A pathology such as duodenogastric reflux (there is no code in ICD-10) is detected in 15% of seemingly healthy people. This is a disease of the digestive tract, which is characterized by the reflux of bile acids and duodenal enzymes into the stomach. The disease very rarely occurs on its own. In most cases, the development of duodenogastric reflux occurs as a result of other diseases, such as gastritis, ulcers, gastroesophageal reflux disease, but there are many other reasons.
general information
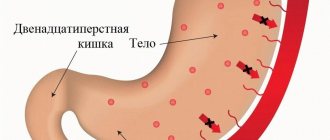
Duodeno-gastric reflux develops when there is a violation of duodenal patency, which results in an increase in pressure in the duodenum. In this case, the closing function of the pylorus of the stomach is noticeably weakened. The pyloric sphincter ceases to properly perform its basic functions, and food that has managed to be partially digested and moves into the intestines returns back to the stomach.
Statistics show that the disease occurs in approximately the same number of men and women. It is often diagnosed in student youth.
Reasons for the development of the disease
As causes of duodenogastric reflux, gastroenterologists identify factors such as:
- pancreatitis;
- lack of the hormone gastrin;
- hepatitis;
- hiatal hernia;
- cholecystitis;
- dysbacteriosis;
- diabetes;
- syndrome of incomplete rotation of the short bowel and intestines;
- obesity;
- inflammatory processes in the gallbladder and pancreas;
- helminthic infestation;
- insufficiency and other diseases of the pancreas;
- pregnancy;
- surgical interventions on the organs of the digestive system (cholecystectomy, suturing of ulcers and other operations).

The following can also lead to the development of pathology:
- smoking;
- alcohol addiction;
- frequent consumption of too hot, spicy and fatty foods;
- irregular meals;
- unbalanced diet, lack of liquid food in the diet;
- long-term use of antispasmodics, antibiotics;
- frequent stress.
Duodeno gastric reflux
Duodenogastric reflux is a functional disorder of the gastrointestinal tract. It occurs when the contents of the duodenum, along with bile salts, instead of passing into the small intestine, return to the stomach. This content mixes with digestive acids and has a toxic effect on the stomach.
Duodenogastric reflux often occurs in people with a removed gallbladder (since the outflow of bile is impaired). However, in 40% of cases, this disease occurs in healthy people.
Once the diagnosis has been made, it is necessary to immediately begin adequate treatment, since duodenal gastric reflux can lead to the development of gastritis over time.
Using natural remedies, you can quickly improve duodenal motility and block the harmful effects of bile acids on the stomach.
- Causes of the disease
- Symptoms
- Treatment at home
Causes of the disease
The causes of duodenogastric reflux are not entirely clear. This disease can be caused by a disruption of the nerve signals entering the duodenum and bile ducts (hence, reflux occurs in patients after gallbladder removal). In addition, it occurs with excessive relaxation of the pylorus, changes in its motility or peristaltic force.
Duodenogastric reflux can be caused by gastric hyperplasia or blood stasis. In addition, the composition of the bile entering the stomach affects the secretion of prostaglandins, which are responsible for the activity of the protective mechanisms of the gastric mucosa, which further aggravates the problem and complicates treatment.
Treatment at home
This disease can be easily treated on your own by following a diet and using folk remedies. Duodenogastric reflux is not a complex disease - it is rather a disruption of the gastrointestinal tract, which can lead to illness in the future. Before this happens, take responsibility for your health into your own hands.
Diet
An important step in treatment is changing eating habits. A sensible diet minimizes the symptoms of duodenogastric reflux and helps improve the functioning of the digestive system.
- Margarine, lard, and lard should be excluded from the diet; it is better to replace them with olive oil. Butter can be eaten in limited quantities (it is very important not to fry anything with it).
- Avoid smoked and fried foods.
- You can eat lean poultry, but you should avoid fatty meats and fatty products (for example, duck, goose, pork, offal, pates).
- For fish, choose low-fat varieties: cod, trout, pollock. Canned fish should be excluded from the diet.
- The diet limits processed cheeses.
- Eliminate strong coffee, cocoa, and strong tea from drinks.
- As for carbohydrates, wheat-rye bread or wholemeal bread, durum pasta, and brown rice will be healthy for you.
- You should minimize the consumption of chocolate, cakes, and cakes with rich creams.
- Vegetables that are contraindicated include cucumbers, all types of cabbage, green beans and citrus fruits. Hot spices (curry, red pepper) can be used in limited quantities.
- The diet completely prohibits carbonated drinks. Alcohol in small doses is not contraindicated.
Phytotherapy
Treatment with medicinal herbs, roots, honey and other folk remedies gives an amazing effect, which in many ways exceeds the effect of medical procedures. After all, it is best to improve the functioning of the body in natural ways - this will help eliminate side effects.
Yarrow, chamomile and St. John's wort
These three herbs are the three “pillars” on which the health of our digestive system is built.
They can treat many diseases - gastritis, heartburn, indigestion, nausea, dysbacteriosis and, of course, duodenogastric reflux.
Mix yarrow, chamomile and St. John's wort in any proportions (that is, take the ingredients “by eye”), pour boiling water over them, and make delicious tea with honey. You need to drink this drink every morning and evening.
Herbs for bilious vomiting
If the disease has worsened so much that you have not only pain, but also vomiting bile, treat with fume grass.
You need to make infusions from it (2 tablespoons of the plant per half liter of boiling water, keep covered for 1 hour). Take 50 ml of infusion every 2 hours until vomiting and pain subside.
Then move on to treatment with chamomile, yarrow and St. John's wort (as described in the previous recipe).
The root of marshmallow is no less effective. You need to make cold infusions from it - that is, pour cold water over the plant at the rate of 2 tablespoons of crushed roots per half liter of water. The mixture should be infused for 5-6 hours. Take it in small portions throughout the day until the bilious vomiting stops.
Flax seed
Treatment with flaxseed is effective for heartburn, gastritis and all types of reflux (including duodenogastric reflux). It envelops the gastric mucosa, protecting it from the negative effects of bile salts.
Pour a tablespoon of seeds with cool water (about 100 ml) and wait until they swell and mucus comes out from the seeds. This mixture should be drunk on an empty stomach before meals.
Additionally, treat with other plants that would support duodenal motility.
Plants for peristalsis
Mix the following herbs:
From this mixture you need to make warm infusions - 1 tsp. pour a glass of boiling water over the herbs, cover with a lid, strain after 20 minutes and drink. For taste, you can add honey to the drink. Drink the medicine 3 times a day an hour after meals.
Rue also has a stimulating effect on duodenal motility. It can be brewed instead of tea. But the easiest way is to simply chew 1-2 leaves of the plant every time after eating.
Nonspecific ulcerative colitis - symptoms and treatment
Source: https://nmed.org/duodenogastralnyjj-reflyuks-lechenie.html
Symptoms of the disease
Signs of duodenogastric reflux can often be confused with symptoms of other diseases of the digestive system. But this disease has its own distinctive feature. All symptoms begin to appear approximately half an hour after eating. This is how much time is usually needed for food to begin processing in the stomach and move on to the next stage. In the presence of a disease, this established process malfunctions, as a result of which food particles, along with enzymes and acids, fall back into the stomach and affect its mucous membrane.
Duodeno-gastric reflux is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Stomach ache. Usually they are localized in the upper part, are paroxysmal in nature, and have medium or high intensity.
- Flatulence.
- Heartburn that occurs almost immediately after eating food.
- Belching with air (in some cases with sour contents).
- Regurgitation of sour contents or small amounts of food.
- Bitter taste in the mouth.
- The appearance of a white or yellowish coating on the tongue.
- Nausea, vomiting with bile (in cases where the disease progresses).

Since the diagnosis of “duodeno-gastric reflux” disrupts the digestive processes, nutrients are no longer absorbed fully. As a result, vitamin deficiency develops, which is characterized by:
- weight loss;
- redness and swelling in the corners of the mouth;
- deterioration of the condition of nails, skin and hair.
If you detect the above-described symptoms of the disease, you should immediately contact a gastroenterologist, who will conduct an examination and prescribe the correct treatment.
Degrees of the disease
Depending on how long ago the development of the disease began and how much bile acids are contained in the parts of the stomach, the pathology is divided into several degrees:
- Duodeno-gastric reflux of 1st degree. This is the initial stage of the disease, during which a minimal amount of duodenal contents is detected in the stomach. As a rule, at this stage there are no signs of the disease. In more rare cases, the patient may notice some symptoms, but does not pay attention to them and thinks that they arose due to poor nutrition and will soon disappear on their own.
- Duodeno-gastric reflux of 2 degrees. It is at this stage that most patients learn about their disease. During diagnosis, enzymes and duodenal acids are detected in the fundus of the stomach. Periodically occurring symptoms force the patient to suspect the presence of an illness and seek help from a gastroenterologist.
- Duodeno-gastric reflux of the 3rd degree. This form of the disease is considered to be the most complex and advanced. The contents of the duodenum can be found in the lower esophageal sphincter and at the bottom of the stomach. The third degree is accompanied by a pronounced appearance of all the symptoms of the disease, which cause great discomfort to the patient.
Diet for duodenal gastric reflux menu
It is important to know! An effective remedy for gastritis and stomach ulcers exists! To be cured in 1 week, it’s quite simple... Read more
Diet for duodenogastric reflux occupies a leading place in the effective treatment of pathology. It is almost impossible to eliminate the pathological reflux of bile into the stomach with medications alone, since a violation of the diet and regimen plays an important role in the pathogenesis of the disease.
Proper treatment of GHD with diet and medications can prevent the development of complications such as reflux gastritis.
Diagnosis of the disease
Often duodenogastric reflux can be diagnosed completely by accident. For example, this can happen during a preventive examination or a comprehensive examination, the purpose of which was to identify a completely different disease of the digestive system.
In other cases, special diagnostics will be required. A visual examination of the patient will give virtually no results. The only thing the doctor can note is a white or yellowish coating on the tongue. Auscultation (listening) and palpation (palpation) of the abdomen are also performed. During these procedures, the presence of pain, peristaltic noises and rumbling in the abdomen is determined.

To identify duodeno-gastric reflux, instrumental research methods are also necessary. It can be:
- antroduodenal manometry;
- measuring the acidity of gastric juice;
- electrogastrography.
If necessary, auxiliary diagnostic methods can be used:
- Ultrasound;
- FGDS;
- plain radiography;
- differential diagnosis.
Before confirming the diagnosis of “duodeno-gastric reflux”, the gastroenterologist will have to completely exclude the presence of ailments with similar symptoms:
- gastritis;
- ulcer;
- duodenitis;
- acute cholecystitis;
- acute pancreatitis;
- acute cholangitis;
- cholelithiasis.
Drug treatment
The use of drugs for duodenogastric reflux is carried out on an outpatient basis. The need for hospitalization arises only in cases of severe pain, severe vomiting and the development of various complications of the disease, as well as for the purpose of conducting additional examinations.
The main goal of drug treatment is to restore the functionality of the digestive system. For this purpose, the patient may be prescribed:
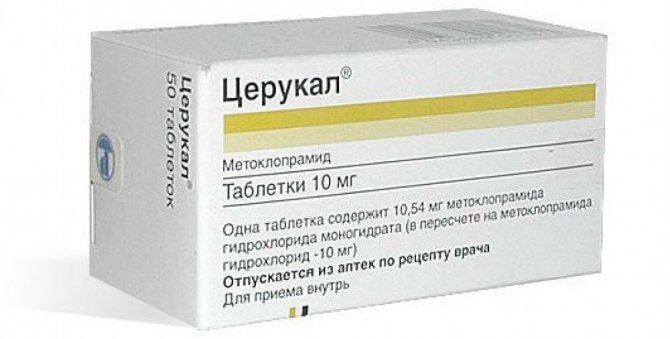
- Prokinetics for faster digestion of food, its better absorption and movement through the small intestine. Such drugs include Domperidone and Cerucal.
- Trimedat will help improve intestinal motility.
- To protect the stomach from the effects of the contents of the duodenum, Nexium and Omez are used.
- Gaviscon, Phosphalugel, Almagel will help get rid of heartburn.
- Mosapride citrate will enhance peristalsis of the upper gastrointestinal tract.
- Ursodeoxycholic acid preparations will make the contents of the duodenum water-soluble, which will reduce its aggressive effect on the stomach.
In cases where drug treatment does not bring the desired results, a decision is made on the need for surgical intervention. But here everything is not so simple. The fact is that it is technically very difficult to perform high-quality plastic surgery of the pylorus of the stomach. And the imposition of an anastomosis (anastomosis) between the intestines and the stomach cannot replace and fully perform the functions of the sphincter.
Duodenogastric reflux
We are not used to taking care of our own health. It is difficult to argue with this sad truth, but if you really want to, this fact can be ignored. Which, by the way, is what the bulk of our compatriots do.
We do not find it necessary to treat our own ailments (even with folk remedies), but with tenacity worthy of better use, we give advice to others. When we say “diet,” we mean daily snacks at the nearest fast food, but at the same time we regularly complain to family and friends about stomach pain.
But when it gets hot and the symptoms get to such an extent that patience runs out, we immediately run to the doctor. We begin to devoutly treat ourselves with herbs, tinctures, herbs and dubious dietary supplements, without thinking at all about how appropriate such “zeal” is.
Duodenogastric reflux (DGR), which we will talk about today, can serve as the best illustration of what has been said.
We will discuss symptoms and possible risk factors below, but the popular belief that GDR can be treated with a variety of folk remedies is an absolute lie.
And the most effective diet, if the body is regularly “polished” with hamburgers and hot dogs, is unlikely to help. Therefore, regardless of the severity of clinical manifestations, you should first of all consult a doctor. And the sooner the better.
Duodenogastric reflux is certainly not a fatal disease. But it does not at all follow from this that he will easily “forgive” a frivolous attitude towards himself.
The essence of the problem
As you know, the acidity level in the duodenum is slightly higher than in the stomach. There is nothing wrong with this, since in a healthy person the conventional pattern of food movement is determined by the “top-to-bottom” formula.
But for one reason or another (pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, a specific and unbalanced diet, lifestyle features) this principle can sometimes be violated.
Thus, duodenogastric reflux is characterized by the backflow of the contents of the duodenum into the stomach, and in the most advanced cases - even into the esophagus.
The symptoms that arise are familiar to almost everyone (more on them below), but to a certain extent they do not pose significant threats to health. As a result, patients are intensively treated with almagel, smecta and various folk remedies.
This will stop the clinical manifestations of GHD, but will not stop the destruction of the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum.
And in one “wonderful moment” the symptoms will turn from harmless to unbearable, and the patient will need emergency help.
Causes
- gastritis;
- postcholecystectomy syndrome;
- stomach ulcer;
- GERD - gastroesophageal reflux disease;
- dysfunction of the lower gastric sphincter;
- duodenostasis;
- peptic ulcer of the duodenum;
- functional dyspepsia;
- complication after surgery;
- stomach cancer.
If the first points on this list can still be overcome with various folk remedies, then an attempt to cope with cancer with the help of herbs is doomed from the very beginning. Therefore, the question “how can GHD be cured” cannot be considered correct in the general case.
Symptoms
GHD is almost always accompanied by pain, but it cannot be considered the only clinical manifestation. Other symptoms, although less significant, can also cause the patient a lot of discomfort:
- chronic heartburn;
- flatulence;
- bloating in the abdomen;
- periodic belching;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- yellowish coating on the tongue;
- frequent vomiting (mainly bile);
- difficulty (painful) swallowing;
- attacks of nausea;
- cough;
- change in voice timbre.
Diagnostics
Detection of GHD usually does not require lengthy, expensive studies or highly qualified physicians. On the other hand, with a formal approach, a gastroenterologist can “look through” a much more severe pathology (cancer, renal failure), therefore, if GDR is suspected, both laboratory tests and instrumental diagnostic methods are equally important.
- fiberoptic spectrophotometry will help to accurately determine the absorption spectrum of bilirubin in the esophagus. The obvious advantage of this method is that reliable results can be obtained regardless of the acidity level;
- daily pH monitoring;
- X-ray examination with contrast of the area of the stomach and duodenum;
- electrogastroenterography can reveal the level of motor activity of the gastrointestinal tract;
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy (visual examination of the mucous membranes of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum). This procedure is not nearly as painful as some patients imagine, but it cannot be called pleasant either. Many particularly suspicious patients, under various plausible pretexts, try to avoid it and try to “treat themselves” with various folk remedies, which, of course, does themselves a disservice;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs.
Treatment
1. A special diet (which, we especially note, should be prescribed by a doctor, and not an all-knowing neighbor!)
2. Maintaining a daily routine
3. Drug therapy (strictly after a comprehensive examination)
- proton pump inhibitors;
- drugs based on ursodeoxycholic acid (they reduce the destructive effect of acid on the gastric mucosa): nexium, omez;
- prokinetics: trimedat, cerucal;
- symptomatic treatment (relieving heartburn): Almagel, Gaviscon, Maalox.
Diet features
The diet for GHD involves following simple rules:
1. Foods that should be avoided during treatment:
- everything is fatty, fried, too salty and spicy;
- apples, pickles and cabbage (in general, any foods that increase stomach acidity);
- alcoholic and carbonated drinks;
- any dishes and products that reduce the tone of the gastric sphincter (pylorus): fresh bread, coffee, cocoa, oranges, garlic.
2. Basic recommendations for catering:
- all food must be thoroughly chopped and always warm (avoid too hot and cold dishes);
- eat more bran (they normalize the chemical composition of bile);
- eat often, but in small portions (best 5-6 times a day);
- drink as much water as possible that is high in magnesium;
- Recommended type of cooking: steaming, boiling and baking.
But what about treatment with folk remedies, which has gained considerable popularity in recent years? Everything is not so obvious here. On the one hand, such methods cannot (!) completely eliminate all manifestations of GHD. On the other hand, if they are approved by your doctor and can help you cope with reflux faster and easier, then you should not refuse them.
Source: https://prosindrom.com/internal-diseases/gastrointestinal-tract/duodenogastralnyj-reflyuks.html
Diet as part of general therapy
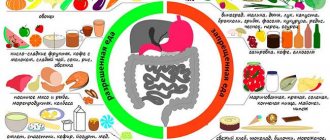
Treatment of duodeno-gastric reflux includes adherence to a special strict diet. Patients are allowed to eat:
- vegetable soups without frying;
- boiled, baked or steamed fish;
- lean meat;
- eggs;
- vegetables;
- non-acidic fruits;
- greenery;
- jam;
- compotes;
- honey;
- jelly;
- dried bread.
Meals for duodenogastric reflux should be fractional, which means eating small portions up to six times a day.

As for restrictions, for the entire period of treatment the patient is prohibited from:
- fried dough;
- fresh bread and pastries;
- lard and fats of animal origin;
- mushrooms;
- spices and seasonings;
- chocolate;
- legumes;
- cakes with butter and butter creams;
- ice cream.
Duodeno gastric reflux: diet, sample menu, dietary recipes
It is important to know! Bad breath is often caused by parasites! To check if you have parasites, add 1 spoon to a glass of water... Read more
Diet for duodenogastric reflux occupies a leading place in the effective treatment of pathology. It is almost impossible to eliminate the pathological reflux of bile into the stomach with medications alone, since a violation of the diet and regimen plays an important role in the pathogenesis of the disease.
Proper treatment of GHD with diet and medications can prevent the development of complications such as reflux gastritis.
General nutritional recommendations for duodenogastric reflux
Most often, pathological regurgitation of bile and pancreatic juice occurs against the background of an existing gastrointestinal disease. This could be gastroduodenitis, duodenitis, chronic gastritis. Thus, dietary recommendations are general in nature for all these diseases.
Basic rules of dietary nutrition for biliary reflux and reflux gastritis:
- Frequent, small meals. Portions should be small, and the interval between meals should not normally exceed 2.5-3 hours.
- Chewing food thoroughly. Do not forget that digestion begins in the oral cavity, and rough pieces of food can injure the mucous membrane and disrupt the motility of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Not a late dinner. Also, a diet for reflux gastritis implies that the last meal should be no later than 3-4 hours before bedtime. This will prevent the reflux of duodenal juice back into the stomach in a horizontal position at night.
- Exclusion from the diet of junk food: everything salty, spicy, fatty and fried. It is not recommended to consume fast food, carbonated sweet drinks, chocolate, and citrus fruits in large quantities.
- Quitting smoking and drinking alcohol.
- Maintaining adequate water regime, introducing mineral water into the diet.
- Eating food at normal temperature. Food should not be excessively hot or, on the contrary, cold.
For successful treatment, it is extremely important to follow the recommendations listed.
Diet for duodenogastric reflux
Properly selected nutrition reduces the severity of unpleasant symptoms and neutralizes increased acidity. Constant reflux of the contents of the duodenum often leads to the development of inflammation in the gastric mucosa (reflux gastritis). Bile acids contained in bile disrupt the integrity of the epithelium, contributing to the appearance of an erosive process.
Nutrition during exacerbation of pathology
The diet for reflux gastritis in the acute stage is aimed at relieving inflammation, reducing the acidity of gastric juice and restoring the mucous membrane.
During the period of exacerbation, it is necessary to give up smoking and alcoholic beverages. Avoid eating semi-finished products and adding spices to dishes. It is also advisable to adhere to a diet - eat at the same time. Organize your last meal 3-4 hours before bedtime.
Such patients are prohibited from eating on the go, dry food, or in a lying position; Do not bend forward sharply, especially after eating. Don't forget to drink at least 200 ml of water before each meal.
Products allowed
List of allowed foods and dishes for bile reflux:
- slimy soups based on cereals and vegetables; puree soups;
- boiled porridge (barley, buckwheat, rice, oatmeal);
- lean fish (hake, pollock), boiled or steamed;
- steamed omelette, dry eggs;
- “yesterday’s” or slightly dried bread;
- lean boiled meat; meat soufflé, cutlets, steamed meatballs;
- vegetable purees;
- fine-grained unleavened cottage cheese, whole fresh milk;
- it is allowed to add butter or vegetable oil to dishes in small quantities;
- cottage cheese casserole, marshmallows;
- dried fruit compote, weak black tea, herbal infusions.
The listed products and dishes in liquid, pureed, semi-liquid consistency, in the form of purees and soufflés contribute to easier and better digestion and do not irritate the mucous and muscular membranes of the digestive system.
Prohibited products
In addition to normalizing the general diet, gastroenterologists and nutritionists recommend completely eliminating the following ingredients during an exacerbation:
- spicy, salty, fried and fatty foods;
- everything marinated and dishes prepared with the addition of a large amount of herbs and spices;
- fresh baked goods, chocolate;
- citrus, sour fruits;
- broths saturated with extractive substances based on fish and fatty meat;
- vegetables that have a coarse fibrous structure or promote flatulence;
- sauces, mayonnaise, spices;
- fermented milk products;
- alcohol, coffee, carbonated drinks;
- any jam, honey.
Sample menu for every day
Sample menu of a therapeutic diet for one week.
Monday:
- Breakfast - oatmeal porridge with water, a glass of cocoa.
- 1st snack – cottage cheese with grated fruit.
- Lunch – pureed vegetable soup, steamed pollock with buckwheat porridge, tea.
- 2nd snack – yogurt, biscuits.
- Dinner – rice porridge on water with a piece of butter, vegetable salad, a glass of cocoa.
- 3rd snack – dry biscuits, a glass of milk.
Tuesday:
- Breakfast - omelet with water from 2 eggs, dried bread, tea.
- 1st snack – cottage cheese casserole with rosehip infusion.
- Lunch – stewed vegetables, 2 fish cutlets.
- 2nd snack – baked red apple, dried fruit compote.
- Dinner – carrot and beet salad, meat soufflé.
- 3rd snack – 150 ml of milk.
Wednesday:
- Breakfast – buckwheat porridge with milk with a piece of butter, tea.
- 1st snack – toast with low-fat curd mixture, compote.
- Lunch – water soup with vegetables and noodles, meat soufflé.
- 2nd snack – unleavened cottage cheese casserole, tea.
- Dinner – vegetable puree, boiled fish.
- 3rd snack – a glass of fresh milk.
Thursday:
- Breakfast - oatmeal porridge in water with pureed non-acidic fruits, tea.
- 1st snack – low-fat yogurt with dry cookies.
- Lunch – vegetable soup with water, mashed potatoes with meat zrazy.
- 2nd snack – low-fat cottage cheese casserole, compote.
- Dinner – 2 soft-boiled eggs, vegetable salad.
- 3rd snack – rosehip decoction.
Friday:
- Breakfast – steamed omelet, tea.
- 1st snack – vegetable salad, compote.
- Lunch – vegetable soup, boiled fish with rice.
- 2nd snack – an apple cooked in the oven, tea with cookies.
- Dinner – pureed vegetables, boiled meat.
- 3rd snack – a glass of whole pasteurized milk.
Saturday:
- Breakfast – 2 soft-boiled eggs, tea.
- 1st snack – bread toast, compote.
- Lunch – buckwheat porridge on water, boiled fish.
- 2nd snack – apple, tea.
- Dinner – mashed potatoes, steamed meatballs.
- 3rd snack – a glass of milk.
Sunday:
- Breakfast - omelette on water, tea.
- 1st snack – low-fat yogurt, dry cookies with compote.
- Lunch – pureed carrot soup, broccoli, bread.
- 2nd snack – unleavened cottage cheese casserole.
- Dinner – vegetable puree, tea.
- 3rd snack – a glass of whole milk.
What nutrition should be like can be found by watching the video.
Tips from our readers
I got rid of parasites in just a week! I was helped by a remedy that I learned about from an interview with a parasitologist...
Read the expert's opinion >>
Diet recipes
Recipe for cottage cheese casserole: you need to mix 500 grams of low-fat cottage cheese, 1 egg, 4 tablespoons each of sour cream, semolina and fructose in a blender. The resulting mixture is placed in the multicooker bowl, after which it is cooked for about 50 minutes in baking mode.
Recipe for puree soup: 500 g of pumpkin and 2 potatoes should be peeled, finely chopped, then add a glass of water and simmer over low heat. Mix the cooled vegetables in a blender. Add the mixture, a pinch of salt and a little ginger to boiling milk and water, then cook for another 4-5 minutes.
Baked apple recipe: core the washed fruit, then add a spoonful of sugar and water inside. The apples are laid out on a baking sheet and placed in a preheated oven for 15 minutes at a temperature of 180 degrees.
Advice from a gastroenterologist
In order to get rid of biliary reflux, gastroenterologists recommend:
- Timely and thoroughly treat any pathology of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Follow the principles of proper nutrition and limit “forbidden” foods in your diet.
- Quit smoking, drinking alcohol, and avoid stress.
- Regularly engage in gentle exercise.
Source: https://GastrituNet.online/bolezni-zheludka/dgr/duodeno-gastralnyj-reflyuks-dieta.html
Possible complications
Duodeno-gastric reflux can cause the development of other, more serious diseases and pathologies. For example, these could be:
- Toxic-chemical gastritis C. Usually the disease occurs as a result of improper or incomplete treatment of duodenogastric reflux. The disease is an inflammation of the gastric mucosa due to constant exposure to pancreatic juice and bile.
- Adenocarcinoma. This is a malignant neoplasm of the esophagus, which occurs as a result of changes in its mucous membrane, proliferation and degeneration of its cells. The main reason why this process occurs is the entry of stomach contents into the esophagus.
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease. Accompanied by reflux of stomach and duodenal contents into the esophagus.
In especially severe cases, complications may arise in the form of “loss” of the stomach and duodenum from the normal act of digestion. In such a situation, the patient will not be able to feed on his own; he will be fed by introducing special substances through the blood.
Nutrition for duodeno-gastric reflux
Reflux esophagitis is an inflammatory disease in which food from the stomach enters the esophagus.
In this case, its mucous membrane is injured, painful sensations, belching, heartburn, a feeling of a lump in the throat are observed, and often everything is complicated by cough, caries and serious inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract.
Is a diet necessary for reflux esophagitis?
Of course, any gastrointestinal disease can be treated not only with medications, but also with diets. Therapeutic nutrition for reflux esophagitis and gastritis provides for a number of restrictions on products. The following are prohibited:
- Chocolate;
- Alcohol;
- Eggplant;
- Coffee;
- Tomatoes;
- Strong tea;
- Bay leaf, parsley, cilantro, dill;
- Spices;
- Fatty meats and fish;
- Fast food and chips;
- Sweets and baked goods
In a therapeutic diet for reflux esophagitis and gastritis, preference is given to the following dishes:
- Low-fat sour cream, cottage cheese, milk kefir;
- Soft-boiled eggs;
- Porridge;
- Lean fish and meat;
- Baked or grated apples;
- Yesterday's bread;
- Compotes (especially from dried fruits).
It is recommended to follow the reflux-esophagitis diet until complete recovery, but, as practice shows, gastritis and esophagitis periodically make themselves felt throughout life. In order to increase the period of remission - and it can last several years - you need to carefully control your diet and not eat prohibited foods.
Diet rules for patients with reflux esophagitis and gastritis:
- During the period of exacerbation, it is necessary to switch to porridges and soups with a mucous consistency, and temporarily refrain from eating solid food;
- It is recommended to eat often, but in small portions;
- Drink rosehip decoction and green tea daily - they relieve the main symptoms.
We also advise you to read the article Treatment of reflux esophagitis with folk remedies.
Diet table No. 1 for reflux esophagitis: menu
To prevent the development of the disease, it is recommended to eat the following foods:
- Puree soups with milk or vegetable broths;
- Vegetable purees;
- Milk pre-mashed porridges;
- Boiled or steamed meat, fish;
- Oils: butter, sunflower or olive;
- Dairy products;
- Steamed omelettes or boiled eggs;
- Stale white bread and crackers;
- Sweet fruits and berries;
- Vegetable juices;
- Rose hip decoction;
- Weak tea or cocoa with milk.
Diet for reflux esophagitis and gastritis
To get rid of heartburn and prevent the development of exacerbations, this example menu is suitable:
- We have breakfast with oatmeal with banana slices;
- For lunch we eat cottage cheese;
- We have lunch with puree soup;
- We have an afternoon snack with yogurt;
- We have dinner with rice porridge and 100 g of meat.
Diet for reflux gastritis
To eliminate belching, heartburn and reduce acidity levels, a gentle diet is used:
- In the morning we eat oatmeal with fruit, wash it down with milk;
- For lunch we eat a salad of boiled vegetables, drink kefir;
- We have lunch with steamed vegetables, boiled eggs and a flatbread made from wheat flour, drink a cup of tea;
- For an afternoon snack we drink a glass of carrot juice;
- We have dinner with stewed vegetables and cottage cheese.
Diet for duodenal gastric reflux
This disease involves the release of products from the duodenum into the stomach, which is often accompanied by pain and vomiting. In order to alleviate the patient’s condition, the following sample menu is used:
Check your body fat %, BMI and other important parameters Height cm Weight kg Waist cm Neck cm Hips cm Gender man woman Activity level sedentary moderate activity active activity Reset Count
- In the morning we eat a portion of rice porridge;
- For lunch - organic yogurt;
- We have lunch with pureed vegetable soup, a piece of fish;
- We have an afternoon snack with a handful of berries;
- We have dinner with steamed vegetables and lean meat.
Diet for gastroesophageal reflux
To eliminate the symptoms of GERD, the following approximate menu option is best suited:
- We have breakfast with a couple of soft-boiled eggs, buckwheat porridge and tea with milk;
- We have a snack with cottage cheese and rosehip decoction;
- We have lunch with vegetarian soup, boiled vegetables and compote;
- We have an afternoon tea with rosehip infusion;
- We have dinner with baked fish and vegetables.
Diet for erosive reflux esophagitis
When erosions occur, it is necessary to follow a gentle diet based on cereals, pureed soups, low-fat meat and dairy products:
- In the morning we eat yogurt, drink non-hot tea;
- For lunch we eat cottage cheese;
- We have lunch with fish dumplings, stewed vegetables and compote;
- We have an afternoon snack with beet salad;
- We have dinner with boiled pasta and meat (100 g).
Diet for reflux gastritis in the acute stage
During this period, you should not eat raw vegetables and fruits, i.e. All products must undergo heat treatment. On the first day of an exacerbation, it is better to refuse food altogether and drink only decoctions and compotes, and then eat according to the following sample menu:
- In the morning we eat any well-cooked cereal porridge;
- For lunch we drink kefir or yogurt;
- We have lunch with low-fat soup, chopped in a blender, as well as mashed potatoes and cutlets;
- We have an afternoon snack with jelly;
- We have dinner with vegetable puree and 100 g of fish.
Diet to prevent reflux gastritis
To prevent the exacerbation or occurrence of this disease, it is recommended to build your diet according to the example of this menu:
- For breakfast we eat cottage cheese with fruit, drink green tea;
- For lunch we snack on berries;
- We have lunch with soup made with low-fat meat broth, eat seafood salad and a couple of cutlets;
- We have afternoon tea with biscuits;
- We have dinner with mashed potatoes, boiled meat and a vegetable salad.
Diet for reflux esophagitis and gastritis: recipes
Herbal infusion recipe
- 1 tsp. Pour boiling water (half a glass) of flax seeds and leave overnight;
- Take the infusion on an empty stomach for 5 days.
Cream soup recipe
- Pour boiling water over a glass of rice and leave for 2 hours;
- Chop potatoes, onions, carrots, boil in water, add a little salt;
- When everything starts to boil, pour the rice into the pan and boil until it is completely boiled;
- When ready, drain off the excess water and blend the remaining ingredients in a blender.
Steamed fish quenelles recipe
- We clean and remove bones from 100 g of fillets of pike, cod and sea bass, grind in a blender;
- Peel the onions and carrots, beat in a blender with the fish again;
- Place the minced meat in a bowl, add raw eggs (5 pcs.), add salt and sugar, mix;
- Pour in carefully boiled cold water, beat again, after adding 1 tbsp. l. matzo;
- Prepare the vegetable broth, bring to a boil and cook for another 10 minutes;
- Place fish balls in boiling broth, cover with a lid, cook for 2 hours;
- We take out the quenelles, place them in a deep container and pour the broth on top so that it covers them.
We also recommend that you read the article Diet for tonsillitis (tonsillitis).
Results, reviews and recommendations from doctors on proper nutrition for reflux esophagitis and gastritis
As a result of a diet for reflux esophagitis, it is possible to get rid of exacerbations in literally 2 days, and if it is used during a period of remission, it can be extended for up to several years.
According to doctors, there is no special prevention for reflux esophagitis and gastritis, but to prevent gastrointestinal diseases it is extremely important to eat right.
Tips on how to avoid reflux esophagitis:
- Watch your diet;
- Limit the consumption of too spicy and fatty foods;
- Be regularly examined by doctors, and if you feel unwell, make an appointment in a timely manner.
Pharmacological properties of the drug
The main therapeutic effect of the drug is the alignment of peristalsis of all parts of the intestine.
The drug is able to regulate the passage of the food bolus, resisting stagnation, as well as unnatural rapid movement.
By normalizing motility, the drug Trimedat eliminates the symptoms of eating disorders, which are associated with a variety of pathologies of the intestines, stomach, esophagus, manifested by:
- increased gas formation;
- nausea and vomiting;
- bloating;
- diarrhea and constipation;
- spasms and intestinal colic;
- heartburn and belching.
Source: https://yazdorov.win/zhkt/pitanie-pri-duodeno-gastralnom-reflyukse.html
Prevention
To prevent the occurrence of such an unpleasant disease as duodeno-gastric reflux, it is necessary:
- regulate your diet;
- avoid overeating;
- promptly seek help from specialists if problems arise with the digestive system;
- do not self-medicate and take medications only under medical supervision;
- engage in physical therapy and perform exercises to strengthen the abdominals and muscle corset.
Be healthy!