Indications for use
This type of surgery has the following indications: peptic ulcer, tumors, dangerous stomach diseases, duodenal ulcer, polyps. Doctors say that often when malignant neoplasms are detected, this operation is the only option that can, if not completely get rid of the problem, then at least prolong life. Another area where gastric resection is used is the treatment of severe stages of obesity. With this surgical operation, up to 2/3 of the organ is removed. The first person to perform this manipulation was the German doctor Theodor Billroth. It was he who, after 1881, developed a technique for performing resection. In the early 2000s, other truncation methods became known, such as longitudinal or vertical.
Billroth I, Billroth II
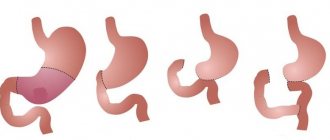
Option Billroth I is as follows. 2/3 of the stomach is removed. The central stump is partially sutured. The lumen that remains is the same size as the diameter of the duodenum. The peculiarity of this type is that after resection of the stomach, the physiological movement of food along with bile is preserved.
When performing the operation according to the second option, the stumps are sutured tightly (stomach and duodenum). The functions of the gastrointestinal tract are restored as follows: an anastomosis is created. That is, the overlap in this case occurs as an “end to side” type. This method has several modifications. One of them is gastric resection using the Hoffmeister-Finsterer method. The duodenal stump is sutured using a continuous continuous suture. The edges of the intestine are sutured to the stomach with several sutures. This procedure involves the gradual release of the contents of the latter. The best results are obtained by gastric resection in the Finsterer modification. In each individual case, the motor activity of the digestive organ changes significantly, and the tone weakens.
Indications and contraindications
Resection (code according to the international classification K91.1) is carried out with the aim of saving the patient’s life or preventing the development of serious diseases. But there are situations when surgery to remove the stomach is impossible. This happens if the patient’s condition is complicated by ascites, metastases, tuberculosis or endocrine diseases. Indications for surgery are usually divided into absolute, when it comes to immediate surgical intervention, and relative, for example, obesity, colitis, proliferation of polyps in the stomach. In Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, when a tumor diagnosed in the pancreas provokes increased gastrin synthesis, removal of the stomach or gland is also indicated. Absolute indications are diseases such as:
- cancer;
- large benign tumors;
- prolonged ulcer bleeding;
- narrowing of the pylorus;
- penetration or perforation of the ulcer.
What is longitudinal gastrectomy?
The main indicators for surgical intervention are a high degree of obesity, the body mass index exceeds values such as 35 kg/m2. This type of surgery is used to reduce the volume of the stomach. At the first stage, a narrow tube is formed, which has a slight curvature. The peculiarity of this method is that the area that is responsible for the production of the hunger hormone is removed. The formed stomach is not stretched; the food in it moves quite slowly and has time to break down. In the second stage, the walls are stitched together to form a tube. At the same time, the main functions of the organ are preserved; this operation is quite simple to use. Nutrition after gastrectomy of this type is of considerable importance.
Consequences of this treatment
There are many of them, and they are not all bad (but not all good either). It is worth discussing them in order:
- Reducing food consumption . A decrease in the volume of an organ leads to the fact that if a person eats a lot, everything that he is trying to cram into himself simply cannot fit into it. This is an artificial restriction for those who cannot control their appetite. This is the basis of bariatric medicine and surgery.
- Weight reduction . This follows directly from the previous point. Eat less - you weigh less. People who undergo surgery to control body weight lose weight, and simply patients who have lost part of an organ lose weight. Therefore, those whose stomach has been resected due to, say, an ulcer are prescribed special nutritional mixtures.
- Scars . If the operation was performed openly, there will be a scar in the middle of the abdomen, if laparoscopically, there will be point scars at the site of insertion of the trocars and endoscope (laparoscope).
- Bleeding . Sometimes, if the circumstances are unfortunate, a complication such as bleeding is possible. Usually it occurs in the remaining stomach, and the person begins to vomit. Vomiting in this case looks either like blood with streaks of mucus, or like coffee grounds (in any case, such vomiting is a reason to immediately consult a doctor).
- Anastomotic failure . Anastomosis is an artificially created connection between the stomach and intestines. If there is an infection, unfortunate circumstances, or the surgeon’s clumsiness, it can rupture, become inflamed, and so on. The failure of this design is the divergence of the seams. This requires emergency surgery and assistance.
- Stump stretch . A person does not always lose weight after surgery. Sometimes it happens that the walls of the organ stretch, and the stump becomes the size of the stomach. This promotes weight gain.
- Digestive problems . Depending on which part was removed, there may be various digestive problems. It’s just that the cells that produce hydrochloric acid for the stomach are not distributed evenly throughout the organ, but only in some of its parts. This leads to the fact that some compounds (for example, fats) begin to be less absorbed.
- Stenosis of the anastomosis site . The stitched parts of the stomach and intestines can become scarred and form a very narrow passage, which will prevent the normal movement of food along the tract. This is not good because it will provoke other stomach ailments. Well, there will also be problems with assimilation of what you eat.
- Getting rid of the tumor . One of the most important points. Gastric resection is often performed in cancer patients to remove the tumor. The doctor gives a person life, additional years, by removing the “bomb” from the body. A cure for such a disease is clearly worth more than “I will lose a little weight after the operation.” That's why many people don't even think about it.
- Getting rid of ulcers . No less important point. For those who suffer from an ulcer, firstly, the pain will disappear, and secondly, the dangers will disappear: for example, the ulcer can become through and lead to peritonitis (food will fall out directly into the abdominal cavity along with gastric juice, which will cause suffering ). It can also degenerate into a tumor and cancer (which is also scary). By removing such an ulcer, a person will obviously heal more calmly.
- Improving quality of life . Compared to the life of a patient with cancer/peptic ulcer/obesity, what happens in the end will be a fairy tale for the patient.
- Increased life expectancy . Nobody even argues here: ulcers and cancer consistently bring people to not the best consequences, while getting rid of them and/or cure will clearly have a good effect on life expectancy. 5, 10 years are also the magic of medicine, and people would like to live them.
- Good life and survival rates . Now this is an operation with almost no consequences, it is not dangerous, it often leads to a positive outcome, and complications are extremely rare.
- Infection . That is why it is necessary to take full courses of antibiotics prescribed by the doctor. After resection, infection is possible, and this will be very bad: the stump may fester, the anastomosis may break apart. But this can be prevented by simply following your doctor's instructions.

Contraindications for longitudinal resection
This surgical intervention has a number of contraindications. First of all, longitudinal resection is not performed during pregnancy. Also, pathologies of the cardiovascular system and peptic ulcers will become obstacles to operations of this kind. Pancreatitis, taking hormonal drugs or steroids, and other diseases of the digestive tract are all contraindications for performing such an intervention as gastric resection. In addition, alcoholism, which has a chronic form, and mental illnesses will not contribute to truncation.
Subtotal resection
Subtotal gastrectomy is performed when malignant tumors are detected. Another option for use is incurable peptic ulcer disease. This removes the upper part of the digestive organ. First of all, the organ is inspected and mobilized, the stomach is pulled down. Through an incision made in the area of the lesser curvature, a clamp is inserted and the lesser omentum and left gastric artery are separated. A loop of the small intestine is prepared, suturing and anastomosis are performed.
Complete resection
In case of extensive damage to the organ, a complete resection of the stomach can be performed. At the same time, a new digestive organ is formed from the tissues of the small intestine. According to reviews, this method is the most effective in the treatment of malignant tumors and is widely used in many countries. But such a surgical intervention makes its own adjustments to the patient’s future life. Nutrition after gastric resection, in which the entire organ is removed, requires a special diet and a special method of eating.
Possible complications
Complications often arise after gastrectomy has been performed. After surgery, the state of anastomotic obstruction is one of them. Often occurs from improper application or swelling. Bleeding into the peritoneal area is dangerous because anemia quickly develops. Intestinal obstruction also occurs. An extremely dangerous condition is postoperative peritonitis. Subsequently, a fistula may form due to incorrectly applied sutures. All these complications arise when the surgical technique is violated. They are extremely rare among experienced specialists. Doctors say that only about 5% of all surgeries require revision surgery. The rehabilitation period includes the following points: for the first six months it is necessary to limit physical activity and wear a special bandage; specialists also prescribe a special diet.
Rehabilitation period
If the operation was successful and without any complications, the patient is allowed to sit on the bed after 2-3 days, and after 3-5 days get up and walk a little. It is recommended to wear a bandage for one to two months after surgery, as well as take enzyme preparations for better digestion.
Physical activity, riding in public transport, as well as taking water procedures in the form of a bath or swimming in open water are subject to mandatory exclusion. Gradually, on the recommendation of a physical therapy doctor, regular therapeutic exercises are introduced. Six months after the operation, sanatorium-resort treatment is indicated.
Nutritional Features
The diet after gastrectomy has some restrictions and features. First of all, the amount of food that the patient can eat at one time changes significantly. The disease that led to the operation is also taken into account. For ulcers, 2/3 of the stomach is usually removed. Therefore, the portion is reduced proportionally, and a person can afford 1/3 of the usual amount of food. In case of malignant tumors, most of the organ is truncated. The amount of food is 50-100 ml. Therefore, the patient eats quite often: 5-6 times a day. After a certain time, the amount of food can be slightly increased. It is also important that food processing changes. Doctors say that in the first weeks, liquid or pureed food is recommended (that is, it must undergo mechanical processing). It is better if the dishes are boiled or steamed. Experts note that after gastric resection, protein absorption deteriorates. Doctors recommend enriching your diet with protein foods, preferably of animal origin.
Results after surgery
The results and success of the operation depend on a number of factors:
- reasons for surgery;
- in case of cancer, the stage of neglect;
- general condition of the patient, etc.
Stomach cancer
As already noted, the most severe disease that leads to resection is cancer. Many people are concerned about how long a person can live after surgery. If cancer is detected in the early stages, the survival rate is about 90% within 5 years. During this time, the patient continues to lead his usual lifestyle, eat his usual food (with minor adjustments and restrictions). At the same time, he retains his usual appetite. Many patients live for many more decades.
After the operation, the main task is to restore the digestive process. When peristalsis is normalized, the patient begins to gradually take his usual food - first in liquid and crushed form, then in solid form. The attending physician points out forbidden foods and describes what and how much can be consumed daily.
As a rule, the hospitalization process lasts 7-14 days and depends on the individual qualities of the body, the patient’s requirements and even the psychological state.
The main recommendations for the postoperative period include:
- fractional meals;
- eating small portions;
- eating protein foods with low sugar content.
Dumping syndrome
Due to the fact that food now enters the rectum much faster, patients often experience dumping syndrome, in which irritation is observed in this area. Dizziness occurs, heart rate increases, and sweating also increases. Against this background, the person complains of general weakness. Some patients note that after eating they experience attacks of nausea and vomiting. They usually go away if you lie down for 20-30 minutes. Most often, this condition is provoked by carbohydrate-rich foods, baked goods, and potatoes. Therefore, it is better to limit them, or even eliminate them altogether.
Prohibited Products
Gastric resection means that the future diet will be somewhat limited. First of all, in the first months you need to reduce the amount of salt you consume. The second ban concerns confectionery products, flour, sugar, and jam. Proteins are especially necessary after this operation, but fatty broths and fried meat will only do harm. Canned food, sausages, and pickles are also prohibited. You should avoid products that contain preservatives, dyes and other chemical additives. Alcohol is also excluded. It is very important to understand that such restrictions are imposed not only for the first year after surgery. These principles should be adhered to throughout the rest of your life.
Prevention
The main preventive measure is strict food restriction. Eliminate foods from your diet that maximize bile secretion. Since the body cannot carry out its functions sufficiently, chew your food thoroughly.
The main requirements for therapeutic nutrition are:
- a sufficient amount of proteins, carbohydrates, vitamins A, B, C;
- warm food (neither hot nor cold);
- lack of table salt.
Life after gastric surgery can be fulfilling. The main thing is to go through the recovery period correctly. To do this, follow all the requirements and prescriptions of your doctor, follow a diet, and avoid physical activity. Surround yourself with pleasant emotions and a positive attitude, this is the only way you can return to your previous lifestyle.
We recommend reading: esophageal vein ligation
Nutrition after longitudinal resection
In the postoperative period, proper nutrition is of great importance. The first week has a particularly strict diet, which includes only liquid food. Basically it is water, broth (but not fatty), milk. The liquid can be drunk in small sips at intervals of 5 minutes. In the second week, the diet expands somewhat. You can eat food that has the consistency of puree. Fermented milk products, pureed vegetables and lean meat (mainly poultry) make up the diet for a month. In the second month, you can introduce fish and other types of meat. Then regular food is allowed, but the portions should be small. It is better to avoid fresh baked goods. Longitudinal gastrectomy receives the following reviews: in 100% of cases, weight loss is observed, mostly the body mass index reaches normal levels.
Recovery period and lifelong diet

Restoring the ability to eat normally takes place in several stages. For the first 2 days, the patient is kept on intravenous nutrition - he receives all the necessary amino acids, vitamins, carbohydrates and partly fats through a dropper. After this period, you are allowed to drink liquids little by little - water, compotes, herbal teas. As the condition improves, infant formula is administered through a tube.
After 2 weeks, the patient can eat independently, adhering to a strict gentle diet and fractional meals. The diet already contains various kinds of purees, vegetable soups, liquid porridges (with the exception of millet), lean meats and fish, and a small amount of dairy products and eggs is allowed. As you recover, food processing methods expand - boiling, baking, steaming. The only exception is fried food.
Meals should be frequent (at least 5 times a day), and you must eat in small portions. Attempts to increase the daily volume of food can lead to repeated stretching of the gastric walls and severe discomfort, even pain. If all doctor's instructions are followed, the risk of complications is greatly reduced.
On a note! Patients with peptic ulcers should limit the amount of acidic and acid-forming foods they eat. The diet must include special mineral waters, antacids and antibacterial agents aimed at eliminating Helicobacter.