Postoperative period after intestinal surgery
The main task of the postoperative period, regardless of the type of intervention, is the most complete restoration of the functions of the organs on which the operation was performed. To accomplish this task, the following goals are set for rehabilitation therapy:
- prevention of complications;
- anesthesia;
- removal of mobility restrictions;
- acceleration of recovery;
- psychological recovery after illness;
- return to an active healthy life.
The postoperative period is divided into 3 types - early, late and long-term. Early is considered to be the period from the completion of the operation to 6 days of hospital treatment. The late postoperative period includes the period from 7 days until the patient is discharged from the hospital. Long-term postoperative period is considered to be the period from discharge until the patient’s complete recovery. For a speedy recovery, all patients who have undergone surgery should follow simple rules:
- Carefully follow all recommendations of your doctor.
- Follow the regime.
- Eat according to the prescribed diet.
- Avoid physical activity.
- Don't drink alcohol.
- Stop smoking.
- Get medical examinations regularly.
- If you experience discomfort, abdominal pain or other symptoms of illness, you should consult a doctor immediately.
Diet
After intestinal surgery, depending on the time that has passed since the intervention and its type, patients consistently adhere to several tables. Therapeutic diets are aimed at restoring intestinal function after surgery:
Table No. 0 – assigned to patients after surgery. Divided into 3 types:
- No. 0A – liquid jelly, light low-fat meat broth. Daily calorie content – 1200 kcal. Number of meals – 6-8. The maximum single serving is 300 ml.
- No. 0B - in addition to the foods allowed by diet No. 0A, the diet includes pureed rice, buckwheat or oatmeal porridge in water, fish or meat puree, steamed egg white omelette, soft-boiled eggs, and vegetable jelly-like soups. Calorie content increases to 1700 kcal. The number of meals is reduced to 5, and the serving size is increased to 400 ml.
- No. 0B – after restoring the functions of the digestive system, add fermented milk and dairy products (low-fat cottage cheese, sour cream, low-fat milk), boiled or steamed main courses from lean meat and fish, white bread crackers (up to 100 g per day) to the already permitted products ). The number of calories increases to 2000-2500 kcal.
Article on the topic: Bronchorus - instructions for use, release form, composition, analogues and price
How do you decide whether to reinstate your job?
In most cases, reinstatement at work is preceded by an appeal to the court, State Tax Inspectorate or the prosecutor's office. A voluntary decision to resume cooperation with someone who was illegally fired is extremely rare .
IMPORTANT!
If a woman dismissed on the initiative of the administration brings a certificate stating that she was pregnant at the time of dismissal, the employer is better off voluntarily reinstating her to her job. If she goes to court, she is highly likely to win the case.
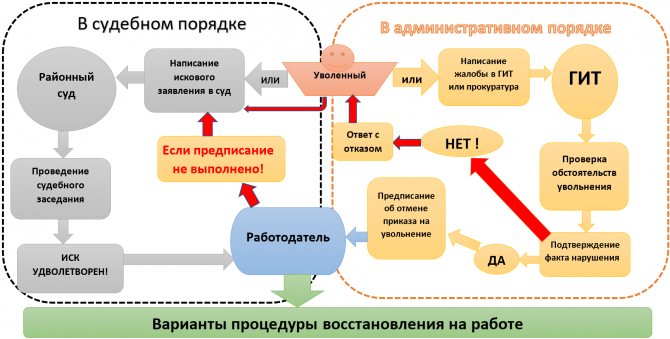
If a citizen believes that he was illegally fired, he has the right to defend his rights:
- in court - by applying to the district court at the place of residence or at the location of the former employer, i.e. by choice (part 2, part 6.3 and part 9 of article 29 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation);
- administratively - by contacting the State Tax Inspectorate or the prosecutor's office.
Gymnastics
Physical therapy in the postoperative period is important to speed up the patient’s rehabilitation. Breathing exercises used to prevent pneumonia in the postoperative period include inflating a balloon and forced inhalations and exhalations. In the early postoperative period during bed rest, therapeutic exercises are performed while lying in bed:
- The patient lies on his back. He places one hand on his stomach and the other on his chest. On the count of 1, the patient inhales at a calm, medium depth, and on the count of 2, exhales. The exercise should be repeated 8-10 times daily.
- The patient lies on his back, arms along the body. On count 1, the patient bends his leg at the knee, sliding his foot along the bed, and on count 2, straightens his leg. Breathing should be calm and of moderate depth. Repeat the exercise 5-7 times for each leg.
- The patient lies on his back, legs bent at the knees, arms along the body. On the count of 1, the patient pulls the socks toward himself, on the count of 2, away from himself. Repeat the exercise 5-7 times.
All physical therapy exercises should be performed at a slow pace. Patients' breathing should be calm. After transferring the patient to the ward mode, the physical therapy complex includes walking around the ward and exercises in a standing position:
- Starting position – the patient stands, arms extended forward. On count 1, spread your arms to the sides and inhale; on count 2, exhale and return to the starting position. Perform 5-7 repetitions.
- Starting position – standing with your hands behind your head. On the count of 1, inhale and arms up, 2 – starting position and exhale.
Physiotherapy
To speed up intestinal recovery after surgery, patients are prescribed physiotherapeutic procedures. The most popular methods are:
- UHF therapy is ultra-high frequency therapy with electromagnetic fields.
- Darsonvalization is exposure to high-frequency pulsed currents.
- Ultratonotherapy is treatment with alternating current of supra-tonal frequency.
- Laser therapy is exposure to a concentrated beam of light with a fixed wavelength.
- Magnetotherapy is exposure to a static magnetic field of various frequencies, durations and shapes.
- Diadynamic therapy is a physiotherapeutic treatment procedure based on the impact of electric current on a person with a frequency of 50 to 100 Hz.
- Electrophoresis is the administration of drugs through the skin using a direct electric current.
Vegetables and herbs
Herbal remedies are widely used for liver problems. Treatment of the digestive system with herbs has been tested for years and does not raise any special questions even among doctors.
Milk thistle-based preparations are often used to treat liver problems. They are quite inexpensive in cost, and at the same time show quite high efficiency. These herbs act specifically on those tissues that are damaged and restore their ability to function normally.
Article on the topic
Fatty liver problem. Steatosis: causes and tactics of control
Artichoke is no less popular. Its positive effect is due to the fact that it restores metabolism, reduces the amount of cholesterol in the blood, and also has choleretic properties.
You can also just drink regular brewed chamomile. It is an excellent remedy for relieving inflammation.
Anesthesia
One of the goals of treatment during the recovery period is adequate pain relief. For this purpose, many medications are used, which include:
- Droperidol is an antipsychotic used for pain relief and sedation during surgical and endoscopic interventions. Reduces the risk of nausea and vomiting during surgery, prevents shock and enhances the effect of anesthesia drugs, but, according to unconfirmed data, it has a carcinogenic and mutagenic effect and affects fertility.
- Ketorolac (Ketanov) is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) with analgesic, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory effects. Contraindicated in the presence of erosive and ulcerative diseases of the digestive system in the acute stage, increases the risk of internal bleeding.
- Diclofenac is an NSAID with a good analgesic effect. It has a gastropathic effect, causing ulceration of the mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines, drug-induced hepatitis, pancreatitis, and gastrointestinal bleeding.
Article on the topic: Submucous uterine fibroids
Therapeutic measures for constipation
Strong laxatives for constipation should not be used frequently, as the body quickly gets used to the excipients, and under the influence of medications the intestines cope with their functions worse. It should be remembered that the purpose of a laxative is to alleviate the patient’s suffering by making bowel movements possible. Laxatives do not treat the cause of constipation, but help cleanse the body and restore natural microflora.
Fast-acting drugs have the greatest effect for constipation caused by sluggish peristalsis. Not intended for long-term use. The drug is taken in the evening so that stool appears in the morning. Thinning medications are contraindicated for anal fissures, uterine bleeding, and hemorrhoids during exacerbation. Drugs in this group include:
The drugs are available in the form of tablets, syrups, suppositories, and drops.
Prebiotics are delayed-acting drugs. The main task of prebiotics is to restore normal intestinal microflora. Drugs in this group are safe for nursing mothers and children. A mild laxative does not act instantly, but, unlike irritating drugs, prebiotics can be used for a long time. The main thing is to follow the instructions. Prebiotics include Duphalac, Goodluck, and Exportal.
Caring for seams
While the patient is in the hospital, suture care is almost entirely provided by medical personnel. After discharge, this responsibility falls on the patient. Recommendations for the care of postoperative sutures:
- The seams should not be wet or scratched.
- Physical activity should be limited.
- Contact sports and swimming should be excluded.
- If pain, redness or swelling occurs, seek medical attention immediately.
Rehabilitation after rectal surgery has some peculiarities, since after each act of defecation the patient needs a sitz bath with potassium permanganate before dressing.
Both at the market and at the pharmacy
Please note that self-medication is unacceptable! All medications, including herbal ones, must be recommended by a doctor. This is due to the fact that many of them have a fairly wide list of contraindications and side effects. For example, herbs can trigger the development of allergies.
It is also not recommended to “prescribe” pharmaceutical products yourself. First, you don't know what kind of liver problem you're dealing with. So, for example, gallstones may already form in the gall bladder, and taking choleretic drugs will begin to move them, which ultimately leads the person to the operating table. Secondly, it is advisable to select the dosage individually, and only a doctor can do this. So if you have digestive problems, first visit a specialist.
It has been proven that taking vitamins also contributes to the high-quality restoration of liver cells. They can be obtained from regular foods.
| Vitamin | Effects on the liver | Contents in permitted products |
| Vitamin A (retinol). May accumulate in the liver itself | Protects against the formation of stones. | Carrots, pumpkin, sweet peppers, broccoli, peaches, apples, apricots, rose hips, milk, cottage cheese, butter. |
| Vitamin E | Protects against cell death. | Vegetable oils, butter, milk, eggs, meat, whole grain bread. |
| Vitamin C. Can accumulate in the liver | Helps increase bile production. | Vegetables fruits. Berries: sea buckthorn, rose hips, black currant. |
| Vitamin B1 (thiamine) | Helps improve carbohydrate metabolism, ensures pigment metabolism, and cleanses the blood of harmful substances. | Bran bread, yeast, potatoes, carrots, cabbage, beef. |
| Vitamin B2 (riboflavin). May accumulate in the liver | The vitamin is involved in the restoration of liver cells, and is especially often used in the treatment of cirrhosis. | Almonds, eggs, yeast, cottage cheese, broccoli. |
| Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) | Takes an active part in fat metabolism, improves bile production and actively restores liver cells. | Sprouted grains, walnuts, potatoes, carrots, white cabbage, tomatoes, citrus fruits, strawberries, cherries, eggs, cereals. |
| Vitamin B9 (folic acid) | Its use improves bile production and the general condition of the liver. | Tomatoes, carrots, beets, eggs, nuts, wheat bread, whole grain rye bread. |
| Vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin) | Improves the liver's ability to process glucose and improves protein metabolism. Its use regenerates liver cells and stimulates bile production. The cleansing function of the liver increases. | Meat, fish, milk, eggs, yeast. |
| Vitamin B15 (pangamic acid) | Improves the regeneration of liver cells and promotes the activation of fat metabolism. | Pumpkin seeds, sunflower seeds, sesame seeds, whole grain bread, melon, watermelon, apricot kernels, nuts. |
| Vitamin PP (niacin) | Allows the accumulation of glycogen, reduces cholesterol levels and normalizes liver function. | Pineapples, rye bread, buckwheat, meat. |
Folk remedies
Folk remedies can be a good help in rehabilitation therapy if they are selected correctly and with caution. Patients who have undergone surgery are advised to:
- Fruit and berry collection of rose hips, black currants and raspberries: mix the ingredients in equal proportions and pour 2 tablespoons of the collection with 250 ml of boiling water. Heat the mixture for at least 5 minutes in a water bath. Leave covered for 2 hours, strain and take 1/2 cup twice a day.
- Boil 500 g of pitted plums for 1 hour in 1 liter of water. Take 1/2 cup of the cooled drink 3 times a day.
Herbs after intestinal surgery
Herbal medicine can be considered as an adjuvant. The selection of herbs and infusions should be coordinated with a competent specialist. Vitamin-rich medicinal herbs to restore intestinal function:
- 1 teaspoon of cumin is poured into 1 glass of boiling water and taken chilled instead of tea during meals.
- 1 tablespoon of chamomile flowers is brewed with 250 ml of boiling water and left for 10 minutes. Take with meals 3 times a day.