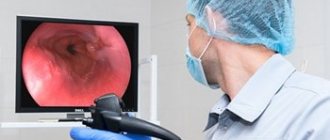
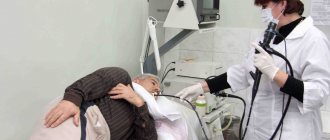
The study is unpleasant, but the most informative of all diagnostic measures existing today. During the examination, the doctor may remove single small polyps or take a tissue sample for a biopsy. The procedure is prescribed for chronic forms of gastritis and ulcerative pathology to confirm the diagnosis and select a treatment regimen.
METHODS OF DIAGNOSIS OF THE STOMACH
There are several methods for medical diagnosis of the condition of the gastric mucosa:
- physical – performed in the doctor’s office;
- laboratory - examine the patient’s tests;
- hardware - using medical devices.
Physical methods are a routine examination performed by a doctor. The doctor listens in detail to the person’s complaints, conducts an initial examination - the oral cavity, tongue, palpates the lymph nodes and the abdominal area.
Laboratory tests are carried out to identify the causes of stomach pathology - what concomitant diseases could provoke the disease? For diagnosis, blood, feces and urine are taken.
Hardware diagnostics include ultrasound and fluoroscopy. In modern medicine, diagnostics are used - gastropanel. This is a paid alternative to gastroscopy - a laboratory blood test.
An absolute contraindication to gastroscopy of the stomach is the patient’s near-death state. Diagnosis is possible even with a heart attack and in the presence of gastric bleeding. However, there are contraindications to the procedure:
- risk of aortic rupture;
- heart ailments - they are treated first;
- hemophilia - there is a risk of tissue injury;
- high blood pressure;
- diseases of the neck area;
- anatomical deviations in the patient's body structure.
If gastroscopy is not possible, gastric diseases are determined using alternative methods.
Preparing for the study
Before carrying out the procedure, it is necessary to undergo preparation.
Before swallowing the tube, it is necessary to determine the presence of contraindications in the patient. Gastroscopy is performed only if the patient agrees to this procedure.
Before the procedure, the patient signs a special form. At the same time, the patient and the doctor discuss the possibility of complications and the specifics of the procedure.
A few weeks before gastroscopy, you should stop taking iron medications. Patients are also prohibited from taking aspirin. If for certain reasons it is impossible to exclude the use of medications, then it is necessary to discuss with your doctor the specifics of their use and dosage.
If this procedure is combined with polypectomy or biopsy, the patient is contraindicated to take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. If this condition is met, the risk of bleeding will be reduced. Also, before the study, the patient is prohibited from using anticoagulants and medications that reduce blood clotting.
Read: Gastroscopy under anesthesia: features and contraindications
Eating and drinking must be stopped 8 hours before the test. Before gastroscopy, the bladder is completely emptied. If the patient has dentures or glasses, it is recommended to remove them before the examination, which will ensure the highest level of safety for the procedure.
The preparatory stage is quite important in conducting the survey. Not only the effectiveness of diagnosis, but also the safety of the patient depends on it.
Easy diagnostics
Simple diagnostic methods are mandatory for use when a patient complains of an acute abdomen, nausea and other symptoms of gastric diseases.
Physical examination
Physical measures are carried out at a doctor’s appointment, the results depend on the qualifications of the medical specialist. The complex includes:
- studying the anamnesis, assessing symptoms from the patient’s words;
- visual examination of mucous membranes;
- feeling painful areas of the body (palpation);
- palpation in a specific body position (percussion).
Based on the results obtained from such an examination, it is extremely difficult to diagnose the disease. The doctor may suspect the presence of pathology, but more in-depth research methods are needed to confirm it.
Microscopic laboratory diagnostics
Laboratory methods involve taking samples from the patient for further study and evaluation of the results. Most often, the following physical and chemical studies are prescribed:
- general urine analysis;
- coprogram (stool analysis);
- clinical blood test. The number of all types of blood cells (erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets) is counted and the hemoglobin level is determined;
- gastropanel. This blood test is aimed at studying the condition of the gastric mucosa. Based on its results, the following is determined: the presence of antibodies to Helicobacter pylori bacteria, the level of pepsinogen proteins produced, the level of the polypeptide hormone - gastrin, with the help of which the acidic environment in the stomach is regulated;
- blood biochemistry. Quantitative indicators of bilirubin, liver enzymes, cholesterol and other blood elements are established.
Tests help identify inflammatory processes and other disorders of organs and systems. If the results differ significantly from the normative indicators, the patient is prescribed an instrumental or hardware examination.
How to swallow a tube correctly
The main recommendation is the ability to breathe correctly during FGDS. Only the nose is involved in the process. Inhalations and exhalations should be slow and deep. It is necessary to concentrate as much as possible so that your breathing is smooth and rhythmic.
During the diagnosis, it is prohibited to: swallow air, talk, swallow drool, move your body and jerk your head. In order for the procedure to go smoothly, you must strictly follow the instructions of medical specialists, breathe correctly, do not be nervous, and try to relax all your muscles.
If you cannot get rid of excessive tension on your own, you can take a sedative an hour before the examination, and inform the medical specialist conducting the examination. In cases where the patient cannot endure stress, the doctor can perform an FGDS under general anesthesia.
When the gastroenterologist considers the procedure complete, he smoothly removes the tube of the device. The extraction process is easy, without causing inconvenience or pain. Do not suddenly move to a vertical position.

Gastroscopy requires special preparation, which the patient is warned about at the time of the procedure.
Laboratory methods for examining the stomach
How can you tell anything about the stomach based on blood results? It turns out that it is possible! Laboratory methods are of great importance in establishing a diagnosis and are actively used in gastroenterology. The material for the study is the patient’s blood, feces, gastric and duodenal juice.
Blood
A general and biochemical blood test is the first thing that any doctor prescribes to diagnose gastritis. Blood counts and their levels can tell a lot about your general condition, the presence of an inflammatory process, infection, and the functioning of digestive enzymes and hormones. Specifically, indicators of gastric function include hemoglobin, leukocytes, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), pepsinogen and gastrin levels. Their fluctuation indirectly indicates the presence of gastritis, ulcer bleeding and other diseases.
The amount of antibodies to Helicobacter pylori (immunoglobulins M and G) is also examined in the blood. Helicobacter is a bacterium that causes inflammation of the gastric mucosa. If it is detected, antibacterial therapy is prescribed.
Feces
Stool analysis shows the presence of hidden bleeding, enzyme dysfunction (changes in coprogram), worm eggs, and signs of dysbacteriosis.
Gastric juice
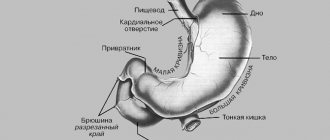
This method will tell you how to determine the functional state of the gastric mucosa. The juice is collected through a thin probe. Each portion of the material is examined separately. pH-metry is also carried out - this is a determination of acidity. The obtained indicators play an important role in prescribing treatment.
All laboratory methods are used to diagnose functional indicators of the stomach, and therefore are not suitable for determining space-occupying formations, narrowing or obstruction of the esophagus, or detecting the source of bleeding.
Swallowing a tube is painful
Swallowing the tube is not painful, just unpleasant. In order for the stomach examination to go smoothly, you should carefully prepare for it, calm down, relax and tune in to it in a positive way. To make the patient less worried, especially if he is undergoing the procedure for the first time, the doctor can help him prepare psychologically - talk about the details of the manipulation and explain how to behave.
When conducting the study, try to relax as much as possible and breathe primarily through your nose, deeply and slowly. Allow saliva and digestive juices to drain onto the towel - don't worry about it, it's a natural process. Swallowing movements should be avoided after passing the probe into the esophagus. After pulling out the hose, it is better to spit everything out of your mouth.
Ultrasound examination (ultrasound)
It is used every day as a diagnostic method for determining many diseases. There is not a single organ that cannot be examined using ultrasound, but more often they examine dense structures and tissues. As for hollow organs, such as the stomach, not everything can be seen there. For example, it will not be possible to determine the types of gastritis, but it is possible to detect a neoplasm, polyp, or change in shape. Thus, if a doctor is faced with a choice of what is better to do: ultrasound or fibrogastroscopy, the answer is obvious! FGS will give the best result.
Anesthesia and sedation
For everyone else, this may be a good way to get through the procedure without unnecessary worry and stress. Sedation for EGD is widespread throughout the world. Read more about it in our article.
General anesthesia is often used in young children, which makes the procedure easier tolerable and easier.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT)
To examine the stomach and esophagus, MRI and CT are used very rarely, but they are quite applicable as an alternative method. The principle of operation of modern computed tomographs is based on emitting a magnetic field on the body and receiving impulses from internal organs, which are recorded on a special film in the form of clear images. The step of obtaining sections (images) is set by the program or the doctor. Thanks to the MRI machine, you can thoroughly study every millimeter of any organ. CT also examines organs layer by layer, only using x-rays.
Today, this examination is considered the most accurate and safe, since doctors have a real opportunity to look inside the body without intervention and examine any structure. As you may have guessed, tomography also has contraindications and disadvantages. A relative contraindication is pregnancy. The disadvantages of MRI include the inability to examine the function of an organ, monitor its functioning, secretory and enzymatic activity. CT is used even less frequently.
You cannot examine a patient with any metal structures in the body (bone pins, screws, vascular clips), and especially with pacemakers. Failure to comply with this condition may cost a person his life.
Not long ago, 2 completely new methods of diagnosing the stomach without the use of a fiberscope and the associated discomfort appeared: gastropanel and capsule gastroscopy.
Indications for a stomach check
The stomach is an integral part of the gastrointestinal tract; the functioning of the entire organism as a whole depends on the work of this organ. Additionally, the stomach is where the digestive process begins. This means that the condition of the intestines depends on the condition of this organ and the quality of the functions it performs.
Important! As for the indications for diagnostics, these include any unpleasant or painful sensation, the slightest manifestation of discomfort, repeated systematically over a long period of time.
You also need to understand that “time period” is a changeable concept. If the discomfort is minor, for example, slight heaviness and bloating of the stomach, slightly increased bowel movements, you should consult a doctor if symptoms do not go away within 3-5 days. If the symptoms are severe, for example, severe pain, it is better to be examined immediately. A gastroenterologist deals with stomach problems.
Gastropanel
This blood test can check several indicators. Based on their level, an experienced and competent doctor will be able to draw conclusions regarding the pathology of the gastric mucosa.
So, the gastropanel explores:
- Antibodies to H. pylori (Helicobacter), the bacteria that causes stomach ulcers.
Antibodies to Helicobacter pylori of the IgG class are detected starting 3 weeks after infection
- Pepsinogen I and II (precursors of the gastric enzyme pepsin). By their meaning one can judge which part of the stomach is affected.
- Gastrin 17 (a hormone that regulates the production of hydrochloric acid).
Based on the totality of all indicators, a conclusion is drawn in which the doctor indicates the degree of dysfunction of the gastric mucosa and possible causes (atrophy, hypotrophy, hyperacidity and others). The examination is expensive and not informative enough, since it is impossible to visually see the condition of the organ from the inside, but sometimes it is an excellent diagnostic method stomach without gastroscopy.
Many diseases, including cancer of the stomach or esophagus, may not manifest themselves and are detected at the last stage.
That is why gastroscopy remains the leading examination for diagnosis.
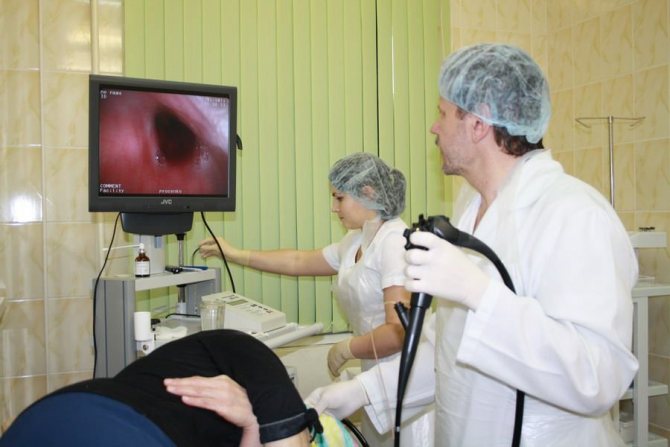
What is the name of swallowing the probe?
Endoscopy is a method for examining the esophagus, stomach and duodenal bulb (duodenum) by examining it with a special optical apparatus. Among patients and many doctors, the study of endoscopy is briefly called gastroscopy, although this is not entirely correct. It is carried out using an endoscope (a probe equipped with a camera). Endoscopy is used for accurate diagnosis of various diseases of the upper digestive tract.
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy is performed by an endoscopist in the left lateral position. Before inserting the endoscope, the pharynx is treated with lidocaine aerosol to reduce sensitivity. The use of the device does not affect breathing in any way. The study can take place both under anesthesia and without it.
The doctor gradually examines the mucous membrane of the internal digestive organs (esophagus, stomach, duodenum and its bulb), performs a biopsy of a suspicious area if necessary, or a biopsy to determine the presence of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori.
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy is performed by an endoscopist in the left lateral position
The gastroscope is removed slowly for a detailed examination of the mucous membrane. The procedure lasts about 10-20 minutes.
Capsule gastroscopy
A new type of examination of the esophagus and stomach from the inside using photographic equipment. We can say that this is a good alternative to gastroscopy of the stomach. The device is a small capsule (10 mm) with a built-in lens that allows you to take many pictures as it progresses. Like any other study, it is carried out on an empty stomach. The patient washes the capsule down with water and can do his usual activities. After 8-9 hours the capsule comes out naturally. Reviewing all the information recorded during this time, the doctor draws conclusions about the condition of the examined gastrointestinal mucosa and the detected formations.
It is worth saying that capsule gastroscopy is not used in all medical institutions due to its high cost. This survey is currently at the innovation stage. Therefore, for a high-quality diagnosis of gastrointestinal diseases, every doctor needs to think not what can replace gastroscopy, but how to overcome his fear and set him up for the necessary examination.
SOURCES: https://diagnostinfo.ru/skopiya/gastroscopy/kak-proverit-zheludok-bez-gastroskopii.html https://apkhleb.ru/endoskopiya/obsledovanie-zheludka-bez-gastroskopii https://proskopiyu.ru/ gastroskopiya/kak-mozhno-proverit-zheludok-bez-gastroskopii.html
In what cases are there no analogues?

- gastrointestinal bleeding (vomiting "coffee grounds" or black stools);
- bleeding from varicose veins of the esophagus (bloody vomiting);
- foreign bodies in the esophagus or stomach.
This is due to the fact that in such cases FGDS is performed not only for diagnostic purposes, but also for therapeutic purposes. it is not possible to eliminate the problem using other methods , it is impossible to replace the procedure.
It is also important to perform gastroscopy in patients with suspected gastric cancer and the need for a biopsy . After all, the patient’s management tactics depend on the results of the study.
Transnasal fibrogastroscopy (FGDS through the nose)
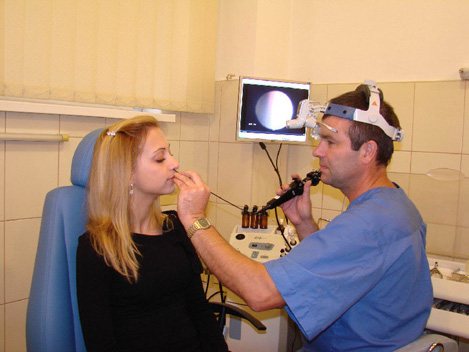
Doing without gastroscopy of the stomach in the classical way has become a reality. Medical institutions offer their patients a variety of techniques, among which gastroscopy through the nose takes the leading place. This method significantly simplifies the examination technique, reduces the stress level of the subject, facilitates the recovery period and reduces the risk of complications. FGDS through the nose completely eliminates the occurrence of pain, swelling in the neck and changes in voice.
The procedure was made possible thanks to special equipment - a gastroscope, consisting of a thin tube and a backlit camera. The patient lies on his side, if necessary, the doctor treats the nasal mucosa with painkillers and, to make it easier to insert the equipment, applies a certain amount of gel into the nostril. After such manipulations, a gastroscope is inserted through one of the nostrils. The image is transmitted to the monitor in real time and makes it possible to assess the condition of the stomach, esophagus and duodenum in a matter of minutes.
What can be replaced?
If the patient has contraindications to FGDS, the doctor prescribes an examination using alternative methods. It is considered advisable to combine several diagnostic procedures to obtain more accurate data and prevent errors at the diagnostic search stage.
Sometimes patients themselves look for an alternative to gastroscopy, experiencing discomfort or fear of the study. In such cases, it is better to coordinate your actions with your doctor and choose a diagnostic method together . After all, to make a diagnosis in each case, a different amount of examination may be required. Below we list the main alternative studies and briefly discuss each of them.