit down or walk.
The pain can last from a minute to several days. Sometimes pain occurs only during bowel movements. Most often the fissure is localized on the back wall of the intestine. As a rule, a fairly strong spasm of the anus (sphincter) occurs. Clinically manifested by difficulty in defecation. Bleeding from the anus also occurs during bowel movements. Blood may appear as a narrow streak on one side of the stool.
Symptoms of anal fissure during a chronic process
One of the characteristic signs of a chronic fissure is pain. It can be short-term with remission (cessation of pain) for 10 -20. The pain intensifies with prolonged sitting. Due to prolonged pain, patients become irritable and suffer from insomnia. Patients often take laxatives because they are afraid of defecation.
Spasm of the anal sphincter is observed constantly, even at rest. This not only brings constant discomfort, but also causes many unpleasant phenomena. The consequence of prolonged spasm is chronic constipation. As a result of prolonged spasm, feces repeatedly contribute to the formation of new cracks. Also, streaks of blood are found in the stool, and there is discharge of pus from the anus.
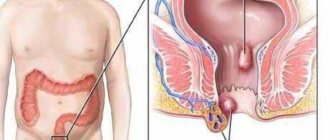
What does an anal fissure look like?
Usually the cracks are located along the back wall of the rectal lining at six o'clock on the dial. But in rare cases it can be seen on the anterior commissure. It has an elongated (elongated) shape and is hidden between the skin folds of the anus. The edges are cascading, but the crack itself does not gape. Length from 1.5 cm, width up to 2 mm. In some patients, the length may be more than 2 cm. The depth does not exceed 3 mm. One end is on the surface of the skin, and the second on the mucous membrane. This is what a sharp crack looks like.
What does an anal fissure look like during a chronic process? In general, there is little difference, there is only one nuance. It consists in the fact that at the outer end of the crack a skin fold appears with undermined edges, the so-called border tubercle, and the inner end has a small tubercle.
Diagnostic methods include
- Visual inspection;
- The internal examination consists of a digital examination of the rectum. The doctor probes the wall by inserting his index finger into it. Thus, you can determine the degree of sphincter spasm, the location of the fissure, and generally find out what an anal fissure looks like;
- The instrumental method of examination includes sigmoidoscopy. It can be used to examine the intestinal mucosa at a distance of up to 35 cm from the anus.
- Anoscopy involves examining the final section of the rectum.
How to treat anal fissures
The choice of treatment method is made by a proctologist after an examination and depends on the stage of the disease and the patient’s condition. Treatment can be conservative or surgical.
Conservative treatment
Cracks in the anus are treated with diet. You need to remove salty and sour foods from your diet, and give up alcoholic beverages and tobacco products. Consume more fruits, black bread, buckwheat porridge, oatmeal, vegetables. The diet should be aimed at eliminating constipation.
Thermal procedures. Warm baths help well in treatment. In addition, hydrotherapy helps strengthen and cleanse the skin, especially during exacerbations. Hot water bottles are used in the form of dry heat;
Physiotherapeutic procedures. Used as auxiliary methods of treatment. Of these, UHF, darsonvalization, and diathermy are used. These methods promote heat accumulation in tissues. They act like thermal baths and heating pads, namely they relieve sphincter spasm, reduce pain, and accelerate wound healing.
During constipation, therapeutic enemas are recommended. This is the most effective, simple and affordable way. It is best to do them in the morning immediately after waking up. The act of defecation after an enema is completely painless. It is recommended to administer an enema before each bowel movement for two weeks.
Combined ointments and suppositories (suppositories) are used for treatment. For example, Relief, Proctosan, Belladonna extract, Hemorrhoids. All of them are used both internally and externally in the form of rectal suppositories or ointments - 2 times a day, after defecation and external toilet of the anus.
Surgical treatment
Indications for surgical treatment:
- Ineffectiveness of conservative treatment;
- Chronic anal fissure;
- Chronic fissure with complications.
Surgical treatment consists of removing the rectal fissure. To prevent recurrent fissures in the future, a partial sphincterotomy is performed. After the operation, a gauze swab soaked in an antiseptic solution is inserted into the anus. Already on the 8th day after surgery, the wound heals.
In the postoperative period, hygienic procedures are carried out - treating the anus with antiseptics, washing the anus after defecation. Also, the stool should be of a soft consistency to prevent suture dehiscence and repeated relapses.
The prognosis for a fissure in the anus is favorable. With timely and correct treatment, a period of recovery begins.
Etiology
A rectal fissure is usually caused by mechanical damage or inflammatory processes in the intestine. In general, the etiological picture consists of the following factors:
- deterioration of blood supply to the anus;
- innervation of the rectal area;
- haemorrhoids;
- anal sex without the use of lubricants and similar substances;
- excessive physical activity or, conversely, prolonged periods of inactivity;
- chronic constipation or frequent and prolonged bouts of diarrhea;
- prolonged spasm of the rectal sphincter;
- natural childbirth with complications.
In addition, predisposing factors for the development of such a disease should be identified:
- gender – in women this disease is more common due to the structural features of the anus;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- unhealthy diet – the diet is dominated by fatty, fried, rough and spicy foods;
- the presence of chronic gastrointestinal diseases;
- frequent use of laxatives;
- previous injuries in the anus or a history of hemorrhoids.
Therefore, preventing such a disease is quite simple.
Rectal fissure in the initial stage