Included: morphological codes M912-M917 with character of the neoplasm code /0
Excludes: blue or pigmented nevus (D22.-)
ICD-10 alphabetical indexes
External Causes of Injury - The terms in this section are not medical diagnoses, but rather a description of the circumstances under which the event occurred (Class XX. External Causes of Morbidity and Mortality. Heading Codes V01-Y98).
Medicines and chemicals - table of medicines and chemicals that have caused poisoning or other adverse reactions.
In Russia, the International Classification of Diseases
10th revision (
ICD-10
) was adopted as a single normative document for recording morbidity, reasons for the population’s visits to medical institutions of all departments, and causes of death.
ICD-10
introduced into healthcare practice throughout the Russian Federation in 1999 by order of the Russian Ministry of Health dated May 27, 1997 No. 170
The release of the new revision (ICD-11) is planned by WHO in 2022.
Abbreviations and symbols in the International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision
NOS
- without other instructions.
NEC
— not classified in other categories.
†
— code of the main disease. The main code in the dual coding system contains information about the underlying generalized disease.
*
- optional code. An additional code in the double coding system contains information about the manifestation of the main generalized disease in a separate organ or area of the body.
Liver hemangioma (ICD 10 code - D18.0) occurs in 20% of the population. These tumors are easily detected by various visual diagnostic methods, but due to the similarity of their external manifestations with metastases, cancer and liver adenoma, an accurate diagnosis is not always easy to establish. The high frequency of detection of hemangiomas in middle-aged and elderly people indicates the acquired nature of this tumor.
Based on their structural features, hemangiomas are divided into:
Most often, hemangiomas are detected by ultrasound examination of the liver, which is facilitated by the combination of accessibility and simplicity of the method with high resolution.
The dimensions of the cavities in capillary hemangiomas are beyond the resolution of CT and ultrasound scanners, therefore the structure of such tumors appears homogeneous, and multiple septations provide hyperechogenicity on ultrasound. Often, an increase in sound is observed behind the hemangioma. Up to 20% of hemangiomas have an atypical echostructure, which is manifested by either reduced or equivalent sound reflection in relation to normal liver parenchyma.
Large cavities of cavernous hemangiomas are clearly differentiated by ultrasound. In addition, as the tumor grows, internal hemorrhages occur, resulting in hyalinosis, as well as thrombosis and fibrosis. Lime deposits are less common. All these changes provide heterogeneity in the structure of large tumors, manifested by hypo- and anechoic areas of various sizes and configurations.
Capillary hemangioma of the liver
Capillary hemangioma of the liver on CT has a homogeneous structure, which makes it difficult to identify it on computer tomograms, while with ultrasound this tumor is well visualized. With contrast enhancement, capillary hemangiomas begin to stain in the arterial phase, in the venous phase their staining increases, and in the delayed venous phase they remain hyperdense relative to the parenchyma (CT photo above).
Cavernous hemangioma of the liver
Cavernous hemangioma of the liver in its structure may contain shapeless areas with a lower densitometric index, which is a reflection of hyalinosis and degenerative changes. For these reasons, large hemangiomas require differential diagnosis with other formations (hepatoma). Fibrous scars in cavernous hemangiomas give the tumor a mottled appearance (CT photo above). The zone of marginal accumulation expands towards the center, as the blood inside the hemangioma slowly flows from the peripheral sinuses to the central ones. Maximum contrast occurs in the late parenchymal phase, when the tumor is completely stained. On tomograms, liver hemangiomas with adequate contrasting appear as hyperdense formations, due to the accumulation of the contrast agent by the interstitial component of the tumor tissue. This is a very specific sign of liver hemangioma. Unfortunately, the perfusion described above with centripetal enhancement and late filling is shown in approximately 54% of hemangiomas.
Symptoms and signs of hemangioma
Pathology is most often detected in infants aged three months and older. Girls suffer from the disease three times more often than boys. It is not possible to determine the presence of a tumor at the stage of intrauterine development. Modern medicine cannot explain the causes of hemangioma.
Scientists have only been able to identify predisposing factors:
- viral diseases that a woman suffered in the first trimester of pregnancy;
- hereditary predisposition;
- diseases that have a negative impact on the vascular system;
- strong ultraviolet irradiation.
Externally, a hemangioma looks like a flat or voluminous spot of purplish-red color with a bluish tint. It constantly grows and bleeds slightly when injured. The tumor is benign in nature, but doctors advise constantly monitoring it. The fact is that it can grow deep into the skin and damage neighboring organs. This is fraught with serious consequences. If a vascular lesion grows near the eye, it can lead to vision loss. If the hemangioma is localized near the ear, the sick child may lose hearing.
Treatment methods for hemangiomas
The choice of therapeutic tactics largely depends on where the formation is located, how it develops, and how deeply it affects the internal tissues. If the tumor is superficial and does not grow, it does not pose a threat to the child’s life. He is constantly monitored, once a month the baby undergoes a dermoscopic examination, ultrasound diagnostics, and angiography.
If the hemangioma grows near natural openings (near the mouth, inside the ear canal, in the anogenital area, in the respiratory tract), it must be removed. The choice of method is made taking into account the age of the child.
In the period up to one month of life, traditional surgery is excluded. If the pathology poses a threat to the baby’s life, it is treated with medications that have a sclerotic effect. They are injected under the skin around the hemangioma, and then into its center. A week later the procedure is repeated.
From the age of three months, surgical treatment can be performed. It is used in exceptional cases in the development of large tumors. It is performed under general anesthesia. Relevant for hemangioma located on the head. From one year onwards, laser therapy can be used. It is safe and less traumatic than traditional surgery. The duration of the session is 15-20 minutes, relapses are rare. The rehabilitation process for a child is easier than for an adult.
When treating hemangioma in an adult, the methods already listed above and other methods of radical treatment can be used. If the tumor is located on the face, cryodestruction (exposure to liquid nitrogen) or electrocoagulation may be chosen.
Make an appointment with a specialist directly on the website. We will call you back within 2 minutes.
We will call you back within 1 minute
Papillomas are polyps on a thin stalk that are the color of normal skin or brown (light brown to dark brown)
method of laser destruction of dense round keratinized skin nodules of a viral nature
Purulent pathologies of the skin and fatty layer of tissue are more often (up to 90% of case reports) caused by infection with staphylococcus
a branch of medicine that studies the structure and function of the skin in normal and pathological conditions, diagnosis, prevention and treatment of skin diseases
The abbreviation “ICD” stands for “International Classification of Diseases”. In 2010, the list of diseases underwent the tenth revision; it contains special codes denoting all pathologies known to modern medicine today. Often, when diagnosing a disease, a lot of information has to be written down in the patient’s card, taking into account possible concomitant ailments. To optimize the process, doctors widely use ICD 10; as a result, the corresponding code is entered into the card. The list contains all existing regulatory definitions of pathologies listed in alphabetical order.
The document includes headings and sub-headings that contain the necessary notes and indicate exceptions for a particular pathology. Statistical data and rules by which the basic causes of local outcome for patients are determined are also taken into account. The list also contains a list of reasons for which hospitalization is carried out. ICD 10 assigns code D18 to hemangioma.
Clinics for treatment with the best prices
Price
Total: 585in 33 cities
| Selected clinics | Phones | City (metro) | Rating | Price of services |
| City Hospital of St. George in the North | +7(812) 511..show Appointment +7(812) 511-96-00+7(812) 576-50-50+7(812) 511-95-00+7(812) 510-01-49 | St. Petersburg (m. Ozerki) | rating: 4.1 | 17695ք (90%*) |
| Family doctor on 1st Miusskaya | +7(495) 152..show Appointment +7(495) 152-59-85+7(499) 969-25-74+7(495) 126-99-31+7(926) 800-07-19 | Moscow (metro station Novoslobodskaya) | rating: 4.5 | 21390ք (90%*) |
| Open Clinic in Kurkino | +7(499) 519..show Appointment +7(499) 519-37-06+7(495) 777-55-80 | Moscow (m. Planernaya) | rating: 4.4 | 23090ք (90%*) |
| NCC JSC Russian Railways on Chasovaya | +7(495) 925..show+7(495) 925-02-02+7(499) 151-43-34 | Moscow (m. Airport) | — | 23423ք (90%*) |
| NCC JSC Russian Railways on Volokolamsk Highway | +7(495) 925..show+7(495) 925-02-02+7(495) 925-68-86 | Moscow (metro station Tushinskaya) | — | 23423ք (90%*) |
| MEDSI in Butovo | +7(495) 023..show+7(495) 023-60-84 | Moscow (metro Dmitry Donskoy Boulevard) | — | 26850ք (90%*) |
| MEDSI in Blagoveshchensky Lane | +7(495) 023..show+7(495) 023-60-84+7(915) 047-23-65 | Moscow (m. Mayakovskaya) | — | 26850ք (90%*) |
| MEDSI on Polyanka | +7(495) 730..show+7(495) 730-57-23+7(495) 152-55-46 | Moscow (m. Polyanka) | — | 26850ք (90%*) |
| MEDSI in Krasnogorsk | +7(495) 730..show+7(495) 730-57-15+7(495) 152-55-46 | Krasnogorsk (metro station Pyatnitskoe highway) | — | 26850ք (90%*) |
| MEDSI on Leninsky Prospekt | +7(499) 519..show+7(499) 519-39-17+7(495) 023-60-84 | Moscow (metro station Shabolovskaya) | — | 26850ք (90%*) |
| * — the clinic does not provide 100% of the selected services. More details by clicking on the price. | ||||
Source
Any pathology in the human body requires close attention, proper diagnosis and treatment. This also applies to hemangiomas of the liver - a neoplasm that is often benign and is not a life-threatening disease. But, like any pathological process, this tumor has certain risks of its existence, which you need to know about and, if possible, prevent them.
Definition of hemangioma
ICD 10 defines hemangioma as a benign neoplasm that forms from the walls of blood vessels. This pathology is very common; of all existing benign tumors, hemangioma accounts for 25%. If we consider all tissue neoplasms, the figure is 45%. Statistics say that at a certain stage in every person’s life, a hemangioma develops in his body. Given the almost complete absence of symptoms, we do not even suspect the occurrence of pathology.
As a rule, this disease is congenital, usually found in newborns, characterized by rapid growth and the absence of metastases. The tumor does not degenerate into a malignant form, but relapses are possible even after fairly successful treatment.
Even if the initial formation was point-like, their rapid growth cannot be ruled out, and vascular neoplasms can reach considerable sizes. Most often, tumors - flat or voluminous - are formed on the skin surface, however, given the young age of patients, the tumor is able to grow in depth, which ultimately negatively affects the internal organs. Ultrasound is often necessary for diagnosis. For example, if the tumor is located in the ear, the eardrum may be destroyed and subsequent hearing loss will occur.
Causes of formation of hemangiomas
Factors influencing the formation of hemangiomas have not been fully determined. However, ICD 10 sees the causes of hemangioma:
• In viral pathologies that pregnant women experience in the first months. It is in the first six weeks that the vascular system is formed in the embryo.
• Heredity may also be a cause.
• Influencing factors include the development of pathologies affecting blood vessels.
• The negative influence of ultraviolet radiation is also possible.
According to statistics, hemangiomas are observed more often in girls than in boys, the ratio being approximately 3:1. Modern equipment does not have the ability to determine a vascular neoplasm in an embryo during a woman’s pregnancy.
Pathology treatment methods
Medicine knows of cases where hemangiomas in newborns resolved on their own over several years. However, you should not rely on this; doctors recommend removing such tumors, especially if the affected area is large and the tumor can cause considerable cosmetic damage. When prescribing treatment, take into account:
• rate of tumor increase in size;
• age group of the patient;
• general condition of the victim.
Several fairly effective methods have been developed to promote high-quality removal of formations, including:
• the surgical method is recommended if it is possible to completely remove the formation, although the procedure cannot be ruled out in several stages;
• therapy using hormonal agents;
• radiation therapy using radio waves;
• use of the injection method;
• cauterization or electrocoagulation – cauterization is carried out using a laser.
To speed up the healing process, patients may be prescribed a variety of ointments.
Symptoms and signs of hemangioma
Pathology is most often detected in infants aged three months and older. Girls suffer from the disease three times more often than boys. It is not possible to determine the presence of a tumor at the stage of intrauterine development. Modern medicine cannot explain the causes of hemangioma.
Hemangioma appears more often in girls
Scientists have only been able to identify predisposing factors:
- viral diseases that a woman suffered in the first trimester of pregnancy;
- hereditary predisposition;
- diseases that have a negative impact on the vascular system;
- strong ultraviolet irradiation.
Externally, a hemangioma looks like a flat or voluminous spot of purplish-red color with a bluish tint. It constantly grows and bleeds slightly when injured. The tumor is benign in nature, but doctors advise constantly monitoring it. The fact is that it can grow deep into the skin and damage neighboring organs. This is fraught with serious consequences. If a vascular lesion grows near the eye, it can lead to vision loss. If the hemangioma is localized near the ear, the sick child may lose hearing.
Treatment methods for hemangiomas
The choice of therapeutic tactics largely depends on where the formation is located, how it develops, and how deeply it affects the internal tissues. If the tumor is superficial and does not grow, it does not pose a threat to the child’s life. He is constantly monitored, once a month the baby undergoes a dermoscopic examination, ultrasound diagnostics, and angiography.
If the hemangioma grows near natural openings (near the mouth, inside the ear canal, in the anogenital area, in the respiratory tract), it must be removed. The choice of method is made taking into account the age of the child.
In the period up to one month of life, traditional surgery is excluded. If the pathology poses a threat to the baby’s life, it is treated with medications that have a sclerotic effect. They are injected under the skin around the hemangioma, and then into its center. A week later the procedure is repeated.
From the age of three months, surgical treatment can be performed. It is used in exceptional cases in the development of large tumors. It is performed under general anesthesia. Relevant for hemangioma located on the head. From one year onwards, laser therapy can be used. It is safe and less traumatic than traditional surgery. The duration of the session is 15-20 minutes, relapses are rare. The rehabilitation process for a child is easier than for an adult.
You can remove hemangioma with a laser from 1 year of age
When treating hemangioma in an adult, the methods already listed above and other methods of radical treatment can be used. If the tumor is located on the face, cryodestruction (exposure to liquid nitrogen) or electrocoagulation may be chosen.
Liver hemangioma (ICD 10 code - D18.0) occurs in 20% of the population. These tumors are easily detected by various visual diagnostic methods, but due to the similarity of their external manifestations with metastases, cancer and liver adenoma, an accurate diagnosis is not always easy to establish. The high frequency of detection of hemangiomas in middle-aged and elderly people indicates the acquired nature of this tumor.
Based on their structural features, hemangiomas are divided into:
Most often, hemangiomas are detected by ultrasound examination of the liver, which is facilitated by the combination of accessibility and simplicity of the method with high resolution.
The dimensions of the cavities in capillary hemangiomas are beyond the resolution of CT and ultrasound scanners, therefore the structure of such tumors appears homogeneous, and multiple septations provide hyperechogenicity on ultrasound. Often, an increase in sound is observed behind the hemangioma. Up to 20% of hemangiomas have an atypical echostructure, which is manifested by either reduced or equivalent sound reflection in relation to normal liver parenchyma.
Large cavities of cavernous hemangiomas are clearly differentiated by ultrasound. In addition, as the tumor grows, internal hemorrhages occur, resulting in hyalinosis, as well as thrombosis and fibrosis. Lime deposits are less common. All these changes provide heterogeneity in the structure of large tumors, manifested by hypo- and anechoic areas of various sizes and configurations.
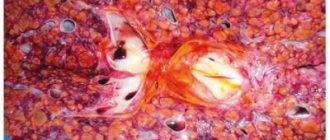
Capillary hemangioma of the liver
Capillary hemangioma of the liver on CT has a homogeneous structure, which makes it difficult to identify it on computer tomograms, while with ultrasound this tumor is well visualized. With contrast enhancement, capillary hemangiomas begin to stain in the arterial phase, in the venous phase their staining increases, and in the delayed venous phase they remain hyperdense relative to the parenchyma (CT photo above).
Cavernous hemangioma of the liver
Cavernous hemangioma of the liver in its structure may contain shapeless areas with a lower densitometric index, which is a reflection of hyalinosis and degenerative changes. For these reasons, large hemangiomas require differential diagnosis with other formations (hepatoma). Fibrous scars in cavernous hemangiomas give the tumor a mottled appearance (CT photo above). The zone of marginal accumulation expands towards the center, as the blood inside the hemangioma slowly flows from the peripheral sinuses to the central ones. Maximum contrast occurs in the late parenchymal phase, when the tumor is completely stained. On tomograms, liver hemangiomas with adequate contrasting appear as hyperdense formations, due to the accumulation of the contrast agent by the interstitial component of the tumor tissue. This is a very specific sign of liver hemangioma. Unfortunately, the perfusion described above with centripetal enhancement and late filling is shown in approximately 54% of hemangiomas.
Convincing signs of hemangioma can be obtained even without the use of bolus contrast techniques. It is enough to inject 40-60 ml of contrast agent into the cubital vein with a regular syringe as quickly as possible. In this case, the hemangioma will also appear with typical staining from the periphery to the center, but the intensity of such staining will be weak, and in the delayed phase the formation will not manifest as hyperintensity, but will be isointense with the parenchyma.
Arteriovenous malformation
an arteriovenous malformation , can simulate a hemangioma . This anomaly also manifests itself in the arterial phase of contrast enhancement as a brightly colored focus, but its intensity quickly decreases in subsequent phases of the study (CT photo above).
In doubtful cases, the use of MRI is very effective to clarify the diagnosis. MRI reliably detects even small liver hemangiomas (MRI photo above). A distinctive feature of hemangiomas from all other focal formations is their ability to increase signal intensity on “heavy” T2-weighted images (TE = 200-250 ms). The exception is cysts and some well-vascularized metastases of tumors such as pheochromocytoma and carcinoid.
Liver hemangioma: what is it in adults, types of vascular tumors
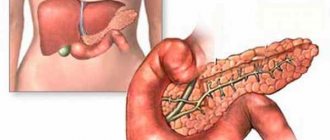
A benign liver tumor (hemangioma) is a node consisting of blood vessels and cavities filled with blood. Such a neoplasm can be either single or multiple. Basically, this tumor forms in the right lobe of the liver; hemangioma of the left lobe of the liver is less common. Multiple liver hemangiomas affect the nature of the liver itself and in some cases can cause more severe pain than a single one, due to the large coverage of the affected area and greater pressure on neighboring organs. In the early stages, the vascular tumor ranges in size from 2 to 6 cm and does not show any symptoms. A threat to the body can only appear if the hemangioma reaches 20 centimeters or more.
The histology of liver hemangioma is divided into three main types:
- capillary hemangioma of the liver. This is a collection of small vascular cavities filled with arterial or venous blood. These neoplasms, as a rule, do not grow larger than 10 cm in diameter. Nutrition in capillary hemangiomas of the liver occurs due to one vessel;
- cavernous hemangioma of the liver. This node consists of connections of vascular cavities located at a short distance from each other. Cavernous hemangioma can grow up to 25 cm in diameter and cause a person great discomfort and pain;
- atypical liver hemangioma. In this case, the neoplasm has a non-standard vascular structure, covered with a keratinized layer of soft tissue.
Ultrasound contrast Dopplerography
For the differential diagnosis of hemangiomas, the use of ultrasound contrast Dopplerography seems very promising. The pharmacokinetics of contrast enhancement and the interpretation of the resulting image with ultrasound are identical to those with bolus contrast enhancement with CT: this is intense peripheral staining of tortuous and lacunar dilated vessels in the arterial phase and prolonged staining of the central part of the tumor. In small formations, point accumulation of contrast agent is more often observed. A convincing differential diagnostic feature is the visualization of the feeding vessel, which is easier to detect with V3 angiography.
We have all met people in our lives who had large “birthmarks” on their faces, although hemangioma is not a birthmark. Hemangioma is a benign vascular tumor that looks like red, purple or blue spots, flat or raised above the skin, which can occupy a significant area - from 0.5 cm to 10-15 cm in diameter.
Hemangioma in children is the most common type of tumor. Its favorite location is on the face or neck, although hemangiomas also occur in other parts of the body, and even hemangiomas of internal organs. Hemangioma can cause harm to health only in rare cases; as a rule, these are hemangiomas of internal organs - the rarest type of hemangiomas. But being located in open areas of the body, having a large size and striking the eyes of others, hemangioma can significantly affect the psycho-emotional state of a person, worsening it, especially when it comes to girls. By the way, hemangioma appears more often in girls than in boys.
Diagnosis of the disease
Since there may be no symptoms for this disease, they first resort to instrumental examination. Then the following are assigned:
- General blood analysis;
- Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of internal organs is the most common way to diagnose the disease;
- Computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) - allow a more accurate diagnosis;
- Angiography (x-ray examination of the condition of blood vessels);
- Scintigraphy (injection of a small amount of radioactive substance to establish the picture of the disease).
A biopsy for hemangioma is not prescribed due to the high risk of bleeding.
Causes of hemangioma
Researchers have not yet learned the causes of hemangioma, but long-term observations and statistics have made it possible to make several assumptions.
Since hemangioma occurs in children, especially young children, there is a disturbance during the intrauterine period of the child’s development. This may include taking certain medications by a pregnant woman, poor environmental conditions in the area where she lives, or possibly a viral disease contracted during pregnancy. Also, endocrine disorders are suspected in the appearance of hemangioma in children, since there is a gender dependence - it occurs more often in girls.
Manifestations of hemangioma
Previously, it was believed that hemangioma does not appear in newborns, and the first signs of hemangioma appear between the ages of several weeks and three months. However, in recent years, cases of hemangioma in newborns have been increasingly reported. Pediatricians find it difficult to name the reason, and suggest that environmental deterioration is to blame.
Hemangioma in newborns, as a rule, looks like a small speck. The color of the spot can vary from light pink to purple-bluish. As a rule, hemangiomas in newborns are dark pink or light red in color.
As already mentioned, such a spot may not appear immediately, but when the baby is several weeks old. Hemangioma in children is usually not immediately recognized as a vascular tumor. The spot is small and dim, and parents simply treat it with anti-inflammatory ointments. However, the spot begins to grow, and sometimes this growth is quite rapid. As a rule, as the hemangioma grows in children, it darkens. Hemangioma grows in children up to one year old, then growth stops.
As a rule, superficial hemangioma does not cause any special manifestations other than external ones. Hemangiomas located internally may have different symptoms, depending on the location and degree of impact on surrounding tissue.
The appearance of the hemangioma, as well as its effect on health, largely depend on the location and type of tumor.
Hemangioma in children has the following localization (list in descending order):
- scalp, especially the back of the head;
- on the face: eyelids (including the inner part of the eyelid), nose, cheeks;
- oral cavity;
- genitals;
- upper body;
- hands;
- legs;
- internal organs, bones, etc.
The following types of hemangiomas are distinguished:
- simple (capillary) hemangioma. It can be flat, tuberous-nodular, tuberous-flattened. It has a red, purple or bluish color, clear boundaries, and is located on the surface of the skin. When pressed, the spot turns pale;
- cavernous (cavernous) hemangioma. It is located under the skin, has the appearance of a node, usually lumpy, covered with either unchanged skin or skin with a bluish tint. When pressed, the knot collapses;
- combined hemangioma. Combines the signs of a simple and cavernous vascular tumor;
- mixed hemangioma. Hemangioma, in which not only blood vessels, but also other tissues are involved in the tumor process. The type of such hemangiomas varies depending on their composition.
Possible complications
Active growth of hemangioma is associated with some risks. During physical exertion and bruises, such a formation can rupture, causing extensive internal bleeding. In rare cases, the development of this complication entails severe anemia. If the course is unfavorable, death is possible if surgical treatment is not carried out in a timely manner and the source of bleeding is eliminated. Significant manifestations of the development of this complication are acute abdominal pain and deterioration in general condition.
In addition, there is a high risk of thrombosis of the vessels that form the hemangioma, as well as compression of the veins that feed healthy liver tissue. In these cases, tissue necrosis and sepsis may develop. These conditions pose a danger to the patient's life.
In rare cases, rapid tumor growth provokes severe liver failure.
Treatment of hemangioma
There is no consensus on how and at what age it is best to treat hemangioma, or whether to treat it at all. The reason for the controversy is that sometimes hemangiomas disappear by the age of seven without any intervention. Therefore, some pediatricians believe that up to this age, just monitoring the tumor is enough.
Another part of the doctors is inclined to believe that removal of the hemangioma is necessary, and this must be done as early as possible, without allowing the tumor to grow. A child operated on before six months will have virtually no scars, but at a later age the cosmetic effect is worse. Another argument for removing hemangiomas: only a fifth of hemangiomas disappear on their own, and even then in most cases these are hemangiomas located on areas of the body covered by clothing.
The need to remove a hemangioma is beyond doubt only when it is located near vital organs and poses a threat to them: on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity, on the inside of the eyelid or nose, on internal organs or bones, on the genitals, where it will be permanent get injured.
Treatment of hemangioma can also be conservative. Typically, conservative treatment of hemangioma is prescribed for extensive tumors. For this purpose, hormonal drugs are prescribed. Self-treatment with hormonal medications is unacceptable due to the possibility of serious side effects.
Surgical treatment of superficially located hemangiomas is carried out mainly by modern means of gentle surgery: cryodestruction, laser exposure, the introduction of sclerosing substances (drugs that cause the walls of the vessels that make up the tumor to grow together) or a combination of these methods. The previously accepted method of removing hemangioma using electrocoagulation is now almost never used, as it is very painful. Classic surgical removal of hemangioma is used when the tumor is located internally.
Hemangioma in the liver - why is it dangerous?
The hemangioma itself does not pose any danger due to its benignity and small size. However, if you do not monitor the growth dynamics of this neoplasm and do not treat large nodes in any way, hemangioma can be fraught with the following complications:
- tumor rupture and massive internal bleeding. Is the biggest danger posed by liver hemangioma;
- compression of neighboring internal organs due to the large size of the tumor. Huge nodes (up to 25 cm in diameter) can cause severe pain due to mechanical pressure on the pelvic organs, gastrointestinal tract, etc.;
- thrombosis and tumor compaction.
Treatment of hemangioma with folk remedies
Treatment of hemangioma with folk remedies is quite common. For example, it is recommended to use celandine juice for this purpose. However, pediatricians strongly do not recommend treating hemangioma with folk remedies.
Mild remedies, such as decoctions and infusions of herbs, are not able to affect the vascular tumor, and strong remedies, such as celandine juice and other cauterizing substances, can cause ulceration of the tumor, and the subsequent addition of a secondary infection.
In addition, although very rarely and only some types, hemangiomas can still become malignant, that is, turn from a benign tumor into a malignant one. Therefore, treatment of hemangioma with folk remedies is permissible only in the form of using a decoction of medicinal herbs that have a disinfecting and hemostatic effect, in cases where the hemangioma has been slightly injured.
© 2013-2017 ICD 10 - International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision
Diet
Today, doctors do not recommend special diets for patients with liver hemangioma. This is due to the small impact that what you eat has on tumor development. At the same time, it is worth reducing the load on the liver and not overloading it. Therefore, in general, the patient’s diet should consist of a vision of a healthy and rational diet:
- It is best to limit the amount of fried, spicy and fatty foods, as this often adversely affects the condition of the liver and digestive tract itself.
- Strong coffee, soda and ice cream should also be consumed with caution.
- Fresh vegetables and fruits should be consumed as often as possible.
- The liver responds well to beets, carrots, citrus fruits and strawberries.
- A balanced diet should also include fish and dairy products, as well as animal liver.
- The latter is due to the high content of vitamin B12 in it.
If you take good care of your health and carefully approach the diagnostic process, then even a disease such as liver hemangioma may not be a problem for a person. By following all the recommendations of highly qualified doctors, the outcome of the disease is favorable.
Source