Diet for a child up to one year
While the baby is breastfed, he is provided with all the necessary enzymes that help absorb vitamins and minerals that enter the baby’s body, and milk also stimulates the strengthening of the immune system and the enrichment of beneficial bacteria.
If a child receives breast milk with dysbiosis, he will recover much faster.
Formula-fed babies cannot get this. But the mixtures contain bifidobacteria and lactobacilli. Enzymes, prebiotics and probiotics normalize the balance and composition of the intestinal mucosa.
There must be a strict diet that excludes foods that cause fermentation and irritation in the intestines. The menu of breastfed children should not include confectionery and flour products, or sour juices from fruit trees.
Nutrition experts divide it into 2 periods:
- 2-3 days of dysbacteriosis. It is allowed to eat vegetables familiar to the child in the form of puree or soup, rice, buckwheat, oatmeal, fermented milk products without sweeteners, dried fruit compote and baked apples.
- 3-5 days. A broth from low-fat fish, chicken breast and dietary rabbit meat is introduced, you can boiled fish, decoctions of dried berries and apples, which must be diluted with clean water in a 1:1 ratio, kefir and rice pudding are allowed. Dishes are steamed, boiled or stewed.
Salads with kefir
You can drink kefir simply in its pure form or add it to different dishes. Salads with the addition of fermented milk product will be useful:
- “Don’t be sick” - the shoots of dandelion, nettle, and watercress need to be thoroughly washed and chopped. Add finely chopped cucumber, dill, parsley to everything. Pour fresh kefir over everything. The salad is ready to eat.
- “Cheerfulness” – you will need dandelion shoots, sorrel (scald with boiled water), then peel. Peel and cut the tomatoes. Mix everything. Pour kefir, lemon juice, green onions into the salad, cut fresh cucumbers, dill. The medicine is ready.

It is very important that the kefir is fresh, one day old. It contains more beneficial bacteria. It is not recommended for adults with increased stomach acidity to take the drink.
What to eat for nursing mothers

Nursing mothers need to eat a nutritious, varied and tasty diet. The diet should contain a lot of fresh vegetables and fruits, fermented milk, protein and grain products. This is very important for the production of high-quality breast milk. It should be enough for the baby, since it contains many antimicrobial substances against pathogenic bacteria, as well as for the colonization of beneficial microflora in the intestines. Therefore, breast milk itself is a cure for dysbiosis.
If you carry out full and regular breastfeeding, without introducing other foods and liquids, then the intestines will quickly return to normal without outside interference.
Safety
For most pathologies of the stomach, kefir whey is included in the diet. But it is better to use a fresh homemade product, not heavy (aged for less than two days), made from whole milk. Rules of use to prevent possible negative effects on the body:
- An acute form of stomach pathology is treated with low-fat kefir.
- Normal acidity is maintained, and low acidity is stabilized with a one-day product.
- Increased acidity is regulated with medication, and kefir is not recommended for consumption. This is explained by the fermentation that causes the product in the stomach cavity, which leads to irritation of the walls and pain due to fluctuations in the acidity of the digestive juice.
- Instead of kefir, you can eat cheesecakes, cottage cheese, casseroles, and lazy dumplings.
- It is better to flavor with honey, but not with sugar.
We recommend reading: Treatment of psoriasis with folk remedies, recipes from our grandmothers
Kefir whey and fermented baked milk are safe products for health. They cannot harm an organism weakened by stomach pathology. The most severe consequence of treatment with the drink is an upset stomach, accompanied by pain, due to the appearance in the organ cavity of microflora different from the internal one. A low-quality, expired product is dangerous from poisoning, therefore it is prohibited:
- leave the open package in a warm place for 2 hours or more;
- heat on the battery;
- drink a product that is known to be expired.
Diet for a child over one year old
The diet for dysbiosis in children should be light and balanced. You should give preference to products such as low-fat cottage cheese and yogurt without various flavoring additives. The child's diet should be gentle, but must contain a sufficient amount of vitamins and minerals. Gentle nutrition means that dishes and products should not put unnecessary strain on the organs of the digestive system and cause irritation to the digestive tract. It is important that after heat treatment the consistency of the dishes is tender, so it will have a beneficial effect on the baby’s stomach and will be easier and faster to digest, especially if they are warm.
Feeding should be strictly timed; it is important to completely eliminate any snacking.
Products that irritate the child’s intestinal mucosa and cause fermentation in it:
- Fatty and fried foods.
- Spices and seasonings.
- Various sauces, mayonnaise, ketchup.
- Smoked meats.
- Sour fruit juices.
- Sweet sodas.
- Conservation.
- Vermicelli and pasta not made from durum wheat.
- Offal.
- Mushrooms.
These products should be avoided during the treatment of dysbiosis. You should not consume flour and confectionery products, whole cow's milk, various candies, ice cream, raw eggs, and fast food is strictly prohibited. With the start of treatment, a rich broth from low-fat varieties of fish, meat and poultry is introduced into the diet, in addition, stewed and boiled vegetables.
From the history of kefir
The Caucasus is considered the birthplace of kefir. For several centuries, the secret of making the product was carefully hushed up. The drink was first mentioned in reports in 1867. The Caucasus has long been used as a health resort for nobles and officers, and was treated in sanatoriums and with kefir.
For industrial production, kefir grains were imported from the Kislovodsk estate of Bekmurza Baichorov. After delivery, production of products was established in Moscow. Muslims firmly believe that they received leaven from Allah (Del). For religious reasons, the secret was firmly kept for generations: if given to foreigners, the drink loses its potency. Leaven was passed down from fathers to sons.
Kefir was even mentioned by Marco Polo in his description of his travels to the East. The drink was used to treat tuberculosis and intestinal diseases. In the middle of the 19th century, Moscow firmly decided to get its hands on sourdough, and the Blandov brothers took on the mission. The cunning men sent the beautiful Irina Sakharova to seduce Baichorov by finding out the secret of kefir, not knowing that the harsh dogmas of the Caucasus prohibit adultery on pain of death. The Chechens, for example, kill both men and women for what they do.
The grains of the prophet remained with Baichorov. Irina and her entourage departed for Kislovodsk, on the way she was intercepted by local bandits and kidnapped, having accidentally overheard that she was to marry Baichorov (the only way to get Irina without adultery). In response, the Russians formed a rescue squad that returned the girl's freedom.
The unlucky groom appeared before the Tsar, who ordered a ransom to be paid for Sakharov’s humiliation in the form of several pounds of sourdough. The kefir substrate arrived at the Moscow plant, and in 1908 the future capital saw the first kefir. Production expanded widely in the 1930s. The most difficult thing was to come up with a method for industrial production; the drink was originally created in bags made of goat skins.
During the day, the bags are hung in the sun, at night they are put away in the hut, and hung directly above the door. Anyone entering or leaving is forced to push the load, mixing the contents. Instead of fermented kefir, fresh milk is poured in and the process is repeated. In the 50s, a method was finally invented that produced a product resembling the original one. The “grains of Allah” reached the USSR along such a complex historical path.
In 1973, Irina Sakharova received a letter of gratitude from the Minister of Food Industry of the USSR for her healing gift to the Union. Today the drink is produced on an industrial scale:
- Finland.
- Czechoslovakia.
- Norway.
- Hungary.
- Switzerland.
- Sweden.
- Poland.
Flavored varieties are popular in the United States.
What to feed a child with dysbiosis

Fermented milk products must be present: kefir, yogurt, yogurt, fermented baked milk. They must be pure, without additives, and low in fat content. They are rich in beneficial bacteria that will help quickly establish the balance of microflora in the intestines. It is recommended to boil compotes from dried fruits, rose hips, and apples. After 2-3 days, when the symptoms of dysbiosis have weakened, you can give fruit juices diluted with water 1:1, steamed meatballs, low-fat cottage cheese, baked vegetables and apples.
When the stool has returned to normal, the child’s diet can be gradually diversified by introducing fresh vegetables and fruits from fruit trees in small portions: carrots, apples, pears, plums, apricots. For older children, regular sweets can be replaced with something tasty based on fructose, but sometimes they can be given in minimal quantities.
Symptoms of intestinal microflora disorders
Symptoms of dysbiosis are not always pronounced. Sometimes they are subtle, occurring only periodically. The most characteristic signs of intestinal dysfunction:
- loss of appetite;
- nausea;
- pain and bloating;
- bowel dysfunction: constipation or diarrhea;
- Putrid or sour smell of feces, the appearance of mucus in them;
- general malaise, headaches, lethargy;
- slight increase in temperature;
- Allergic skin reactions may occur.
Important: At the first signs of illness, you should definitely contact your pediatrician. Timely prescribed and carried out treatment will make it easier to cope with the disease and prevent the occurrence of complications.
What foods are necessary for the intestines?
Nutrition for dysbiosis in children should contain fiber, pectins, vitamins, and lactic acid drinks. Fiber is needed for the normal growth of beneficial intestinal bacteria. Fiber is a basic component during the creation of such important probiotics for the intestines, which are needed in order to create suitable conditions for the growth and reproduction of lacto- and bifidobacteria, E. coli with constant enzymatic properties and other beneficial microorganisms. Fiber is found in vegetables and fruits such as carrots, zucchini, beets, and apples. It is also present in cereals. For children with dysbiosis, instant cereals with the addition of pre- and probiotics have been invented.
Pectins are natural sorbents. They cleanse the intestines of toxins, waste and help the growth of beneficial bacteria. Pectins can be found in black currants, apricots, apples, carrots, cabbage and beets. Apple puree, baked apples, homemade apple marmalade with a minimal amount of sugar can suppress the growth and reproduction of pathogenic bacteria within a couple of hours. Vitamins take part in all metabolic processes and help increase the body's resistance to infections, including opportunistic bacteria. Fruits and berries in the form of compotes, purees, juices with pulp can increase immunity and appetite, the child will cheer up.
Fermented milk products: kefir, fermented baked milk, cottage cheese, yogurt, yogurt. You should only purchase such products that are labeled “baby food”; they must have a normal expiration date. Such products are filled with beneficial bacteria and increase the effectiveness of probiotics. All dishes, without exception, should be warm at a comfortable temperature, this will facilitate digestion and reduce stress.
Dietary recommendations for diarrhea, constipation and flatulence
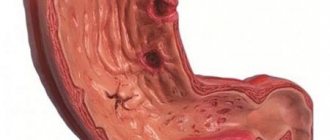
What is intestinal dysbiosis?
This is a disruption of the normal microflora in any part of the intestine and its replacement with the so-called opportunistic flora (fungi, staphylococci, Proteus, streptococci, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, etc.).
Causes of intestinal dysbiosis:
– various diseases of the gastrointestinal tract of infectious and non-infectious nature (pancreatitis, cholecystitis, gastritis, colitis, helminthic and parasitic infestations, etc.); – the period after acute viral and bacterial infections, including non-intestinal localization; – chronic inflammatory and allergic diseases; – radiation sickness, leukemia and other malignant processes, post-radiation syndrome; – use of antibiotics and cytostatics. These dysbacterioses are the most stable and can have serious consequences.
This disease manifests itself in different ways, most often with the following symptoms: frequent loose stools (diarrhea)
or, on the contrary,
constipation,
or alternating both. Nevertheless, there are general principles of diet for patients with dysbiosis.