FCS (fibrocolonoscopy) is a common and multifunctional method for diagnosing various disorders in the intestine.
With the help of a colonoscope, not only the condition of the mucous membrane is examined, but also many other manipulations that are not available in most modern devices.
If necessary, the area of interest is photographed, and the doctor has the opportunity to point the lens as accurately as possible.
Also of interest to patients is taking a biopsy and removing tumors as they are detected. All these functions are available and actively used by professional specialists.
Features of intestinal colonoscopy
Colonoscopy of the intestine is a modern examination technique. Thanks to her you can:
- assess the condition of the mucous membrane, motility of the digestive organ and identify the presence of inflammatory processes;
- clarify the diameter of the intestinal canal and, if necessary, expand it due to scar tissue;
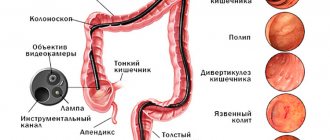
- recognize even the slightest changes in the intestinal walls, various pathological formations in the form of cracks, polyps, hemorrhoids, ulcers, diverticula, tumors and foreign bodies;
- remove any foreign bodies you see and take a small piece of mucous membrane for examination;
- remove small benign formations. This process will avoid surgical intervention;
- recognize the causes of intestinal bleeding and eliminate them using the thermocoagulation method.
The procedure can be performed in any public or private clinic. It is recommended for people over 40-45 years old, as well as for those who have complaints of abdominal pain, nausea, constipation or diarrhea.
In general, the pain medication and sedative you receive before your colonoscopy should limit the discomfort you may feel. You may also feel discomfort from lying down for long periods of time. If you feel cramping, taking slow, deep breaths can help relieve the pain.
Rarely, a colonoscope may puncture the wall of the colon, and surgery may be required to repair the hole. Talk to your doctor if you have concerns about this small risk. You will remain at the facility where you had your procedure for up to 2 hours. You must wait until the effects of the sedative wear off. If you receive anesthesia or sedation, you should not drive, operate a machine, or make critical decisions for the rest of the day.
Indications for bowel examination
Who is indicated for colonoscopy of the large intestine? Examination of the digestive tract using this technique is prescribed:
- when complaining of pain in the abdominal area;
- in the presence of discharge from the rectum in the form of mucus or pus;
- with bleeding from the intestinal tract;
- in case of intestinal motility disorders;
- with weight loss, development of anemia, low-grade fever, presence of cancer;
- when a foreign body enters the intestinal canal;
- when identifying benign formations.
Also, colonoscopy of the large intestine is prescribed for suspected intestinal obstruction, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis and malignant tumors. This diagnostic method helps to detect various diseases of the mucous membrane and take material for histology.
A friend or family member can drive you home. You can expect to resume your normal activities the day after your colonoscopy. Contact your doctor immediately if you have. Severe abdominal pain Bloodthirsty bowel movements. . Before your colonoscopy, ask your doctor to answer the following questions.
Why are you recommending a colonoscopy for me? What happens if I fail this exam? Who will perform the colonoscopy? What will happen during the test? How long will the procedure take? What are the risks and benefits of a colonoscopy? Should I avoid any activities after a colonoscopy?
Colonoscopy for ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease
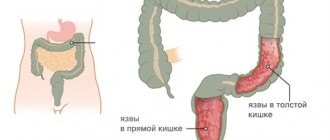
Consider ulcerative colitis. With this disease, swelling of the intestinal mucosa is observed. In addition to this symptom, tissue necrosis is present. With nonspecific ulcerative colitis, erosions and ulcerations of the rectum occur. The pathology is characterized by the appearance of purulent exudate. Symptoms of nonspecific colitis manifest themselves in different ways: much depends on the degree of the disease. Colonoscopy allows you to identify the nature and extent of the pathological process. With nonspecific ulcerative colitis, a significant part of the rectum is affected.
Crohn's disease is characterized by swelling of the tissues of the rectum. With this pathology, small ulcers and cracks in the form of slits appear. There is hyperemia and swelling of the rectal mucosa. If the atrophic process develops, the mucous membrane becomes thinner. Ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease may not be accompanied by erosions. To check the functioning of the rectum, you need to do a colonoscopy. If the doctor detects polyps in the colon, he recommends a colonoscopy and taking tissue fragments for a biopsy. Thus, malignancy can be detected in time.
Restrictions on bowel examination
A colonoscopy of the rectum is an excellent way to identify various problems that occur in the digestive tract. But there are a number of restrictions such as:
- infectious processes of an acute nature, which are characterized by an increase in temperature, poisoning of the body and weakness;
- pathological processes in the cardiovascular system. This includes heart failure, myocardial infarction, the presence of artificial valves;
- a sharp drop in pressure;
- pulmonary insufficiency;
- peritonitis, perforation of intestinal walls;
- diverticulitis;
- acute inflammatory processes in the presence of ulcerative colitis;
- severe intestinal bleeding;
- umbilical and inguinal hernia;
- pregnancy;
- pathological processes that lead to blood clotting disorders.
The above conditions increase the risk of side effects. Therefore, this technique is being replaced by other types of research. It is worth noting that rectal colonoscopy has nothing in common with colposcopy. The second type of study involves taking material from the cervix of women.
What procedures can be performed during a colonoscopy?
Who will explain the results to me? But what type of colorectal cancer screening test should you get? Many people choose colonoscopy, the gold standard for colorectal cancer screening and prevention. But there is another option - a virtual colonoscopy.
What diseases can a colonoscopy detect?
Colonoscopy: recommended every 10 years. During a colonoscopy, your doctor will use a flexible tube to insert a tiny camera into your colon through your rectum. They will look for polyps or other problems when the tube is removed. Polyps are small growths on the wall of the colon. If left untreated, they can grow and develop into cancer over time.
Preparing for intestinal colonoscopy
How is the intestinal colonoscopy procedure performed and what is needed to prepare for the examination? In fact, it occupies one of the important places. The better the patient prepares for the manipulation, the better and more truthful the result will be.
Minor discomfort—Your doctor may give you medication to help you stay relaxed and comfortable during the exam. Complications - This is not common, but insertion of the area can cause bleeding and tearing of the colon. Polyp removal – Your doctor may remove polyps during a colonoscopy. . Virtual colonoscopy: recommended every five years.
These images show polyps and other abnormalities inside your colon and rectum. Fewer complications - You won't have to worry about bleeding or rupture of your colon. If your doctor sees a polyp or something else unusual during your virtual colonoscopy, you will need to get a traditional colonoscopy to remove the polyp or perform a biopsy. Radiation Exposure – A virtual colonoscopy exposes you to a low dose of radiation.
- Less invasive—your doctor inserts a tube into your rectum and colon.
- But it will be shorter than the tube used for a colonoscopy.
- In more detail, your doctor may be able to see the area outside the colon.
- This allows other problems in the pelvic area to be identified.
- Follow-up colonoscopy.
If you're leaning toward a virtual colonoscopy so you can skip prep for a colon cleanse, think again.
Preparatory measures are based on compliance with a special diet and high-quality cleansing of the large intestine.
Following a specialized diet
A proper diet will free the intestinal walls from toxins and remove fecal stones. Preparatory measures should begin two to three days before the procedure.
Both tests require a clean colon. This means that you may only have clear liquids the day before the test and you will have to take a lot of laxative solution. No screening exam is 100% accurate. Your doctor may not find every polyp during your exam. This is especially true for polyps that are more difficult to detect, such as small or flat polyps.
What is a colonoscopy of the rectum?
But, research shows that both exams are good options for screening for and preventing colorectal cancer. The cost and coverage of screening exams varies. Before scheduling an exam, ask your insurance company if the exam will be covered.
Products in the form of:
- fruit and vegetable crops;
- greenery;
- berries, legumes and nuts;
- fatty meat, fish and sausages;
- porridge You cannot eat oatmeal, pearl barley and millet porridge;
- pasta;
- carbonated drinks;
- black bread;
- whole milk and coffee.
All of the above dishes are poorly absorbed by the body, which leads to increased gas formation.
Start a discussion about colorectal screening at your next checkup. If you are, talk to your doctor to find out when you should be screened. Regardless of what you choose, don't put off this test for fear of discomfort.
How is the procedure done?
Information provided by the American Gastroenterological Association. The term colonoscopy means looking inside the colon. This is a procedure performed by a gastroenterologist, a highly trained specialist. It begins with the cecum, which is attached to the end of the small intestine, and ends at the rectum and anus. The colon is a hollow tube about five feet long and its main function is to store unabsorbed food until it is eliminated.
Before the procedure, the patient is allowed to eat:
- wheat bread;
- boiled lean meat in the form of beef, chicken;
- fish in the form of pink salmon;
- vegetable-based broths;
- dry cookies in the form of biscuits;
- fermented milk products in the form of kefir, curdled milk, yogurt.
The last meal should be the day before at twelve o'clock in the afternoon.
Over the next 24 hours, you can only drink water or tea.
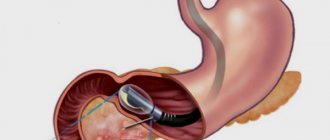
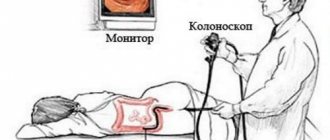
The main instrument used to look inside the colon is a colonoscope, which is a long, thin, flexible tube with a tiny video camera and a light at the end. By adjusting the various controls on the colonoscope, the gastroenterologist can carefully guide the instrument in any direction to look at the inside of the colon.
Colonoscopy is more accurate than x-rays. This procedure also allows other instruments to be passed through the colonoscope. They can be used, for example, to painlessly remove a suspicious growth or to take a biopsy - a small piece for further analysis. Thus, a colonoscopy may help avoid surgery or better determine what type of surgery may be needed.
Colon cleansing
Colonoscopy of the rectum and large intestine involves mediocre cleaning. It is performed using laxatives or enemas.
If cleansing is done with an enema, then the night before you need to give two enemas. To do this you will need an Esmarch mug and two liters of water.
A shorter version of a colonoscope is called a sigmoidoscope, an instrument used to screen the lower part of the colon. A colonoscope, however, is long enough to look at the entire colon and even part of the small intestine. Colonoscopy is a safe and effective way to evaluate problems such as blood loss, pain and changes in bowel habits such as chronic diarrhea or abnormalities that may be first detected by other tests. Colonoscopy can also identify and treat active bleeding from the intestine.
If laxatives are preferred, they are taken little by little throughout the day. Fortrans is most often prescribed, since it does not lead to disruption of the water-salt balance. About three to four liters of solution should be consumed per day, depending on the patient’s weight.
Colonoscopy is also an important way to check for colon cancer and treat colon polyps, which are abnormal growths on the inner lining of the intestine. Polyps vary in size and shape, and while most are not cancerous, some can develop into cancer. However, it is impossible to tell just by looking at a polyp if it is cancerous or potentially cancerous. This is why colonoscopy is often used to remove polyps, a technique called polyectomy.
How to prepare for the procedure?
There are important steps you should take to prepare for the procedure. First, be prepared to provide a complete list of all medications you take, as well as any allergies you have to medications or other substances. Your healthcare team will also want to know if you have any other medical conditions that may require special attention before, during, or after your colonoscopy.
How is an intestinal colonoscopy performed? This type of manipulation frightens patients, because during the procedure a special tube is inserted into the intestinal canal.
The execution scheme is as follows.
- The patient lies on the couch on his left side. The legs are bent at the knees and pressed towards the stomach.
- The doctor treats the anus with an antiseptic and carefully inserts the tube.
- If the patient has increased sensitivity, then before performing the manipulations, anesthetic drugs in the form of gels are used.
- After this, the doctor slowly and carefully moves the device further. Meanwhile, the intestinal walls are examined, and the image is displayed on the monitor.
- To straighten the folds near the intestines, air is supplied from the tube.
The duration of the procedure is about 15-20 minutes. If a colonoscopy is performed as a therapeutic or diagnostic procedure, the duration may increase to 30-40 minutes.
Advantages of the procedure and technique
Endoscopic examination is required for a malignant process in the colon. The doctor determines the histological structure of the tumor. Thanks to video colonoscopy, you can choose the appropriate treatment method for rectal cancer. A diagnostic procedure for colon cancer allows you to make a prognosis regarding the tumor. Colonoscopy is safe for the patient.
The procedure requires short-term anesthesia. Colonoscopy is uncomfortable, but the discomfort can be tolerated. During this procedure, stabbing pain may occur in the rectal area. If severe pain is felt during a total colonoscopy, the procedure should be replaced with an alternative examination technique. A colonoscope looks like a flexible tube with a lens and a light source. Thanks to the lens, the image of internal organs can be displayed on the monitor. If you properly prepare for the procedure, the doctor will be able to examine the smallest tissues.
The endoscope has channels with which you can remove tissue fragments and send them for histology. Instruments for video colonoscopy allow you to remove polyps and inject liquid and carbon dioxide into the intestine. Gas is supplied through a special device designed to open the rectum. During the supply of air, colic may occur, and the stomach may swell. First, the doctor examines the anal area: the specialist can identify fistulas, fissures, and hemorrhoids. Then the rectal mucosa is examined.
Next, the endoscope is inserted into the sigmoid colon. The doctor examines the mucous membranes of the rectum. The colon must be examined to determine the condition of the cecum. If the endoscope cannot be brought to the cecum, the information content of the examination is reduced, since inflammation and tumors are often localized in this area. Before the procedure, you should stop taking aspirin and iron supplements. These medications may cause bleeding. Before a colonoscopy, it is recommended to cleanse the intestines. On the day of the procedure, it is better to completely refuse food. The procedure is performed by a proctologist.
Possible complications of colonoscopy
During the examination, air is pumped into the rectum. At the end of the procedure, it is suctioned back. But at this time the patient may feel an unpleasant bursting feeling. To avoid this phenomenon, doctors advise taking activated charcoal. To do this, it must first be dissolved in water.
A colonoscopy of the colon should be done in a specialized institution where only experienced doctors work. It is best if it is a public clinic. If all recommendations are followed, then everything will go without complications, and the technique will be harmless.
In rare cases, a number of complications occur during colonoscopy, such as:
- perforation of the intestinal walls. The mucous membrane is damaged, as a result of which a purulent process can begin. Then the patient urgently undergoes surgery to restore the damaged tissue;
- bleeding from the rectum. It can also appear due to damage to the mucous membrane or blood vessels. Eliminated by cauterization or injection of adrenaline;
- painful sensations in the abdominal area. Most often it manifests itself against the background of removal of benign formations. You can eliminate the unpleasant feeling with the help of antispasmodics or analgesics.
If adverse complications develop, the patient should urgently consult a doctor. This is especially important if the symptoms are accompanied by nausea, vomiting, dizziness and weakness. Other unpleasant consequences may also occur in the form of loss of consciousness, diarrhea with blood, and vomiting of feces. Then an urgent call for an ambulance is required.
Who is suitable for video colonoscopy in a dream?
Modern endoscopic equipment at ON CLINIC allows you to minimize discomfort during bowel examination, but the procedure may still cause bloating and the urge to defecate. To avoid unpleasant sensations, you can undergo the procedure in your sleep - the patient is given a drug that causes a state close to physiological sleep. As a result, no discomfort, restful sleep, and upon completion of the procedure, you will receive a video recording of a colonoscopy.
Video colonoscopy while sleeping is suitable for anyone who wants to avoid discomfort during the procedure. Before the procedure, the patient undergoes an examination and undergoes a series of tests (for example, a blood test) to identify possible contraindications. We have our own clinical diagnostic laboratory, so test results can be obtained as soon as possible.
The patient, who is in a state of drug-induced sleep, is under the continuous supervision of an experienced anesthesiologist during the study.
Alternative methods for examining the intestines
If for some reason the patient has contraindications, then you can choose a different examination technique. These include:
- sigmoidoscopy. A small device called a sigmoidoscope is used, which is inserted into the rectum to a depth of 30 centimeters;
- irrigoscopy. This method of research involves the use of x-rays with a contrast agent;
- channel. This is a modern method that does not require the insertion of tubes into the digestive tract. A scanner is used for research, so manipulations are considered gentle and harmless.
The doctor will tell you which method is best to choose based on the indications and limitations.
Colonoscopy is one of the leading methods for examining the rectum in proctology. With its help, dangerous diseases that pose a threat to the health and life of the patient are identified, and some of them are treated.
Despite certain difficulties in its implementation, with proper preparation of the patient and the competence of the doctor, it is a fairly safe and painless procedure, the implementation of which is recommended for all people over 45 years of age, provided there are no contraindications.
This helps to identify deviations from the norm in time and carry out timely therapy.
How endoscopic research methods developed
Instrumental methods for diagnosing diseases of the large intestine developed gradually.
In the early stages, their capabilities were limited.
The invention of the rectosigmoidoscope made it possible to examine the patient's rectum, but did not make it possible to move further, because the device was distinguished by its rigidity.
In some cases, radiography helped, but it did not show oncological processes and polyps on the intestinal walls. Doctors had to examine him surgically through small incisions on the patient's body, which often led to the development of complications.
The invention of the sigmoid camera in the early seventies, capable of moving along a special conductor in the patient’s body, made it possible to examine the entire intestine, but blind photographs of such an extended area were uninformative.
In the mid-seventies, a fiber colonoscope with a flexible end was invented. This was a breakthrough in endoscopy and allowed the doctor to go beyond previously available capabilities.
The development of a colonoscope model, which made it possible not only to examine the surface of the mucous membrane, but also to record images in photographs, significantly improved the technique. If we take into account the fact that during the procedure it became possible to take part of the biological material for analysis, then significant progress has been observed in the field of diagnosing diseases of the large intestine. With proper preparation of the patient's body, which consisted of a special waste-free diet and the use of laxatives and enemas to cleanse the intestines, colonoscopy made it possible to qualitatively examine the inner surface of the intestine.
What is a colonoscopy and what equipment is used to perform it?
To examine the intestines using colonoscopy, an optical probe or fiber colonoscope is used. Due to the flexibility of the device, it can pass all anatomical curves of the intestine almost painlessly. With its help, not only a diagnostic study is carried out, but also a biopsy and removal of polyps.
This procedure uses a transmitting device that is inserted through the anus. It is equipped with a backlight to improve visibility inside the intestines. The image obtained as a result of the examination is recorded. If necessary, the doctor can review it again.
Advantages of the method
The importance of colonoscopy as a method for diagnosing diseases of the large intestine cannot be overestimated. It is more effective than conducting a virtual examination (MRI), since its reliability is estimated to be no more than 80%. If deviations from the norm are detected, it will still be necessary to conduct an instrumental study to make an accurate diagnosis, and in some cases, eliminate them.
Colonoscopy allows you to find polyps, which over time can narrow the intestinal lumen, even to the point of stenosis, and also, under unfavorable circumstances, degenerate into oncological formations.
Modern technology allows, when they are detected, to immediately remove and take part of the biological material for histological examination. Another advantage of colonoscopy is the possibility of local anesthesia; general anesthesia is prescribed only in exceptional cases, or at the request of the patient.
Unlike rectoscopy, in which the doctor examines a section of the intestine that does not exceed 30 centimeters in length, using colonoscopy you can obtain information about the condition of a much larger section of the intestine.
Videocolonoscopy at ON CLINIC
Conducting video colonoscopy at ON CLINIC has its advantages:
- At ON CLINIC, intestinal examination is performed using a Japanese PENTAX video colonoscope with the highest resolution. This device is the leading standard in endoscopic technology worldwide.
- Maximum comfort for the patient is ensured during the procedure, both with conventional video colonoscopy and with video colonoscopy while sleeping.
- Diagnosis of the earliest stages of gastrointestinal diseases is carried out.
- A biopsy and some interventions (for example, removal of polyps) may be performed during diagnosis.
- The experience of our specialists allows us to perform video colonoscopy as quickly as possible.
- After the examination, the patient receives the results of video colonoscopy in digital form.
Colonoscopy of the intestine: indications, contraindications and side effects
The health of the human body depends on the proper functioning of all organs and systems. Medicine is constantly developing and improving methods for diagnosing diseases that may occur in a patient, including pathologies of the large intestine.
Malfunctions in its functioning can lead to imbalance in the entire body, because it is responsible for performing such important functions as digesting food, absorbing nutrients and water, and excreting feces. Intestinal colonoscopy is a modern method for diagnosing colon pathologies that can lead to the development of serious complications.
Indications for testing
The large intestine performs an important task for the entire body, which is to digest, assimilate and eliminate food. With excessive stress and poor nutrition, its function may be impaired due to the development of pathological processes on its inner surface.
This may be expressed by the appearance of the following symptoms, which are indications for intestinal colonoscopy:
- The presence of constant and prolonged constipation.
- The appearance of abdominal pain of unknown etiology.
- Discharge from the rectum is both bloody and purulent.
- Significant weight loss for no apparent reason.
- Severe flatulence and bloating.
- Painful bowel movement.
Colonoscopy of the intestine is prescribed in preparation for some operations, and it is also mandatory for patients with suspected diseases of the large intestine.
Contraindications
To avoid damage to the colon, colonoscopy is not recommended for patients with the following conditions:
- Ulcerative colitis in the active stage
. With this disease of the colon, caused by the interaction of genetic and external factors, the integrity of the mucous membrane is compromised, which can lead to its perforation. - Crohn's disease
. It can affect any part of the intestine, including the area examined during colonoscopy, and is characterized by an inflammatory process, lymphadenitis with the formation of ulcers and scars. This granulomatous disease has a severe chronic course and is difficult to treat. - Presence of an umbilical or inguinal hernia
. - Pregnancy
in women in any trimester. - Problems with blood clotting
, as this procedure can cause bleeding. - Peritonitis
.
What is found during a colonoscopy?
Normally, the intestinal mucosa should be pink, homogeneous and free of foreign formations. Unfortunately, intestinal pathology is very common. Diagnose:
- Inflammatory diseases (colitis, sigmoiditis).
- Diverticula (protrusions of the mucous membrane).
- Polyps (dangerous in terms of degeneration into cancer).
- Immune diseases (Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis).
- Cancer.
The endoscopist gives the conclusion to the patient 15-20 minutes after the procedure. The results of the biopsy analysis will take 1-2 weeks. Based on all the data obtained, a diagnosis is established.
Possible complications of colonoscopy after examining the intestines using an endocolonoscope
In some cases, intestinal colonoscopy may cause undesirable consequences.
Disruption of normal intestinal motility and bloating, which is caused by the introduction of air into the intestinal lumen. This can be eliminated with the help of special drugs or a gas outlet tube.
Injury to the anus due to insufficiently careful insertion of the colonoscope. Unpleasant sensations are removed with the help of analgesics, and to heal the injured area, gels and ointments with anesthetics are prescribed. In most cases, the procedure is painless, although unpleasant for the patient.
Diarrhea and defecation disorders caused by the use of enemas and laxative powder in preparation for a colonoscopy, which goes away on its own. In some cases, the doctor prescribes medications to normalize stools and restore normal bowel function.
Pain and bleeding at the site of polyp removal. Another factor leading to complications is oncology, which disrupts the intestinal lumen and can contribute to its injury.
The most dangerous complication of intestinal colonoscopy is intestinal perforation. This phenomenon is very dangerous, especially if it is not detected in time by a doctor. The patient feels severe pain, which is very difficult to endure. If the intestines are poorly cleansed before a colonoscopy, feces can enter the peritoneum through the resulting hole and lead to inflammation.
In this case, an urgent operation is needed to close the resulting hole. In the case of medical negligence, when the damage is not detected in time, everything can end in resection of part of the intestine, installation of an ostomy, or even death.
The following factors can lead to intestinal perforation:
- Inexperience and low qualifications of the doctor.
- Dystrophic phenomena and thinning of the intestine.
- Poor cleaning of the rectum and intestines from feces.
- Excessive bowel activity.
Injury during colonoscopy usually occurs in the area of natural bends of the intestine, in the area of the hepatic and splenic angles. In this case, it is easy to damage nearby organs: the liver and spleen, which leads to severe blood loss and sometimes to the removal of the spleen. Therefore, an intestinal colonoscopy must be performed in a medical clinic, so that in case of complications, the necessary assistance can be provided immediately.
Patient reviews
Galina, 44 years old
At first I wanted to do FCS under anesthesia, but the doctor dissuaded me, as it poses an increased risk of injury to the mucous membrane. Everything turned out to be not so bad, although before the diagnosis I heard a lot of negative comments from friends. When inserting the tube, practically nothing is sensitive at all. Pain appears only when air is pumped. The good news is that this process rarely lasts more than 10 minutes.
Vasily, 35 years old
I did it once and that was enough for me. Not only is the tube shoved into the butt, but all this is also accompanied by a maximum of unpleasant sensations. I don’t recommend it to anyone, only if you really need it.
Daria, 29 years old
Tolerable. The doctor said that I might have to go to the hospital, but due to the situation at home I can’t do that. I agreed to the FCC. Based on the results, the doctor said there was nothing to worry about, so I’m glad.
Ekaterina, 59 years old
I have a high pain threshold, so I don't tolerate FCS well. If I do it again, I will have to take anesthesia. During the entire manipulation you feel discomfort, so I advise you to do it only with clear and reasonable indications from a doctor.
Vladimir, 48 years old
I had FCS for quite a long time. This is a full examination, but it does cause pain. If I go through this procedure again, it will only be as a last resort.
Intestinal inflammation: symptoms and treatment with medications, folk remedies.
Find out from this article how to properly dilute Smecta powder.
Instructions for use for Gastritol - https://vashjeludok.com/lekarstva/kapli/gastritol-instrukciya-po-primeneniyu.html
How a colonoscopy is done, why preparation for intestinal colonoscopy is so important
Proper preparation for intestinal colonoscopy is very important for successful examination. This will reduce the risk of complications and increase the information content of the procedure. The patient needs to approach it with all responsibility and strictly adhere to the doctor’s instructions, who will prescribe a special diet and take the necessary medications before the colonoscopy. Its result and safety depend on this.
Preparation for intestinal colonoscopy consists of measures that will help make the procedure easier for the doctor and the patient, and will also increase the information content of the study:
- Preliminary preparation involves the abolition of iron supplements, activated carbon and bismuth, as well as hormones and cardiac drugs.
- To prepare for the procedure, a slag-free diet is prescribed. They begin to adhere to it 3-4 days before the date of the colonoscopy. In this case, the following products are excluded from the diet: mushrooms, legumes, cereals and grain-containing products, some vegetables and fruits and berries, nuts, dairy products (except fermented milk), carbonated drinks, fatty meats and fish, canned food and sausage products, as well as smoked meats and pickles. The consumption of sweets is strictly limited to the permitted list. The day before the procedure, the consumption of clear broths and colorless liquids is allowed, the consumption of which ends 2 hours before the start of taking bowel cleansing drugs.
- Colon cleansing should be done with medications prescribed by the doctor, without enemas with petroleum jelly. Stimulant laxatives are usually prescribed. If the patient has prolonged constipation, then their dose is doubled or they are used in combination with osmotic-type agents. Bowel preparation is carried out using the drug Fortrans, or cleansing enemas and castor oil are used.
Carrying out the procedure in detail
Patients who are scheduled for testing are interested in how a colonoscopy is done and what they need to be prepared for when going to the clinic. As a rule, the procedure takes place in a separate room of the clinic, equipped with the necessary equipment. The patient undresses and lies down on the couch in the fetal position on his left side. The study takes place under local anesthesia, under the influence of drugs with lidocaine. This anesthesia is usually sufficient so that the patient does not experience much discomfort.
The colonoscope is carefully inserted by the doctor through the anus.
He controls its progress through the intestines, focusing on the camera’s indicators. To increase the lumen of the intestine and smooth out its folds, which simplifies diagnosis, gas is supplied into the intestine, which is felt by the patient as bloating.
Excess air is removed using the apparatus used for the study through a special channel. The advancement of the colonoscope in particularly difficult areas, where there are physiological bends of about 90 degrees, is controlled by the doctor and his assistant using palpation. Information about how a colonoscopy is performed will help the patient be aware of what is happening and reduce anxiety during the examination.
The duration of the procedure on average does not exceed half an hour. After this, the device is removed and sent for disinfection. These studies are documented by the doctor in the form of a protocol, in which he gives the patient the necessary recommendations and referral to a specialist of the appropriate profile.
Women should remember that colonoscopy is not performed during pregnancy. During menstruation, it is done only in exceptional cases; it is better to wait until the discharge ends. In case of chronic hemorrhoids, colonoscopy is not only not contraindicated, but will also help to more clearly see the clinical picture of the disease and determine the patient’s treatment strategy.
What happens after video colonoscopy
After a video colonoscopy has been performed, the patient may experience abdominal discomfort in the form of bloating or colic for some time. In some cases, a small amount of blood may be released from the anus.
Important! If the bleeding has not stopped within 24 hours, the body temperature has risen, the pain and cramps in the abdomen do not subside, you should contact the doctor who conducted the examination again.
After a video colonoscopy, you should abstain from eating for some time, especially if a biopsy was taken during the procedure or the doctor removed polyps. During the first hours you are allowed to drink a small amount of water or warm tea. For 2-3 days you should follow the following diet:
- eat jelly, slimy porridges and soups, pureed vegetables and cereals;
- drink warm tea without sugar, jelly, fresh (daily) kefir and other fermented milk drinks;
- eat steamed meat (veal, poultry fillet, beef), lean fish;
- as a side dish, cook boiled vegetables or puree them, pureed porridge in water;
- For breakfast and dinner there are steamed omelettes, pureed non-sour cottage cheese, soft unsalted cheeses.
Exclusions from the menu include rich broths with lots of vegetables, fatty meats, fresh vegetables and fruits, pickles and pickled vegetables, jams and preserves, berries with small seeds and seeds, baked goods and rye bread.
Colonoscopy of the rectum: what shows what diseases are diagnosed with its help
Colonoscopy of the rectum and other parts of the large intestine helps to examine the condition of the mucous membrane, find tumors if they are present, take biological material for research and carry out treatment in some cases. It is good if the patient is informed what a colonoscopy shows, so that he has no doubt about the need for the procedure if indicated.
Despite the presence of contraindications and the possibility of side effects, the benefits of this diagnostic method for maintaining human health cannot be overestimated.
Virtual diagnostic technologies cannot provide as accurate information as examination using a fiber colonoscope camera.
The patient’s immunity depends on the health of the large intestine, since it is formed in particular by the microbial flora in it. Over an area of about two meters, water, vitamins and amino acids are absorbed. Disorders in this organ can lead to a deficiency of substances important for the body and the development of various pathologies.
What does a colonoscopy normally reveal?
Despite the fact that colonoscopy of the rectum is unpleasant from a psychological point of view, its implementation helps to detect emerging diseases in a timely manner and treat them, which will help preserve the patient’s health, and sometimes even life.
Using rectal colonoscopy, all parts of the large intestine are examined for compliance with the following indicators:
- The color of the mucous membrane should normally be yellow or pink, distinguished by pallor. If the color changes, this indicates the presence of inflammation or erosion.
- The shine of the intestinal mucosa indicates a sufficient amount of mucus on its surface. The areas where pathology develops do not reflect light well.
- The surface of the intestine is almost smooth; the presence of unusual bulges and tubercles is a sign of the development of pathology.
- The vascular pattern also carries information about the condition of the intestine; it should look in a special way, and any changes in its pattern should be further studied.
- The overlays of the mucous membrane should be light, but if they are too dense and have a different color, this is a sign of possible pathology.
Can there be consequences after the procedure?
FCS is a relatively easy procedure, so if it is performed correctly, complications are very rare. In most cases, after the examination, the patient immediately has the opportunity to begin taking food and the necessary fluids.
Sedatives used before the test may have side effects. To minimize the risk of their occurrence, it is necessary to inform the doctor about the presence of allergic reactions, chronic intolerances or diseases of the hematopoietic organs and excretory system.
There is a risk of bleeding. They usually appear after taking a biopsy or resection of a small polyp. Most often, this process is quickly stopped or controlled by a competent specialist. The colonoscope may tear or perforate tissue. This is an extremely rare complication, however, if the procedure is not carried out carefully, the design of the device can cause damage to the mucous membrane.