At first glance, headache, diarrhea and fever have little in common: the temperature usually rises with viral respiratory tract infections.
At the same time, diarrhea indicates intestinal disorders, and headaches occur with increased blood pressure or fatigue.
In fact, doctors often have to deal with just this combination of patient complaints.
Such symptoms may indicate the development of a variety of diseases in the body. And each of them is very important when making a diagnosis.
For example, diarrhea is a symptom of food poisoning or dysentery. But if it is accompanied by a high temperature, typhoid fever or rotavirus can also be suspected. Headache is one of the typical signs of general intoxication of the body, and can accompany almost any pathology.
Intoxication of the body occurs both from food or chemical poisoning and from influenza. It is caused by waste products of pathogenic microorganisms that actively multiply during infectious diseases.
Causes of weakness, nausea, severe diarrhea and headache, what it could be
The entire list of causes can be divided into pathological and physiological. What can cause diarrhea, nausea, severe headaches, what could be the physiological (non-dangerous) and pathological causes of such dangerous and unpleasant symptoms? The most common cause of severe weakness, nausea, diarrhea and even vomiting without fever is food poisoning, most often due to spoiled food or improper preparation.
The second place that causes severe weakness, nausea and diarrhea is an infectious lesion, an infection entering the body of an adult or child. In this case, defecation disturbance manifests itself very strongly in the form of frequent and very loose stools. Diarrhea during infection in an adult can be mixed with pus, mucus, bile, and inclusions of blood (scarlet or black (blood during diarrhea can be black if it manages to coagulate while passing through the gastrointestinal tract)). If there are clear traces of yellow, green, white or clear mucus in the diarrhea, then such symptoms are likely to indicate a pathological cause of diarrhea. If the diarrhea with blood is scarlet or black (dark brown), then this is a sign of internal bleeding. If blood appears from the rectum during diarrhea, which does not stop, and scarlet blood from the anus only intensifies or does not stop for a long time, it is necessary to call emergency medical help (especially if the person becomes very weak or loses consciousness).
Impurities in stool and abdominal pain along with nausea often become one of the common symptoms of chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (pancreas, gall bladder, intestinal diseases or stomach, the formation of inflammatory processes in them or ulcerative lesions of the mucous membrane of the stomach or intestinal area). If there is frequent aching or pulling in the stomach, a feeling as if there is a lot of nausea, then such symptoms cannot be ignored. Sluggish chronic diseases often cause aching, mild nagging pain in the abdomen, dull pain in the stomach. More serious and acute forms of pathological processes and diseases lead to the appearance of symptoms such as acute, throbbing or cramping pain in the abdomen, very severe sharp, burning pain in the intestines or stomach, and sometimes there may be cramps (cutting pain in the abdomen). Further details about the causes of pain in the lower abdomen with diarrhea, weakness and severe nausea, depending on the factors that provoke them.
Stress and bowel problems
Severe weakness, reluctance to do anything, drowsiness and loose stools may indicate excessive tension and nervous excitement. Stress is often accompanied by headaches. A person does not consciously feel anxiety or fear, but the body clearly gives a signal: it’s time to rest.
Causes of loose stools and temperature of 37 degrees
The appearance of fever, weakness and loose stools is usually associated with the development of intestinal viruses and infections. In this condition, rotavirus is often detected. Sometimes low-grade inflammation can be a sign of gastroenteritis. Infection occurs in several ways:
- unwashed plant products;
- unboiled water;
- water from reservoirs that gets into the mouth;
- communication with infected people.
On the 2nd day, a person infected with rotavirus becomes dangerous to others. The acute stage of the disease begins. Loose stools occur up to 10 times a day, the temperature gradually rises to 38-38.5 degrees. Characteristic signs of intestinal flu are sneezing and sore throat.
There is pain in the abdomen, the stool becomes clay-like, and the color varies from yellow to gray. Sometimes mucus appears in the stool.
Useful information: Why does vomiting and diarrhea occur after sea in adults and children?
Indications for visiting a doctor
The main reason for seeking help for diarrhea is the risk of dehydration and increased intoxication. Contact your doctor if you have the following symptoms:
- dry lips and mucous membranes of the mouth;
- constant thirst;
- confusion;
- rare urination;
- general weakness;
- lowering blood pressure.
The presence of severe pain in the abdominal cavity, accompanied by intoxication, is a dangerous symptom that requires medical intervention.
Treatment methods
Doctors may prescribe medications to combat weakness after diarrhea. An excellent remedy widely used to alleviate the condition both during and after diarrhea is Regidron. The product is intended for rehydration. Corrects electrolyte and fluid imbalances in the body. Sold in powder form for dilution in water. Used to treat adults and children.
Severe weakness after diarrhea will pass in a short time if you follow your doctor's recommendations. To quickly restore strength, it is recommended that after complete recovery from stool disorder, you eat a lot of protein foods and foods containing vitamin C. The complex effect and replenishment of the necessary substances by the body with the help of proper nutrition will improve the condition and fill you with energy in a short time.
Physiological (non-pathological) causes of diarrhea, nausea and weakness
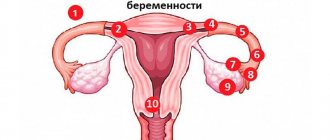
Weakness and mild nausea may appear due to overwork, prolonged exposure to direct sunlight, causing overheating of the body, due to moderate alcohol intoxication or due to fluctuations in blood pressure. Loose stools are sometimes one of the side effects of drug therapy. A separate discussion is the state of pregnancy in women, when the work of all organs and systems is being restructured, aimed at increasing energy potential, which will ensure the body’s ability to cope with double the load. This can cause temporary discomfort, so if the woman has not used protection, it is worth purchasing a pregnancy test. When pregnancy is confirmed, a woman should contact a gynecologist, who will prescribe a course of maintenance therapy that eliminates unpleasant symptoms.
Colds and loose stools
With acute respiratory infections and acute respiratory viral infections, severe weakness occurs, during which it is impossible to get out of bed. Appetite sharply deteriorates due to a runny nose, sore throat, and loss of smell. Diarrhea can occur as a result of taking medications (especially those treated with sore throat lozenges).
Specific causes of diarrhea, weakness and nausea are the presence of parasites in the body, excessive fasting with enthusiasm for various diets. Loose stools often occur during a sudden transition from strict restrictions to normal nutrition.
Useful information: Loose stools and pain in the lower abdomen: diseases hiding behind them
Frequent loose stools and weakness can be treated only after a full diagnosis and testing. Timely identification of the causes of unpleasant symptoms is the best way to quickly get rid of the disease without the development of complications and associated pathologies.
Appendicitis
A dangerous disease that can affect anyone. Characteristic symptoms: loose stools or constipation, nausea, vomiting and fever. Severe pain can begin from the center of the abdomen and move to the right hypochondrium. In a child, appendicitis develops rapidly and is difficult to diagnose.
Advice! If there is severe pain, consult a doctor immediately with your child, as the symptoms increase very quickly and peritonitis may develop.
Diseases as a cause of symptoms
Nausea and loose stools with fever develop during exacerbation of certain gastrointestinal diseases:
- acute gastritis with inflammation of the mucous membrane;
- exacerbation of pancreatitis - pancreas;
- attacks of cholecystitis - problems with the gallbladder;
- acute enterocolitis or colitis;
- dysbacteriosis;
- neoplasms in the gastrointestinal tract at stages 3-4 with additional symptoms;
- appendicitis.
Useful information: Causes of bloating and flatulence during pregnancy and methods of treating them.
Symptomatic treatment in this case is only possible in parallel with the main treatment of the disease, as well as in cases where the main treatment does not help.
If there is diarrhea, nausea, severe weakness - pathological causes (diseases)
Pathological causes include those that provoke the development of diseases, sometimes very serious:
1 If a person feels sick and nauseous, it may be food intoxication;
2 intestinal infections (severe and frequent diarrhea, high body temperature (37, 37.5, 38 degrees));
3 parasitic infestations (often causing headache, diarrhea, joint pain, weakness and fatigue);
4 enteropathy (severe and excessive weakness due to diarrhea, swelling in the tongue, a feeling of strong and unbearable itching in the throat, heartburn and nausea, pain in the abdomen (sharp pain in the stomach as a reaction to an allergen entering the body)), dehydration;
5 diseases of individual organs of the digestive system;
6 disorders of the vestibular system (mild or mild nausea, dizziness, feeling of absent-mindedness);
7 cardiovascular disorders.
Most often, when there is diarrhea, weakness, nausea, there is a suspicion of food poisoning. This is a condition when the body is intoxicated through the action of harmful substances ingested with poor-quality or stale food. If appropriate measures are not taken in a timely manner, toxic substances from the intestines will enter the bloodstream, spreading them throughout the body. This threatens general intoxication, which is very dangerous for health.
Helminthiases, which develop as a result of damage to body tissues by parasites, are often accompanied by nausea, increased fatigue, weakness, and dizziness. A local reaction to waste products of helminths, which poison the body’s fluids with their toxins, often manifests itself as diarrhea syndrome. Tissues affected by parasites lose the ability to fully perform their functions, and the processes of normal food processing and absorption are disrupted. General malaise occurs, patients complain of loss of strength against the background of progressive nutritional deficiency.
With severe weakness, regular diarrhea and nausea, the development of enteropathy can be suspected. This disease is characterized by a chronic course and has a non-inflammatory etiology. It is less common than well-studied diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, and has its causes in the form of individual intolerance or an allergic reaction of the body to certain products (celiac disease, malabsorption syndrome). Some types of enteropathies develop against the background of lymphovenous and arterial disorders of the circulatory system of intestinal tissues. The clinical symptoms of enteropathy are expressed in diarrhea of varying intensity, painful tingling in the area around the navel, and periodic nausea.
In the instructions for medications, in the list of side effects, nausea and diarrhea are often indicated. Therefore, if a patient notes the severity of these phenomena during a course of therapy with a certain medication, this should be reported to the doctor. If there is an option to replace the drug with another, the doctor will change the treatment regimen. But in some situations this possibility is not available, when it comes, for example, to anticancer drugs. Their use has a negative impact on the general condition of the patient; improvement should occur only after completion of the course of treatment. Vegetative-vascular disorders and low blood pressure can also cause headaches, mild nausea, and general malaise. With cardiovascular pathologies, the body does not receive the amount of oxygen it needs, so the patient may be bothered by a state of constant weakness and increased fatigue. The patient complains of excessive sweating, dizziness, with constant nausea, food is poorly digested and diarrhea appears.
First aid for fever, diarrhea and vomiting
With a combination of severe symptoms, you need to remember that standard methods are prohibited or are ineffective:
- You should not immediately take drugs that stop diarrhea, if it is not every 40 minutes, and less often - Loperamide, Phthalazol and other similar drugs. Diarrhea and vomiting should cleanse the body of toxins; if this does not happen, intoxication with complications will occur;
- if you know that the cause is poisoning, drink a liter of water and induce vomiting to cleanse the stomach;
- then you can take a sorbent to remove residual harmful substances - Polysorb, White Coal, Smecta. Activated black carbon acts more aggressively on the body;
- Remember to drink plenty of water to restore balance, as dehydration may occur after severe diarrhea and vomiting.
To prevent leaching of minerals, drink Regidron solution or similar preparations with salt components.
Treatment
Symptomatic therapy is only a temporary relief of the condition. The primary treatment for diarrhea depends on the cause of symptoms and the etiology of the disease. There are 3 criteria for therapy - diet, medications, recovery period. In case of infectious diseases, the patient is placed in an inpatient department, where he is under the supervision of medical personnel.
Drug treatment
Medications are prescribed by a doctor. Main groups of drugs:
- broad-spectrum antibiotics for infections;
- sorbents for removing toxins;
- antidiarrheal;
- antispasmodics;
- analgesics;
- antipyretics;
- probiotics to restore intestinal microflora.
To restore lost fluid and water-salt balance after diarrhea, a large volume of solutions is injected intravenously.
Traditional methods of treatment
Traditional medicine is used only in case of short-term symptoms that are not associated with serious illnesses. Recipes are aimed at improving digestion and eliminating diarrhea. To do this, take rice water and follow a diet with boiled eggs. To eliminate headaches, apply a cold compress to the forehead.
Other causes and psychosomatics
An unpleasant condition that prevents you from getting out of bed can also arise as a result of other factors. They are completely unrelated to the course of gastrointestinal disease:
- prolonged depression and emotional turmoil;
- VSD and problems with the nervous system;
- change in climate and diet, for example, when moving to the Middle East.
Some believe that such symptoms may be a sign of pregnancy. However, it is not characterized by a prolonged increase in temperature and constant loose stools with or without impurities.
Other illnesses causing diarrhea (diarrhea), nausea and headache with severe weakness
What could happen if nausea and diarrhea appeared at the same time? If everything is in order with your diet, the food is fresh and of high quality, but after eating it you are bothered by an unpleasant feeling of nausea and diarrhea, it is worth checking the functioning of your digestive organs. Many gastrointestinal diseases are manifested by diarrhea, nausea against a background of general weakness and headaches:
1 Gastritis and feeling of nausea and weakness, problems with stool. When the gastric mucosa is inflamed due to the influence of stress factors, allergies, excessive dosage of medications, consumption of hot, spicy, fatty foods, attacks of nausea and diarrhea appear. Such symptoms, in the form of stool disturbances (diarrhea like water), weakness and a feeling of nausea, are characteristic of the acute course of the disease. If the patient consults a gastroenterologist in time, the course of therapy helps restore the integrity of the mucous membrane, relieve the inflammatory process and help normalize the digestive function of the stomach. The chronic form of gastritis requires much longer therapy, a strict diet for the entire period of the disease until complete recovery. The sharp pains that occur after each meal, periodic nausea and diarrhea should gradually go away.
2 Pancreatitis. This disease is characterized by abnormalities in the functioning of the pancreas caused by an inflammatory process in its tissues. Disorder of the pancreas functions disrupts the entire digestive process. The pancreatic juices secreted by the organ contain a set of certain enzymes involved in the breakdown of food into its component parts, which must be absorbed by the body. Inflamed gland tissue is not able to provide sufficient levels of enzymes, which means proteins, fats and carbohydrates are not subject to a sufficient level of breakdown. During the acute form of the disease, the patient suffers from severe epigastric pain radiating to the back area. Often they become encircling in nature. Severe nausea appears periodically, accompanied by headache and diarrhea. Pancreatitis requires an urgent course of therapy, since pancreatic tissue is restored very slowly, and a chronic process can lead to the development of pancreatic necrosis.
3 Inflammation of the appendix - nausea, diarrhea and temperature of 37 and above. When the appendix is inflamed, there may not be a fever, but pain in the lower abdomen on the right, in the center or in another part of the abdomen, along with severe nausea, are some of the common symptoms of appendicitis. Moreover, a nagging pain in the lower abdomen, in the right side, may appear; sometimes, along with nausea during appendicitis, vomiting, cramping or acute pain in the lower abdomen appears. This process is provoked by two factors: blockage of the lumen of the appendix of the cecum or activation of pathogenic bacteria in this part of the intestine, which causes severe pain in the right lower abdomen. Symptoms of appendicitis are expressed in sharp pain in the abdomen, aggravated by sneezing and a coughing attack. The patient develops diarrhea and nausea, and a possible increase in body temperature. If inflammation of the appendix is suspected, the patient needs to undergo a thorough diagnosis in order to provide all the necessary assistance in a timely manner, otherwise complications may arise in the form of peritonitis, which threatens the patient’s life.
4 If you feel sick and have diarrhea in the morning, it may be an ulcerative lesion of the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum. Due to constant irritation of the mucous membrane, small defects first form on its surface, and then wounds that deepen into the tissues of the organs. The formation of wounds leads to erosion, and the more serious the damage to the mucous membrane, the more extensive the erosive defects. The appearance of ulcerative lesions is provoked by a complicated course of gastritis, inflammation in the tissues of the pancreas, and the activity of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. Peptic ulcer disease during its acute course is characterized by the presence of intense pain of a spasmodic nature in the epigastric region. The patient suffers from heartburn, belching, nausea, which is accompanied by diarrhea syndrome. For many, the disease has a pronounced seasonal nature, with periods of exacerbation occurring in spring or autumn. Symptoms are pronounced after overeating, eating fatty foods rich in spices, and drinking alcohol.
5 Liver disease may be accompanied by symptoms such as nausea and diarrhea without fever. With the development of inflammation and swelling of the liver parenchyma, the patient complains of dyspepsia, his sense of taste is distorted, and stool instability is manifested by alternating states of constipation and diarrhea. After eating, you begin to feel sick, and in the morning you often feel an unpleasant taste in your mouth, giving off a bitter taste. Similar symptoms are observed with cholecystitis.
Intestinal (stomach) flu – fever, vomiting, diarrhea – Diagnostician
Yesterday, for the first time in my life, I shit and vomited at the same time. I didn't even think that this was possible. Dmitry
Every year, 25 million people on planet Earth suffer from viral gastroenteritis. This scourge is popularly called intestinal or stomach flu.
Fever, aches, headache, nausea, VOMITING, DIARRHEA
Affecting the stomach and intestines, rotaviruses, enteroviruses (noroviruses), astroviruses, and adenoviruses cause repeated vomiting and uncontrollable diarrhea.
Intestinal (stomach) flu is transmitted from person to person through kissing and coughing, as well as through dishes, hygiene items and the toilet. You can get infected through water - bleach does not kill the virus!!! By attacking everyone around, the virus spreads quickly. Often entire families, classes, departments, divisions get sick...
. Uncontrollable vomiting by the whole family
The health of those infected can vary greatly, from mild illness to life-threatening conditions. The most vulnerable are young children and the elderly. Do not give up! It will be unpleasant, but not for long. In adults, intestinal flu lasts 12-48 hours, and in young children up to 5-7 days.
IMPORTANT!!! 3-5 days after recovery, the person is still contagious.
A cure for intestinal (stomach) flu has NOT yet been invented
Antibiotics (ersefuril, furazolidone, chloramphenicol, etc.) do not act on the virus, but they destroy the normal intestinal microflora.
Domestic know-how : instrumentation, viferon, arbidol - do not affect the duration and severity of intestinal flu. However, in Russia they have become an important means of psychotherapy - something must be done.
If you have vomiting and/or diarrhea:
- stop eating;
- do not push medications into yourself, for example, activated carbon or smecta - vomiting will intensify;
- drink liquids (water, tea, compote, jelly) in small sips - unfortunately, in the first hours of illness this also increases vomiting;
- if there is repeated vomiting, and even diarrhea, it’s time to drink saline solutions (gastrolit, rehydron, glucosalan);
How to make your own saline solution for dehydration! Water or weakly brewed chamomile tea 700 ml + decoction of dried apricots and/or raisins 300 ml + 4-8 teaspoons of sugar + 1 teaspoon of table salt + 1/2 teaspoon of soda. Drink in small sips.
- if there is no vomiting or it has already stopped, take smecta, enterosgel or activated charcoal.
Recipe for “BLUE” jelly from Natalia (see comments): At the first sign of poisoning, medicinal jelly is an amazing thing! I advise you to take note of this recipe: bring 800 ml of water to a boil, pour in a mixture of 200 ml of water + 5 tsp in a thin stream. potato starch + 5 tsp. sugar + 5 times citric acid on the tip of a knife.
Boil for a minute and turn off. The jelly definitely needs to be cooled!!! For 1 glass of warm (attention, not hot) jelly, 1 TEASPOON of pharmaceutical iodine. The jelly will turn BLUE. People call it that way: “BLUE KISSEL”. Take 1-2 tbsp. spoon every 10 minutes so as not to provoke vomiting. It will get better very quickly.
Be sure to save this recipe and stay healthy!!!!
Stopping vomiting and diarrhea is NOT recommended
Vomiting and diarrhea remove viruses and their toxins from the stomach and intestines. By stopping vomiting and diarrhea, you lock toxic toxins inside. They are absorbed into the blood and poison the body. Very often, an hour after taking motilium or cerucal, a high temperature rises, chills, and a headache appear - these are poisonous toxins that penetrate the blood.
If vomiting and diarrhea are physically unbearable for you or you have an important business meeting, then:
- suppress vomiting - motilium (by mouth), cerucal (injection);
- stop diarrhea - loperamide (Imodium, Lopedium, Enterobene, Suprilop), lispafen, Reasec, Debridate.
Fever, aches, abdominal pain, headache - what to do?
- You can afford a little painkiller - Nurofen or paracetamol. In large doses, drugs have a bad effect on the stomach.
- Never give children aspirin or analgin - there are a lot of side effects. Analgin, also known as metamizole sodium, is banned in Europe, America and 40 other countries.
IMPORTANT!!! If you still have stomach pain, fever, or blood in your vomit or stool after 36 hours, see your doctor.
After 12-24 hours, you can gradually begin to eat. For starters, crackers, bagels, rice porridge with water, bananas, and mashed potatoes are suitable. You need to eat in small portions. For a while you will have to give up fried, fatty, spicy foods. And also exclude milk, alcohol, coffee, and fast food from your diet.
You are already better... It will take time to improve the functioning of the stomach, intestines, liver and pancreas. Some people cannot do without the help of pills.
- Enveloping agents (phospholugel, maalox, almagel) will protect the mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines: take 1 hour after meals and at night 3 times a day - 5-10 days.
- Enzymes (Creon, Mezim, Pancreatin, Abomin) for better digestion of food: take with meals - 7-14 days.
IMPORTANT!!! Viral gastroenteritis can be confused with gastroenteritis caused by bacteria (salmonella, E. coli, yersinia, etc.) or parasites (giardia, amoeba dysentery).
Bacterial gastroenteritis is treated with antibiotics. If loose stools persist for more than 48 hours, test the stool for intestinal group, worm eggs and protozoa. Take an intestinal antibiotic - just in case of emergency.
For example, furazolidone, ersefuril, levomycin.
You can get the stomach flu again and again. Some people get sick 2-3 times a year.
Take care of yourself, Your Diagnosticer .
Thank you, dear commentators. A lot of interesting. And most importantly - from life.
Source: https://diagnoster.ru/interesnoe/kishechnyj-gripp/
Diet therapy
After a person recovers, no matter what intestinal disorder he had, he must follow a diet until complete recovery.
- It is necessary to exclude absolutely all dairy products from the diet. An exception can be made only for special, non-acidic kefir.
- Fruits, vegetables and berries should not be eaten raw. The same applies to various juices.
- You should still try to drink plenty of fluids.
- Any porridge cooked in water is welcome.
- You can eat steamed vegetables along with porridge.
- As prescribed by your doctor, you need to take enzymes for some time to facilitate digestion.
- There is no need to force yourself to eat. You need to eat as much as you want. This also applies to the child.
- It is better to eat in small portions, but more often, without overloading the digestive system.
Dietary adherence
During diarrhea, nutrients, micro and macroelements leave the body very quickly. Therefore, special attention should be paid to the diet. It should be aimed at eating foods rich in essential minerals. Vitamin complexes are included. You need to eat small portions every three hours. Weakness after diarrhea can be prevented by observing the following aspects:
- clean water can be replaced with decoctions of rose hips or dried fruits (prunes are an exception). The liquid is consumed in small portions throughout the day. It is recommended to drink at least two liters per day;
- Rice water or oak bark tincture has a good fixing effect;
- boiled porridge in clean water, without the use of oil (rice, buckwheat, oatmeal);
- if your condition improves, you can take small portions of chicken broth with rice;
- mashed potatoes;
- Crackers can be an alternative to fresh bread at the time of illness.
All food consumed should be warm. During illness, drinking mineral or other water with gas is strictly not recommended. Drinking milk can worsen the disease. Alcohol, spicy and fried foods, various pickles and marinades are absolutely excluded. After eliminating the cause of diarrhea, the diet will need to be followed for 7 to 10 days. Favorite foods are introduced into the diet carefully and gradually. Food such as black bread should be consumed only 10 days after the end of diarrhea. A positive effect comes from taking yoghurts that contain live bacteria.
Vomiting temperature weakness in an adult treatment
Both vomiting and diarrhea are unpleasant symptoms that can accompany a wide range of diseases. They not only disrupt the usual rhythm of everyday life, but cause physical discomfort, cause general weakness, and in some cases can even pose a threat to life.
Vomiting and diarrhea in an adult are signs of intoxication. This condition may be accompanied by an increase in temperature. The combination of two or three factors indicates that the body requires urgent, and most importantly, the right help. What are the causes of the condition, what to do, how and with what to treat the patient in this case?
Provoking factors
Sudden diarrhea and vomiting in an adult are protective reactions of the body, which thus tries to get rid of toxins that have entered it. In some cases, this symptom complex indicates the development of serious diseases, as well as organic changes in the walls of the gastrointestinal tract. The most common causes of diarrhea and vomiting:
- Banal poisoning from low-quality products.
- Overeating, abuse of fatty foods with enzyme deficiency.
- Entering the body with a bacterial infection (salmonellosis, dysentery, cholera).
- Viral infection (rotavirus, hepatitis).
- Stomach diseases (gastritis, peptic ulcer).
- Inflammation of the pancreas.
- Cholecystitis.
- Enterocolitis, irritable bowel syndrome.
- Poisoning with poisons and toxins (mercury vapor, nitrates, poisonous mushrooms).
Some features
Sometimes nausea and diarrhea occur without fever in an adult. In this case, overeating or mild poisoning is assumed.
The condition resolves without medical intervention, through symptomatic therapy.
Prolonged vomiting and diarrhea without fever indicate irritable gastrointestinal syndrome, which can occur against the background of nervous shock. The use of sedatives is added to general therapy.
Diarrhea and a temperature of 38° are observed with tumor diseases, but, as a rule, they are accompanied by an increase in severe painful sensations, and therefore early appearances of these symptoms are detected. Vomiting without fever and diarrhea may indicate overstretching of the stomach walls, for example due to the consumption of large amounts of food or liquid.
First aid
If an adult experiences symptoms such as nausea, fever, vomiting, diarrhea, chills, weakness, or abdominal pain, it is important to know how to provide first aid. Of course, it is better to call a doctor so that he can determine the causes of the ailment, and then begin to treat the patient using the correct method, but in some cases you can do it on your own.
The necessary measures are sufficient drinking, rest, and medications that relieve symptoms.
If diarrhea and nausea are very severe, then it is better to call a doctor without delay, without blurring the picture of the disease with medical intervention. When you are sure of food poisoning, you are allowed to immediately begin gastric lavage.
To do this, you need to drink a large volume of clean water or a weak solution of potassium permanganate, and then induce vomiting artificially.
Drug therapy
Depending on the causes of occurrence, medication for vomiting and diarrhea may have some features. We list its main rules:
- You cannot take medicine for diarrhea that suppresses peristalsis (Imodium, Loperamide) without a doctor’s recommendation, since the symptoms that arise are a natural attempt by the body to cleanse itself. By trying to stop the release of toxins, you give them the opportunity to enter the bloodstream, and as a result, cause more serious consequences.
- First of all, sorbents are taken. These can be tablets of regular Activated Carbon (about 10 pieces) or Smecta, Enterosgel, Sorbex in the recommended dosage. The disadvantage of taking Activated Charcoal is its ability to give stool a dark color, and this coincides with a sign of intraintestinal bleeding. Such symptoms may prevent a specialist from making a correct diagnosis.
- If a person is nauseous and it is not possible to take the sorbent orally, it is advisable to do an enema with its addition.
- If vomiting and diarrhea are severe or prolonged enough, there is a risk of dehydration. To avoid it, you need to drink more water and also take Regidron solution.
- When overeating or enzymatic deficiency is suspected, drugs with pancreatin (Mezim, Festal) will help eliminate the symptoms.
- If the doctor has determined that the cause of the disease is bacterial, treatment with antibiotics or antimicrobial drugs is necessary. However, you should not self-medicate, since if you make a mistake, taking them can be harmful (for example, with dysbacteriosis). A drug approved for adults that can treat intestinal infections is Nifuroxazide (Enterofuril).
- When a person vomits too often, it is necessary to drink a lot of water to reduce the stress on the stomach walls. Drugs such as Diazepam and Metoclopramide will help stop vomiting in an adult.
Separately, the treatment of an adult patient with a high temperature (38-39 degrees) should be discussed. As you know, high temperature is not only a sign of inflammation, but also the body’s main protective reaction; it does not always need to be brought down.
You can take antifever medications if the temperature exceeds 38°.
If the fever rises higher and higher, be sure to call a doctor, and before he arrives, provide the patient with rest, wipe him with a damp towel, give him water to drink, or better yet, Regidron solution.
Folk remedies
Vomiting and diarrhea can be effectively treated with traditional medicine. Some recipes will relieve such unpleasant symptoms as nausea, chills, weakness, improve the general condition of the patient, and give him strength. For example:
- Chamomile decoction helps with spastic intestinal pain.
- Chills and high fever can be treated with linden and cranberry tea, as well as rose hip decoction. The sweating that occurs when taking them relieves heat naturally.
- Fennel seeds are also good for stomach pain; they gently relieve cramps, bloating, and normalize digestion. You need to drink the decoction several times a day in small portions.
- Vomiting, diarrhea, and fever can be easily relieved with ginger tea, but it must be taken one tablespoon at a time. It has been verified that with this intake a person stops vomiting, and nausea is noticeably weakened.
Treatment with folk remedies is recommended to be used as auxiliary therapy. Very often, these methods help to significantly alleviate the patient’s condition, as well as to recover from an illness.
Recommendations for nutrition and care
In addition to targeted treatment of vomiting, diarrhea and fever in an adult, you can alleviate his condition with proper care. What can be done to make the patient feel better?
- Ensure proper dietary nutrition. What you can eat during diarrhea should be well absorbed and not create additional stress on the stomach. It is better to eat low-fat kefir, crackers, rice water, vegetable or light chicken broth. Under no circumstances should you overeat.
- During the rehabilitation period, give preference to porridges with water, as well as lean varieties of meat or fish.
- Follow the drinking regime for diarrhea and vomiting: drink often, but little by little
- Wipe the patient with a damp towel, provide fresh cool air in the room.
- If there is a lot of vomiting, the patient should rinse his mouth with a decoction of mint or chamomile.
Source: https://borodaprofi.ru/medicina/rvota-temperatura-slabost-u-vzroslogo-lechenie.html
Prevention
Since nausea, fever and diarrhea often occur due to infections, the main preventive rule is to wash food and hands. This way you can avoid most infections. The second point: treat infectious diseases in a timely manner. Untreated flu can easily migrate to the intestines. And finally, if you suspect an illness, you need to go and talk to a doctor. The sooner treatment begins, the faster it will end in success.
Fever, nausea and diarrhea occur for various reasons, one of the main ones being infections. In next place are poisonings, then chronic gastrointestinal diseases. These 3 reasons can be treated or controlled, the main thing is to do it on time.
Particularly dangerous when absent?
Symptoms: vomiting, diarrhea, temperature, weakness in an adult
Throughout life, a person encounters or suffers from various diseases, which are accompanied by a wide variety of symptoms.
Ailments such as nausea, diarrhea, fever, and weakness indicate pathologies in the digestive system. These signs can appear individually, in combination, or be accompanied by other complaints. Pathologies in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) can be temporary (a case of mild alcohol poisoning) or a long-term infectious process is possible.
If there are no visible explanations for the manifestation of such symptoms, you need to urgently contact a medical institution for an accurate diagnosis of the disease.
Fever, nausea, weakness, diarrhea: what does it mean?
Nausea, vomiting, fever, weakness - these are signs of what, what are the reasons for such manifestations? A normal question that arises from a person experiencing such unpleasant conditions.
Gastric disorders of various types most often accompany symptoms of this nature.
These ailments are often aggravated by conditions such as dizziness, dehydration, fever, chills, etc.
First of all, you need to exclude poisoning of the body:
- food;
- alcohol, drugs;
- medicinal;
- chemical.
Next, the possibility of human infection is analyzed. Stomach infections can be caused by various pathogenic microorganisms:
Any microbe can lead to very serious consequences. Stomach diseases are acute or chronic. In the acute course of the disease, symptoms appear suddenly. Dizziness, fever, nausea, diarrhea, headache, and weakness quickly develop. In this case, you need to seek medical help as soon as possible.
The chronic form of the disease is characterized by stages of exacerbation followed by remission. At moments of exacerbation, symptoms develop as rapidly as in the acute form. During remission, ailments may completely disappear. Then the main task becomes to delay the stage of subsidence of the disease for a longer period.
Vomiting, headache, fever, weakness: relationship with poisoning
The foods that a person consumes daily are designed to provide the body with essential nutrients, vitamins and minerals. But the quality of modern products leaves much to be desired, so their use brings less and less benefit, and the negative effect increases.
Food poisoning caused by staphylococci, which actively multiply in meat and dairy products, is especially dangerous. Symptoms: vomiting, diarrhea, fever, weakness in an adult may indicate such poisoning.
Often the situation is aggravated by the following ailments: dizziness, headache, aching bones.
Approximately the same manifestations are caused by other types of poisoning: alcohol, medications, chemicals. In this case, the patient is advised to drink plenty of fluids, gastric lavage, and any sorbent substances (Polysorb, Activated Carbon, Atoxyl).
In case of any poisoning, you must immediately call emergency help, since only a qualified doctor can assess the degree of intoxication. Only obvious mild alcohol poisoning can be removed at home.
With chemical intoxication, medication and narcotic intoxication - go to the hospital.
Impact of intestinal infections
Different types of pathogens can cause various serious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, including toxic infections:
- staphylococci;
- clostridia botulism;
- salmonella;
- bacteria Bacilluscereus.
If the patient is worried about weakness, nausea, vomiting, fever, the reasons may be infection with one of the listed parasites. In this case, diarrhea, temperature of 39 ° C, weakness, aching bones, headache and other phenomena are possible. The course of the disease can manifest itself in different ways, depending on the individual characteristics of the organism and the infecting microorganism.
Important! For example, an infection caused by clostridia botulism, if properly treated, goes away in one to two days. In the worst case, they can cause paralysis of the respiratory muscles. Failure to provide qualified assistance leads to death
Nausea, diarrhea, fever, weakness as signs of gastrointestinal disease
With any gastrointestinal disease, the patient may feel nauseous and vomit. Diarrhea, increased body temperature up to 39 ° C, and also in this case, there may be aching in the bones, weakness, headache, dizziness, belching, stomach pain, discoloration of stool. These symptoms significantly aggravate the situation and may indicate an exacerbation:
- ulcers of the stomach, duodenum;
- cholecystitis;
- pancreatitis;
- gastritis;
- hepatitis A;
- gastroparesis, etc.
Each of these diseases requires specialized and timely treatment, because delaying treatment can leave a person disabled for life
Vomiting, fever, weakness in an adult - what to do
If symptoms such as fever, dizziness, weakness, diarrhea and vomiting are observed, you must first determine what they are a sign of.
To correctly diagnose the disease, it is necessary to contact a medical institution, and not self-diagnose and independently prescribe any treatment.
There, the patient is sent for the necessary examinations, on the basis of which a diagnosis is made and adequate therapy is prescribed.
Gastrointestinal diseases should not be considered minor or not serious. We all love to eat delicious food, and an advanced stage of the disease can eliminate forever the consumption of such favorite fatty, fried foods. Therefore, it is better to enjoy your favorite food, but in moderation and monitor your well-being, trusting specialists in a timely manner.
If an adult has a fever, nausea, and diarrhea, this indicates the presence of an inflammatory process in the body.
Inflammation is caused by:
- Viral hepatitis.
- Intestinal infection.
- Food poisoning.
Bacilli that cause nausea, loose stools and fever:
- Intestinal amoeba.
- Staphylococcus.
- Rotavirus.
- Salmonella and E. coli.
People with weakened immune systems are most often susceptible to infection.
Causes of diarrhea, vomiting and fever
Any treatment must always begin with identifying the cause of the disease, otherwise the likelihood of relapse is very high. Medications will only treat symptoms.
The simultaneous occurrence of nausea, vomiting and fever indicates a serious illness.
These include:
- Infections in the gastrointestinal tract. Negative reactions are caused by: dysentery, salmonella and intestinal flu.
- Crohn's disease. Severe gastrointestinal pathology, characterized by the appearance of inflamed nodules.
- Local inflammation in the digestive system. These include: ulcers and gastritis.
- Negative effects of heavy metals. In everyday life, this is mercury poisoning.
Less dangerous reasons are:
- Allergy to certain foods.
- Binge eating. The body is trying to get rid of excess food.
- Poisoning from low-quality products.
- Frequent stress. A hormonal surge occurs, which causes similar symptoms.
- Change of residence. The body gets used to the new climate.
- Pregnancy period. If toxicosis occurs in the first trimester, it is not scary. But to alleviate the condition, you should consult a doctor who will prescribe the necessary medications.
These reasons rarely cause an increase in temperature, although it does happen.
First aid for diarrhea and nausea with fever
Emergency elimination of such symptoms does not imply complete treatment. The goal is to alleviate the condition.
Experts recommend carrying out certain activities:
- Gastric lavage. This must be done when there is confidence in poisoning. This procedure is carried out as follows: drink about 6 glasses of water with the addition of potassium permanganate and induce vomiting. Lavage is done until clean water comes out of the stomach. If the procedure is not successful, an ambulance is immediately called.
Use of absorbents. The most famous and popular medicine is activated carbon. Take 1 tablet per 1 kg of body weight. This remedy is used if there is a suspicion of poisoning or infection. Then, be sure to empty your intestines, otherwise toxins will begin to be absorbed into the colon.
- Taking antispasmodics. The use of these drugs is necessary to reduce pain caused by spasms of the liver and intestinal muscles. Medicines used: Duspatalin and No-shpa.
- It is advisable to do an enema, which will immediately improve your well-being.
- You should not take medicine for diarrhea without a doctor's prescription. First, the body tries to eliminate harmful bacteria on its own, and medications deprive it of this opportunity.
- To prevent dehydration, you need to drink salted water.
- Self-medication is allowed only to reduce symptoms, and full treatment should be carried out by specialists. Self-therapy can worsen the patient's condition.
Relief from diarrhea and nausea with fever
Naturally, the best option is to contact a specialist who will select a treatment regimen. But many try to alleviate the condition on their own, at home.
To do this, you should follow important recommendations:
Source: https://morewomen.ru/info/simptomy-rvota-ponos-temperatura-slabost-u/
Nausea diarrhea temperature weakness in an adult than to treat
- 1 Fever, nausea, weakness, diarrhea: what does it mean?
- 2 What does vomiting, diarrhea and fever indicate? 2.1 Infectious diseases
- 2.2 Gastrointestinal diseases
- 2.3 Food poisoning
- 2.4 Others
Throughout life, a person encounters or suffers from various diseases, which are accompanied by a wide variety of symptoms.
Ailments such as nausea, diarrhea, fever, and weakness indicate pathologies in the digestive system. These signs can appear individually, in combination, or be accompanied by other complaints.
Pathologies in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) can be temporary (a case of mild alcohol poisoning) or a long-term infectious process is possible. If there are no visible explanations for the manifestation of such symptoms, you need to urgently contact a medical institution for an accurate diagnosis of the disease.
Features of symptoms of food poisoning
If the diet contained low-quality food products, they could become a source of microorganisms, specific substances and toxins. They lead to nausea, vomiting, loose stools and fever. Almost always, when poisoning occurs, pain begins in the stomach area; the temperature itself does not rise above 38 degrees.
If a child has eaten any household substances - powder, soap, unripe vegetables - poisoning almost always occurs within 2-3 hours.
When food poisoning occurs, symptoms develop rapidly. One moment the person was not tormented by anything, but an hour later he begins to have attacks of diarrhea, severe nausea and weakness. And the temperature is gradually rising. Diarrhea during poisoning can occur 15-20 times a day.
Weakness always accompanies poisoning, and this condition lasts no longer than 2-3 days. If the symptoms only intensify and the temperature rises, you need to consult a doctor.