Diseases and conditions associated with damage to the human gastrointestinal tract are widespread, and according to WHO, Helicobacter pylori infection in Russia (a bacterium that penetrates the stomach) is 80%. This means that the likelihood of developing gastritis and peptic ulcers is very high. Drugs that have a protective effect on the gastric mucosa include the so-called gastroprotectors - pharmacological agents of different structures and chemical effects, which have a positive effect on the inner layer of the stomach lining.
Physiology of the stomach
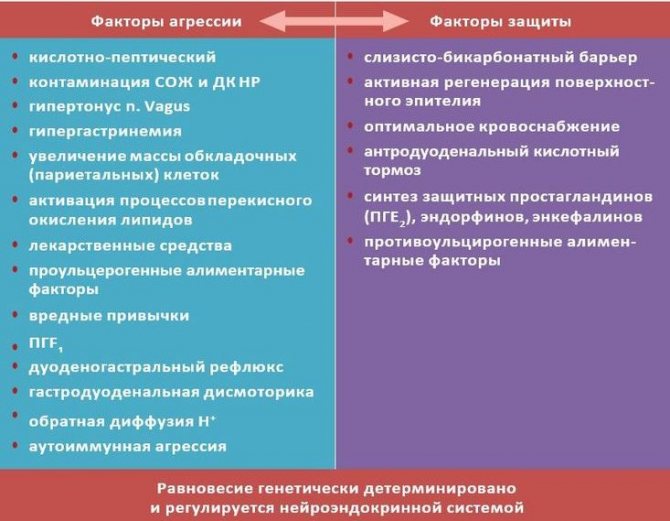
Factors of aggression and protection of the stomach
In a healthy person, the aggressive effect of acidic gastric juice and irritants on the mucous membrane is compensated by protective factors, such as:
- sufficient amount of mucus;
- secretion of own bicarbonates;
- good blood supply and nutrition to all layers;
- the presence of prostaglandins in gastric juice;
- regular gastric emptying and so on.
Normally, the balance is maintained by physiological regulation. When the balance between the factors of aggression and defense is disturbed, with a predominance of the former, the gastric mucosa reacts with inflammation and even the development of a defect or ulcer. Gastroprotectors will help protect the mucous membrane from the aggressive effects of gastric juice and aggressive food components.
Physiotherapy
For gastritis and pancreatitis, physiotherapy improves the general condition. Sinusoidal modulated currents are used, which have an anti-inflammatory effect on the gastrointestinal tract. UHF therapy, based on an electromagnetic field that reduces increased secretory function, gives a good result. Ultraphonophoresis allows you to get rid of pain symptoms due to the effects of medication and ultrasonic vibrations.
UHF therapy gives good results.
Classification of gastroprotectors
There is no single generally accepted classification. According to the most common classification, all gastroprotectors are divided into 2 groups:
- Preparations that exert a protective mechanical effect by forming a film on the gastric mucosa or an enveloping effect: bismuth or aluminum preparations, sucralfate.
- Agents that enhance the protective effect of the mucous membrane and its resistance to irritating influences: cytoprotectors, activators of regenerative processes, stimulators of mucus production.
For each medicine there are indications and contraindications for use, so self-medication is unacceptable; consultation with a doctor is necessary before use.
Features of application
It is important to know:
- It must be taken into account that most gastroprotectors reduce the ability of some drugs to be absorbed into the blood. It is worth taking breaks between medications (1.5-2 hours is enough).
- Antacids can affect salt metabolism in the body.
- The drugs can mask the symptoms of some gastroenterological diseases, so it is recommended to undergo examination before starting use.

Mechanism of action
Representatives of gastroprotectors differ in chemical structure, but their action is based on either mechanical protection of the gastric mucosa or enhancement of the action of protective factors.
Bismuth preparations (De-nol, Escape, Vikanol) form complexes with glycoproteins, which act as a barrier to hydrochloric acid. These compounds increase the viscosity of mucus, which also reduces the aggressive effect of gastric juice. This group reduces acid production, stimulates the production of prostaglandins, and has a bactericidal effect on Helicobacter pylori.
Sucralfate (Venter, Sukrat) under the influence of the acidic environment of the stomach is converted into a paste-like substance, forms a protective film and reduces local inflammation.
Medicines based on aluminum in combination with magnesium (Almagel, Maalox, Phosphalugel) neutralize the existing acid in the lumen of the stomach, reducing its aggressive effect on the mucous membrane.
Misoprostol (Mirolyut, Cytotec) has antisecretory activity, enhances the formation of mucus and bicarbonates, has a cytoprotective effect and promotes the healing of ulcerative defects.
Methyluracil accelerates mucosal restoration processes, increases protein synthesis, and activates regeneration.
Biogenic stimulants (Actovegin, Solcoseryl) are produced from the blood of calves. They improve blood flow in the stomach wall, activate cellular metabolism, and accelerate the healing of erosions. Herbal preparations with biogenic action include Kalanchoe juice, royal jelly, propolis, and sea buckthorn oil.
Herbal remedies based on licorice activate mucus formation in the stomach; cabbage juice also has a similar effect.
Treatment of gastritis in children
Acute gastritis in children can be diagnosed already at school age. If the secretory activity of the child’s stomach is reduced, Ranitidine and Famotidine are prescribed. If the baby has a fever or dizziness, Nurofen syrup and Ibuprofen suppositories are recommended for treatment. Sorbents (activated carbon, Sorbex), enzyme preparations (Creon, Festal) are recommended. Treatment agents are selected only by a doctor.
Find out more about how gastritis is treated.
Indications
Gastroprotectors are used for diseases of the stomach that require protecting its mucous membrane from the aggressive effects of food components and other factors.
Gastroprotectors are used in the treatment of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, such as:
- gastritis, acute and chronic, including erosive;
- peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum;
- stress or symptomatic ulcers;
- ulcers with frequent use of painkillers;
- dyspepsia.
Each of these diseases has its own cause, course and clinical features, so it is better to take medications after consultation with a specialist.
Diet for acute gastritis
The main rule of nutrition is that food during an acute inflammatory process should be gentle and not irritate the mucous membrane. For this reason, boiled, steamed dishes, almost without salt, are recommended for the treatment of acute gastritis. They can be eaten pureed, without the use of herbs and various seasonings. For patients with acute gastritis and gastroduodenitis the following is contraindicated:
- fruits vegetables;
- sour cream;
- confectionery;
- black bread;
- baked goods;
- fried, smoked food;
- alcohol, coffee;
- chocolate;
- canned foods;
- instant porridge.

- Echinacea - medicinal properties of the herb. Instructions for use of Echinacea tablets and tinctures for immunity
- Inhalers for asthma
- Mannik with cottage cheese: recipes with photos
What can you eat if you have acute gastritis? List of permitted products:
- porridge, for example, buckwheat, oatmeal;
- crackers;
- boiled potatoes, mashed potatoes;
- vegetarian soups with cereals;
- low-fat boiled meats, steam cutlets;
- for high acidity: soft-boiled eggs, milk, yogurt, yogurt;
- for low acidity: kefir, natural cottage cheese.
In the first 2 days of illness, due to dyspeptic syndrome, you should only drink liquids. This can be rosehip infusion, strong tea, Borjomi. On day 2, liquid food is introduced into the diet: chicken broth, mucous soups, milk. On the fourth day, the patient can eat rice, semolina or oatmeal, soft-boiled eggs, crackers, fruit jelly, and drink jelly. From the 5th day onwards, it is allowed to include poultry and fish, water porridge, cauliflower, carrots, and dried bread in the menu.
Side effects
The most common side effects include bowel problems such as constipation or diarrhea, nausea and abdominal pain, lower back pain, itchy rash, dizziness and drowsiness. Bismuth preparations are not recommended for long-term use due to the accumulation effect.
Folk remedies
Treatment of pancreatitis and gastritis with folk remedies is auxiliary. To eliminate inflammation, stool disorders and abdominal pain, various herbs are used: St. John's wort, calendula, chamomile, yarrow, etc.
Application of herbs
Medicinal herbs for gastritis and pancreatitis help with inflammatory processes in the stomach and duodenum, and are also effective for enzyme deficiency. Yarrow and St. John's wort will be required in equal quantities. 2 tsp. the mixture of herbs must be poured with 300 ml of boiling water and allowed to brew for 30 minutes. Then filter and take 100 ml 3 times a day 20 minutes before meals. The course of treatment is 1 week.

To prepare the decoction you will need yarrow.
To get rid of inflammation during gastritis and pancreatitis, a mixture of chamomile, linden and calendula will help. 1 tbsp. l. pour 400 ml of boiling water over the herbs and leave for 20-30 minutes. Then strain, take 2 times a day 15 minutes before breakfast and dinner. The course of treatment should be at least two weeks.
Cherry tinctures
You will need 1 kg of dried pitted cherries.
The raw materials for preparing the tincture for the treatment of gastritis and pancreatitis must be thoroughly washed and dried.
Additionally, you will need 1 liter of vodka, which you need to pour over the berries. Then add 200 g of honey. Infuse in a dark place and always in a glass container for a month, shaking occasionally. The resulting medicine should be taken 30 ml with meals 3 times a day for two weeks. This remedy improves appetite and speeds up recovery from gastritis and pancreatitis.
List of drugs
Bismuth preparations (De-nol, Vis-nol and others) are one of the most widely used groups of gastroprotectors
The most common gastroprotectors today are:
- De-nol. The bismuth preparation has a bactericidal effect on Helicobacter, stimulates the production of prostaglandins, mucus and bicarbonates, and has a regenerating effect. The tablets are taken in courses and are contraindicated during pregnancy.
- Venter. In the stomach, under the influence of acid, it is converted into a polymeric substance that covers the affected areas. Increases the synthesis of prostaglandins, reduces the activity of pepsin. Do not take with drugs that reduce acidity, as there will be no effect. Contraindicated during pregnancy and lactation.
- Maalox. Tablets based on aluminum and magnesium salts. Neutralizes the acidity of gastric juice and has an enveloping and adsorbing effect. Not recommended for children; use with caution during pregnancy.
- Misoprostol. A synthetic analogue of prostaglanlins, inhibits the production of hydrochloric acid, increases the amount of mucus, improves microcirculation, and has a wound healing effect. Animals were observed during pregnancy; no consequences were identified. However, pregnant women should take it with caution and strictly as prescribed by the doctor.
- Methyluracil. Activates metabolism, improves tissue nutrition and mucosal regeneration processes. Do not use in younger children, when carrying a child, only after discussion with a doctor.
- Actovegin. More often used in the form of injections, it has a metabolic healing effect, improves microcirculation and oxygen utilization.
- Rebagit. Enhances prostaglandin and mucus production, improves blood flow and healing. When using the product, the effectiveness of antiulcer therapy increases. The effect on pregnant women and children has not been studied.
The variety of drugs and mechanisms of action on the human body suggests the widespread use of gastroprotectors. It is important to understand that these medications are not the mainstay in the treatment of gastritis or ulcers. They are part of complex therapy, depending on the situation. Therefore, the use of drugs in this group requires an accurate diagnosis and medical prescriptions. Be healthy!
Contraindications
Medicines are not always allowed to be used, as they can cause complications.
Contraindications include the following conditions:
- The period of lactation and childbearing. Only some medications are allowed to be used at this time, but in each case, consultation with a specialist is required.
- Acute cerebrovascular accident.
- Diagnosing intestinal obstruction, in which the use of medications can provoke severe complications.
- Acute or chronic severe renal failure.
- Detection of severe forms of liver failure in patients with impaired functioning of the organ.
- Intolerance to any component in a particular medicine.
- Colitis in acute form with disruption of the large intestine.
- Intestinal atony, when the passage of food through it is disrupted. At the same time, many medications can provoke complications and aggravate symptoms against the background of stagnation.
- Childhood. Each medicine has its own age restrictions, so you should first consult with a specialist.
- Acute period after myocardial infarction.
Any drug may have other contraindications, so it is important to first study the instructions for use, which describe all the features. Medicines are used with caution in the treatment of elderly patients who suffer from severe pathologies of the heart and blood vessels.