Various antibacterial drugs are used to treat many diseases. But they all have a significant disadvantage, which is the negative impact, in addition to pathogenic microorganisms, on the beneficial flora of the digestive organs. That is, they indiscriminately inhibit both beneficial and pathogenic bacteria. Young children are most susceptible to this pathological process. In order to prevent unpleasant phenomena from occurring, you should understand in more detail why they can develop and how to recover after completing a course of antibiotic therapy.
What is dysbiosis
The term was first introduced in 1916 to refer to a disorder of the microflora of the mucous membrane and putrefactive processes in the intestines. Dysbacteriosis is characterized by a quantitative or qualitative change in the composition of the flora. Normally, the human intestine is populated by beneficial and harmful bacteria; when their percentage changes, the absorption of beneficial substances is impaired and irritation of the mucous membrane occurs. The waste products of pathogenic bacteria affect the general condition of a person, he becomes irritable, appetite disappears, headaches, malaise, diarrhea and abdominal pain appear. The severity of symptoms depends on the severity of dysbiosis and the reasons for its development. These factors also influence how long it will take for the microflora to recover; usually the period ranges from 1 week to several months. Correctly selected treatment can eliminate the disease in less than one month.
Where does microflora come from?
At birth, the baby's intestines are completely empty; they are repopulated after birth. The recruitment of the necessary flora occurs through the mother’s birth canal, which during pregnancy becomes overgrown with strains characteristic of the intestines. The same process occurs in the nipples of a nursing woman; while feeding the baby, the necessary bacteria enter the body. It has been proven that children born by Caesarean section have problems with the formation of flora. Therefore, it is so important to place the baby on the mother’s breast immediately after birth; milk contains the nutrients and bacteria necessary to feed the biocenosis. Breast milk contains:
- macrophages;
- lymphocytes;
- immunoglobulins.
These substances are necessary for the intestinal microflora, which will ensure the normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. In order to nourish the biocenosis for an adult, it is necessary to include the following products in the diet:
- fermented milk products and milk;
- chicory;
- artichoke;
- cereals;
- garlic;
- onion.
With a mild degree of dysbiosis, you can cope with the disease in 7-10 days by changing your diet and eliminating foods that provoke flatulence and fermentation.
Medical therapy
If digestive disorders are diagnosed in infants or toddlers under the age of one year, then combination therapy is acceptable. Doctors advise focusing on the nutrition of a child who develops dysbiosis, as well as resorting to the help of certain medications.
Let's start with nutrition and consider the basic rules:
- Complementary feeding products should be introduced gradually or complementary feeding should be postponed for a while until therapy is completed, so as not to burden the gastrointestinal tract.
- Ensure adequate drinking regime, give the baby clean, warm water in the required quantity.
- Monitor the quality of food. If a mother is breastfeeding, then she should eat only healthy, easily digestible foods, do not exclude fermented milk products, and avoid stale food.

Therapy should only be comprehensive in the first place, since only in this case will it be possible to achieve the desired result.
Prebiotics
These medications also promote the production of enzymes. They allow you to restore the balance of microflora in the intestines. As a result, digestion improves and the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract is normalized. In pediatrics, preference is given to the following prebiotics: Hilak Forte, Normaze.
Probiotics
Intestinal infections are often treated with these drugs, and they are also prescribed after antibiotic therapy. This group includes drugs containing strains of normal bacteria living in the human intestine. These may be the following medications:
- Linux;
- Lactobacterin;
- Acipol;
- Bificol.
Using probiotics twice: during medication treatment and after completing the course is normal practice to minimize possible risks.
Medicines of this class are given to nursing mothers when taking antibiotics; by taking medications, the baby’s mother improves his digestion in this way. This way the drugs are better absorbed by the baby’s body.
Agents that suppress the development of pathogenic microflora
These are drugs that help improve the functioning of the digestive organs and have a certain effect on the body. Often we are talking about drugs that have a combined effect due to the presence of several components:
- Symbiotics are products that have a combined effect; they combine the effects of prebiotics and probiotics, while the components complement each other, which allows you to get a good result.
- Synbiotics are complexes containing beneficial bacteria and components of a nutrient medium. Such drugs include only modern 4th and 5th generation drugs.
- Combination products are a class of drugs that contain several types of beneficial bacteria. This group includes medications such as: Laminolact; Bifilakt Extra. Mostly prescribed to children.
- Antiseptics are used if dysbiosis has reached a severe stage. Along with antibiotics, such drugs are selected by a doctor.
- Vitamins - allow you to compensate for the lack of nutrients that arose against the background of disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Treatment of dysbiosis in children has its own characteristics; if measures are taken in a timely manner, modern medicine will help eliminate unpleasant symptoms and improve the child’s digestion. The main thing in such a situation is not to miss the moment, since the disease progresses quickly and can cause unwanted complications.
Classification and form of the disease
Treatment of dysbiosis depends on the stage of the pathological condition:
- Initial. There is a slight deviation from the norm in the number of bifidobacteria and lactobacilli. The stage is not characterized by pronounced symptoms. Correction of the condition occurs through normalization of nutrition; the microflora is completely restored within 7-14 days on its own.
- Second. The concentration of beneficial bacteria is critically reduced, and the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms increases. Patients experience bowel dysfunction for several days. This stage requires correction of nutrition and taking prebiotics, which helps get rid of the disease in 1-2 weeks.
- Average. There is a rapid proliferation of harmful bacteria, which affects the patient’s well-being, worsening mood, diarrhea and constipation, poor appetite and flatulence.
- Heavy. A large concentration of pathogenic bacteria leads to dehydration of the body; beneficial bacteria are practically absent. This condition is dangerous to health, since nutrients do not fully enter the blood, the production of vitamins slows down, and the heart rhythm is disrupted. This degree requires immediate treatment using a whole range of drugs. It is possible to restore the microflora in 2-3 weeks, in some cases it may take about a month.
The disease is also divided according to the nature of its development and has the following forms:
1. Latent - symptoms are sluggish or absent altogether, indicators have slight deviations, the form does not have a clear manifestation. 2. Subcompensated – characterized by the presence of bowel dysfunction for several days and mild nausea. 3. Decompensated - the protective forces of the immune system are reduced, erosion forms on the mucous surface of the small and large intestines, the symptoms are pronounced.
How long does dysbacteriosis last after antibiotics?
If a violation of the flora was caused by taking antibiotics and there is severe abdominal pain, diarrhea, fever and blood in the stool, then this condition is equated to stage 3-4 of the severity of the disease. In the absence of help and proper treatment, dysbiosis can last more than a month, and there is a risk of the acute form becoming chronic.
Stage 1-2 usually lasts up to two weeks, with normalization of the balance of bacteria in the intestines most often occurring without special therapy. Experts recommend that at the first signs of illness, contact a specialist who will adjust your diet and prescribe medications based on the causes of development, which will help avoid complications. Particularly dangerous complications are megacolon and pseudomembranous enterocolitis, which can lead to disability in adults and death in children and the elderly.
Gastrointestinal pathology provoked by a potent drug
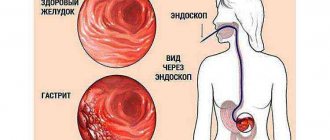
Disorders that occur in the gastrointestinal tract after taking potent antibacterial drugs are called dysbiosis. This pathology refers to a significant imbalance between pathogenic microorganisms and, directly, one’s own beneficial bacteria. The imbalance occurs mainly in the intestines; the stomach is affected much less frequently. Pathology is always accompanied by the following set of symptoms:
- sudden sharp pain occurs in the abdomen;
- a person’s stool becomes unstable, liquid or mushy, but pathological inclusions in the form of pus or blood are not noted in it;
- There is bloating, rumbling in the abdomen and severe flatulence.
This pathology, provoked by taking antibiotics, differs from an intestinal infection in that discomfort in the abdomen accompanies a sick person constantly, regardless of the use of any products or meals. During its development, the digestive organs are not able to function normally, so the human body loses the opportunity to fully satisfy the need for minerals, vitamins and nutrients necessary for normal life.
If you suspect the development of dysbiosis, you should consult a specialist and undergo an appropriate diagnostic test, which will rule out an intestinal infection.
Its main method is stool analysis. Thanks to it, the direct ratio of beneficial and harmful microorganisms localized in the intestines is revealed, which gives a complete understanding of how great the changes have occurred in the digestive organs.
Treatment of dysbiosis after antibiotics
Treatment of dysbiosis after antibiotics in adults involves an integrated approach, including normalization of the patient’s condition and restoration of the microflora. First of all, it is necessary to cleanse the body of toxic substances that are products of the life of harmful bacteria, after which it is necessary to restore the balance in the microflora.
Medications are used as treatment, which when combined with traditional methods give effective results. Quite important in the treatment of dysbiosis is a diet designed to improve the functioning of the digestive tract and reduce the load on the stomach.
According to statistics, in 80% even simple treatment can restore the microflora and eliminate unpleasant symptoms. By following a diet and taking probiotics, such as Linex, it is possible to get rid of the disease in 1-3 weeks. In the absence of treatment, taking into account the mild severity of the course, the microflora can recover on its own in a few weeks.
To restore lacto- and bifidobacteria, it is necessary to include fermented milk products in the diet. To create an acidic environment in the intestines, it is recommended to take Duphalac, which creates uncomfortable conditions for pathogenic microbes.
Recovery after a course of therapy
After the treatment measures are completed, care must be taken to restore the digestive organs after taking antibiotics and not to provoke the development of a new disease in them. For this purpose, experts recommend carrying out comprehensive restoration work. It involves following an appropriate diet, multivitamins, immunomodulators, adaptogens and biological products.
The restoration of intestinal microflora begins with nutritional correction. The duration of adherence to the diet selected by the gastroenterologist is at least 3 months. Its meaning lies in the fact that from the diet there are products that contribute to the development of pathogenic microflora - yeast bread, confectionery and sugar.
You need to be very careful when consuming milk and potatoes. But fermented milk products should be consumed daily, as they contain beneficial bifidobacteria.
To restore the functional activity of the intestines, the use of minerals and vitamins in a preventive dose is also useful. This will help to quickly normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. From all of the above it follows that only an integrated approach will help solve the problem of restoring the functional activity of the stomach and intestines.
How long does it take to treat dysbiosis in adults?
Dysbacteriosis is not an independent disease; this diagnosis is generally accepted only among doctors, so treatment is always prescribed in a comprehensive manner, which allows you to get rid of not only the unpleasant illness, but also the underlying disease. It has been proven that an imbalance of microorganisms can occur as a result of a number of diseases, so doctors cannot give an exact answer to how much dysbiosis is treated in adults, since each case is individual and depends on the severity of the disease, the type of microorganisms and the underlying disease. With a mild degree of dysbiosis, you can cope with the disease in 7-10 days by changing your diet. In more severe cases, drug treatment is required; symptoms are eliminated in the first days of therapy; complete recovery, confirmed by test results, occurs no earlier than after 3 weeks.