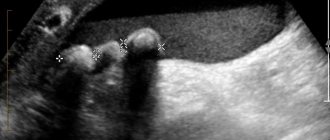
Gallstone disease is considered a common disease of the bile ducts. The disease is observed mainly in women. Signs of cholelithiasis: sharp stabbing pain under the right rib, nausea, vomiting. This disease leads to dangerous complications. Therefore, when a person experiences the first symptoms, he needs to consult a specialist who will prescribe medication or surgical treatment.
What it is?
A pathology accompanied by a change in metabolism, in which stones appear in the gall bladder and bile ducts, is called cholelithiasis (ICD-10 code: K80). It is considered one of the most common abdominal diseases.
The pathogenesis of cholelithiasis is that the gallbladder is filled with bile of increased concentration, then its stagnation occurs, and small clots first appear, which later turn into stones.
How does the elimination mechanism work?
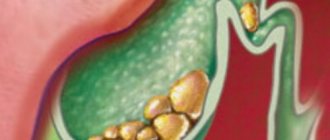
The following types of stones form in the gallbladder:
- Cholesterol - 9 out of 10 of all bladder stones are like this.
- Pigmented (much less common), consist of bilirubin and a bile component - lime.
- Mixed - they contain “harmful”; cholesterol, bile pigment - bilirubin and lime.
Stones form in all internal organs, the gallbladder is no exception, due to an imbalance of substances in the gallbladder, clumping of cholesterol particles and bile salts.
Non-surgical methods for removing hard stones are effective only against cholesterol adhesions, since lime and bilirubin do not dissolve and can be removed by surgical treatment.
Sand and stones up to 1 cm in size can be removed naturally. They pass through narrow ducts along with healthy bile, enter the intestines from there and are subsequently excreted naturally.
The entry of a stone-like fusion into the neck of the gallbladder or into the narrow thin cystic duct causes an attack of gallstone colic. This is a severe pain that is difficult to bear. Firstly, the stone injures the delicate walls of the cystic neck or ducts, and secondly, they begin to contract in spasms, trying to push the stone out.
Spasm adds pain to the overall pain picture. Additional pain comes from strong cramping contractions of the gallbladder. The calculus passes through the duct very slowly, preventing the flow of bile into the intestines. The organ contracts strongly and painfully in an attempt to free itself from accumulated bile. Analgesics and antispasmodics help alleviate the condition a little, but there will be no significant relief.
If it turns out that it is very difficult for the stones to pass, the patient considers options on how to remove them. This can be done through surgery, or through non-surgical methods. Let's consider the advantages and disadvantages of the latter.
Advantages and disadvantages of natural stone removal
The advantages of natural removal are that the patient can carry out measures to remove stones in a familiar home environment, at a time convenient for him. It is psychologically easier for him to endure the discomfort at home in the family.
The most significant disadvantages are:
- pain and heaviness in the area of the gallbladder - the right hypochondrium, attacks of pain during the movement of stones are almost unstoppable, the pain is prolonged and increasing;
- risk of blockage or rupture of the duct with a large stone;
- risk of injury to the duct with subsequent inflammation;
- the risk of developing pain shock - a dangerous condition for the body.
The danger of trying to remove stones and grains of sand from the gallbladder on your own
Even with an ultra-precise tomographic study, it is impossible to accurately determine the size and composition of all stones present in the gall bladder. Therefore, there is a high risk that stones larger than 1 cm in size will begin to move towards the bile ducts. Such stones are guaranteed to get stuck in the duct, causing severe pain and spasms.
The danger of the situation is that the duct may not withstand it and burst, then peritonitis will develop in the abdominal cavity. Stagnation of bile and damage to the gallbladder and liver are possible. These conditions require immediate surgical intervention.
And an emergency operation is always a high-risk event, because doctors do not have time to assess the patient’s condition, conduct the required studies and take tests. A condition with a rupture of the gallbladder or bile duct is threatening, so help should be provided immediately.
According to medical statistics, up to a third of all emergency operations for rupture of the duct or gallbladder against the background of independent removal of stones result in the death of the patient.
Even after the removal of stones, there is a high risk of developing adhesions in the bile ducts, their fusion due to injury and other unpleasant consequences. These consequences can also lead the patient to the surgical department.
This is what a complication looks like when stones block the normal functioning of the excretory system:
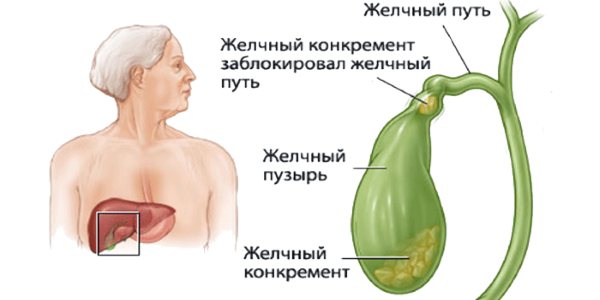
Types of illness
The disease is classified according to its stage:
| Stage | Features of manifestation |
| Initial | Only the composition in the urine changes |
| Asymptomatic | Stones are detected in the gallbladder or ducts, the patient does not show any symptoms, and the stones are discovered by chance |
| Symptomatic | The first signs of the disease appear, which may be uncomplicated or complicated. |
Classification of the disease by localization:
| Localization | Peculiarities |
| Presence of stones at the bottom or in the body of the gallbladder | This option often occurs without symptoms |
| Stones in the neck of the gallbladder | Often occurs with severe symptoms of the disease |
Types of disease:
| Type | Characteristics |
| Acute form | The main characteristic is severe symptoms, which progress quickly and have a high risk of complications. With this option, cholecystostomy is indicated. |
| Chronic form | It manifests itself as aching pain in the projection of the biliary tract. Nausea and heartburn after eating are also observed. |
Types of stones
The following types of stones are distinguished:
- Cholesterol type. They contain cholesterol (80%), which crystallizes when the level of bile acids and lecithin in the bile decreases. This happens due to impaired liver function, endocrine pathologies and consumption of junk food.
- Pigment type. The composition includes bilirubin and other breakdown products of hemoglobin. A lot of bilirubin appears in diseases of infectious etiology, autoimmune process, chronic poisoning, and taking certain medications. These stones are small in size - up to 0.1 cm, and of different colors (dark green, black, gray), placed in several pieces.
- Calcareous. They are formed due to the deposition of calcium salts near the cholesterol crystal, desquamated epithelial cells, and bacteria. This type of stones is formed when the structure of the gallbladder wall is damaged due to frequent inflammation.
- Mixed type. Calcifications are layered on the cholesterol and pigment type of the stone. As a result, they have a layered structure. Their formation occurs under the influence of inflammatory processes in the wall of the gallbladder. They are yellow and brown and are found in large numbers.
Traditional methods of removing stones from the gallbladder without surgery
Removing stones from the gallbladder without surgery can be done in one of the most effective ways - drinking freshly squeezed vegetable juices. This method will help not only get rid of stones, but also increase the level of metabolism in the body.
Recipes for vegetable juices and decoctions:
- Sauerkraut juice.
Drink 3 times a day before meals in the amount of 100-200 ml for 1.5 to 2 months.
- Lemon juice.
Squeeze the juice from the lemon and dilute it with hot water. Drink the resulting drink one glass 3 times a day for a whole month. Drink the rest of the juices in the same way.
- Beetroot broth.
Boil 2 beets, peeled and cut into large pieces, until thick
consistency of the decoction. Drink a quarter glass a day before meals.
- Birch leaf decoction.
2 tbsp. spoons of dry leaves pour 200 ml of boiling water and cook until the volume of the decoction evaporates by half. Drink the cooled decoction after straining 3 times a day before meals. Continue the course for 3 months.
- Radish juice with honey.
Pass the radish through a grater and squeeze out the juice from the resulting mass. Then mix with honey in a 1:1 ratio. This recipe is universal, as it helps with atherosclerosis and cleanses the liver.
- Herbal infusion.
Combine 5 parts each of sweet clover, celandine, wormwood and 3 parts each of chicory, valerian, dandelion and gentian roots and pour one glass of boiling water over the composition. Drink the prepared infusion a quarter at a time in the morning and evening.
- Olive oil.
Take 1 teaspoon orally half an hour before meals.
- Carrot juice
Combine 10 parts of carrot juice with cucumber and beet juice, 3 parts each.
Mix 10 parts carrot juice and 6 parts spinach juice.
Combine 10 parts carrot juice, 5 parts celery juice, 2 parts parsley juice.
- Corn silk
One of the most effective means for removing gallstones without surgery is a decoction of corn silk.
Dilute 1 tablespoon of corn silk with a glass of boiling water. After an hour, strain the infusion. Drink 1 tablespoon of decoction every 3 hours. Can be replaced with pharmaceutical extract - 30 drops before meals, 2 times a day.
Reasons and factors
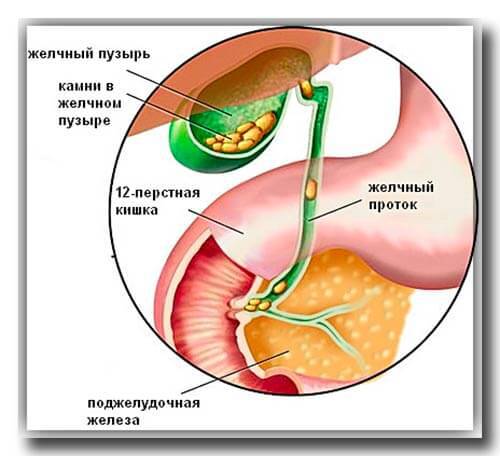
The etiology of cholelithiasis is different. The disease very often appears in people over 40 years of age, especially in those who live in urban areas. Often stones are found in the bladder, less often in the ducts. The main causes of cholelithiasis: stagnation of bile in the bladder, deterioration of metabolism, changes in the bladder wall due to inflammation.
The following disease factors are identified:
- eating junk food;
- infectious diseases;
- deterioration of gallbladder motility;
- hormonal imbalance;
- drinking alcohol;
- meat food in larger quantities;
- inactive lifestyle;
- liver disease.
Causes of stone formation
The appearance of gallstones can be caused by:
- Genetic factor. If close relatives suffered from cholelithiasis, it is necessary to adhere to a diet and undergo regular examinations.
- The patient has certain diseases. Liver cirrhosis, Caroli syndrome, diabetes mellitus, hemolytic anemia, and Crohn's disease lead to stone formation.
- Alcohol abuse. Alcohol leads to stagnation of bile. Bilirubin crystallizes to form bilirubin stones.
- An inflammatory process in an organ filled with stones.
- The presence of a large amount of bile pigment, cholesterol and calcium in bile.
- Decreased contractility of the diseased organ. If the organ does not contract intensively enough, the patient experiences bile stagnation.
- Poor nutrition. The disease is caused by long breaks between meals, fasting and drinking insufficient amounts of fluid (less than 1 liter per day). Stones are more likely to form in people who prefer fatty and spicy foods.
- Taking certain medications, for example Clofibrate, Cyclosporine.
Stone formation is often observed in obesity and after certain types of surgery. In women, the disease can be triggered by taking estrogen hormones or a large number of births.
Symptoms of gallstone disease
Symptoms of gallstone disease in women are the same as in men. This disease can be asymptomatic for a long time and be discovered by chance, during a medical examination or diagnosing other diseases. But most often, the first clinical manifestations of symptoms appear due to a stone getting stuck in the duct or in the area of the bladder neck. The pain in gallstone disease is very strong, it appears sharply, and it is also cutting, stabbing, localized on the right side in the hypochondrium and in the projection of the stomach, radiating to the lower back, right arm, and scapula. Nausea and frequent vomiting and yellowness of the skin also appear.
If stones remain in the bladder for a long time and there is stagnation of bile, this leads to the development of a chronic form of the disease. With this form, patients experience a nagging, mild pain, which intensifies after eating junk food. There is also bloating, diarrhea (discolored stools), a bitter taste in the mouth and heartburn, and an increase in body temperature.
Symptoms of biliary colic
With a sudden change in body position, consumption of large amounts of fatty or spicy foods, or severe stress, stones can begin to move along the bile ducts. This is accompanied by a clear clinical picture of the disease:

- a feeling of compression in the right hypochondrium;
- nausea and vomiting without relief;
- pain is sharp and cramping in the area of the projection of the biliary system;
- when the duct is blocked - yellowness of the sclera, skin, and mucous membranes.
This condition requires immediate medical attention. The stone can clog the duct, which can provoke an inflammatory process, spasm and the flow of bile acids into the blood. This leads to complications in the form of damage to the liver and pancreas. If you contact specialists in a timely manner, the treatment prognosis is favorable.
Mechanism of pain
With this disease, pain occurs due to the following processes:
- with mechanical irritation of the inner membrane of the bladder or ducts with a stone;
- when the bladder is overstretched due to increased intracavitary pressure;
- with spasm of the muscles of the bladder and ducts.
These ailments occur when the stone moves and gets stuck in the neck of the bladder. This attack appears:
- after a sudden movement;
- abnormal loads;
- eating fatty or spicy foods in large quantities.
Symptoms of the appearance of stones in the cavity of the gallbladder
As mentioned above, gallstone disease can be asymptomatic for many years. External signs of this pathology appear, as a rule, when the stone migrates into the bile duct, the lumen of which it partially or completely blocks.

This migration is accompanied by severe pain in the right side of the abdomen (under the ribs) and is called biliary or hepatic colic.
The pain is explained by the fact that the stone is pinched in the bile duct as a result of spastic contraction of its muscle walls when trying to throw bile into the duodenum along with the stone. Often, the so-called Vater nipple, which is located in the duodenum, also takes part in this process. If gallstones pass through the bile duct and enter it, the person experiences severe and sharp pain.
Read also: What causes weakness after gallbladder removal?
The intensity of a pain attack may increase after eating heavy fatty or spicy foods, as well as with increased physical activity and as a result of stress. In men, pain can be caused by a long drive in a car or other vehicle, since the condition of our roads makes such movement very bumpy, and this can cause movement of stones in the cavity of the bladder. Although, nowadays, more and more women drive cars, so this risk factor for hepatic colic can be considered “asexual”.
In addition to severe pain, there are other symptoms that accompany gallstone disease during an exacerbation:
- pain that occurs in the right hypochondrium can radiate to the right shoulder blade, right shoulder and even to the neck;
- At the same time, bloating is possible, when pressed, the pain intensifies;
- general weakness occurs;
- breathing becomes difficult;
- Nausea occurs, turning into vomiting that does not bring relief.
Basically, for such an attack, protective tension of the abdominal muscles (hard belly) is not observed, but often biliary colic is accompanied by symptoms of tachycardia, in which the pulse goes off scale beyond one hundred beats per minute.
All of the listed external manifestations of the disease can disappear as suddenly as they appeared. Most often, the duration of such an attack does not exceed half an hour, but it is possible that the pain syndrome may persist with either increasing or decreasing intensity for several hours or even days.
If severe hepatic colic does not go away after two hours (despite taking antispasmodic and painkillers), this is a very alarming signal. Such a symptom may indicate the occurrence of serious complications, the development of inflammation (cholecystitis) and requires immediate emergency medical assistance.
The reasons that can provoke blockage of the bile duct and the occurrence of inflammation of the bladder walls can be:
- development and reproduction of pathogenic microflora in the organ itself and/or in the intestines;
- taking medications for a long time that have a stimulating effect on the secretion of bile and digestive organs;
- factors of a mechanical nature (increased pressure on the affected gallbladder, stretching of its walls, and so on).
Diagnosis of the disease
Diagnosis of gallstone disease includes the following stages:
- At the first manifestations of the disease, you should definitely contact a gastroenterologist and surgeon. They will collect an anamnesis of the disease, conduct an objective examination, palpation and percussion of the abdominal organs (tenderness at the point of Coeur and positive Murphy's syndrome, Mussy), and make a differential diagnosis.
- General blood and urine tests. The blood test showed an increased number of leukocytes and ESR. A urine test reveals a large amount of bilirubin.
- Blood biochemistry - high levels of bilirubin, increased levels of alkaline phosphatase, ALT, GGT, AST, and cholesterol.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs.
- CT and MRI.
- Scintigraphy of the biliary tract.
- Cholecystography.
Treatment and nutritional features
Surgical or drug treatment can only be prescribed by a doctor.
Before treating gallstone disease, you should definitely consult a doctor. He will examine the patient, give recommendations, and prescribe surgical or medicinal treatment. If the disease is treated with medication, drugs are prescribed to dissolve stones: “Ursohol”, “Ursofalk”; To relieve pain, antispasmodics and painkillers are used: “No-shpa”, “Duspatalin”; When inflammation occurs in the biliary tract, antibiotics of the penicillin series - Ampicillin - are needed. Tetracycline antibiotics and nitrofuran drugs are widely used. To protect the liver during inflammation in the gallbladder and bile ducts, and improve its functioning, hepatoprotectors are prescribed: “Essentiale”, “Antral”. Vitamins are also prescribed.
An effective method of treating this disease is shock wave cholelithotripsy. Its essence is to crush large stones into small ones using a sound wave. The indications for treatment with this method are stones up to 3 cm. The classical method of removing the gallbladder and the laparoscopic method are used as surgical methods of treatment.
Features of alternative therapy and dietary nutrition
Another type of alternative medicine called homeopathy is used to treat gallstone disease. The following medications are prescribed as homeopathic treatment: “Choledius”, “Chelidonium”, “Gepar compositum”. These drugs help relieve acute inflammatory processes, stop stone formation and regulate digestion.
The Bolotov method is also used as traditional medicine. The method is used to dissolve salts and stones in the gallbladder and duct. Take 10 kg of black radish, squeeze out the juice, put it in the refrigerator, and add honey and whey to the remaining cake. The product is mixed well and stored warm. Take 1 tsp. after meal.

To treat cholelithiasis, dietary nutrition is prescribed.
Diet No. 5 is mandatory for the treatment of such a disease. Patients exclude fried, fatty, spicy, salty and sweet foods. The diet should be rich in vitamins and microelements. To do this, eat: dairy products, fruits, vegetables, herbs, lean meat and fish, soups and broths, various cereals. You need to eat fractionally, in small portions. The amount of fluid consumed per day should be at least 2 liters.