Sharp pain in the anus is not just a very unpleasant phenomenon, but a signal that you should pay close attention to the problem. If the pain does not subside for a long time, you should consult a doctor. Such problems are dealt with by a proctologist who will conduct the necessary research, make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment. The pathology in question can become a symptom of a serious disease.
What can cause discomfort in the anus?
Often, when seeking medical help, patients complain of discomfort in the anus. Discomfort is a general concept that combines the following symptoms: itching, burning, feeling of a foreign object, spasm. Often discomfort is combined with pain. What diseases cause itching, burning, spasm and pain in the rectum?
The human anus is penetrated by many blood vessels and nerves. With various infectious and inflammatory diseases, irritation of the receptors occurs, which provokes discomfort in the anus. Often the discomfort includes a burning sensation. This symptom occurs when:
- violation of personal hygiene rules;
- hemorrhoids;
- cracks in the rectal mucosa;
- traumatic damage to the skin in the anus;
- diabetes mellitus;
- fistulas;
- parasitic diseases (enterobiasis).
Discomfort in the anus can be caused by wearing low-quality underwear or thongs. Very often, synthetic-based underwear causes skin irritation. A burning sensation in the anus can occur as a result of diaper rash. This is typical for obese people due to increased sweating. The cause of this condition is regular shaving of hair.
A large number of people who complain of discomfort have itching. It can be a manifestation of various diseases or a simple allergic reaction. The most common causes of itching include:
- anal fissures; condylomas;
- fistulas;
- benign neoplasms;
- chronic proctosigmoiditis;
- giardiasis;
- enterobiasis;
- changes in intestinal microflora;
- urethritis;
- venereal pathology (chlamydia, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis);
- thrush;
- allergic reactions to various medications (suppositories, ointments);
- diabetes;
- neurological diseases;
- stress.
Itching is a common symptom of skin diseases. If the anus is itchy, it may be caused by psoriasis, lichen ruber, seborrheic eczema, or pediculosis. This problem with the anus may be associated with diabetes. If a person goes to see a doctor complaining only of itching, an allergic reaction can be suspected.
Allergies can occur to food, medications, and alcoholic beverages. Itching is not always associated with organic pathology. It can be triggered by depression, stress, and obsessive states. In this situation, consultation with a neurologist or psychiatrist is required. In women, the most common cause of itching is thrush. This condition is not dangerous.
There are many known problems with the anus. Discomfort and pain often occur. A similar condition occurs with prostatitis, hemorrhoids, and anal fissures. In medical practice there is such a term as proctalgia. It means pain in the rectal area. It is often caused by muscle spasms. The causes of proctalgia are different. They include:
- inflammation of the external anal sphincter;
- haemorrhoids;
- inflammation of the crypts;
- anal fissures;
- presence of fistulas;
- rupture of the anal canal;
- malignant neoplasms (cancer).
In men, the cause of discomfort can be chronic prostatitis (inflammation of the prostate gland). In this case, discomfort occurs during bowel movements. Prostatitis can cause constipation. Characteristic signs of prostatitis are pain, difficulty urinating, changes in the nature of urine, and impaired sexual function. Pain can be felt in the back, abdomen, anus, groin. Disorders of urination are caused by spasm (compression of the urethra).
If it bakes and burns in the anus, the nerve roots of the anus become severely irritated over a long period. Shootings in the anus in men impulse to the brain. Throbbing pain without proper therapy affects the state of the sphincter, which is responsible for pushing out feces. The pain intensifies.
Unpleasant sensations and discomfort in the rectum are classified as signal pains from the category of proctalgia, which can occur in patients suffering not only from diseases of the digestive tract. This kind of trouble accompanies more than 90% of all pathologies of the peri-rectal region, both inflammatory and oncological in origin.
Often, proctalgia has an increasing character, manifesting itself first as tingling or discomfort in the anal canal and reaching unbearable constant pain. Therefore, you should not put off visiting a doctor until the pain in the rectum is not severe and only bothers you after bowel movements or prolonged sitting.
An unpleasant and often dangerous symptom, pain in the anus, can also occur for other reasons. The list of diseases and pathological conditions is supplemented by:
- injuries;
- tendency of the rectum to prolapse;
- intestinal polyposis;
- acute proctitis and paraproctitis;
- cryptite;
- papillitis in the anus;
- diseases transmitted through sexual intercourse;
- growth of condylomas around the anus;
- dysfunction of the urinary organs.
In men, the anus area hurts when prostatitis develops. In women, the symptom is observed during pregnancy, indicating a possible ectopic pregnancy, rupture of an ovarian cyst, and is characteristic of endometriosis or adnexitis. Aching, dull pain in the anus often precedes menstruation.
Causes of pain
Pain in the anus can occur for a variety of reasons:
- In case of severe hypothermia or reduced functioning of the immune system.
- If viruses, infections and microbes enter the human body.
- Failure to comply with personal hygiene rules.
- During the period of promiscuity.
Hemorrhoids and fissures
Quite often, the appearance of pain is diagnosed during the period of hemorrhoids or in the presence of cracks in the rectum. When this disease occurs, the hemorrhoidal veins become inflamed in the rectal area.
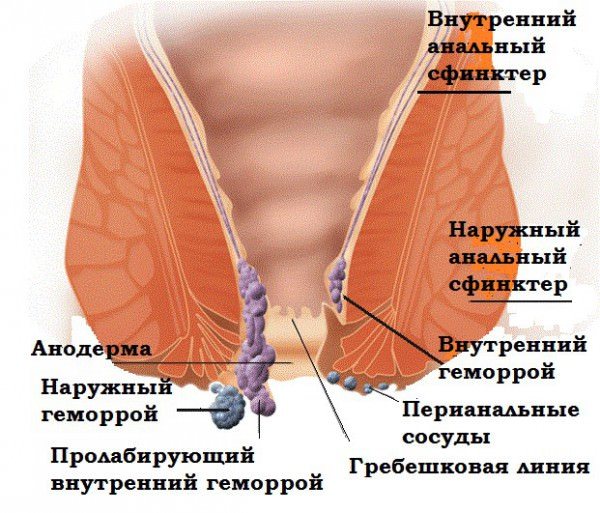
In the initial stages, the disease is accompanied by itching and discomfort in the rectal area. If not treated in a timely manner, these sensations are accompanied by pain.
These symptoms are often combined in patients. With hemorrhoids, bleeding of varying degrees of intensity may occur after bowel movement.
Paraproctitis
Around the human rectum there is fatty tissue that fills the pelvic area. When this fatty tissue becomes inflamed, patients are diagnosed with paraproctitis.
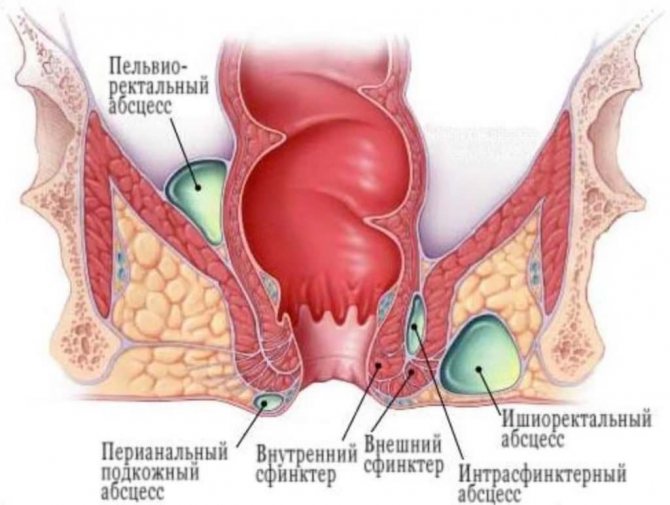
During the course of the inflammatory process, the appearance of severe pain syndrome is observed. This is because inflammation irritates the nerve endings.
The appearance of acute purulent paraproctitis is observed quite abruptly. At the same time, patients complain of weakness and malaise. The disease is accompanied by an increase in body temperature.
When paraproctitis appears, pain is observed, which intensifies. At the same time, the anal muscles become overly tense.
Rectal prolapse
Rectal prolapse is a serious pathological process that is accompanied by unbearable pain. Most patients experience shock when this disease occurs. Elderly women are at risk for this disease.
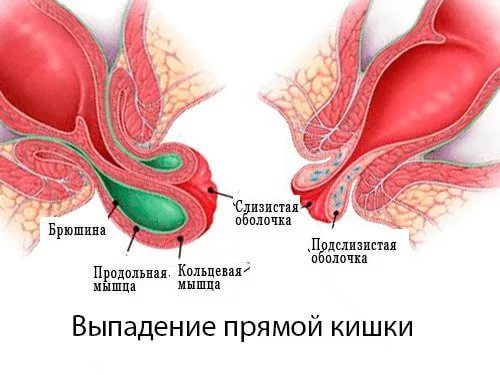
The disease occurs due to weak fixation of a certain area of the rectum. At the same time, the nerve endings are pinched, which causes severe pain. In some cases, when this disease appears, there is no pain.
Haemorrhoids
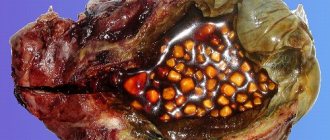
The classic symptom of the condition is sharp pain in the anus with an enlarged bluish lump (blood clot) at the anal border. If the clots are large, they cause discomfort when walking and sitting. Stagnation of blood and injury to the anal vessels due to deformation are the common denominator in the development of thrombosis. High pressure within the clot can cause erosion of the overlying skin and thus lead to bleeding.
A rational approach to the condition is to eliminate stasis, trauma and excess load. Since excessive straining during bowel movements is usually caused by constipation, softening the stool is key to preventing excessive straining.
Severe pain in the anus in men is observed in the first few days (48-72 hours), after which it gradually subsides. If the condition does not respond to conservative treatment, including laxatives, warm baths, analgesia, increased dietary fiber and fluid intake, complete surgical removal of the clot is necessary. The operation is performed in a hospital under local anesthesia.
Acute thrombosed external hemorrhoids must be differentiated from complicated internal hemorrhoids and from anal pigmented melanoma. The practical point is that this type of condition is covered by the anoderm and the blood clot formation lies under the skin, whereas internal hemorrhoids are covered by the anal mucosa and anal pigmented melanoma represents a long history of pigmented skin lesions.
The cause of hemorrhoids is a combination of several factors. The main ones include:
- passive lifestyle;
- increased intra-abdominal pressure due to heavy physical exertion or straining to defecate;
- frequent consumption of alcohol, spicy foods;
- hypothermia.
The rectum is densely entwined with spiral veins, which are presented in the form of nodes. Their inflammation reflects the essence of hemorrhoids. There are many reasons for its development:
- frequent and prolonged constipation, which causes trauma to the rectal mucosa;
- a sedentary and sedentary lifestyle, which results in increased stagnation of blood in the pelvis and a decrease in metabolic processes;
- lack of proper hygiene in the anal area, which provokes an inflammatory process;
- the presence of tumors in the rectum that interfere with the natural passage of feces, irritating the mucous membrane.
There are two types of hemorrhoids:
- Internal, when hemorrhoids located directly inside the rectum become inflamed.
- External, in which the inflamed nodes come out through the anus, causing unbearable pain.
Type of pain: Acute, throbbing pain. It intensifies immediately at the time of defecation and after it.
It may be accompanied by bloody discharge from the anus, which indicates a violation of the integrity of the hemorrhoid.
The source of pain is in close proximity to the anus, but can radiate to the groin, lower abdomen, perineum, tailbone, thigh. In addition to pain, hemorrhoids also manifest themselves with such manifestations as:
- itching in the anus;
- a feeling of a foreign body inside the rectum, which is most noticeable when sitting on a hard surface;
- mucus secretion;
- bloating;
- feeling of incomplete bowel movement.
Diagnostics If external hemorrhoids are present, its presence is visualized during examination by a proctologist. In cases where there is a suspicion that internal hemorrhoids are inflamed, sigmoidoscopy is performed. This type of examination involves inserting a microscopic probe into the rectum to assess the condition of the mucous membrane and identify hemorrhoids.
In advanced forms, surgical intervention is required when the nodes are completely excised.
Non-infectious causes
Sometimes pain may not be associated with diseases. This is possible in the following cases:
If foreign bodies enter the anus, acute pain in this area appears. Traumatic injury can occur from an object entering the rectum either from the inside or from the outside.
For example, a fish bone, passing through all parts of the gastrointestinal tract, can injure the intestinal mucosa and lead to an inflammatory process.
When large objects are inserted into the anus, the anus is stretched. The result will be pain and disruption of regional blood flow.
If there is a rupture of the rectal mucosa, stabbing and cutting pain will be observed.
Any traumatic injury causes pain. Their intensity will depend on the type of impact and the degree of its influence.
When a bruise occurs, the pain is dull. In such cases, all manifestations will disappear after 5-7 days.
If there is a rupture of the rectal mucosa, stabbing and cutting pain will be observed. When the coccyx is fractured, the resulting sensations irradiate to the anal area.
At the end of a long working day, it is very common to experience pain from sitting on a hard chair. Similar phenomena are common among office workers. To get rid of discomfort during the working day, periodic exercise will help to improve blood flow in the anus.
Acute thrombosed external hemorrhoids
Thrombosis develops when blood flow in the hemorrhoid is impaired. This happens if a person with hemorrhoids continues to sit in one place for a long time, impairing the natural blood flow in the rectum. At the same time, the node itself becomes even more inflamed, acquires a bluish tint, and also interferes with living peacefully.
Type of pain: The pain is sharp, shooting, stabbing, dagger-like. It intensifies at the time of defecation, but subsides after. Localization The anus with radiation to the coccyx and perineum. Additional symptoms Thrombosis is accompanied by a feeling of fullness from inside the rectum, as well as the appearance of a characteristic pulsation and burning sensation, which is especially pronounced when sitting.
Diagnosis Before conducting an internal examination of the rectum, the doctor examines the area around the anus by palpating it. Palpation helps to assess the extent of damage to the node, as well as the need for surgical intervention. Treatment The most adequate treatment in this case is surgery to excise the affected nodes.
If there is no effectiveness, surgery is the only way to return normal life.
A complication of hemorrhoids, in which severe pain occurs in the anus, is thrombosis of the veins of the anal area. The mechanism of its development consists of several points. First, in the section of the rectum where the characteristic lump appears, the inner wall of the vessel is damaged. Here a blood clot begins to form and grow, which interferes with normal blood flow, causes congestion in the vessel, then a focus of inflammation and swelling appears. Such changes are accompanied by constant discomfort. Excruciating pain makes the process of bowel movement very difficult.
Therapeutic measures
To eliminate discomfort in the anal area, it is necessary to establish the underlying cause and make a diagnosis.
Diagnostics includes sigmoidoscopy, external examination, patient interview, digital examination of the rectum and prostate, laboratory testing (blood, stool, urine tests, smears for sexually transmitted diseases). If itching and burning are caused by allergies, antihistamines are prescribed. In the presence of proctosigmoiditis, diet, astringents and enveloping drugs, antibiotics, and probiotics are indicated.
If hemorrhoids are detected, suppositories (Relief, Posterizan, Anestezol) or ointments, diet, and vascular-strengthening drugs (Detralex) are prescribed. If there is severe sphincter spasm, antispasmodics are indicated. If the itching is caused by helminthic infestation, then anthelmintic drugs are prescribed. For enterobiasis, Mebendazole or Vermox is indicated; for giardiasis, Metronidazole is indicated.
Anal fissure
The occurrence of an anal fissure is associated with a violation of the structure of the mucous membrane of the anus. It is usually formed on its back wall, 1-2 centimeters long, the width and depth usually does not exceed a few millimeters. Factors that can provoke such a change are injuries to the anal area, a tendency to constipation, stress when lifting and carrying heavy objects, playing “heavy” sports, and the presence of a source of infection in the body. In women, such a crack forms during childbirth, in the postpartum period.
A common anorectal condition presenting with a small tear when the rectum is opened. Its exact etiology is debated, but there is a clear association with increased anal sphincter pressure. The fissure is thought to be caused by trauma to the anal canal and includes damage to the anoderm during the passage of hard and dense stools, local irritation from diarrhea, anorectal surgery and anal intercourse.
- Sharp pain in the anus, described as tearing.
- Bleeding (bright red blood may be noted on toilet paper or drip into the toilet).
- Sensitivity of the fold of skin covering the outer end of the anal fissure (“border tubercle”).
The acute stage lasts several minutes, and then turns into an aching, throbbing pain that can last for hours. The vicious cycle of anal spasms and hard stools exacerbates further traumatic and ischemic damage to the anoderm and prevents the healing of the fissure.
The fissure is localized along the posterior midline, and there are several explanations for this phenomenon:
- Elliptical placement of the external sphincter posteriorly, resulting in less support of the anal canal.
- Relative ischemia of the posterior commissure of the anal canal.
- Contusion of vessels passing vertically through the internal sphincter muscle in the posterior midline, resulting in a compromise of blood supply.
Most patients believe that if pain radiates to the anus, then it is caused by hemorrhoids, and are reluctant to accept the diagnosis of anal fissure. Physical examination by gently separating the buttocks usually reveals a fissure, although sphincter spasm may prevent adequate visualization. A thorough examination with endoscopic equipment should be performed when the patient is pain-free to rule out other diseases of the male anus.
The rectal mucosa is rich in nerve endings that control the process of bowel movements. In the case when the mucous membrane is damaged, an anal fissure may develop, the causes of which are as follows:
- frequent constipation, injuring the mucous membrane;
- ingestion of sharp objects into the intestines along with food;
- decreased elasticity of connective tissue;
- insertion of foreign objects into the anus.
Type of pain The pain is sharp, acute, which gradually turns into spastic. Worsens with defecation.
Severe pain in the anus may subside when lying on your stomach.
Aching pain in the anus is localized at the anus, but can radiate to the perineum and groin. A fissure can also manifest itself with symptoms such as:
- bleeding after defecation, while the blood is scarlet;
- swelling of the anus and skin hyperemia;
- a burning sensation inside the anus and a false urge to defecate.
If an infection occurs, purulent mucus may come out of the anus. Diagnosis The fissure is visualized during a rectal examination.
If its localization is difficult to identify, they resort to hardware research.
They use wound-healing suppositories that have a complex effect, relieving pain, tightening the crack site and disinfecting the anus.
Risk factors and causes of pain in the anus in men
Pain in the anus in men creates inconvenience and discomfort in everyday life. There are nerve endings in the anal area, so any injury in the form of cracks, ulcers and growths is very painful. Pain increases with diarrhea, constipation accompanied by additional symptoms (itching, irritation, rash). Men scratch the area that is bothering them, which causes more pain.
The causes of pain in the anus in men are very diverse. But they all boil down to one thing. The constant discomfort that accompanies pain causes a lot of inconvenience for the patient. Unfortunately, many people do not want to go to the doctor because they are embarrassed. It is important to remember that monitoring your own health is nothing that could cause condemnation from the outside.
The essence of the problem
The anus, or anus (in everyday life - the anus), is the final section of the distal rectum, intended for the removal of feces through defecation. The anus is regulated by the sphincter, which encloses it in a ring, and the smooth muscles of the rectum, tensing, ensure that feces are pushed out through the opening.
The movement of the mass is facilitated by folds on the mucous membrane, one of which has a spiral shape. Protection from injury during defecation and free movement of feces is provided by thick, viscous mucus secreted by numerous glands of the rectum. In the area of the anus there is a plexus of veins that provide blood flow into the inferior vena cava.
The analysis of the anatomy of the anal area shows that the so-called anus has a rather complex structure, and therefore endogenous and exogenous factors can significantly interfere with the functioning of the mechanism for excreting feces. Violations in this area lead to various manifestations: itching, burning, bleeding, irritation, swelling, etc. Pain syndrome is one of the most common and unpleasant symptoms.
Why does pain occur? There are two main categories of provoking factors: pathological and non-pathological. Non-pathological causes are associated with a direct external impact on the element in question, causing irritation, injury, etc. Often, pain in the anus becomes an indicator of pathological processes developing in the anus or in various internal organs. The main influence is through the digestive system, blood supply and nervous regulation.
Pain in the anal area can be aching, stabbing, pulling, shooting, cutting, or sore. Particularly noticeable is the throbbing pain in the anus, as well as an unbearable burning sensation. Painful manifestations can be acute with an unexpected onset and equally unexpected subsidence. Moreover, the acute phase can have a certain periodicity over a long period of time. In such cases, we can say that the pain syndrome has a chronic course. In general, pain in the anus in women and men occurs frequently and with approximately equal probability, but with an increase in the frequency of manifestations in pregnant women.
Paraproctitis
This disease is determined by the presence of an inflammatory process in the rectum, which is provoked by several pathogenic factors:
- parasitic infections;
- poor nutrition;
- lack of proper hygiene;
- constipation;
- the presence of foreign objects in the anus.
Type of pain: The pain is acute, intense, and intensifies as feces pass through the damaged intestine. Localization The source of pain is concentrated near the anus, but in the presence of an inflammatory process higher up the intestines, painful sensations can occur in the lower abdomen and in the sacrum area. Additional symptoms Proctitis is characterized by manifestations such as :
- increased body temperature;
- nausea and vomiting;
- bleeding after defecation;
- sphincter spasms and false urge to defecate;
- a feeling of intense burning, which decreases with complete relaxation of the sphincter.
Diagnostics Making a diagnosis is impossible without conducting a detailed study, which includes:
- Visual examination of the anus and rectum, as well as palpation and assessment of sphincter spasm.
- A smear for pathogenic microflora from the anus.
- Hardware endoscopic examination by inserting a microscope into the rectum.
- Biopsy.
Treatment Before starting a course of treatment, the cause of the disease is determined for the patient. If these are helminths and other parasites, use antibacterial and anthelmintic therapy. Medicines are selected taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient. Local treatment consists of using rectal suppositories that have anti-inflammatory and wound-healing effects.
To normalize the intestinal microflora, a course of probiotics is prescribed: Linex, Bifiform, Lactiale, Laktofiltrum.
An inflammatory process that involves fatty tissue located on the inner wall of the rectum. A distinctive feature of the disease is the addition of a purulent process, as well as hyperemia of the skin. The cause of the development of the disease is the active proliferation of pathogenic microflora, as well as an advanced inflammatory process caused by bacteria such as:
- coli;
- streptococci;
- staphylococci;
- actinomycosis;
- tuberculosis bacillus;
- clostridia and salmonella.
Risk factors that contribute to the development of paraproctitis are:
- chronic infections of the digestive tract;
- hemorrhoids and anal fissures;
- stool disorder;
- decreased local and general immunity.
Type of pain The pain is aching, spastic, mild.
Accompanied by the release of purulent contents.
The anal area and perineum. Also, paraproctitis can provoke severe itching and discharge of ichor from the anus, which is not associated with defecation. The formation of a fistula and the development of a purulent process in it leads to irritation of the rectal mucosa. Symptoms may include:
- fever and increased temperature;
- severe burning and itching in the anal area;
- painful bowel movement.
Diagnostics The diagnosis is made based on the following studies:
- palpation of the anus;
- sigmoidoscopy;
- fistulography;
- anoscopy;
- ultrasonography.
A smear is also examined for pathogenic microflora, assessing the degree of irritation of the rectum. When pus is isolated, it is also taken for analysis. Treatment The main task of treatment is to open and drain the purulent focus, which is achieved through surgery.
In parallel, the patient is prescribed antibacterial therapy, which helps reduce the manifestation of the inflammatory process.
Impact of endogenous factors
Painful symptoms in the anal area can be provoked by processes whose focus is located far from the anus. The following pathologies can be highlighted:
- Prostatitis. This problem is most common among men over 45–50 years of age and is especially noticeable in a sitting position, when the unpleasant syndrome creates the impression of sitting on a hard ball. At times, men with prostatitis are bothered by a nagging pain in the anus.
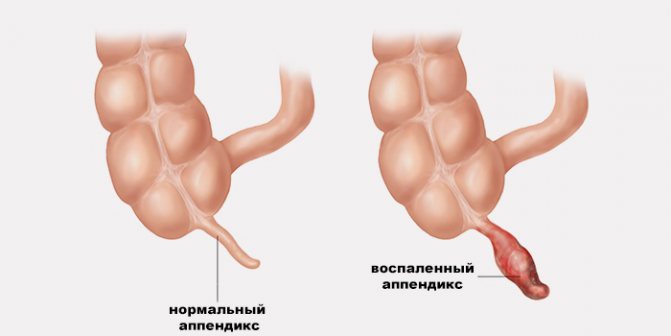
- Attack of appendicitis. With an acute inflammatory process in the appendix, severe, sharp pain appears. At the same time, characteristic symptoms are detected: fever, stool disturbance, nausea and vomiting.
- Diseases of the reproductive system. Most inflammatory pathologies in this category are characterized by pain that sensitively extends to the anal area.
- Disorders in the urinary system. The bladder and other elements of the system are located in close proximity to the anus, which means that pathological processes in them significantly influence the onset of pain. The most prominent diseases are urolithiasis, cystitis, and tumor formations.
- Sexually transmitted diseases (venereal diseases).
Foreign bodies in the rectum
Diagnosing persistence of foreign bodies in the rectum can be problematic for the physician, as many patients are unable to describe the exact history of their entry due to fear or embarrassment and often make some independent efforts to remove them. The most common reason is sexual pleasure.
Foreign objects can be sharp or blunt, of various shapes and sizes. Digital rectal examination may reveal only some parts, but it is necessary to assess whether there is evidence of rectal perforation or damage to the anal sphincter.
Symptoms indicating rectal perforation:
- stitching pain in the anus;
- fever;
- tachycardia;
- peritonitis;
- colic in the stomach.
The development of this pathology is directly related to a decrease in the tone of the ligamentous apparatus. Most often, this pathology occurs in weightlifters, as well as women who have had more than 5-6 births. With increased load, part of the rectum protrudes into the anus, after which it is pinched by the sphincter.
The pathology is very life-threatening, requiring immediate surgical intervention. Type of pain: The pain is sharp, dagger-like, shooting, and can provoke the development of a state of shock. Localization: Anus and lower abdomen. Additional symptoms The patient can feel an elastic neoplasm in the anus that pulsates.
In the absence of treatment, the risk of injury to the prolapsed intestine increases, which affects the process of defecation, and also promises the addition of a purulent-inflammatory process.
The anus is palpated, and if necessary, seek help from sigmoidoscopy. An urgent surgical operation is indicated, in which part of the compressed intestine is excised (if destructive and irreversible processes have begun in it), and the rest of the intestine is returned to its usual anatomical position.
Infectious causes
The main reasons leading to the development of pain in the anus are the following pathologies:
Painful sensations begin to appear during the process of defecation. The patient feels sharp and acute pain.
With anal fissure, pain in the anus in men occurs suddenly. The causes of this pathology are traumatic injuries to the mucous membrane of the lower rectum.
Painful sensations begin to appear during the process of defecation. The patient feels sharp and acute pain.
Hemorrhoids are one of the most common causes of discomfort in the anus. Almost always this is not the first symptom of a new disease. Very often, the patient has been suffering from itching and burning of the anus for a long time. Painful sensations appear if the process develops further. They can disturb the patient constantly and be sharp and stabbing in nature.
Complications may also develop. These include thrombosis and strangulation of hemorrhoids. These conditions are characterized by increased pain and swelling of the anus. In addition, disturbances in the general condition of the patient occur.
Proctitis is a disease of the rectum, accompanied by inflammatory changes in its mucous membrane. In this condition, the pain in the anus is severe and sharp.
The general condition of the patient changes. Constant malaise appears, body temperature changes. During the act of defecation, discharge may be detected that is purulent and bloody in nature.
This disease can also occur in two forms; acute and chronic. In the chronic course, the pain is not so pronounced, but is constantly present.
Paraproctitis is a purulent inflammation of the tissue surrounding the rectum. Due to irritation of a large number of nerve endings that are located at the anus, acute and severe pain appears.
In addition to local signs, changes in the general condition of the patient are detected. Malaise, weakness appear, and body temperature rises. With further development, fistula tracts may appear.
- Rectal prolapse.
If the rectum prolapses, the pain in the anus is so severe that the patient may develop a state of shock. Most often, older people suffer from this disease.
The patient must be provided with emergency assistance. The prolapsed intestine must be reduced or surgery performed on the altered area.
All neoplasms can become a source of pain. In addition to pain, bloody streaks appear in the stool. Treatment of tumors involves removing them.
Neoplasms and anal cancer
Although it is a rare disease, anal cancer is increasingly being diagnosed in patients with certain risk factors, mainly the human papillomavirus. The most common tumor of the anal canal and perianal skin is squamous cell carcinoma. Other predisposing factors include immunosuppression and smoking.
Most anal HPV infections are sexually transmitted, and the risk of cancer increases in homosexual men. During the course of malignancy, human papillomavirus causes anal intraepithelial neoplasia, which progresses from low-grade to high-grade dysplasia and ultimately to invasive cancer.
Many symptoms associated with cancer are common to benign diseases:
- bright red rectal bleeding;
- diarrhea and constipation;
- bloating, tingling and abdominal pain.
Indeed, some patients are initially treated as if they had a benign anal pathology (fissure or hemorrhoids). When a clinically suspicious lesion is identified, diagnosis relies on cytological or histological confirmation. Anal cancer is sensitive to chemoradiation, but early diagnosis is critical.
The appearance of neoplasms has practically no prerequisites, but for the rectum, constipation and the presence of chronic inflammatory processes can serve as pathogenic factors. Neoplasms can be of two types:
- Benign (polyps) - appear on the mucous membrane of the rectum in the form of seals (nodes) consisting of a clot of connective tissue.
- Malignant (cancerous tumors) - appear as a result of the degeneration of healthy cells into cancerous ones.
Type of pain The danger of this disease is that it is almost impossible to detect in the early stages. Pain occurs only when the tumor exceeds the size of 10 rubles, putting pressure on the intestinal walls and irritating it.
The pain can be spastic, throbbing, intensifies with defecation, but can go away on its own, masquerading as hemorrhoids.
Anus and rectum. Suspicion of the presence of polyps and cancer arises when the patient experiences constant constipation and loses weight. Chronic fatigue and signs of intoxication appear. The presence of neoplasms is detected by palpation, as well as during a hardware examination of sigmoidoscopy. Surgery is indicated, and in the presence of oncology, chemotherapy is simultaneously administered to help reduce the level of cancer cells and their metastases. This is a collective disease that is provoked worms that live in the human large intestine. They feed on digested food that comes from the stomach, while releasing dangerous toxins - products of their own vital activity.
Toxins, along with nutrients, are absorbed into the body and spread through the general bloodstream to all organs, causing large-scale intoxication.
There is no pain as such, but the patient experiences a constant feeling of burning, itching and movement in the anal area. This includes manifestations such as:
- signs of an infectious process with the addition of nausea and vomiting, as well as an increase in temperature;
- skin rash in the form of small white pimples;
- frequent constipation and lack of stool for more than 4 days.
Diagnostics If the presence of helminths is suspected, the patient is asked to take a stool test for worm eggs, as well as a rectal smear for pathogenic microflora. For a more accurate study, it is recommended to examine the blood for the presence of parasitic infections. Treatment Oddly enough, the fight against helminths is not difficult. The course of treatment is 2-4 days; with the right medicine, relief begins from the first day.
What does discomfort in the rectum mean?
Along with food, sharp fish bones, pieces of mussel or shrimp shells, apricot pits, and plums can enter the human body. In the stomach they are enveloped in mucus, but for the intestines, the lumen of which is several times smaller, they can cause damage to the mucous membrane. Type of pain The pain is acute, aching, spastic, sometimes accompanied by severe spasm and pain in the lower abdomen.
Localization Anus, perineum, lower abdomen and sacrum. Additional symptoms When the integrity of the mucous membrane is damaged, bleeding occurs, which intensifies with defecation. Diagnosis The presence of a foreign body in the rectum is quite difficult to determine, so sigmoidoscopy is used, which allows you to track every centimeter of the intestinal mucosa. Treatment The foreign body is removed. by curettage or incision, after which drainage is installed to remove suppuration.
At the same time, powerful antibacterial therapy and a strict diet are prescribed.
Prevention
As preventive measures you should:
- avoid sitting in one place for long periods of time;
- exercise;
- give up unhealthy foods, especially fast food;
- exclude strong physical activity;
- maintain hygiene and use linen made from natural cotton.
Thus, pain in the anus in men, for which there are many causes, is a consequence of metabolic disorders in the pelvis, which entails the formation of stagnant processes.
In men, treatment proceeds more slowly, since it is the stronger sex who are inclined to delay diagnosis, considering it a humiliating procedure.
Self-treatment of pain in the anus and its area is always very dangerous. It is necessary to undergo diagnostic procedures, determine exactly why the symptom occurs, and only then begin treatment measures; they must be supervised by a specialist doctor.
If a person has pain in the anus, it is not only unpleasant, the symptom often indicates the development of pathologies. You should immediately make an appointment with a doctor if you have the following symptoms:
- the pain is constant, aching, sharp or sharp;
- there is severe pain in the anal area after defecation, the process itself is very difficult;
- stool disorders often occur;
- blood discharge appears from the anus, impurities of pus or mucus are present in the stool;
- hemorrhoidal cones and veins become inflamed;
- There is deterioration in health, low ability to work, weight loss, and fatigue.
The main method of preventing pain in the anus is timely identification and treatment of diseases that provoke the symptom. The doctor advises patients to change their lifestyle, avoid maintaining a sitting position for long periods of time, increase physical activity, walk more, and do exercises. It is recommended to avoid constipation.
To prevent discomfort in the anus in women, doctors recommend undergoing annual scheduled examinations by a gynecologist. Perhaps the discomfort is caused by sexually transmitted infections, urinary or genital diseases, thrush, injury to the uterus or vagina.
Treatment
To eliminate pain in the anal area, it is necessary to identify and treat the underlying disease that caused its occurrence.

To eliminate the unpleasant symptom, the use of symptomatic treatment is recommended. Highly effective in this case are suppositories that include an anesthetic, for example Proctoglivenol, Relief Advance.
You can also use anti-inflammatory drugs. You can use products in the form of ointments and creams that have an analgesic effect or eliminate inflammation, for example Heparin ointment, Levomekol, Proctosan.
Anal injuries

If there are careless movements, falls or accidents, the pelvic area and anus may be injured. The type of pain and its duration directly depends on the type of injury:
- Bruise - acute, spastic pain. Peak pain in the first 24 hours after injury. Over the next 3-5 days, the painful sensations gradually fade away.
- Violation of the integrity of the anus - the pain is dagger-like, ultra-sharp, and can provoke the development of shock. Accompanied by heavy blood loss.
- Fracture of the pelvic bones - the nerve endings of the rectum are pinched, which is accompanied by acute pain.
Which doctor should you contact?
What to do if there is constant pain in the anus and rectum? A proctologist will reliably determine why the anus hurts. This specialist “works” specifically with diseases of the intestines - colon, anal area. After examining the patient, if there are characteristic symptoms, the specialist may refer him for consultation or further observation to doctors with specializations:
- venereologist;
- infectious disease specialist;
- oncologist;
- traumatologist;
- gastroenterologist;
- nephrologist;
- surgeon
If there is pain in the anus in women, in many cases an examination by a gynecologist is required. If a similar symptom occurs in men, they need to make an appointment with a urologist.
In a number of situations, medical assistance should be provided as quickly as possible, which will save a person’s life and prevent the disease from worsening. You should not ignore going to the doctor if:
- Constipation began to occur more often than 5 times a month.
- After defecation, pulsation is noted in the anus.
- Pain in the anus occurs with prolonged sitting.
- Difficulty defecating, as well as the appearance of scarlet blood or clots in the stool.
- Body temperature rises, accompanied by chills.
Types of pain
Pain in the anus can occur suddenly and unexpectedly or be constant for a long time. Acute pain manifests itself more sharply and develops over 1-2 days. It passes in the same short time as its beginning.
Chronic pain is less pronounced, but lasts longer. They can persist for several months.
For only 990 rubles you will receive the latest development in the field of medicine! With its help you can get unprecedented pleasure! Read the couple's interview. >>
The nature of the pain can be:
- aching;
- cutting;
- piercing;
- pulling;
- night;
- permanent;
- short-term.
These signs indicate to the doctor the type of pathology that led to the appearance of symptoms.
Other anorectal disorders
Anorectal abscess and fistula are among the most common conditions found in adult men. Essentially they should be considered as acute and chronic phases of the same anorectal infection.
Abscesses are thought to begin as an infection in the anal glands, which spread to adjacent areas and lead to fistulas. If left untreated, they will become painful and progress to serious generalized infections, affecting other parts of the body, especially the groin and rectum areas. Patients with long-standing fistulas are at risk of developing cancer.
Typically, inflammation is caused by infection with bacteria common in the digestive system (like E. coli) that collect in one place or another. There are various reasons for this. Most anorectal abscesses are easily diagnosed by physical examination. Pain in the perianal area is the main symptom of anorectal abscess. It can be pulling, aching or throbbing, worsened by coughing and aggravated when a person changes body position or before defecation.
Signs and symptoms include:
- constipation;
- rectal discharge;
- palpable mass near the anus;
- fever (fever and chills).
Anorectal abscess requires drainage surgery. There is no antibiotic therapy as a "conservative" management. The abscess wall contains occluded and necrotic blood vessels, and the antibiotic never penetrates the cavity.
Some anorectal disorders may occur in emergency situations. A detailed history and thorough physical examination are important for the correct diagnosis and treatment plan. It could be:
- Perianal hematoma.
- Coccydynia.
- Anal itching.
- Rectal prolapse.
- Solitary rectal ulcer;
- Proctitis (ulcerative proctitis).
- Infectious disease (Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis).
- Spastic proctalgia, characterized by severe episodic pain in the rectum and anus.
Anorectal diseases affect men of all ages. For anal pain in men, treatment is prescribed by a general practitioner, family doctor, gastroenterologist, or colorectal surgeon. But it is extremely important to understand the basic principles of diagnosis and treatment of these pathologies in order to best alleviate the problems of patients.
Due to blockage of the anal gland, the emergence of a source of infection in it causes an anorectal abscess. Pus accumulates in the cavity of the gland, and areas located next to the rectum are “involved” in the process. Against the background of elevated temperature (above 38 degrees), chills, the anus hurts greatly, the sensations are not associated with the process of natural emptying.