Restoration of intestinal microflora
There are several medicinal ways to restore the intestines after a rotavirus infection. The doctor prescribes the following drugs when the acute stage of the disease has already passed:
- Maxilak. This product contains pre- and probiotics. It is prescribed to adults and children. It helps well if constipation is a consequence of intestinal flu. The release form is a powder that dissolves in clean water. Duration of treatment – 2 weeks. You need to take 2 sachets of the product daily (in the morning and before bed).
- Linux. Includes bifidobacteria, which help quickly restore the gastrointestinal tract after infection. Relieves constipation and diarrhea. Children are given 1 capsule, and adults – 2 capsules 3 times a day.
- Bifidumbacterin-forte can be purchased in several forms: capsules and powder. The composition includes bifidobacteria, which restore the microflora inside the intestines. It is recommended to take the drug at least 3 times a day. Children drink 1 capsule, adults - 2. The powder dissolves in liquid. Be sure to take the product with meals.
A specialist should determine how to restore the stomach after a rotavirus infection. Each patient has his own individual method. Only a doctor can prescribe it correctly, based on the medical history, the consequences of the problem and the characteristics of the body.
How does the disease progress?
Despite the fact that rotavirus is considered an intestinal infection, it begins to infect the human body from the upper respiratory tract. It is observed more often in children under 5 years of age. It is during this period that the immune system is easily exposed to the virus, which is why children get this disease more often than adults. Rotavirus affects the mucous membranes of the intestines, stomach and duodenum, causing disorders and dehydration.
The virus, entering the child’s body, may not manifest itself in any way during the first 5 days (incubation period). Afterwards comes the stage of exacerbation and during this period the first signs begin to appear. The child begins to worry and cry for no apparent reason. It gets especially bad for him on the first day.
The pathogens are released along with the feces, so the sick person is considered a carrier of infection to all family members and others.
Is it possible to get re-infected with the virus?
Detoxification
For this purpose, patients diagnosed with intestinal flu are prescribed:
- Smecta. For children - in the first 3 days, take 4, then 2 sachets per day. The therapeutic course is 5-17 days. The composition of the sachet is diluted in 0.5 cups of water. Adults – up to 6 sachets per day. Duration of treatment is 5-7 days.
- Enterosgel. Children: a tablespoon three times a day. The product should be taken 60 minutes before meals with plenty of liquid. Adults 1.5 hours, l. also three times a day before meals.
It is also useful to take activated carbon. The drug cleanses the body well of pathogenic microbes and toxins.
Restoring water balance
An important task of the recovery period after rotavirus is to normalize the water balance. Otherwise, the patient faces dehydration. The following solutions can be purchased at the pharmacy:
There is a home recipe for how to restore water balance after a rotavirus infection:
- A liter of water is boiling.
- The hot liquid is mixed with a small spoon of salt, 4 large spoons of granulated sugar and half a teaspoon of soda.
- If desired, add a slice of lemon to the resulting drink to improve the taste.
The resulting solution should be drunk 20 ml every 15 minutes.
Possible complications and consequences
The course of the disease in most cases is moderate. With the right treatment tactics, complications do not occur, but sometimes the infection becomes life-threatening for the child.
What is dangerous:
- severe dehydration;
- acetonemic syndrome;
- convulsions;
- neurological disorders (neurotoxicosis);
- acute renal failure;
- diarrhea or constipation;
- asthenic syndrome;
- cough;
- repeated rotavirus.
Such complications occur more often in children from 6 months to a year or in older children with impaired immune system function. A rotavirus infection can be accompanied by bacterial pathogenic microflora, which also aggravates the course of the disease and can cause severe toxicosis with exicosis (reduction in the required amount of fluid in the tissues).
As a rule, after rotavirus the child has a stomach ache. The most common cause of pain in the epigastric region is dysbacteriosis.
Depending on the location of the pain and the child’s complaints, the doctor may prescribe:
- means for relieving attacks of intestinal colic;
- herbal decoctions or mineral water;
- sorbents;
- oral rehydration solutions.
If the pain is accompanied by:
- vomit,
- heat,
- diarrhea with bloody impurities,
you need to seek medical help. You should also not delay if the pain does not go away within 30 minutes after home treatment.
It is much more dangerous if the cause of pain is pancreatitis. It develops against the background of a virus affecting the digestive system.
With this disease, the child experiences:
- severe pain of a girdle nature,
- repeated vomiting and diarrhea,
- Purple spots may appear on the abdomen.
In such cases, a mandatory consultation with a doctor is necessary.
After an infection, stool can be restored within a week, sometimes up to a month. The damaged mucous membrane needs time to restore its structure and normalize its function.
Meals during this period should be frequent and fractional, in small portions. As little as possible dairy products, fresh vegetables and fruits, especially apples.

Prolonged diarrhea is also caused by dysbacteriosis. When the mucous membrane is restored, the intestinal microflora is normalized, bacteria will begin to perform their functions and diarrhea will stop. Probiotics are prescribed as an adjuvant.
If in older children this condition is corrected with the help of diet and certain medications, it is much more difficult to deal with diarrhea in children under 1 year of age.
Against the background of rotavirus infection and after it, some children may develop secondary lactase deficiency. This means that the body cannot process milk (lactose), which makes up almost 100% of the child’s diet.
The stool is usually clear, yellowish-white, and often foamy. May occur without previous stimulation. Such children gain weight poorly, lose it, and lag behind in development. They are very restless and weak, and often suffer from colds.
In the treatment of secondary lactase deficiency, the following are important:
- dieting,
- the use of enzyme preparations and probiotics,
- symptomatic treatment (for example, against flatulence).
But another important factor is time. As a child develops with a proper diet, the body's enzyme systems are formed, and the diet becomes less dependent on milk and at an older age, dairy products are normally absorbed.
Even the mildest degree of the disease weakens the body. Since the virus affects the respiratory and intestinal tissues of the organs, children are very exhausted during recovery. Dehydration also leads to general weakness. Intoxication and accumulation of toxins from the pathogen poison the body and thereby weaken it.
At the height of the illness, the child is usually lethargic, may refuse to eat, and the food that enters the body is processed very slowly. The reason for this is that the infection slows down metabolic processes, since at this time all resources are aimed at fighting the disease. Metabolic processes in the synapses of neurons slow down in a similar way, which is clinically manifested by lethargy, drowsiness and weakness.
In severe cases of the disease, weakness can develop into asthenic syndrome. Asthenia, unlike ordinary fatigue, does not subside even after long-term sleep or prolonged rest, lasts longer and requires mandatory treatment.

To restore a child you need:
- normalize the regime and diet high in vitamins and proteins;
- include light physical activity (exercise) in the mode;
- massage;
- do not neglect walks in the fresh air (including before bedtime);
- it is enough to stay in the sun;
- phytotherapy.
These recommendations focus on three main points that are important for combating weakness after illness:
- proper nutrition,
- restoration of muscle tone,
- relaxation of the nervous system.
If after 2-3 weeks the child remains lethargic and tired, you should consult a specialist.
Constipation (stool retention) is a common consequence of infection. Constipation can be caused by the disease itself or its treatment.
Causes of constipation:
- penetration of antibodies into the intestinal mucosa. Since rotavirus is sensitive to receptors for milk-processing enzymes, they provoke antibodies to fight them, destroying the intestinal mucosa. Thus, it cannot function properly and process food;
- inflammatory processes. As a result of illness or subsequent dysbiosis, enterocolitis occurs. The intestinal wall cannot conduct elements and water, as a result of which feces remain in the lumen of the organ;
- disruption of enzyme systems. They are disrupted when the pancreas and duodenum are affected, and less commonly the liver. They contain hormones that, under the influence of food, stimulate the production and release of enzymes. In their absence, food is not processed and remains unchanged.
Clinically, constipation is manifested by the absence of stool with a normal diet. And if it appears, the stool will be dry and hard. Children will complain of stomach pain and bloating.
In such cases, it is necessary to remove the cause of the pathological condition. If this is inflammation, you need to:
- stick to a strict diet,
- continue to replenish the fluid level,
- take sorbents.

Antibiotic therapy is not appropriate in this case, because these drugs do not act on the virus and can aggravate dysbiosis.
When it comes to enzymopathies, you cannot do without multienzyme drugs. They should be prescribed by a doctor according to the age and weight of the child.
In addition, if antidiarrheals are used incorrectly, constipation may occur. In such cases, the use of these drugs should be discontinued. There is no need to change your diet.
Diet after illness
Proper, light nutrition also contributes to recovery from rotavirus infection. Rules to follow:
- All dairy products will have to be excluded from your diet for a while. The exception is infants who drink their mother's milk. It is better to replace milk with plain water. Children can be given herbal teas with the addition of ginger to relieve stomach pain.
- It is better for children to prepare soups, broths, and purees from various vegetables.
- Adults are recommended to adhere to dietary table No. 4. It includes crackers, fish, various broths, rice and semolina porridge. Salt is completely eliminated for a while.
- You need to drink water, tea, cocoa and various decoctions.
- Vegetables, fruits and berries can be included only after diarrhea has passed.
- You will have to completely give up pearl barley and barley porridge, cabbage, garlic, pasta, all kinds of pickles, fatty and spicy foods, smoked meats, onions, coffee and carbonated drinks.
What to eat for a sick person: diet for intestinal flu
Diet during rotavirus infection is also an element of complex treatment.
Adult meals
In the acute stage of the disease, appetite is usually reduced or absent altogether, and the mere thought of food causes nausea. Therefore, in this case, it is necessary to maintain a drinking regime to replenish fluid loss.
In adults, this intestinal nuisance does not produce significant manifestations, and food intake often continues, but it is worth temporarily excluding a number of foods from the diet.

- Dairy products, which serve as a favorable environment for the life of the virus;
- drinks containing caffeine, which irritates the intestinal mucosa;
- fried and fatty foods, sausages and canned food. Digesting heavy food is undesirable for the body, which is currently fighting the invading virus.
Important! In the acute period of the disease, you need to limit the amount of food you eat and pay special attention to maintaining a drinking regime to prevent dehydration.
Organization of nutrition for children
Children infected with rotavirus almost always refuse to eat in the first days of the disease. You should not force your child to eat, but maintaining a drinking regime is fundamentally important. In addition to the rehydration medications mentioned above, you can offer your baby dried fruit compote, low concentration fruit drink, and weak tea. Drinks should not contain a lot of sugar.
Similar article - Pinched nerve in the lumbar spine symptoms
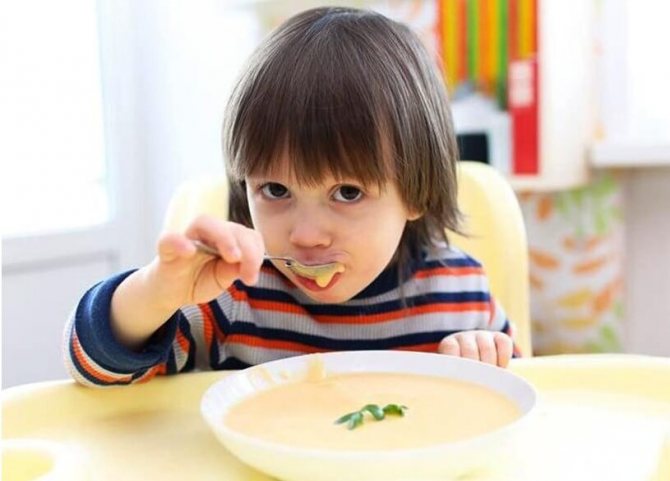

What to give to a child when acute symptoms are no longer bothersome, but the digestive system has not yet returned to normal? Offer your little patient light meals: semi-liquid porridge with diluted milk or water, pureed vegetable soups, lean meats, vegetables (boiled, stewed), baked apples, jelly.
Important! Even if, with the relief of the condition after rotavirus infection, the child develops a good appetite, during the recovery period large meals should be avoided and the consumption of a number of foods should be limited.
In the acute and recovery periods of illness, the following are prohibited:
- whole milk, and in some cases other dairy products;
- raw fruits, vegetables (primarily cabbage, garlic, radishes);
- rich bakery products, sweets;
- everything fried and smoked;
- sausage products;
- It is undesirable to consume certain types of cereals (pearl barley, millet).
In case of acute manifestations of the disease, you should not self-medicate; an intestinal infection is a reason to consult a doctor to make a correct diagnosis. Properly prescribed complex treatment in combination with a gentle diet will overcome the disease in a short time.

Work experience more than 7 years.
Professional skills: diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and biliary system.
Rotavirus infection or intestinal flu is a disease of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) with severe vomiting, light, watery, green stools with a pungent odor up to 10 times a day, leading to dysbacteriosis and dehydration.
After rotavirus infection, problems with stool and digestion are observed. To speed up regeneration after illness, it is worth following the recommendations, monitoring the baby’s sleep and nutrition.
Possible consequences
With proper treatment, complications from the disease do not occur. However, sometimes the infection becomes life-threatening. The consequences of severe forms of rotavirus can be different:
- convulsions;
- severe dehydration;
- neurological disorders;
- vcetonemic syndrome;
- diarrhea and constipation;
- renal failure;
- cough;
- relapse.
Most often, these complications affect children whose immunity is still very weak. The most severe option may be the addition of bacterial microflora to rotavirus infection. The result is severe toxicosis and lack of fluid in the body tissues.
It is important to promptly and correctly eliminate all consequences in order to restore the child after rotavirus infection as quickly as possible.
Abdominal pain
After suffering from rotavirus, the child begins to have a stomach ache. The reason is dysbacteriosis. Pathogenic microflora in the intestines leads to a large accumulation of gases. No antispasmodics or painkillers need to be given. Depending on where the pain is localized, the doctor may prescribe:
- mineral water;
- herbal decoctions;
- remedies for intestinal colic;
- sorbents;
- rehydration solutions.
Treatment of a child
It is worth talking about the treatment of a child separately, since children are much more susceptible to the disease.
Children begin to experience the disease with attacks of vomiting, sometimes multiple times. Also, in most cases, the child is lethargic and sleepy. As a rule, vomiting begins at night.
Then the body temperature rises to thirty-nine degrees and above.
It is worth saying that at a body temperature of thirty-nine degrees, call emergency help, since the temperature with rotavirus is difficult to reduce with antipyretics. With severe vomiting and diarrhea, the child quickly becomes dehydrated.
We recommend reading: Pancreatogenic diabetes mellitus - causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
Stool upset begins, cramping or constant pain in the abdomen occurs, accompanied by rumbling. The stool is mostly foamy with an unpleasant sour odor and yellow or light in color.
Vomiting and diarrhea accompanied by an elevated temperature can lead to dehydration.
- No urination for more than two hours;
- Crying without releasing tears;
- Lethargy, for falling eyes;
- Cloudiness of consciousness;
- The temperature does not decrease after taking medications for it;
- Heart problems;
- Convulsions are possible.
In serious condition, the baby is hospitalized in a hospital. Where treatment is carried out by restoring the water-salt balance through droppers and treating associated symptoms.
How to reduce fever with rotavirus:
- For children, the most effective remedy for fever is paracetamol in the form of suppositories, which is especially effective for repeated vomiting;
- Rubbing with a water-vodka solution;
- Do not wrap the baby.
- In case of repeated vomiting, antiemetics are used in ampoules, vomiting stops after half an hour (Cirukal);
- Regidron - restores water-salt balance;
At home, to urgently help a child, if you don’t have Regidron in your medicine cabinet, you can make an analogue of a water-salt solution: take a tablespoon of sugar and a teaspoon of salt per liter of boiled water. Stir, drink one tablespoon every fifteen minutes. You must consume at least two hundred milliliters of solution per day.
- Among the folk remedies, decoctions of medicinal herbs perfectly relieve gagging and reduce inflammation of the mucous membranes: chamomile, ginger root.
Or, freshly squeezed orange juice is a great way to help with dehydration.
For severe diarrhea use:
- Preparations based on nifuroxazide (Enterofuril, Stopdiar);
- Medicines based on unicellular yeast fungi of the order Saccharomycetes (Enterol);
- Semiticon-based products (Smecta, Neosmectin);
- From folk remedies: bird cherry, oak bark.
Prevention of recurrent disease
It is important not only how to recover from rotavirus infection as an adult or child, but also how to protect yourself from this problem in the future. To prevent the virus from returning, it is recommended to follow simple preventive rules:
- clean the apartment using disinfectants;
- maintain hygiene: always wash your hands with soap after going outside, before and after eating, etc.;
- pay close attention to the freshness and quality of products;
- treat toys.
It is very important to restore normal functioning of the body after rotavirus infection. If you leave everything to chance and don’t follow your doctor’s recommendations, the recovery period will take a long time. There may even be a relapse.
What mothers should pay attention to
Mothers complain of child lethargy after rotavirus. A balanced diet, vegetables, fruits rich in vitamins, and fresh air help to recover.
I’m interested in what day is it permissible to wash. It is necessary to wipe the child with a damp towel in the first days of illness, when the high temperature does not allow swimming. After the temperature subsides, it is permissible to wash in the bathroom or take a shower.
Moms ask about walking with rotavirus. It is easily transmitted to others - the sick person is isolated from healthy children, provided with individual utensils and hygiene items. Take a closer look at how the child recovers from an illness and at his nutritional habits.
The condition improves on days 3-5, the temperature drops, and the baby is bathed. You should not have contact with healthy children; avoid going for walks.
10-15 days after the onset of the disease, intestinal function normalizes, the child becomes active and begins to eat. It is permissible to walk outside, not forgetting about hand hygiene: immunity to rotavirus is not developed, and there is a possibility of relapse.
You should refrain from going to the bathhouse or public places with your child to avoid infecting others. The baby's room and used areas are disinfected.

The disease has several names: rotavirus gastroenteritis, stomach or intestinal flu, rotavirus infection. It is bacterial in nature. A child’s stomach ache after rotavirus is precisely because of bacteria. The incubation period lasts up to 5 days. An adult or child who has become infected with this disease is considered a carrier of the infection throughout the entire period from the moment of infection until complete recovery. The duration of the disease depends on the age and capabilities of the body. Adults tolerate it more easily; with proper therapy, they begin to recover on the seventh day.
Similar article - Free al drug
Causes of constipation
Constipation after rotavirus infection occurs as a result of an intestinal disease and the development of antibodies that destroy the intestines and gastrointestinal microflora. The motility of the colon is impaired.
Reasons for interrupting the act of defecation:
- Penetration of antibodies into the intestinal mucosa.
- Inflammation of the mucous membrane.
- Low content of enzymes that normalize digestion.
Causes of constipation:
- Poor nutrition, insufficient drinking regimen, early transfer to artificial feeding.
- Vomiting, sweating, fever (stool dehydrates the body).
- Congenital constipation occurs when:
- Dolichosigma - the sigmoid section of the colon is elongated, the lumen diameter and wall thickness remain unchanged.
- Agangliosis - the development of the nerve plexuses that provide innervation to the colon is impaired.
- Atresia – absence of the anal canal, underdevelopment of the rectum.
- Sedentary lifestyle, prolonged bed rest, diathesis, rickets, malnutrition, chronic gastroduodenitis, peptic ulcer.
- Inflammation of the skin of the anus due to chemical, physical, microbial exposure under a diaper.
- Paraproctitis, the appearance of anal fissures in the anus.
- Psychological factor - if defecation is painful, the child ignores going to the toilet.
- Intoxication of the body due to uncontrolled use of medications.
- Hypotonic constipation occurs when:
- Rickets - mineral metabolism, bone formation are disrupted, the musculoskeletal system, nervous system, and internal organs change. Vitamin D is prescribed with medicinal baths, massage, and gymnastics.
- Hypotrophy is a chronic malnutrition accompanied by insufficient growth of the baby’s body weight in relation to height and age.
- Gastroduodenitis is inflammation of the antrum of the stomach and duodenum. Characteristic symptoms are heartburn, nausea, decreased appetite, broken stools, and pain in the epigastric region.
Constipation due to rotavirus infection
The main danger of rotavirus infection is associated with dehydration due to severe diarrhea.
Rotavirus infection (synonyms Rotavirus gastroenteritis, stomach flu, intestinal flu) is one of the forms of acute intestinal infection, the causative agent of which is human Rotavirus of the genus Rotavirus . get rotavirus infection , but most often children from 6 months to a year or two get sick.
In some countries (for example, the USA), intestinal influenza accounts for up to 40% of all cases of acute intestinal infections in children. Adults become ill with rotavirosis (rotavirus infection ) by contracting it while caring for sick children.
Source of rotavirus infection and development of the disease
The source of Rotavirus infection is a sick person or a healthy virus carrier. The virus multiplies in the cells of the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract and is excreted in the feces. Isolation of rotavirus begins from the first days of the disease, simultaneously with the appearance of the first symptoms of the disease. The main mechanism of transmission of rotavirus infection is through food.
In children's groups, rotavirus infection can cause outbreaks of acute diarrhea (diarrhea).
Rotavirus affects the mucous membrane of the stomach and small intestine, causing gastroenteritis (gastro-stomach, entero-small intestine). Damage to the mucous membrane of the digestive tract disrupts the digestion of food and leads to the development of severe diarrhea and dehydration.
What does a mother urgently need to do to make her baby’s nose breathe?>
Symptoms of rotavirus infection
The incubation period for rotavirosis lasts from 1 to 5 days. The disease with rotavirus infection begins acutely: the first symptoms of rotavirus are abdominal pain (acute, cramping), vomiting (up to 3-4 times a day), malaise, fever (up to 38 C).
the described symptoms . A patient with rotavirus infection has profuse diarrhea of a yellowish color with a sharp, unpleasant, sour odor.
When examining a patient with rotavirosis, you may notice redness of the conjunctiva of the eyes, mucous membrane of the pharynx and palatine arches (inflamed throat).
The main danger of rotavirus infection is associated with dehydration due to severe diarrhea. The course of rotavirus infection is usually benign.
The disease ends after 4-7 days with complete recovery.
The described symptoms should be distinguished from the symptoms of cholera, salmonellosis, and food poisoning. After suffering from the “stomach flu,” strong immunity remains, so recurrent rotavirus infection is rare.
An adult may not even notice that he is
a carrier of rotavirus infection ;
the disease, as a rule, occurs with mild symptoms: a short-lived, possibly one-time case of diarrhea, loss of appetite, short-term fever. But during this period the person is contagious!
Treatment of rotavirus infection
There is no specific treatment for rotavirus infection (stomach flu). is indicated : treatment of diarrhea (mainly adequate rehydration of the body), lowering the temperature, a light diet and enzyme preparations (Smecta, Creon).
The most common scenario for the development and treatment of rotavirus infection in a child:
The child wakes up in the morning lethargic and may vomit even immediately on an empty stomach. There is no appetite, after eating the vomiting starts again, vomiting even after a few sips of water. These symptoms of rotavirus infection include a gradual increase in temperature to more than 39 degrees Celsius and diarrhea.
The temperature is difficult to reduce with medications and can remain elevated for up to 5 days. With such symptoms, immediately exclude any dairy products from the child’s diet, including fermented milk products: milk, milk porridge, kefir, cottage cheese, etc. The exception is breastfed children. Call your local doctor.
Don't force your child to eat.
To replenish the water-salt balance, prepare a rehydron solution - 1 sachet per 1 liter of water and let the child drink 50 ml every hour. Do not give large portions to drink - you may vomit immediately. Drink in small sips.
What can you feed during rotavirus infection: diet for the first 2-3 days - liquid rice porridge with water, chicken broth, jelly (water, starch, any homemade jam - boil until tender).
How and with what to bring down the temperature in a child with rotavirus infection: When the temperature rises above 38 degrees, cefekon suppositories will help reduce it (dosage according to the child’s age), suppositories are practically safe for use at any age, these suppositories can be placed every 2 hours, but not overdo it, bringing down the temperature; it should not be lowered below 38 degrees, since the rotavirus infection virus (rotavirus) dies at 38 degrees. Wet wipes with a weak alcohol solution are very effective in reducing fever. You should wipe the entire body, and not individual parts of it (so that there is no temperature difference between them); after wiping, put on cotton socks. Don't wrap up the child! When sleeping, cover with a sheet, not a warm blanket. If the temperature persistently rises above 39 degrees, a child from one and a half to two years old can be given half a tablet of paracetamol along with a quarter of analgin - a good remedy to bring down the high temperature.
For abdominal pain due to rotavirus infection: if a child cries and/or complains of abdominal pain (only with a confirmed diagnosis of rotavirus infection!), no-spa will help relieve them. Buy ampoules (2 ml each), give 1 ml in the child’s mouth for pain, wash it down with tea.
To prevent the development of intestinal bacterial infection, enterofuril is prescribed (dosage according to the age of the child, from 1 to 2 years - 1 tsp 2 times a day for 5 days) or enterol (but enterofuril is better).
To treat diarrhea due to rotavirus infection, smecta is prescribed (2 sachets per day in half a glass of water).
Source: https://cross-bones.ru/zapor-pri-rotavirusnoj-infekcii/
Symptoms of constipation
Constipation in a child after rotavirus has a detrimental effect on the gastrointestinal microflora. The abundant release of toxic substances into the body affects the intestines, delaying bowel movements.
- Weakness.
- Fast fatiguability.
- Frequent headaches.
- Irritability.
- Neuropsychiatric disorders.
- Urge to vomit.
- Decrease in the level of hemoglobin and red blood cells in the baby’s plasma.
- Pale skin.
- Purulent-inflammatory rashes.
- Absence of defecation for more than a day.
- The consistency of stool is impaired.
- There is a feeling of incomplete bowel movement after stool.
- Pain, bloating.
- The presence of plasma droplets in the stool.
- Painful sensation during bowel movements.
If symptoms appear, it is recommended to call a pediatrician.
Accumulated feces and disturbed intestinal microflora contribute to the occurrence of colitis, causing increased constipation in the baby. Retention of stool moves the distal part of the rectum beyond the anal sphincter.
Intestinal infection without diarrhea: does it happen and why?
It often happens that at the very beginning, when an intestinal infection is observed, there is no diarrhea, and sometimes constipation may even appear. The acute process begins with an increase in temperature, and diarrhea gradually develops. It happens that when infected, for example, with helminthic infestations, the infection immediately manifests itself as profuse diarrhea and all other unpleasant symptoms occur simultaneously.
Not a single infectious intestinal disease, of course, is complete without diarrhea, and then specific treatment and rehydration are required to avoid dehydration. Typically, 2-3 days after infection, the immune system begins to develop resistance to viral invasion.
The main thing is to hold out for the first few days. Dehydration of the body, which can occur due to rapid loss of fluid due to frequent, profuse diarrhea and vomiting, should not be allowed. It is important for parents not to miss the moment when their children show primary signs of an intestinal infection.
Features of intestinal infection without diarrhea
Symptoms when the intestines are infected with one or another intestinal pathogen directly depend on its type, as well as on the degree of release of toxins. For example, in case of salmonella infection, a child may not have diarrhea, but the following signs appear:
- nausea;
- vomit;
- headache;
- muscle spasms;
- joint pain;
- cramping pain in the abdomen.
After 2-3 days, liquid stool with mucus, blood or pus may appear when a viral infection is associated with an acute respiratory viral infection or acute respiratory infection. Additionally, patients complain of the following symptoms:
- high temperature;
- severe weakness;
- vomiting and nausea;
- decreased appetite;
- rapid weight loss in a child;
- stomach ache;
- diarrhea of a watery liquid consistency, but without blood, pus or mucus.
When infected with parasites, a longer incubation period is observed, which reaches up to 4 months, and occurs with an increase in temperature, acute abdominal pain, and profuse diarrhea, which can lead to serious complications: swelling of the lungs, brain, and liver.
When infected with Giardia, watery yellow diarrhea is usually observed in children. In this case, the child develops symptoms of flatulence and abdominal colic, cramps, anemia, and weight loss.
These symptoms are dangerous for children. If vomiting and diarrhea do not stop for more than 2-3 hours, then you should immediately consult a doctor.
Dehydration of the body may quickly occur, in which case urgent restoration of fluid balance will be required.
Why does diarrhea occur with an intestinal infection?
Intestinal infection begins acutely, its symptoms directly depend on the number and nature of pathogens that have entered the intestines, as well as the characteristics and state of the immune system.
The subsequent development of dysbacteriosis is possible, which usually happens when adenylate cyclase is activated against the background of the spread of bacteria.
Helicobacter pylori, salmonella, as well as enterotoxins from other bacteria inevitably lead to a malfunction of the gastrointestinal tract, and diarrhea can begin at almost any time even before the onset of infection: after eating stale food or unwashed vegetables and fruits.
Typically, the acute course of an intestinal infection lasts up to 2 weeks and, in addition to diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and fever are often present. It happens that infection in children immediately begins with profuse diarrhea with incontinence, which then gives way to constipation.
The condition returns to normal during the recovery period; unpleasant symptoms may go away after 1-2 weeks, but in the first days it is not easy for children.
Although in the case of a cold, acute respiratory viral infection, or acute respiratory infection, if the immune system is excessively vulnerable, the activation of viruses and bacteria in the body may begin again after some time, and the symptoms will recur, but with less intensity.
Can constipation occur due to an intestinal infection?
Difficulties with defecation are usually caused by helminthic infestations (infection with parasites).
The so-called irritable bowel syndrome occurs when the infection is accompanied by prolonged constipation and the inability to pass feces in a timely manner, which leads to aggravation of the process.
The intestines are affected, and their motility deteriorates. When too many parasites accumulate in an organ, they can completely clog the lumen. Constipation may also be associated with this.
But usually the infection still begins with diarrhea. This way the body is forced to get rid of toxins, which leads to weakened peristalsis and the release of contents from the intestines to the outside.
Further, the child’s intestinal motility will gradually recover on its own, but dysbiosis leads to severe disruption of the microflora and restoration of intestinal functions is required.
Often, due to a violation of the natural microbial biocenosis, constipation, alternating with diarrhea, develops.
Symptoms of intestinal infection
The main symptom of an intestinal infection is diarrhea, and its appearance should serve as a signal to contact doctors for help in order to prevent severe dehydration of the body. This is especially true for babies in the first 2 years of life, when passing copious loose stools more than 5-6 times a day inevitably leads to dehydration and urgent fluid replacement is required.
A rehydration procedure is carried out using saline solutions and glucose. Children can be given fruit drinks and compotes to drink in small sips.
When contracting an intestinal infection, you need to navigate the situation. If there is continuous vomiting and diarrhea, then you can give Smecta and provide plenty of fluids every 15-20 minutes to replenish fluid in the body.
You need to approach treatment responsibly and pay attention to the existing signs, since in rare cases there may not be diarrhea at all, but other unpleasant symptoms are present. Young children experience particular discomfort, but cannot talk about it on their own. Parents need to be extremely careful. Some symptoms should alert you:
- a sharp increase in temperature to 39°C;
- severe intoxication of the body;
- restlessness of the baby, twisting of the legs and pressing them towards the tummy;
- loss of appetite or complete refusal to eat;
- frequent regurgitation in breastfeeding infants;
- bloating, constipation;
- flatulence;
- discharge of watery, liquid or foamy diarrhea with streaks of blood and particles of undigested food;
- weakness, lethargy;
- absence of tears at the time of crying, absence of urine for 6-8 hours;
- rolling up the orbits of the eyes;
- dry skin.
The listed signs require immediate medical attention. A severe form of intestinal infection can lead to the development of cardiovascular failure and death.
Rotavirus is more severe in a child with a weakened immune system, but after the illness, stable immunity is developed. The main thing is to prevent dehydration and consult a doctor if you are unable to achieve improvements on your own at home within a day from the moment diarrhea appears.
As first aid for an intestinal infection, you should not immediately resort to medications (Levomycetin, Phthalazol). It is unknown what pathogen causes diarrhea, and in case of a viral infection, antibiotics are generally useless. These drugs also do not affect the spread of intestinal invasions.
Antibiotics are not able to destroy and remove E. coli from the body and are also detrimental to the beneficial microflora in the intestines.
Often, doctors, especially for infants, try to replace antibiotic drugs with safer agents:
- eubiotics;
- enterosorbents;
- Activated carbon.
If diarrhea does not go away for a long time after an intestinal infection, you should try to restore the lost fluid and salts with ready-made medications: Regidron, Glucosolan, Oralit. You just need to dilute the powder in water. If a child is worried about constipation, then it is useful to give children green tea, dried fruit compote, and still mineral water.
Source: https://nashainfekciya.ru/kishka/kishechnaya-bez-ponosa.html
Diagnosis of the disease
After a rotavirus infection, a child experiences stool retention, so it is necessary to seek the help of doctors so as not to cause complications. Diagnosis of the baby takes place with the participation of a doctor, who, based on the tests obtained, determines the onset of the disease, frequency, and consistency of stool.
The pediatrician must identify bloating, identify fecal stones, assess the strength of the sphincter, and exclude an organic malformation.
The main methods for diagnosing stool retention:
- Examination of feces for the quantitative and qualitative species composition of intestinal microflora.
- Advanced diagnosis of feces, determining the functional activity of the gastrointestinal tract, the breakdown of nutrients, the speed and quality of food digestion.
- Examination of stool for the presence of worms.
- Biochemical analysis of plasma.
- Ultrasonic echolocation of the pancreas for possible damage: size, contour, structure are determined.
- Esophagogastroduodenoscopy – the esophagus, stomach, duodenum are diagnosed for changes in the mucous membrane, chemical, traumatic damage.
- The distal parts of the colon are examined by ultrasonography - intestinal ischemia, colitis, abscess, Crohn's disease, and colon tumor are diagnosed.
- Irrigography is an X-ray examination of the large intestine after filling with a barium suspension. The method determines abnormal development of the large intestine, the presence of foreign bodies, and intestinal obstruction.
- X-ray visualization - advancement of contrast through the small intestine. A tumor, enteritis, malabsorption, and small intestinal motility are detected.
- X-ray of the abdominal cavity for the presence of fluid, free gases, and foreign bodies.
Intestinal infection in adults: signs, symptoms and treatment – About constipation
› Diseases ›
Intestinal infection is a group of diseases that arise due to human infection with pathogenic microorganisms through the gastrointestinal tract.
The incubation period - the period from the onset of infection to the appearance of the first symptoms - varies from 2-3 hours to several days. An intestinal infection can be asymptomatic, but the patient will be a source of pathogenic bacteria and viruses for others.
The most common infectious agents include:
- enteroviruses;
- rotaviruses;
- salmonella;
- staphylococci;
- shigella;
- cholera vibrios;
- coli.
According to the type of pathogen, the disease will be called:
- entero- or rotavirus infection;
- salmonellosis;
- dysentery;
- cholera;
- Escherichiosis.
Causes of intestinal infection in adults
There are several factors contributing to the occurrence of intestinal infection:
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- swallowing water while swimming in the sea, river or lake;
- violation of sanitary standards for food processing;
- lack of suitable conditions for storing prepared dishes.
The peak incidence of intestinal infections occurs in the summer season - in the heat, food spoils faster, while the diet often contains vegetables, fruits and herbs “straight from the garden.”
Confidence in their undeniable benefits often leads to the fact that a person forgets about the need to thoroughly clean root vegetables from adhering earth and sand, and neglects heat treatment.
Thus, along with a portion of vitamins, pathogenic microbes penetrate into the body. This method of contracting an infection is called enteral.
Nature has provided reliable mechanisms of protection against the threat of intestinal infection:
- saliva produced during chewing of food contains bactericidal enzymes;
- gastric juice (at a normal acidity level) destroys the cells of most microbes;
- intestinal microflora suppresses the activity of foreign agents;
- local immunity in the intestines destroys pathogenic microorganisms, preventing their growth and reproduction.
But sometimes natural mechanisms are not able to cope with the threat for a number of reasons:
- a person chews food poorly - due to dental problems or the habit of eating “on the go”;
- the digestive tract does not work properly due to chronic diseases;
- intestinal microflora is disturbed after drug treatment or poor nutrition;
- the body is weakened due to systematic smoking, alcohol abuse, lack of sleep and rest;
- bacteria and viruses are too strong.
Providing first aid for intestinal infection
If symptoms of an intestinal infection appear, you should consult a doctor for a diagnosis and correct treatment. Before his arrival, you can provide first aid to the victim:
Perform gastric lavage. If the source of infection has recently entered the body with food, this measure will eliminate some of the toxins and prevent their further absorption. In case of an intestinal infection, the patient is given plenty of fluids and vomiting is stimulated by pressing the fingers on the root of the tongue. The procedure is repeated several times until the vomit is clear.
For the same purpose, intestinal lavage is performed. You can give an enema with warm water, a solution of potassium permanganate, or give the patient a saline laxative. Some of the pathogenic microorganisms that have already settled in the intestines are removed with the help of enterosorbents.
If they are not in your home medicine cabinet, any analogue will do. The patient is provided with plenty of warm fluids. It is desirable that the temperature of the liquid corresponds to the level of body temperature - then the absorption of water from the stomach into the blood will be as fast as possible.
A person with symptoms of an intestinal infection must be isolated from other family members. In adults, the disease is much milder than in children. The patient is given separate dishes and a towel, and all common items are disinfected.
Try to determine the source of intestinal infection - find out what the sick person ate and whether he followed the rules of hygiene. If pathogenic microorganisms enter the body with food, separate it from other products, and then transfer it to a medical laboratory for analysis.
A patient with an intestinal infection should not be left unattended. Some of the intestinal infections - cholera, botulism - lead to coma if not treated in a timely manner. An ambulance should be called immediately if:
- vomiting does not stop for more than 2 hours;
- no urge to urinate for more than 6 hours;
- blood clots were found in the stool;
- body temperature rose sharply;
- diarrhea stopped simultaneously with increased vomiting;
- a pregnant woman or small child has fallen ill.
Intestinal infection: treatment in adults
To determine how to treat an intestinal infection, as well as differentiate it from food poisoning, laboratory tests are performed:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- bacteriological examination of feces and vomit;
- analysis of drinks and products - suspected sources of contamination.
In general, treatment of intestinal infection in a hospital will be based on the following principles:
- prevention of dehydration by taking water-salt solutions - Regidron, Orasan, Reosolan, as well as infusion therapy (intravenous fluids);
- acceleration of detoxification with the help of enterosorbents - Atoxil, Smecta, Sorbex, and in extreme cases - through hemodialysis and plasmapheresis;
- destruction of pathogenic microorganisms by administering antibiotics if the patient is in serious condition - Levomycetin, Norfloxacin, Vilimixin (taking into account the type of pathogen);
- stopping vomiting (if necessary) with prokinetics - Cerucal, Dibertil, Melomid;
- support of the gastrointestinal tract with the help of enzymes - Pepsin, Pancreatin, Acidin;
- normalization of intestinal microflora thanks to the intake of probiotics - Bioflora, Linex, Hilak.
Symptomatic therapy is performed as necessary. If, during an intestinal infection, the patient's temperature exceeds 38 degrees, he is given an antipyretic.
A special diet plays an important role in the treatment of intestinal infections. Since during an exacerbation of the infection the functioning mechanism of the digestive tract is disrupted, the patient is given only easily digestible food that does not contain an excess of fats, acids, or artificial additives.
If the intestinal infection is mild, the disease can be cured at home. To do this, it is enough to know how to treat intestinal infections in adults and follow the doctor’s instructions. In addition, it is important to ensure that the patient is isolated from other family members to prevent them from becoming infected. The essence of outpatient treatment is the same, but the medications used must be agreed with the doctor:
- You can buy a water-salt solution at a pharmacy, or prepare it yourself at home by adding a teaspoon of salt and sugar to a glass of warm boiled water.
- Enterosorbents can be anything. Inexpensive activated carbon will do.
- You can stop vomiting and diarrhea with medications only on the recommendation of a doctor. These processes help the body get rid of germs.
- If you use folk remedies, make sure they are compatible with traditional therapy.
- It makes sense to take antibiotics only after determining the type of pathogen. These drugs have a large number of side effects and contraindications, and act against a specific group of bacteria; They are ineffective for norovirus and rotavirus infections.
- You can put the gastrointestinal tract in order not only with the help of medications. Fermented milk products - kefir, homemade yogurt - will bring no less benefit.
If a patient with an intestinal infection has no appetite at first, there is no need to force feed him, the main thing is to ensure he drinks plenty of fluids. The volume of fluid for an adult should be at least 2–2.5 liters per day. It is allowed to give weak sweetened tea, dried fruit compote, rosehip infusion.
On days 2–3, you can transfer the patient to treatment table No. 4. Meals are divided, 5-6 times a day. Recommended dishes for intestinal infections are semi-liquid, boiled or steamed. Any ingredients that irritate the mucous membranes are prohibited until complete recovery, and the return to a normal diet should be smooth and gradual.
Preventative measures for intestinal infection
To minimize the risk of intestinal infection, it is necessary to take preventive measures:
- Wash your hands thoroughly after going outside and using the toilet;
- Do not drink water when swimming in open water;
- Store prepared foods in the refrigerator separately from raw ingredients;
- Fresh herbs, vegetables, fruits and mushrooms should be washed under running water until dirt and sand are completely cleaned;
- It is better not to eat raw seafood and eggs at all;
- Food products should not be purchased at spontaneous markets;
- Fish, meat, milk must be subjected to sufficient heat treatment.
All family members must take precautions.
The most famous treatment for intestinal infections in adults Link to main publication
Source:
Intestinal infection
Intestinal infections are a large group of infectious diseases of a bacterial and viral nature, occurring with intoxication, intestinal syndrome and dehydration.
In the structure of infectious morbidity, intestinal infections occupy second place, second in frequency only to acute respiratory viral infections. They affect children much more often than adults.
Source: https://taghospital7.ru/diagnostika/kishechnaya-infektsiya-u-vzroslyh-priznaki-simptomy-i-lechenie.html
Treatment of adiarrhea
Constipation due to rotavirus infection is a common problem in children. Main methods of therapy:
- Physical activity.
- Increase fluid intake.
- Diet – add vegetables and fruits to your diet; low-calorie fish; boiled meat; oatmeal; desserts containing gelatin; fermented milk products.
- The use of probiotics with beneficial bacteria and sorbents that remove toxins from the body.
- Enemas – cleansing, hypertonic oil.
- Use of laxatives.
- Hypotension is eliminated by massage with elements of therapeutic movements. Blood circulation and tissue metabolism are normalized.
- Physiotherapy:
- Galvanization is the effect of electric current on the body. Electrodes are applied to areas of the body in contact with the area of influence through special pads moistened with water.
- SMT therapy uses alternating modulated current. Currents (depending on the purpose) differ in frequency with an analgesic, vasodilating effect.
- Electrophoresis - medications are administered through the skin and mucous membrane using an electric current.
- Paraffin treatment - paraffin is applied to the affected areas of the skin for 30-40 minutes, covered with oilcloth and wrapped in a warm blanket.
After an intestinal infection, a child develops psychogenic constipation. A visit to a child psychologist is not superfluous.
Recovery after rotavirus infection in children
The first stage in the fight against rotavirus infection is replenishing fluid in the body.
The disease is accompanied by dehydration - water, salts, glucose, electrolytes and microelements are lost. Without them, the organs of adults and children do not function. Recovery from rotavirus is impossible without drinking. Severe diarrhea leads to dehydration; Give the patient a rehydration solution, purchased at a pharmacy or prepared independently.
- 1 liter of warm boiled water;
- 1 tbsp. salt;
- 2 tbsp. Sahara;
- 1/2 tsp. soda;
- 100 g raisins, lemon or ginger.
Mix the ingredients, drink a couple of tablespoons every two hours; if severe vomiting occurs, give a teaspoon every 15 minutes; Give the child something to drink from a pipette every 5 minutes. Alternation with teas and decoctions will help not to disturb the salt balance.
If it is impossible to stop vomiting and loose stools, resort to hospitalization. In the hospital, dehydration will be prevented with medications and IVs.
Recovery from an intestinal infection in children is accompanied by a decrease in immunity - introduce fresh vegetables, fruits (citrus fruits) with vitamin C into the diet.
Cleansing the body
Rotavirus attacks the intestinal microflora, leading to intoxication of the body. The second stage of treatment is the removal of toxins.
To get rid of rotavirus and toxins, the patient is prescribed enterosorbent medications that bind toxins, remove them from the body, and normalize digestion.
Antibiotics are not used: they do not fight the virus, disrupt the functioning of the inflamed intestines, killing beneficial bacteria.
If you have an intestinal infection, you should not treat the symptoms - runny nose and cough. The symptoms will go away after the virus is eliminated from the body. Additional medications (antibiotics) will weaken the body. Antibacterial medications will aggravate the condition and increase diarrhea in children.
There are no drugs that kill rotavirus. The only way to improve digestion and stool is a restorative diet that excludes foods that are dangerous for a patient with rotavirus infection.
Treatment of adiarrhea
Constipation due to rotavirus infection is a common problem in children. Main methods of therapy:
- Physical activity.
- Increase fluid intake.
- Diet – add vegetables and fruits to your diet; low-calorie fish; boiled meat; oatmeal; desserts containing gelatin; fermented milk products.
- The use of probiotics with beneficial bacteria and sorbents that remove toxins from the body.
- Enemas – cleansing, hypertonic oil.
- Use of laxatives.
- Hypotension is eliminated by massage with elements of therapeutic movements. Blood circulation and tissue metabolism are normalized.
- Physiotherapy:
- Galvanization is the effect of electric current on the body. Electrodes are applied to areas of the body in contact with the area of influence through special pads moistened with water.
- SMT therapy uses alternating modulated current. Currents (depending on the purpose) differ in frequency with an analgesic, vasodilating effect.
- Electrophoresis - medications are administered through the skin and mucous membrane using an electric current.
- Paraffin treatment - paraffin is applied to the affected areas of the skin for 30-40 minutes, covered with oilcloth and wrapped in a warm blanket.
Diet for rotavirus
The third stage of recovery is proper nutrition. A method of intestinal rehabilitation after rotavirus infection is diet.
Prohibited Products
Rotavirus destroys the enzymes in the intestine that are responsible for the breakdown of lactose; lactose intolerance occurs in children from 6 months to 5 years of age. Eliminate milk and dairy products from the diet. Sour cream, cheese, cottage cheese, milk, kefir, low-fat homemade yoghurts cause irritation of the intestinal tract - remove from the diet at the first manifestation of rotavirus infection.
Adults - refrain from coffee, caffeinated drinks, fried, fatty foods that aggravate intestinal inflammation. The body in a healthy state has a hard time tolerating the mentioned food.
Mothers of children infected with rotavirus complain that the child does not eat. The reason is impaired intestinal function and the inflammatory process. When your appetite appears, avoid eating the listed foods until you recover, focus on drinking plenty of fluids, and replace unhealthy drinks with juices, fruit drinks, and compotes.
Diet for rotavirus in adults
For adults, the consequences of the infection are not so difficult, but diet is required. Rotavirus affects the gastrointestinal tract in adults who lead a healthy lifestyle and do not have stomach problems; the disease is the cause of weight loss.
For adults, porridges, mainly semolina and rice, will help to recover from rotavirus - they envelop the intestinal walls. Use broths with crackers, lean boiled meat, fish without salt and spices. Avoid dairy products. Grated low-fat cottage cheese is allowed.
Follow the drinking regime, you need a lot of liquid, vary it with blueberry, raspberry, currant infusions, dried fruit compote, tea.
An adult with rotavirus infection is advised to avoid baked goods, brown bread, dried fish, sausages and smoked meats, spicy and salty foods.
After diarrhea and pain decrease, gradually eat lean meat, fish, mashed potatoes, and vegetable soups.
Source: https://mmc-optima.ru/infekcii-zhkt/stul-posle-rotavirusa-u-rebenka.html
Prevention of stool retention
After eliminating all possible causes of constipation, the act of defecation and the nature of stool are normalized. The worst-case scenario is that constipation enters a chronic phase and occurs in adulthood.
Self-medication using laxatives and enemas is not allowed.
- natural breastfeeding;
- creating a favorable psychological atmosphere;
- balanced diet;
- gymnastics class;
- accustoming a child to a chair on time;
- identifying the causes of constipation;
- elimination of identified causes.
Rotavirus is an infectious disease that occurs against a background of poor diet or is transmitted by water or airborne droplets. Children are in the first risk group for the disease due to weakened immunity or artificial feeding. The infection is accompanied by vomiting, diarrhea, fever, runny nose and sore throat, but constipation is especially dangerous in the post-infection period. It can be stated with certainty that an inflammatory process has begun when a child does not have stool for 48 hours, which subsequently acquires a liquid consistency.
Useful video
Dr. Komarovsky about rotavirus in children:
Rotavirus intestinal infection has not spared a single person. Everyone (regardless of their immune status, gender and race) has suffered from this disease at least once. And those who were recently born will still have to get sick with rotavirus. That is why the famous children's doctor Evgeniy Komarovsky considers it his duty to tell parents what this disease is and how to act correctly when a child gets sick.
Symptoms of defecation disorders after rotavirus
An infectious disease that has left lesions has a destructive effect on the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Due to the excessive release of toxins into the body, the intestines delay bowel movements, causing constipation in children, which in turn causes the patient to experience the following conditions:
- weakness and dizziness;
- insomnia;
- obsessive headache;
- systemic vomiting;
- pallor;
- lack of appetite;
- tearfulness;
- rapid weight loss;
- sudden changes in body temperature.
And this is only a small fraction of the unpleasant sensations that characterize the patient’s general condition. After a rotavirus infection, a child experiences severe gastrointestinal disorders.
Symptoms of intestinal damage:
- lack of stool for at least a day;
- increased flatulence;
- stabbing abdominal pain;
- ineffective urge to defecate;
- change in stool consistency.
If the above symptoms are observed in children, an urgent call to the doctor is required and hospitalization is recommended. Obvious signs of complications of an infectious disease are constipation alternating with loose stools, mucous consistency of stool with blood, and pain with incomplete emptying.
How does the disease progress?
Despite the fact that rotavirus is considered an intestinal infection, it begins to infect the human body from the upper respiratory tract. It is observed more often in children under 5 years of age. It is during this period that the immune system is easily exposed to the virus, which is why children get this disease more often than adults. Rotavirus affects the mucous membranes of the intestines, stomach and duodenum, causing disorders and dehydration.
The virus, entering the child’s body, may not manifest itself in any way during the first 5 days (incubation period). Afterwards comes the stage of exacerbation and during this period the first signs begin to appear. The child begins to worry and cry for no apparent reason. It gets especially bad for him on the first day.
The pathogens are released along with the feces, so the sick person is considered a carrier of infection to all family members and others.
- dieting,
- the use of enzyme preparations and probiotics,
- symptomatic treatment (for example, against flatulence).
Treatment of constipation in children after rotavirus
Constipation with rotavirus infection is the main factor that all doctors’ treatment is aimed at to prevent aggravating consequences. If they occur, and the delay in bowel movements has become long-lasting, doctors use two types of therapy.
Medication methods:
- prescribing enzyme preparations that improve the digestion process;
- introduction of probiotics containing beneficial bacteria;
- the use of sorbents that help remove toxins from the body;
- treatment with saline laxatives for strong, painful urge to defecate.
Healthy diet for constipation in children:
- regular, but not excessive consumption of vegetables and fruits;
- low-calorie fish;
- boiled meat;
- borscht and chicken broth;
- oatmeal;
- desserts containing gelatin;
- milk afternoon snacks;
- mineral drinks, juices and compotes.
If you have constipation, you need to exclude any viscous foods. If a child is breastfed, then it should not be stopped and the body should not be deprived of its immune protective functions. When intoxication occurs, characterized by dehydration of the body as a result of constipation, a saline solution of sodium and potassium is used, which removes toxins from the intestines.
Treatment process
From the material described above, it becomes clear that the question is: how to treat rotavirus? - does not always receive an answer. The reason for this is the responsibility of the patient himself. In one case, a person does not take any action at all, and in the other, he actively begins to take a variety of medications. In this case, you should not delay visiting the doctor. Only experienced personnel will be able to understand the causes of the disease, establish its name and prescribe the correct course of treatment.
What complicates the healing procedure is that to date this disease remains insufficiently studied.
There are no comprehensive control methods aimed at eliminating the cause, namely the virus itself.
Doctors can only hope to eliminate individual symptoms:
- The sorbent helps to cope with intoxication.
- In case of complications, a glucose solution is administered.
- Antibiotics are prescribed only if the virus is accompanied by other diseases.
- A variety of antiviral drugs are used. They are often supplemented with enzymes that soothe the gastrointestinal tract.
There are no drugs that kill rotavirus. The only way to improve digestion and stool is a restorative diet that excludes foods that are dangerous for a patient with rotavirus infection.
Symptoms of rotavirus development
- Since children are most vulnerable to the disease’s viruses, their symptoms are often more pronounced than in adults.
- At first glance, some symptoms coincide with other ailments, but their combination with each other rarely leaves doubt in the doctor’s diagnosis.
- The main symptoms of rotavirus infection are:
- high fever that lasts up to 4-5 days;
- weakness;
- diarrhea with a sour odor, possible change in the color of stool;
- gagging;
- nausea;
- dizziness;
- lack of appetite;
- flatulence;
- signs of a runny nose, sore throat.
If such symptoms occur in your baby, you should immediately avoid consuming kefir, fermented baked milk, cottage cheese and other fermented milk products, as they aggravate the course of the disease.
It is important to give your child enough water, not liquids like tea or cocoa, but water. This will help avoid dehydration and significantly speed up the process of flushing harmful substances from the body.
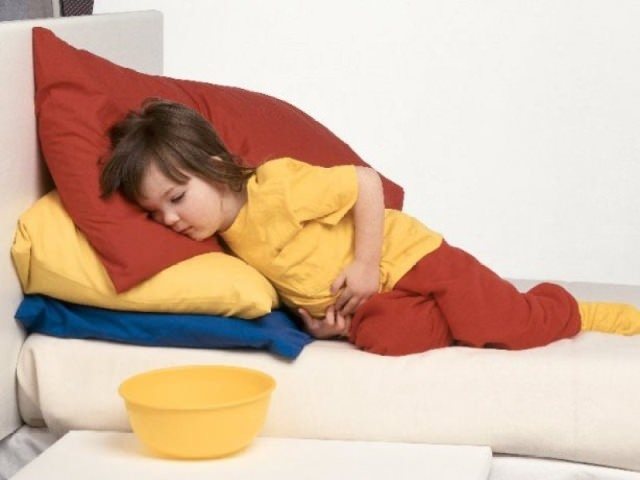

It is important to give your child enough water, not liquids in the form of tea or cocoa, but water
We recommend reading: How to treat rotavirus, how to cure rotavirus infection in children and adults
Diet for intestinal infection in children: sample menu for the day
- Breakfast. Invite your child to eat cottage cheese, porridge with water or a steam omelet, weak sweet tea, and a few crackers.
- Snack: banana or baked apple.
- Lunch: soup with low-fat broth, for the main course - boiled meat or fish, steamed cutlets with mashed potatoes or rice, as well as apple compote or rosehip infusion.
- Afternoon snack: berry jelly, cookies, biscuits.
- Dinner: buckwheat porridge with meatballs, black tea.
- Before going to bed, you can give your baby a glass of kefir or yogurt.
- Viral. The causative agent is rotavirus or intestinal flu, enterovirus, coronavirus, adenovirus.
- Bacterial: dysentery, staphylococcus, salmonellosis, E. coli, fungi.
Try to ensure that even during illness the baby’s diet is varied and the dishes are tasty.
If your baby has no appetite at all, try decorating the food and placing it on bright children's dishes.
What is OKI, its types
Acute intestinal infection (AIE) is an intestinal disease with a fecal-oral (enteral) mechanism of infection. It affects all parts of the gastrointestinal tract: intestines, stomach, duodenum.
The main causes of intestinal infection in children:
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules: unwashed hands after walking and visiting the toilet;
- contact with insects or animals;
- poisoning from products stored in improper conditions or with expired expiration dates;
- poorly washed fruits and vegetables;

- raw or undercooked products;
- drinking contaminated water;
- swimming in dirty ponds;
- contact with sick children (use of shared hygiene items or toys).
What is important to know about rotavirus infection
The development of such an infection is especially dangerous in children who are still fed breast milk. The virus multiplies in the walls of the small intestine, its cells help digest carbohydrates.
The villi that are located on these cells are damaged due to the active development of the virus. As a result, the process of digesting the sugar contained in milk is disrupted.
That is, with rotavirus infection, milk absorption decreases.
The consequences of the virus are the most difficult to treat.
- poor hygiene;
- previously suffered flu and colds;
- contact with common objects;
- consumption of food containing rotavirus;
- water with virus;
- contacts with infected people;
- getting mucous secretions of an infected person onto your hands or food.
Loss of appetite with gastritis and more
When a person suffers from chronic gastritis and experiences pain after lunch, he often loses interest in even the most tempting foods.
Thus, an unhealthy digestive system tries to protect itself from unnecessary work.
But the body still continues to need nutrients and vitamins.
If you simply give your stomach some slack and cut your diet in half, it will not be difficult to acquire a bunch of new, equally unpleasant chronic diseases, or at least bring yourself to severe exhaustion.
Patients who have lost their appetite during an exacerbation of the disease sometimes lose up to 10 kg. weight. They feel lethargic, drowsy, and become susceptible to infections.
Why don’t you want to eat and what to do about it?
We will name the reasons not only gastroenterological, but also of another nature. Perhaps this information will be useful to someone in a practical sense.
Factors that contribute to loss of appetite:
- diseases of the digestive system - gastritis (inflammation of the stomach), duodenitis, colitis (inflammation of the intestines), ulcers;
- parasite infection;
- hormonal disorders;
- viral infections (various colds) associated with general weakness;
- use of certain medications;
- overwork.
Protect yourself from stress, which can also kill interest in food. Having trouble relaxing? Find suitable relaxation exercises, do yoga.
Nervous tension can manifest itself in gluttony (many ladies complain that during an exciting working day and a fussy evening at home, only constant tea drinking and snacking saves them from a nervous breakdown), and in complete indifference to food. What to do? Take a few days off and put things in order in your life - rearrange your routine, decide on your goals, and calm down.
Another common cause of loss of appetite is physical inactivity. You may have noticed that if, say, on Sunday, you sit at home all day in front of the TV or at the computer, lunch and dinner turn out to be undesirable: you get bored at the table for a long time and pick at your plate without any enthusiasm. Don't be lazy, move.
Walk to the store and to your place of work, run in the morning, and do exercises. For an overweight person who has not done any gymnastics for a long time, simple physical therapy for gastritis is ideal.
Several ways to quickly fix the problem
If your problem is lack of appetite:
- eat more green vegetables - cucumbers, cabbage;
- make a decoction of dried raspberries for yourself, drink half a glass several times a day;
- if your stomach doesn’t hurt, try eating a spoonful of sauerkraut or a slice of pickled cucumber half an hour before meals;
- drink soothing infusions of medicinal plants;
- Hang beautiful photos of food in your kitchen.
Train yourself to eat at the same time. When the body gets used to receiving food strictly according to the clock, it will be better prepared for each next meal.
Sometimes the process of cooking helps restore the taste for food. Try to make an original dish yourself that you haven’t tried before.
digestive disorders symptoms of gastritis
- UC in children - causes, features of the course, approach to treatment
- Diet for Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis: basic requirements
- Exacerbation of UC: description, recommendations
- Tests for Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis: description
- Diet for gastroduodenitis: main rules and restrictions
Sometimes recovery from an illness takes longer than the illness itself. This is exactly the situation with rotavirus, the consequences of which can be felt up to several months after recovery. That is why it is worth knowing the alarming symptoms of severe consequences in order to seek medical help in time.