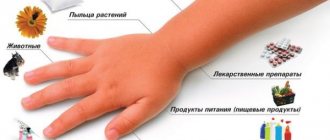
Causes of appearance in adults and children
Candida fungus is part of the normal microflora. However, under unfavorable conditions, the microorganism begins to actively multiply and provokes intestinal candidiasis. The causes of the pathology are the same for children and adults. Most often, yeast fungus is found in stool when:
- long-term and uncontrolled use of antibiotics, hormones, immunosuppressants;
- weakened immunity, including those caused by influenza, ARVI, HIV;
- vitamin deficiency, exhaustion;
- sexually transmitted diseases, as well as thrush of the genital organs;
- diabetes mellitus, obesity;
- hormonal disorders, including those caused by pregnancy, menopause;
- allergies and autoimmune disorders;
- chronic diseases and damage to the gastrointestinal tract, dysbacteriosis;
- malignant neoplasms, chemotherapy and radiation therapy;
- poor nutrition, abuse of sweets, flour, coffee;
- bad habits: alcoholism, smoking;
- stress, overwork, nervous disorders;
- unfavorable ecology, climate change;
- exposure to poisons.
Elderly people over 75 years of age are also at risk.
Broadcast about fungal infection of the intestines
Additional causes of fungus in stool in children
Yeast fungus in a child’s stool is most often detected in the first 1–2 years of life. This is due to the immaturity of the immune system, with the intestines not fully formed.
In addition to factors common to people of all ages, intestinal candidiasis in children often results from:
- eating unwashed fruits and vegetables;
- dirty hands;
- licking various objects and toys;
- inclusion of carbonated drinks, chips, crackers and sweets in the diet;
- stress, difficult psychological conditions in the home, garden or school;
- teenage hormonal changes.
Yeast fungi in a baby's stool often develop as a result of candidiasis (thrush) in the mouth.
What are yeasts in the stool of an adult?
The normal functioning of the digestive system is determined by the balance of beneficial and pathogenic bacteria that are constantly present in the human body. Under unfavorable conditions, the microflora is disrupted, which leads to the colonization of the intestines by pathogenic organisms. These are yeast fungi of the genus Candida. They cause candidiasis in various organs, including the intestines, in adults.
With this disease, a fungus appears in the stool of an adult, which is discovered during the analysis of this biological material. Reproduction of the pathogen occurs constantly and includes several stages:
- During its life, yeast releases toxins that accumulate in the blood and on the walls of the intestines.
- As a result, adults experience difficulty defecating, weakness, general malaise, and yeast in the stool.
- Over time, the fungus can affect the urinary or reproductive system, as well as neighboring organs.
When the pathogen multiplies too actively, inflammatory processes develop, which, in addition to the main symptoms, cause pain in the intestinal area. The danger of Candida fungus is that, along with other diseases, it can cause cancer in adults. The pathogen prefers to reproduce in a sweet environment, so one of the signs of damage to the body is a person’s special craving for sweets.
Symptoms
Clinical manifestations of intestinal candidiasis are the same for adults and children. Minor differences in the course of the disease can be observed only in the case of infants. This is due to the immaturity of the internal organs and systems of babies.
Yeast in the stool of an adult and a child: general symptoms
If Candida fungi actively multiply in the intestines of an adult or child, the patient will experience the following symptoms:
- pain in the lower abdomen or around the navel: the symptom intensifies after eating fatty foods;
- loss or decreased appetite;
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract: belching, heartburn, rumbling, bloating, increased gas formation, nausea, vomiting;
- diarrhea or constipation;
- unpleasant and pungent odor of feces;
- changes in the color and shape of stool;
- feces “do not sink”: they are poorly flushed down the toilet and remain on the surface of the water for a long time;
- the presence of whitish, cheesy pieces in the stool;
- itching of the anus;
- whitish-yellow coating on the tongue, unpleasant taste in the mouth;
- yellowness of the skin;
- allergic skin rash, acne, brittle nails and hair.
The more a fungal infection spreads, the more pronounced and aggressive the symptoms become. In advanced cases, difficulty swallowing and weight loss, blood and mucus in the stool, fever, general weakness, daytime drowsiness, insomnia, irritability, headaches, and pallor may occur.
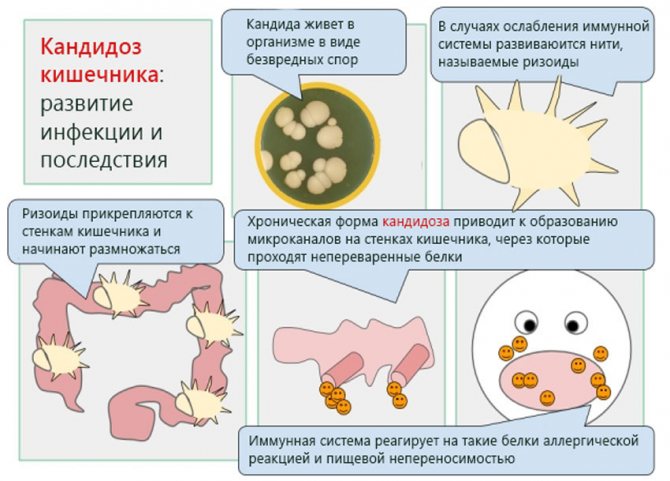
Yeast in a child's stool: additional symptoms
Symptoms of intestinal candidiasis are the same for both children and adults. However, the course of the disease in children in the first years of life has a number of features.
Due to postpartum stress, weak immunity and unformed intestines, Candida may appear in the first months of a baby’s life. Fungi in a baby's stool destroy the beneficial intestinal microflora and cause characteristic symptoms:
- colic, constipation, flatulence;
- white coating on the tongue;
- stomatitis, oral thrush;
- poor appetite or refusal to eat;
- weight loss;
- diathesis, atopic dermatitis - skin rashes;
- general restlessness, frequent crying.
With age, the child’s immunity strengthens and the growth of fungi is gradually suppressed.
Since the baby cannot complain, parents should pay attention to the nature of the stool, appetite, weight gain, level of moodiness and well-being, as well as compliance with the stages of physiological development. Older children most often complain of abdominal pain, lack of appetite, and difficulty defecating.
Symptoms of intestinal candidiasis in children

The infant digestive system is highly vulnerable to a variety of bacteria and pathogens. Thrush is especially dangerous for newborn babies. It can cause growth retardation and weight gain in the child, and affect overall development.
If during a medical examination fungi of the genus Candida are found in the feces of a baby, this is not always candidiasis. If the concentration of yeast-like fungi is within acceptable limits, then treatment is not required. Prescribe medications only in cases where laboratory tests show an excess of normal levels.
Symptoms of the proliferation of Candida fungi in the intestines:
- Painful sensations in the abdomen. The baby refuses food, constantly cries and is capricious, and may lose weight;
- Disorders of the digestive tract, belching;
- Bloating;
- The feces contain whitish inclusions similar to cottage cheese;
- Diarrhea (sometimes mixed with blood);
- Severe itching in the anal area.
If you observe such clinical manifestations, you must immediately consult a doctor and undergo all relevant tests. The earlier treatment is started, the less likely it is to develop complications of the pathology.
Signs of complicated intestinal candidiasis

In the absence of timely assistance to the baby, intestinal candidiasis tends to progress, as a result of which it becomes a chronic form of the disease. At this stage, Candida fungi can penetrate internal tissues and organs, destroying their integrity.
Description of the fungus of the genus Candida
The disease progresses slowly, but is fraught with numerous negative consequences that are difficult to medically correct with specialized medications.
Signs of complications in babies:
- Bleeding in the intestines.
- Formation of cracks.
- Violation of the structure of the mucous membranes.
- Prolonged diarrhea with blood.
- The appearance of ulcerative formations.
Important: all these symptoms pose a direct threat not only to the health, but also to the life of the newborn child.
Despite the fact that the fungus is an opportunistic microflora, it is dangerous and therefore requires timely medical intervention.
Diagnostics
Intestinal candidiasis in adults and children is detected using the following methods:
- Microscopy of feces and smears from the intestinal mucosa. The biomaterial is examined under a microscope. As a result, the number of fungi in the stool is determined, and the exact type of candidiasis pathogen is determined.
- Bacterioscopy, bacterial culture on nutrient media. Fungal colonies are grown in a nutrient medium. Through analysis, it is possible to determine the sensitivity of the microorganism to various antifungal drugs. The method allows you to prescribe an effective course of treatment.
- Additional tests. Blood test for the content of immunoglobulins and antibodies to Cand fungi > Signs of the presence of fungi in the intestines. Alexander Ogulov
Yeast in feces: causes, symptoms, treatment methods, prevention
In small amounts, yeast fungi are found in stool in 80–90% of absolutely healthy adults and children. However, if the norm is exceeded, they speak of intestinal candidiasis.
The disease is caused by Candida yeast fungi and is considered a type of dysbacteriosis (microflora disorder).
In some cases, the infection affects not only the small and large intestines, but also the esophagus, stomach, and gall bladder.
Causes of appearance in adults and children
Candida fungus is part of the normal microflora. However, under unfavorable conditions, the microorganism begins to actively multiply and provokes intestinal candidiasis. The causes of the pathology are the same for children and adults. Most often, yeast fungus is found in stool when:
- long-term and uncontrolled use of antibiotics, hormones, immunosuppressants;
- weakened immunity, including those caused by influenza, ARVI, HIV;
- vitamin deficiency, exhaustion;
- sexually transmitted diseases, as well as thrush of the genital organs;
- diabetes mellitus, obesity;
- hormonal disorders, including those caused by pregnancy, menopause;
- allergies and autoimmune disorders;
- chronic diseases and damage to the gastrointestinal tract, dysbacteriosis;
- malignant neoplasms, chemotherapy and radiation therapy;
- poor nutrition, abuse of sweets, flour, coffee;
- bad habits: alcoholism, smoking;
- stress, overwork, nervous disorders;
- unfavorable ecology, climate change;
- exposure to poisons.
Elderly people over 75 years of age are also at risk.
Broadcast about fungal infection of the intestines
Additional causes of fungus in stool in children
Yeast fungus in a child’s stool is most often detected in the first 1–2 years of life. This is due to the immaturity of the immune system, with the intestines not fully formed.
In addition to factors common to people of all ages, intestinal candidiasis in children often results from:
- eating unwashed fruits and vegetables;
- dirty hands;
- licking various objects and toys;
- inclusion of carbonated drinks, chips, crackers and sweets in the diet;
- stress, difficult psychological conditions in the home, garden or school;
- teenage hormonal changes.
Yeast fungi in a baby's stool often develop as a result of candidiasis (thrush) in the mouth.
Symptoms
Clinical manifestations of intestinal candidiasis are the same for adults and children. Minor differences in the course of the disease can be observed only in the case of infants. This is due to the immaturity of the internal organs and systems of babies.
Symptoms of fungi in the intestines are often confused with the clinical picture of other diseases. To clarify the diagnosis, it is necessary to take a stool test.
Yeast in the stool of an adult and a child: general symptoms
If Candida fungi actively multiply in the intestines of an adult or child, the patient will experience the following symptoms:
- pain in the lower abdomen or around the navel: the symptom intensifies after eating fatty foods;
- loss or decreased appetite;
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract: belching, heartburn, rumbling, bloating, increased gas formation, nausea, vomiting;
- diarrhea or constipation;
- unpleasant and pungent odor of feces;
- changes in the color and shape of stool;
- feces “do not sink”: they are poorly flushed down the toilet and remain on the surface of the water for a long time;
- the presence of whitish, cheesy pieces in the stool;
- itching of the anus;
- whitish-yellow coating on the tongue, unpleasant taste in the mouth;
- yellowness of the skin;
- allergic skin rash, acne, brittle nails and hair.
The more a fungal infection spreads, the more pronounced and aggressive the symptoms become. In advanced cases, difficulty swallowing and weight loss, blood and mucus in the stool, fever, general weakness, daytime drowsiness, insomnia, irritability, headaches, and pallor may occur.
Yeast in a child's stool: additional symptoms
Symptoms of intestinal candidiasis are the same for both children and adults. However, the course of the disease in children in the first years of life has a number of features.
Due to postpartum stress, weak immunity and unformed intestines, Candida may appear in the first months of a baby’s life. Fungi in a baby's stool destroy the beneficial intestinal microflora and cause characteristic symptoms:
- colic, constipation, flatulence;
- white coating on the tongue;
- stomatitis, oral thrush;
- poor appetite or refusal to eat;
- weight loss;
- diathesis, atopic dermatitis - skin rashes;
- general restlessness, frequent crying.
With age, the child’s immunity strengthens and the growth of fungi is gradually suppressed.
Since the baby cannot complain, parents should pay attention to the nature of the stool, appetite, weight gain, level of moodiness and well-being, as well as compliance with the stages of physiological development. Older children most often complain of abdominal pain, lack of appetite, and difficulty defecating.
Diagnostics
Intestinal candidiasis in adults and children is detected using the following methods:
- Microscopy of feces and smears from the intestinal mucosa. The biomaterial is examined under a microscope. As a result, the number of fungi in the stool is determined, and the exact type of candidiasis pathogen is determined.
- Bacterioscopy, bacterial culture on nutrient media. Fungal colonies are grown in a nutrient medium. Through analysis, it is possible to determine the sensitivity of the microorganism to various antifungal drugs. The method allows you to prescribe an effective course of treatment.
- Additional tests. Blood test for the content of immunoglobulins and antibodies to Candida fungi, urine test for dysbacteriosis.
- Colonoscopy. Examination of the intestines using an endoscope - a device with a camera. The method allows you to assess the condition of the mucous membranes and the degree of their damage by the fungus. During the procedure, scrapings and biopsies are often taken to further analyze tissue and cells.
Signs of the presence of fungi in the intestines. Alexander Ogulov
Treatment methods
In the absence of proper treatment, yeast fungi in the stool of an adult and a child can cause intestinal perforation, ulcers and bleeding, and even sepsis - blood poisoning. Therefore, you should not ignore the disease or self-medicate, but consult a doctor.
Treatment of intestinal candidiasis takes 2–6 months and requires an integrated approach. Therapy is based on several techniques:
- taking antifungal tablets;
- restoration of microflora;
- regulation of intestinal functions;
- strengthening the immune system: vitamins, immunomodulators;
- dieting and giving up bad habits;
- treatment of genital candidiasis and other fungal-provoking diseases;
- use of folk remedies.
Medications
Treatment of intestinal candidiasis depends on the causes, type of pathogen and course of the disease. The complex includes:
- antifungal tablets - for a course of 4-6 weeks and in the maximum dosage: Fluconazole (Diflucan), Intraconazole, Ketoconazole, Pimafucin, Nystatin;
- antifungal suppositories for a course of up to 2 weeks: prescribed only for colon candidiasis, they have active ingredients similar to tablets;
- probiotics to restore microflora - a course of at least a month: Linex, Hilak Forte, Laktovit, etc.;
- enzyme agents for normalizing gastrointestinal tract functions - a course of at least a week: Mezim, Festal, etc.;
- sorbents for removing toxins - a course of at least 10 days: activated carbon, Smecta, etc.;
- vitamin complexes.
To relieve spasms, Drotaverine is used, for flatulence - Espumisan, motherwort, valerian. Funds are prescribed as needed.
If therapy is ineffective, it may be necessary to change the antifungal drug and repeat the course.
Drug treatment for children
Yeast fungi in a child’s stool are treated according to the same scheme as in adults, but with the dosage halved. From the neonatal period, children are allowed antifungal drugs Pimafucin (Natamycin), Nystatin and Fluconazole (Diflucan) in syrup. At the same time, Pimafucin and Nystatin are absolutely safe, since they are not adsorbed by the intestines and do not enter the blood.
If there are bacterial complications, children are prescribed antibiotics Vancomycin or Neomycin. Throughout therapy, children are prescribed probiotics to normalize the microflora.
Diet
In addition to the main therapy, doctors prescribe a diet that inhibits the vital activity of Candida fungi and normalizes the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. This type of nutrition includes:
- Active consumption of low-fat fermented milk products, such as kefir. The drink contains a large number of probiotics necessary to restore microflora.
- Including healthy foods in the diet: yeast-free wholemeal bread, lean meats and fish, cereals (buckwheat, rice, pearl barley, oatmeal), vegetables, fruits and berries (except cabbage, grapes, bananas, sour apples, citrus fruits, plums and cherries) . Dishes must be steamed, boiled, stewed or baked.
- Refusal from fatty, fried, smoked, salty, sweet, flour and yeast foods (bread, beer, blue cheese), as well as legumes, canned food, fast food, wheat products, milk, coffee, alcohol, carbonated drinks, spices and herbs, ketchup, mayonnaise.
The diet must be followed by both adults and children. When choosing a more gentle diet for babies, you should completely avoid sugar and yeast. Products stimulate the proliferation of Candida fungi.
Treatment methods
In the absence of proper treatment, yeast fungi in the stool of an adult and a child can cause intestinal perforation, ulcers and bleeding, and even sepsis - blood poisoning. Therefore, you should not ignore the disease or self-medicate, but consult a doctor.
Treatment of intestinal candidiasis takes 2–6 months and requires an integrated approach. Therapy is based on several techniques:
- taking antifungal tablets;
- restoration of microflora;
- regulation of intestinal functions;
- strengthening the immune system: vitamins, immunomodulators;
- dieting and giving up bad habits;
- treatment of genital candidiasis and other fungal-provoking diseases;
- use of folk remedies.
Treatment
Therapy for damage to the adult intestine by yeast fungi is complex. It is important for the patient to provide a calm psychological environment and healthy nutrition. The main condition for treatment is the elimination of factors that provoke the proliferation of yeast fungi. If the cause is an abundance of sweets, then such foods should be excluded. When candidiasis in an adult is provoked by other diseases, they need to be treated. This is the only way to stop the proliferation of yeast fungi.
Articles on the topic
- Green feces in an adult - why it appears and what diseases it indicates, examination methods and therapy
- Yeast fungus in women - treatment with traditional and alternative methods, possible complications
- Yeast in a child’s stool - symptoms and manifestations, methods of treatment and prevention
The mainstay of treatment is taking antifungal drugs. In the presence of yeast fungi in the intestines, rectal suppositories are more often used - they manifest their effect directly in the area where the pathogen multiplies. If such treatment does not help, then the yeast fungi are affected from the inside by ingesting tablets. General treatment regimen for intestinal candidiasis:
- taking antifungal drugs;
- correction of existing diseases affecting the intestines;
- taking enzymatic preparations, probiotics, symbiotics, enteroseptics;
- following a yeast-free diet.
Pharmacy drugs
Yeast in the stool of an adult indicates a violation of the intestinal microflora. For this reason, the main goal of treatment is to inhibit the proliferation of yeast. To eliminate the pathogen, antifungal drugs are used:
- rectal suppositories – Pimafucin, Diflucan, Nystatin;
- capsules and tablets – Fluconazole, Ketoconazole, Itraconazole;
- powders for the preparation of solutions for infusions – Vancomycin.
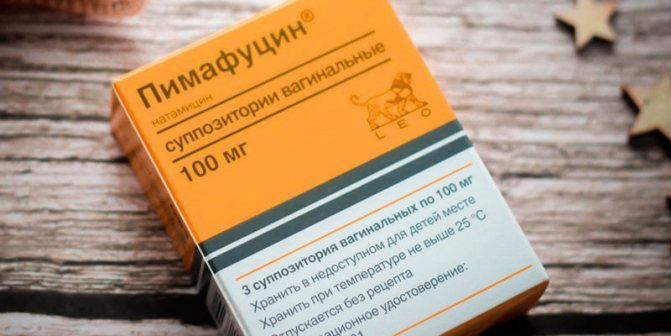
One of the effective antifungal drugs is Pimafucin suppositories. The active substance in their composition is natamycin. This component binds sterols inside the cell membrane of yeast fungi, causing their death. The advantage of natamycin is the absence of systemic action when used locally. The substance is not adsorbed through the intestinal mucous membranes.
The disadvantage of Pimafucin is that adults may require different numbers of suppositories to treat intestinal candidiasis. If the course is too short, the disease may recur. For this reason, during treatment with Pimafucin, special attention is paid to symptoms and therapy is continued until all signs of candidiasis disappear. There are other indications for the use of these suppositories:
- therapy with antibiotics, cytostatics, corticosteroids;
- vulvitis;
- vulvovaginitis;
- balanoposthitis.
If local treatment does not help, then antifungal tablets are added to the treatment. The drug Fluconazole is popular. The substance of the same name in its composition inhibits the synthesis of sterols in yeast fungi, leading to the death of their cells. The main advantage of Fluconazole is that its active component penetrates deeply into tissues, exerting a fungicidal effect at all stages of yeast development. The disadvantages include the impossibility of use during pregnancy and lactation. General indications for treatment with Fluconazole:
- candiduria;
- mucosal candidiasis;
- infections caused by candida;
- genital candidiasis;
- pityriasis versicolor;
- cryptococcal infection;
- dermatomycosis;
- prevention of fungus during radiation or cytostatic therapy.
The second direction of treatment for intestinal candidiasis is to normalize the level of beneficial bacteria, since when affected by yeast, their balance is disturbed. To achieve this goal, the following groups of drugs are used:
- probiotics – Hilak Forte, Laktovit, Linex, Bifidumbacterin, Laktiale;
- enzymes – Festal, Mezim Forte, Creon.
Bifidumbacterin has good reviews among these drugs. It contains live bifidobacteria, which are part of the normal intestinal microflora. The advantage of the drug is that it is available in several forms: ampoules, powder, suppositories, capsules. The main effect of Bifidumbacterin is an antibacterial effect on pathogenic and opportunistic microorganisms. Additionally, the drug exhibits immunomodulatory properties. There are no downsides to the drug. Indications for its use:
- dysbacteriosis;
- intestinal dysfunction;
- inflammation of the large or small intestine;
- acute intestinal infections.
The third direction of treatment for candidiasis is symptomatic. It is necessary to alleviate the patient’s condition and eliminate his unpleasant intestinal symptoms. For this purpose, the following groups of drugs are used:
- eliminating flatulence - Espumisan, Simethicone, Simicol;
- relieving spasms - Meverin, No-shpa, Drotaverin;
- removing toxins – activated carbon, Enterosgel, Atoxil.

Therapeutic diet
An integral part of the treatment of intestinal candidiasis is a special diet. It is prescribed as an addition to taking medications. The diet helps create conditions in which it is more difficult for the fungus to multiply, and in addition, it promotes faster recovery. All food should be light and healthy, containing many vitamins. It is recommended to include in the diet:
- mashed potatoes;
- fish;
- low fat fermented milk products;
- rice, buckwheat, pearl barley;
- fresh fruits and vegetables;
- low-fat vegetable soups;
- meat of rabbit, turkey, chicken.
Products can be stewed, boiled, baked or steamed. It is better to exclude fried foods from the menu. You should also avoid the following products:
- fat milk;
- citrus fruits;
- coffee;
- alcohol;
- sweets;
- canned food;
- cherries;
- apples and plums;
- white cabbage;
- mayonnaise, sauce;
- soda;
- spices;
- yeast bread and other baked goods.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine recipes can only be used as an auxiliary method to the main treatment and only with the permission of a doctor. After consultation, the following remedies can be used:
- Grind 4 cloves of garlic, mix with 1 tsp. honey Take the product daily on an empty stomach, 1 tsp. until the symptoms of the disease disappear.
- Wash and peel a few aloe leaves, then grind them into a paste. Add 1 tsp to it. honey, mix. Between doses, store the product in the refrigerator. Take 2 tsp morning and evening. 20 minutes before meals.
- Drink 2 tsp daily before meals. olive oil. It has bactericidal and anti-inflammatory properties. The procedure is carried out over 10 days. Instead of olive oil, you can use sea buckthorn oil.
- For 400 ml of boiling water, take 1 tbsp. l. chopped St. John's wort. After mixing the ingredients, leave the product for 2 hours, then strain through a couple of layers of gauze. You can add a little honey. Consume the entire infusion within 24 hours. Use daily until symptoms of intestinal candidiasis disappear.
Prevention
Prevention of intestinal candidiasis requires compliance with a number of requirements:
- rational nutrition, diet;
- increasing immunity;
- compliance with personal hygiene rules;
- normalization of the daily routine, regular rest, creation of a calm environment;
- rejection of bad habits;
- timely treatment of genital candidiasis, diabetes mellitus, obesity, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, reproductive and urinary systems.
A. Ogulov - Cleansing the stomach from mushrooms
Yeast fungus in the stool of an adult and a child is no joke. The condition requires timely treatment and careful attention to yourself. Follow preventative measures and stay healthy!
A mandatory test for many examinations is stool microscopy: it reveals the presence of yeast fungi. This indicates intestinal candidiasis, a disease associated with the manifestation of dysbiosis. It is accompanied by unpleasant symptoms, and treatment is prescribed by a doctor after identifying the causes and characteristics of the patient’s problem.
What is yeast fungus
The mold variety of Candida fungi is called yeast. The presence of these cells in the microflora of a healthy person is the norm, but under unfavorable factors they grow greatly, leading to candidiasis. Fungi multiply and accumulate toxins in the body, which affects the patient’s health. Yeasts are detected in stool with the following symptoms:
- pain in the abdomen and intestines;
- feces have an unpleasant odor;
- diarrhea, constipation;
- digestive tract dysfunction;
- decreased or increased appetite;
- skin allergies;
- weight loss;
- itching of the anus;
- flatulence;
- feces of unusual shape and color.

What should you do if your child has yeast in his stool?
Most completely healthy children have moderate amounts of yeast in their stool Exceeding the maximum permissible amount of fungus in patients' stool can result in intestinal candidiasis, which is one of the many variations of dysbiosis. In the advanced version, in addition to the intestines, the entire digestive system is affected.
What are yeast fungi
Yeast is a modification of a fungal infection that is caused by the pathogenic microorganism Candida. Infection with this type of fungus manifests itself in damage to a person’s nail plates, mucous membranes and skin on the extremities.
In any living organism, a limited number of various microorganisms are constantly present, which, if the body is in a satisfactory state, do not exhibit their pathogenic properties. As a result of a decrease in the protective functionality of the immune system, fungi begin to actively divide, leading to the formation of the disease.
Reasons for the appearance of yeast fungi in a child’s stool
Yeast fungi in a child’s stool are usually detected under the following circumstances:
- Yeast fungi spread at high speed after the use of antibacterial therapy, which can disrupt the intestinal microflora, creating the necessary conditions for the proliferation of the fungus.
- Inadequate and unbalanced nutrition, if the correct ratio of protein, fat and carbohydrate components of the diet is not observed.
- Intestinal obstruction.
- Yeast fungus in children's feces tends to appear as a result of climate change. The child has difficulty adapting to the new climate, putting stress on the immune system, which contributes to the development of a fungal disease.
- The influence of toxic substances.
- The presence of parasitic microorganisms obtained from contact with animals.
- Metabolic disorders.
- Liver diseases.
Yeast fungi appear in the stool of children under one year of age more often than in adults due to the incompletely formed digestive and immune systems of the child’s body. The fungus is transmitted to a newborn from a sick mother during labor, when pathogenic microorganisms penetrate the baby’s oral mucosa and then into the digestive system.
With a severely weakened immune system, pathogenic microorganisms are activated that can disrupt intestinal motility, which occurs as a result of a lack of production of digestive enzymes in the baby due to the immaturity of the digestive organs.
Stool test for yeast fungus
The study of feces is a rather complex process, including a comprehensive study of biomaterial. The composition, color and consistency of the stool are subject to assessment.
To obtain the most complete picture of the disease, microscopy of stool and intestinal smears and inoculation of the biomaterial on a nutrient medium should be performed.
Based on the results of such studies, it is possible to establish the resistance of microorganisms to a variety of drugs.
Preparing for tests
To obtain accurate results, the baby should be properly prepared for the test:
- 3 days before the collection of biomaterial, enemas are stopped;
- It is prohibited to perform radiography of the digestive system;
- stop taking antibiotics 12 hours before;
- biomaterial is collected upon completion of urination and hygienic treatment of the perineum;
- a sterile vessel with a screw cap is used;
- The period of storage of the selected biomaterial is no more than 3 hours.
Traditional medicine
When using soda for treatment, you need to remember that this is a very active substance that should not be abused. A solution of half a teaspoon of baking soda in a glass of water is used for daily rinsing of the mouth. This helps eliminate fungal plaque caused by intestinal fungus.
It is also recommended to wipe the anus with this solution if the patient has itching. A clean napkin is moistened in a soda solution to treat the affected areas. If you have constipation, you can give enemas with a solution of a teaspoon of soda per liter of water.
To eliminate excess amounts of pathogenic fungi, it is necessary to acidify the body. To do this, you can drink 1/3 cup of lemon juice on an empty stomach daily. To treat small children, lemon juice is diluted in water.
Why do yeast-like fungi appear in stool?
The reasons why yeast molds appear in feces are:
- impaired immunity - congenital or acquired, this can be facilitated by HIV, taking certain drugs, hormones, antidepressants, and many serious diseases leading to exhaustion;
- death of beneficial microorganisms due to antibiotics;
- reduced acidity in the stomach, which increases the proliferation of bacteria;
- dysfunction of intestinal valves;
- decreased digestive function due to acute microbial or viral diseases;
- tendency to constipation, intestinal obstruction;
- diabetes mellitus, intestinal and liver infections;
- influence of industrial poisons, radiation;
- allergic reactions;
- oncology;
- eating disorders;
- unfavorable ecology, sudden climate change.
Stool test for yeast fungus
If yeast mold cells are detected in a person, then during treatment, monitoring is constantly carried out in the laboratory, the pathology is eliminated and the microbial environment - the natural flora - is restored. Scatological examination of stool is a complex procedure that includes a complex analysis. The patient must submit the material following the rules:
- 3 days before the test, stop using laxatives, suppositories, enemas;
- It is prohibited to examine the intestines using X-ray contrast;
- 12 hours before the test, stop taking antibiotics;
- stool should be collected using sterile containers with a tight stopper, after urinating and washing the perineum with soap and water;
- The maximum shelf life of collected stool for research is 3 hours.
The laboratory technician, having received feces, places it in a nutrient medium to find out how quickly the mold yeast culture multiplies. With an increased growth rate, the doctor makes a diagnosis of mycosis. In addition to feces, you need to examine the blood for the level of immunoglobulins, antibodies to candida, and urine for traces of fungal activity. Of the secondary ones used:
- endoscopic examination for the presence of ulcers and plaque;
- radiograph;
- a study of cystology and histology, where scraping and biopsy are used - the study of pieces of tissue and cells for disease.
We think little about how many potential dangers surround us and our pets in everyday life. Meanwhile, there are a lot of them. The real “saboteurs” include yeast fungi. Under normal conditions, they are not only completely harmless, but are even partly symbiotic microorganisms. Peaceful coexistence ends if the animal’s body is weakened by some kind of infectious disease, chronic stress or poor quality nutrition. In this case, yeast dermatitis in dogs may develop.
Yeast in stool: is it dangerous and is treatment necessary?
Yeast fungi are representatives typical of the normal microflora of the human digestive canal that belong to the group of opportunistic pathogens.
This means that yeast fungi cause the disease only under certain conditions, with a significant decrease in immunity and/or the presence of severe pathologies.
The detection of yeast fungi in stool can either indicate pathology or be regarded as a variant of the norm - a doctor’s consultation and a comprehensive examination are necessary.
How dangerous is the pathogen?
Yeasts are a whole group of microbial agents that are also called Candida spp., that is, candida. The results of a regular coprogram do not indicate the type of candida; the answer looks like “yeast detected.” The variety of this fungal agent is not important for the choice of further treatment tactics and management of the patient.
Any type of candida is dangerous if there are a lot of yeast cells. Various toxic substances enter the human blood, the integrity of the intestinal mucosa is disrupted, and the likelihood of the proliferation of other pathogenic microorganisms increases.
As already mentioned, yeast fungi can cause significant harm to the human body only in conditions of immunodeficiency. In this case, severe clinical symptoms and even complications may develop:
- severe gastroenterocolitis with impaired absorption and digestion of food;
- generalization of the process involving the respiratory system;
- development of a fungal septic process.
In the case of fungal sepsis, the prognosis for the patient’s life is unfavorable, since there are pronounced disturbances in all metabolic processes, and antifungal drugs are not always effective.
Routes of transmission and growth conditions
Yeasts are ubiquitous not only in the environment, but also in the tissues of the human body. In more than half of completely healthy people (50-70%), these microbes are found on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity, inside the feces, and on the surface of the mucous membrane of the final sections of the intestine.
We recommend reading:
Why does black loose stool (melena) occur?
In the case of infection with yeast fungi, it is not entirely correct to talk about the routes of infection, since these microbes settle inside the human body from newborn age. The microbial agent penetrates as follows:
- in direct contact with the mother;
- during breastfeeding;
- upon contact with infected objects.
Thus, the route of transmission of yeast fungi is predominantly contact.
The growth of yeast fungi is promoted by serious influences that inhibit the functions of the immune system. These factors include:
- systemic connective tissue diseases;
- recurring or protracted infectious diseases of another etiology;
- powerful and long-term antibiotic therapy with a wide spectrum of effects without covering with nystatin;
- significant and long-term nutritional errors with a deficiency of microelements, proteins, vitamins;
- organ transplantation followed by immunosuppressive therapy.
All factors related to traditional sanitary and hygienic standards prevent the reproduction and growth of yeast fungi. The most important among them are:
- proper balanced nutrition;
- timely treatment of chronic pathology;
- rational therapy of infectious processes.
The likelihood of developing a systemic fungal infection in a healthy person and even with compensated chronic pathology is low.
Norms for content in feces
The answer to this question is short - normally there should be no yeast fungi in the stool of a healthy person.
Their detection without clinical symptoms (change in general condition) should not be considered a disease, that is, the fact of detection is not a basis for prescribing therapy.
If there is a significant change in health, yeast fungi found in stool are a reason to consult a doctor and further examination.
Associated symptoms
Yeast can cause 2 variants of the pathological process: invasive and non-invasive.
Non-invasive is characterized only by the active growth and reproduction of fungi on the surface of the intestinal mucosa without penetration into the deeper layers. The processes of absorption and digestion are disrupted, but generalization of the infection does not develop.
An invasive process is a lesion of the entire intestinal wall, with the penetration of fungi into the systemic bloodstream, involving other organs and tissues in the process.
Intestinal manifestations
There are no specific signs of intestinal damage by yeast fungi. The diagnosis is based on a complex of clinical symptoms and laboratory examination. Intestinal yeast infection should be suspected if the patient notes:
- loss of appetite up to anorexia;
- prolonged nausea with possible episodes of vomiting;
- abdominal pain without clear localization and moderate intensity;
- unstable stool (alternating constipation and diarrhea);
- flatulence and excessive discharge of gases;
- areas of undigested food, mucus, and less often blood may be noticeable in the stool.
The patient may notice periods of improvement in general condition and deterioration in health. A long period of increased clinical symptoms requires special attention.
Extraintestinal manifestations
Possible if we are talking about a systemic fungal infection or a severe immunodeficiency state. A person may note:
- an increase in temperature with fluctuations during the day of 2-3 ° C, combined with chills and sweating;
- unmotivated weakness and constant fatigue;
- pallor of the skin, whitish lesions with uneven edges are also possible;
- the appearance of a cheesy coating on the oral mucosa, which is easily removed and just as easily appears again.
In such a situation, there is a need to consult a doctor as soon as possible, since a successful outcome is possible only with early hospitalization.
Specific therapy (fighting the pathogen)
A component of specific treatment that eliminates yeast fungi is antifungal drugs. In this situation, we are talking only about systemic medications in tablet or injection form. Can be assigned:
- ketoconazole;
- itraconazole;
- amphotericin B.
Old antifungal drugs (nystatin, levorin) are ineffective in the case of a systemic process.
Nonspecific (additional) therapy
In complex therapy of fungal infections, the following are used:
The duration of therapy is several weeks, it all depends on the severity of the patient’s condition.
Forecast
Unfavorable in the case of fungal sepsis, mortality varies from 80% to 100%. Only the early start of specific therapy and massive detoxification can save the patient.
Prevention
Includes all concepts related to a healthy lifestyle. Please pay attention to:
- balanced diet;
- rehabilitation of chronic foci of infection;
- timely anti-relapse treatment of chronic pathology.
A healthy person should not worry about the problem of systemic fungal infection.
Source: https://ProKishechnik.info/zabolevaniya/drozhzhevye-griby-v-kale.html
What it is?
This is what inflammation of the skin is called. As a rule, the “classic” causative agent of such a disease is fungi from the genus Malassezia . Such dermatitis is dangerous not only in itself: fungi weaken the body’s already damaged defense system, which can result in more serious diseases, including even autoimmune pathologies. In addition, the practice of veterinarians around the world clearly shows that dogs with yeast dermatitis are 70% more likely to have food allergies. Getting off topic: Despite the theoretical possibility of transmitting the disease to another dog, your cat (if you have one) is completely safe. In cats, yeast dermatitis occurs in extremely rare cases, and they usually develop against the background of a catastrophic decrease in the activity of the immune system (which often happens with long-term use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs).
Malassezia pachydermatis (Pityrosporum) is an inhabitant of the skin, rich in sebaceous glands, since the yeast is very fond of the secretion secreted by the latter. Because of this, the fungus is especially common in the external auditory canals, as well as in the groin area. In addition, yeast of this genus is often found even in the rectum of an animal. All of this causes a significant variety of symptoms that your pet may develop with yeast dermatitis.
It is interesting that this disease often occurs in humans, and it was in humans that seborrheic dermatitis was first described in detail in 1847 by a doctor, after whose name the entire genus of these yeasts was subsequently named. It is known that these microorganisms have the ability to enhance the secretory activity of the sebaceous glands (we have already noted that Malassezia loves lipids). What is the reason for such a “useful” feature of these microorganisms? It's quite simple: they secrete a huge amount of lipases (i.e. enzymes that break down fats). Because of this, the body is simply forced to constantly increase the production of sebum, since the latter is necessary to moisturize and protect the outer epithelial layer.
Fungi need warmth and humidity; they often enter into a symbiotic relationship with bacteria, simultaneously causing inflammation of the skin on which they settle. Generalized allergies or endocrine disease (hypothyroidism is especially dangerous) can predispose to candidiasis.
Experienced doctors believe that if an animal has a staphylococcal infection, the growth of fungi is significantly accelerated. It is easy to find a scientific explanation for this curious fact: the fact is that staphylococci secrete a powerful toxin. It is not dangerous to the yeast itself, but the poison destroys their competitors and also dramatically weakens the body’s defenses. New research suggests that yeast is the cause of many atopic dermatitis , which many experts consider idiopathic (i.e., without a specific cause). Don't blame the doctors: it is not so easy to grow a Malassezia culture, and without this it is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis.
Predisposed breeds and most commonly affected areas of the body
There is no age or gender predisposition, but the breed factor most likely plays an important role in the development of fungal dermatitis. As international veterinary experience shows, the disease is most often detected in: Shih Tzu, Lhasa Apso, Cocker Spaniels, Jack Russell Terriers, Poodles, Mountain Terriers, Collies, Labradors, Chihuahuas, Maltese, Basset Hounds, German Shepherds, Dachshunds, golden retrievers.
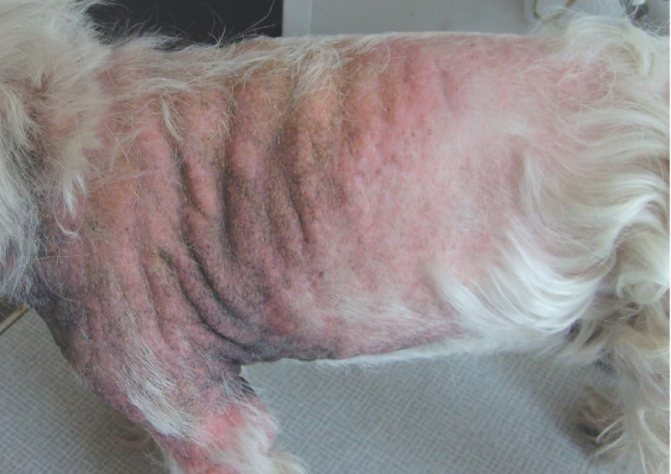
The most typical symptoms include: itching, an unpleasant and even offensive odor from the affected areas of the skin, the coat becomes greasy and sticky, and possible erythema and lichenification.
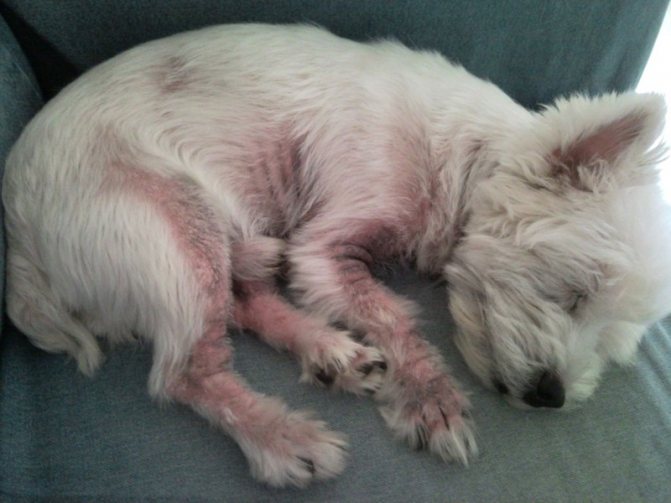
As for specific locations, most often all folds of the skin . The lower part of the neck, armpits, groin, navel area, perineum, muzzle and ears are especially affected. In some dogs, the muzzle of this disease begins to itch so much that the owners call the veterinarian. They cannot even think about itching: in this case, their pets behave as if they are having an attack of some dangerous mental illness. In any case, the signs are similar. Other dogs are calm... or rather, depressed. They are little interested in what is happening around them; such pets practically do not eat, preferring to sleep for a long time in the most remote and dark corners of an apartment or house.
Diagnostic techniques
The fastest and easiest way to diagnose the presence of Malassezia is a cytological examination of pathological material taken from a sick animal. Moreover, to select it, you can simply take a clean glass slide and “blot” the affected area of skin with it. If there is yeast on the skin of a sick animal, it will inevitably later end up in the field of view of the microscope. In more complex and doubtful cases, you can use cotton swabs or swabs soaked in sterile saline solution.
Stain the preparation according to Gram. The sample should be examined under an oil immersion lens. Malassezia are visible as round or oval cells, 3-8 µm in diameter. They are painted dark blue, and therefore are easy to identify even for an untrained specialist. Yeasts are often single, sometimes groups are observed, fungal cells are often tightly adjacent to keratinocytes.
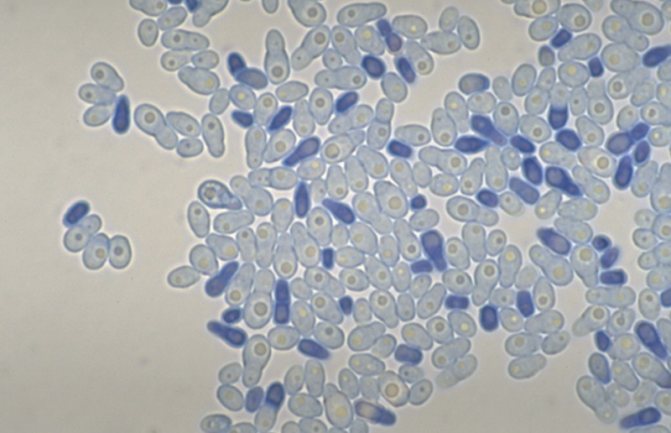
Normal yeast counts range between 3-6/hpf (in simple terms, one to two fungal cells per microscope field). If this amount is exceeded, yeast dermatitis is present. Growing the crop is necessary only in doubtful cases. Sabouraud medium is used. It is very useful to add a small amount of fat to agar, since the latter greatly accelerates the growth of all microorganisms of the genus Malassezia.
In addition, it is recommended to conduct microscopy of hair follicles taken from the most affected areas: if a large number of yeast cells are found in them, treatment should be started immediately, since the identified strain undoubtedly has pronounced virulence. Again, if the diagnostic methods described above did not allow identifying the pathogen, they resort to diagnosis based on the response to the therapy (if the dog feels better after starting treatment, fungal dermatitis is suspected).