CHEAP MEDICINES FOR HEPATITIS Hundreds of suppliers bring medicines for hepatitis C from India to Russia, but only IMMCO will help you buy sofosbuvir and daclatasvir (as well as velpatasvir and ledipasvir) from India at the best price and with an individual approach to each patient!
But if an ultrasound shows increased echogenicity of the liver, it means that for specific reasons pathological changes are occurring in it - from fatty inclusions, scars, abscesses to acute viral hepatitis, tumors or cell destruction. The average capacity of a healthy liver allows sound waves to pass through the tissues of the organ.
Liver imaging with computed tomography
The liver is the largest organ of the human body, visualized by computed tomography as a homogeneous structure with a density (without contrast) within +55...+70 Hounsfield scale units.
A decrease in liver density on CT below +55 units indicates fatty hepatosis (infiltration of liver tissue with adipose tissue cells), more than +70 units indicates metallosis (deposition of metal salts in the parenchyma - this is how, for example, hemosiderosis manifests itself). Observations (CT of the liver) demonstrating pronounced fatty infiltration of the hepatic parenchyma before contrast administration (left). It can be seen that the parenchyma density is only -8 units on the Hounsfield scale, while normally it should be at least +55. The image in the middle shows that even after the administration of contrast, the parenchymal density increased slightly and is only -4 HU. Compare the image data with the norm (on the far right liver scan).
In the structure of the liver, it is customary to distinguish two lobes (main) - right and left, as well as the so-called. the caudate lobe is smaller in size. For more accurate localization of pathological foci, the liver is usually divided into segments. The blood supply to the liver is carried out by its own hepatic artery, which is a branch of the celiac trunk; venous outflow is carried out through the hepatic vein into the inferior vena cava system. In addition, at the porta hepatis, CT scan can visualize another large vessel that collects venous blood from the stomach, large and small intestines, pancreas, and spleen - the portal vein. Normally, the width of the portal vein on computed tomography of the liver is 10-20 mm (such a wide variation is mainly due to differences in body size). It is also necessary to evaluate the width of the splenic and superior mesenteric veins, which form the portal vein, and also carefully examine their lumen for the presence of filling defects caused by blood clots, as well as pathological changes in the lumen.
Contrast in computed tomography of the liver. Blue arrows indicate the portal and splenic vein.
Arterial and venous vessels during CT angiography of the liver: on the left, the abdominal part of the aorta is marked with number 4, the celiac trunk with number 5, and the hepatic artery with number 6. The blue numbers mark the veins: 1 – portal, 2 – splenic, 7 – superior mesenteric, 3 – inferior vena cava.
The portal vein system (left) and the vessels of the celiac trunk (right). Number 1 on the left indicates the portal vein, 2 – splenic vein, 3 – superior mesenteric vein, on the right, red numbers mark the arterial vessels of the liver (CT angiography): 1 – celiac trunk, 2 – hepatic artery, 3 – splenic artery, 4 – abdominal aortic section.
MRI of the liver (for comparison with CT and radiographs).
Another example of liver imaging with MRI. Liver on radiographs. With X-rays, you can only evaluate the edges of the liver, approximately its size (as in the image on the left), as well as the presence of high-density objects (as in the X-ray of the liver on the right - metal staples after endoscopic cholecystectomy are circled).
Another point that you need to pay attention to when interpreting a computed tomography scan of the liver is the presence of lymph nodes with an altered structure and shape in its gates, which can be observed with hematogenous metastasis of gastrointestinal tumors to the liver. It is also necessary to carefully evaluate the structure of the liver, highlighting areas of different density in its parenchyma - cystic or solid in nature.
Liver contrast on CT
Liver CT with intravenous contrast allows you to visualize the arterial and venous vessels of the liver, identify and differentiate space-occupying formations in its parenchyma, and visualize their structure. In the early arterial phase, the celiac trunk and its branches, including the hepatic artery, are contrasted - the width of its lumen (presence of intraluminal thrombi), course, tortuosity, abnormal arterial-venous drainages, etc. can be assessed. In the portal vein phase, it is well visualized v. porta and the vessels that form it, in the delayed phase one can see formations in the liver parenchyma that accumulate contrast well and retain contrast for a long time.
Characteristic appearance of liver metastases on CT. Arrows indicate multiple hypodense (dark) rounded lesions. The patient has rectal cancer with hematogenous metastasis to the liver through the portal vein system. The patient has cystic liver reconstruction. CT. Multiple hypodense liver foci are visualized in all segments, confluent in nature, of various sizes. A long-term condition (these lesions were identified in the liver more than 10 years ago and do not manifest themselves in any way). An example of aerobilia on a CT scan of the liver - gas is visualized in the hepatic bile ducts, which entered there as a result of surgery (cholecystectomy). Images demonstrate liver cirrhosis and ascites. CT. Pay attention to the edge of the liver, marked with arrows (estimate the size of the liver - it is only slightly larger than the spleen). Fluid on both flanks of the abdominal cavity is marked with an asterisk “*”.
Causes of increased echogenicity of the liver on ultrasound
Increased echogenicity of the liver or another change in this indicator identified during the examination indicates the development of pathology. This usually indicates the presence of compactions of a different nature (usually diffuse). The disease is detected by ultrasound diagnostics.
Basic information about the liver and its diseases
The liver is the only organ in the human body that helps cleanse and remove various toxins and poisons. That is why it is necessary to take care of it.
The organ performs about 500 functions, and many important and complex processes occur in it. The gland takes part in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, purification of blood and plasma. It is because of this that the liver is often subject to the development of serious pathologies, which quite quickly lead to cirrhosis and tissue death.
The most common diseases: hepatitis, liver failure, cancer. All of these diseases are the result of a person’s inattention to their health. As a result of the diagnostics, increased echogenicity of the liver is often detected - this means that a pathological process has been started in the organ.
What is the echogenicity of an organ?
Echogenicity can be increased or decreased. This concept is a medical term that refers to the ability of the organ being examined to reflect ultrasound rays, creating a kind of “wave”.
Attention! Impaired liver echogenicity can occur in a child over 10 years of age or in an adult.
Echogenicity is directly related to the density of the organ being examined. For example, liquid reduces the ability to reflect sound waves, so the more liquid there is, the worse the examination is.
Increased values
In most patients, the echogenicity of the liver is increased due to impaired nutrition of its tissues. As a result, droplets of fat accumulate in the cells. Hyperechogenicity may be associated with the development of cirrhosis, inflammation or chronic diseases. During diagnosis, the exact cause of the condition is revealed.
Increased echogenicity of the liver is an important indicator that needs to be given special attention, because this condition indicates abnormalities in the functioning of the gland.
Moderate values
Isoechogenicity is the rate of sound conductivity of an organ, which can be moderately increased or decreased. It also denotes the homogeneous structure of the liver.
The average level of echogenicity is characteristic of a healthy liver. This diagnostic result indicates that there are no pathological processes in the organ.
Slightly increased or decreased echogenicity is equivalent to moderate values. This usually indicates the onset of liver disease or individual characteristics.
Reduced values
Low echogenicity of the liver is a condition that indicates either the presence of edema or neoplasia. Such indicators can occur in the acute type of hepatitis, when the structure of the organ becomes heterogeneous and thickens. Sometimes echogenicity may increase if the disease becomes chronic.
Also, liver swelling can be caused by poor blood flow from the organ to the vena cava and heart. Sometimes this is a manifestation of heart failure, defects, or chronic lung diseases.
Reasons for increased echogenicity of the liver
Often, patients, seeing the results of their tests, wonder what the echogenicity of the liver (increased) is. An increase in the indicator may be due to a number of reasons:
- long-term use of medications;
- cirrhosis;
- excess weight;
- fatty liver degeneration;
- chronic hepatitis;
- diabetes;
- problems in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- alcohol overdose;
- relapse of the disease.
Sometimes the causes of increased echogenicity remain unidentified. However, treatment is possible.
Associated symptoms
Symptoms of a pathological condition can appear both in the patient’s tests and in his well-being. The patient feels the following changes in the functioning of the body:
- deterioration of immunity - colds, fatigue, general malaise;
- increase in organ size;
- reddish color of palms;
- gynecomastia;
- menstrual irregularities;
- weight gain;
- the appearance of swelling;
- yellowish color of the skin and eyeballs;
- itchy skin;
- brown coating on the tongue;
- nausea;
- gagging;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- diarrhea.
When donating blood for biochemistry, a number of typical signs of this disease are revealed:
- decrease in the amount of proteins, disturbed ratio of their fractions;
- increased glucose levels;
- lipid imbalance;
- increased levels of bilirubin, ALT, AST, alkaline phosphatosis.
Manifestations of pathology can be of varying intensity for each patient. It all depends on the general condition of the patient and the presence of associated problems.
Necessary diagnostics
The critical level of liver echogenicity is determined using ultrasound. Often diagnostics show unevenly distributed “foci” when deciphered. Such heterogeneity in the structure of the organ is another indicator of poor cell nutrition.
The disease can also be confirmed using other diagnostic methods:
- Patient complaints. If the information collected coincides with the signs of disease development, and the results of an ultrasound of the liver show increased echogenicity, this means that a diagnosis can be made.
- Visual inspection. The abdominal cavity is palpated, the doctor looks at the condition of the skin and eyes.
- Lab tests. Studying the level of sugar, bilirubin, liver enzymes, the presence of HIV and hepatitis helps to make a correct diagnosis.
- CT. The diagnostic measure helps to identify the location of the area with increased echogenicity.
- Biopsy. The study is carried out if cancer is suspected and to detect cirrhosis.
Additional diagnostics may be required in the presence of metastases in the liver parenchyma and other organs. The attending physician must decipher the studies.
It is important to know! Diagnosis of the disease is carried out to identify the cause of the disease. This is necessary to prescribe the correct treatment.
Treatment tactics
Treatment of liver diseases relieves the patient not from the symptoms of the pathology, but from its causes. Therapy involves changing your lifestyle, giving up bad habits, and maintaining a proper diet. Usually the diet is combined with drug treatment. If there is discomfort, use a heating pad with warm water and medications that relieve spasms.
Hepatitis B and C, which caused an increase in the echogenicity of the liver, is a reason to take drugs that fight viruses. Oncology requires surgery and chemotherapy.
Nutrition correction
Experts are of the opinion that with increased echogenicity of the liver, nutrition should be dietary. Food can be stewed, boiled, baked and steamed. Eating fried, fatty and salty foods is strictly prohibited, because such foods are “hard” for the liver and the manifestations of the disease may intensify.
Patients are recommended to consume fermented milk products, cereals, vegetables, lean fish and dietary meat. Fasting days are arranged 1-2 times a week. You need to eat 5-6 times a day in small portions. In the evening, eat no later than two hours before bedtime.
Following these recommendations will help not only the liver, but also the pancreas. The diet can also reduce the risk of complications and is suitable as a preventive measure.
Preventive measures
According to specialist research, liver problems in 80% of cases are associated with an unhealthy lifestyle: drinking alcohol, unhealthy diet and lack of body weight control.
Prevention should be carried out for each of the possible causes of the development of increased echogenicity of the liver. Therefore, it is important to maintain personal hygiene, give up alcohol, and use medications for the time specified by the doctor.
If characteristic symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor. Timely initiation of treatment will prevent the development of pathology.
Source: https://gepatologist.ru/proverka/ehkhogennost-pecheni-povyshena-chto-ehto-takoe.html
Liver density is normal at CT 46 54
For many years, fatty liver disease was considered a relatively benign disease, often developing with type 2 diabetes mellitus, obesity, hyperlipidemia, and alcohol abuse. In the year Ludwig first described the clinical features. This determines the high sensitivity of hepatocytes to the damaging effects of alcohol, viruses, various Widespread alcoholization of the population, especially in mining regions, the formation of liver pathologies in the presence of chronic alcohol intoxication, CAI, makes it urgent to develop treatment methods aimed at correcting metabolic homeostasis and Liver pathology is widespread throughout the world. In Ukraine there is a clear tendency towards its steady growth.
Changes in parenchyma in various diseases
The structure of liver tissue begins to change in the following diseases:
- Hepatitis (both acute and chronic);
- Cirrhosis;
- Fatty infiltrates;
- Other liver diseases.
If a person develops hepatitis, the organ itself increases in volume due to inflammation, but the parenchyma may remain unchanged. In cases where hydrophilicity increases, the liver tissue changes. The overall echogenicity decreases (this indicator may differ in different areas), and sound conductivity becomes higher. The swelling of the parenchyma increases along with the increase in inflammation of the organ; the patient requires proper treatment, since hepatitis can develop into cirrhosis.
In cirrhosis, the parenchyma of the affected liver is characterized by diffuse heterogeneity, and the number with different echogenicity indicators increases. The area of heterogeneous areas is from 5 to 20 mm2. Sometimes changes in the parenchyma are a consequence of stagnation in the liver ducts, damage to the organ due to improper metabolism, and ailments associated with fatty degeneration of the liver.
The parenchyma will also change in the presence of tumors, cysts, and stones. In this case, the changes will be local in nature.
Diagnostic capabilities of liver CT
The liver is an unpaired parenchymal organ; it consists entirely of hepatic tissue. This organ is located in the abdominal cavity in the right hypochondrium. The basis of the parenchyma is made up of hepatic lobules, between which blood vessels and bile ducts pass. The bile ducts supply bile to the gallbladder, after which this fluid flows through the bile duct into the duodenum, where it connects with the pancreatic duct. Diseases of the liver and gall bladder always affect the condition of the pancreas, and vice versa, the health of the pancreas speaks about the condition of the liver and gall bladder. An ultrasound examination can detect liver diseases, but laboratory and instrumental studies are necessary for an accurate diagnosis.
The liver is a unique organ in the human body.
Liver CT observations demonstrating severe fatty infiltration of the hepatic parenchyma before contrast administration on the left. The image in the middle shows that even after the administration of contrast, the parenchymal density increased slightly and is only -4 HU. Compare the image data with the normal one on the far right liver scan. In the structure of the liver, it is customary to distinguish between two main lobes - right and left, as well as the so-called.
Decreased liver density
The liver is the largest human gland; its functions are diverse and necessary. The two most important are the detoxification liver, which cleanses the blood of toxins and breakdown products, and the digestive liver, which produces bile enzymes and fatty acids. In addition, the liver participates in the metabolism of proteins and fats, maintains blood glucose levels, synthesizes a number of vitamins and biologically active substances, regulates water-salt metabolism, and fights antigens that penetrate the bloodstream due to active phagocytosis by astrocytes of the liver capillaries. It is not surprising that any disruption to the functioning of such an important organ leads to a deterioration in a person’s well-being, and often to various diseases. Ultrasound examination provides information about the liver in both children and adults. The child’s liver has sonographic features, which will be discussed below. The liver is a vital organ that is located under the diaphragm, in the right hypochondrium.
WATCH THE VIDEO ON THE TOPIC: Interpretation of a CT scan of the abdominal organs with contrast with calcifications in the liver and spleen
Interpretation of the computed tomography report
The largest gland in our body is the liver. It has an asymmetrical shape, reminiscent of a mushroom cap. The parameters of this organ, such as size, structure, shape, contours, do not depend on the age, weight or gender of a person. Hepatologists, specialists involved in liver treatment, consider the following sizes to be normal for the right lobe: The weight of this gland in an adult man is on average 1.5 - 1.6 kg, in an adult woman - 1.2 kg. Many liver diseases can be painless and asymptomatic for a long time. Timely and accurate diagnosis allows you to identify them at an early stage and prescribe the necessary treatment. If the patient’s primary complaints are pain in the right hypochondrium, nausea, weakness and general malaise, the doctor must identify possible unfavorable factors: alcohol abuse, intoxication, taking a variety of medications, the presence of infectious diseases, heredity. This method allows you to determine the size, consistency, density, tenderness and location of the liver.
Diagnosis and treatment
If ultrasound cannot immediately accurately diagnose liver disease, then each subsequent study is prescribed by a specialist based on the data from previous procedures.
A biochemical blood test will help detect markers of hepatitis and HIV.
When, based on the results of ultrasound, the doctor sees that the echogenicity of the liver parenchyma is increased and a diffusely heterogeneous structure is observed, additional diagnostic methods will be proposed. This will allow us to find out what caused the anomaly. Held:
- Blood chemistry. Needed to clarify data about processes occurring inside the liver, or to detect markers of hepatitis or HIV.
- Computer or magnetic resonance imaging. It is confirmed that the echogenicity of the liver is increased.
- Biopsy. Allows you to identify or exclude neoplasms in a separate area if local heterogeneity of echogenicity is observed.
The final diagnosis is made based on a combination of data from a medical examination, general tests, patient complaints, and liver ultrasound. Therapy is aimed at eliminating the disease that caused the increase in echogenicity. When treating, doctors use a method to relieve symptoms:
- severe pain is relieved with antispasmodics;
- congestion of the hepatic ducts is removed with choleretic drugs;
- for excess accumulations in the abdominal cavity, diuretics are prescribed.
To normalize and protect liver cells, hepatoprotectors such as Essentiale and Hepa-Merz are used. To restore the normal functioning of blood vessels and the flow of nutrients into the body, antiplatelet agents are prescribed. If inflammation is present, a course of antibiotics is required. When hepatitis or cirrhosis is diagnosed, the patient undergoes treatment, selected by the doctor for each person individually.
Return to contents
Diet for liver problems
When liver problems begin, diet is a mandatory addition to the main treatment. The doctor will advise you to limit the use of fats and prescribe a complex of vitamins or medications with essential phospholipids that restore damaged liver cell membranes. In case of serious complications, doctors prescribe therapeutic diet No. 5. The healing menu includes:
- raw, boiled or baked vegetables;
- dairy or vegetarian vegetable soups;
- steamed or baked chicken, turkey, beef;
- milk, kefir, yoghurts, cottage cheese;
- boiled or baked low-fat fish;
- cereal porridges and pasta;
- sauerkraut (not very sour);
- compote, jelly;
- honey and jam;
- tea with lemon, fresh juices from vegetables and fruits.
It is recommended to avoid the consumption of alcohol, tobacco, fatty meat and fish, smoked meats, pickles, legumes, fried foods, chocolate, coffee, etc. Take medications only as prescribed by a doctor. You need to know that antibiotics, antivirals, antihistamines and some diuretics can have negative side effects.
Source: InfoPechen.ru
The most interesting:
Tomography news
The computed tomography method is based on the principle of recording the X-ray density of complex objects with a moving X-ray tube and allows you to create images in the form of slices. In the year G. Hunsfield created the first computed tomograph, which was tested in clinical practice by Ambrose [cit. He also created a system of diagnostic approaches to tomography, including the technique of contrast enhancement of the resulting image. The main advantage of computed tomography is the identification of small focal formations of 0.5-1.0 cm, which cannot be visualized by other methods.
About heartburn
Liver indicators during ultrasound diagnostics of the abdominal cavity are data indicating the health of the whole organism. What characteristics of the liver are recorded using ultrasound? First of all, these are dimensional parameters, data on the ultrasonic permeability and echogenicity of organ tissues, and an anatomical description of structures in a healthy state. These standard, generally accepted criteria are needed to compare them with the figures obtained as a result of the study. Based on comparative characteristics, a conclusion is made about the normal or pathological state of the organ. Contents 1. About the human liver 2.
Increased echogenicity of the liver
Ultrasound examination is one of the most effective methods for diagnosing liver diseases. Its informative content allows you to study the condition of the gland and its blood flow. And if, according to the results of an ultrasound, it is discovered that the liver has increased echogenicity, then this is a serious reason for additional examination and treatment of the organ.
Echogenicity - what is it?
The high efficiency of ultrasound is based on the natural properties of ultrasonic waves. Easily distributed in various environments, they can be absorbed or reflected by body tissues. Absorption is typical for tissues containing fluid - the more fluid there is, the darker they appear on the monitor screen of an ultrasound machine.
Reflection is possible when a section with high acoustic resistance appears along the wave path.
It could be some kind of compaction with a low fluid content - a calculus (stone), fat deposits, scar, tumor or abscess.
In this case, on the screen of the device, the image of the organ being examined will have light areas with increased echogenicity, which indicates their pathological nature.
In addition, reflection of ultrasonic waves is possible when they reach the boundary separating tissues with different acoustic resistance. The greater this difference, the stronger the response signal, the higher the echogenicity, and therefore the lighter the area on the screen.
Tissues with a high fluid content will appear completely black on the monitor screen, which indicates the development of an inflammatory process, which is accompanied by accumulation (stagnation) of blood, pus and fluid.
Thus, the concept of “echogenicity” means the ability of body tissues to absorb or reflect ultrasonic waves. Thanks to this characteristic, specialists can assess the condition of the organ.
Visually, on the screen of an ultrasound machine, the condition and echogenicity of the liver may look like this.
- Light areas indicate pathology with increased echogenicity.
- Gray areas (of varying intensity) – moderate echogenicity, which indicates the normal state of the organ.
- Very dark and black areas are a pathology with reduced echogenicity.
Increased echogenicity of the liver is not a disease. This is a kind of symptom indicating the presence of problems with the gland. The reasons for their occurrence may be different.
In most clinical cases, the echogenicity of the liver increases due to the accumulation of fat in its cells - fatty degeneration of the gland develops. Fat has a dense structure and reflects sound waves well. Therefore, its accumulations are immediately noticeable on the monitor, and the gland itself looks heterogeneous.
Features of individual liver segments on CT
The liver is an organ that plays a large role in metabolic and digestive processes. In addition, the functioning of the organ affects immunity and the accumulation of necessary substances. The liver segments are clearly visible on CT. Such diagnostics makes it possible to identify pathology in a certain segment, which greatly facilitates diagnosis and further treatment becomes more effective.
The liver takes part in the processes of digestion and metabolism
In this article you will learn:
What segments does the liver divide into?
The liver has eight segments. They are located near the goal area. Their development occurs thanks to the veins of the liver. The segments are formed while the fetus is inside the womb. In medicine, such segmental delineation of the liver is an important element, since it helps to identify and localize all changes in the tissues of the organ. In addition, knowing the exact location of a certain segment helps doctors carry out manipulations without injuring other parts of the organ. To diagnose the liver and its segments, a CT scan is performed.
Liver segments are formed during intrauterine development of the fetus
Modern doctors more often use the Couinaud method of dividing the liver. It was proposed back in the 50s. According to this diagram, the liver has two lobes:
- Left. It consists of three sectors, as well as four segments. The dorsal sector has one segment - the caudate, the left lateral - the posterior segment, and the paramedian - the anterior left and quadrate segment.
- Right. It has two sectors - the right lateral (infero-posterior and supero-posterior segment) and paramedian (infero-anterior and supero-anterior segment).
On CT and MSCT of the liver, all parts of the organ are clearly visible. Research helps determine the localization of pathology by sector and assess the condition of all segments. Thanks to this, doctors can make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment for the patient.
The liver segments are described in detail in the video:
What are the features of segments
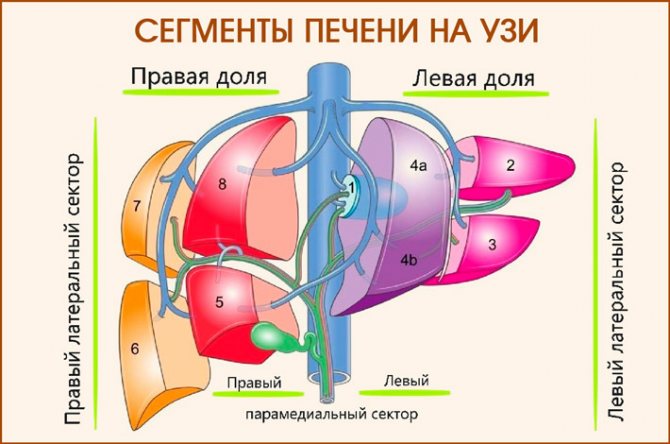
The right lobe of the gland consists of a lateral as well as a paramedian zone. The left lobe has two components. The diagram of liver segments on CT divides the organ into eight separated from adjacent elements, as indicated in the table.
| Segment | Location |
| №1 | It is fully a reflection of the caudate part. |
| №№ 2,3 | They are components of the left lobe of the organ. |
| №4 | Located in a square lobe. It is separated from the first segment by the hilum of the organ, and from the third segment by the hepatic groove. |
| №5 | The area is located near the gallbladder (its bed), but a little to the side - laterally. |
| №6 | Located below the previous segment. May occupy up to a third of the entire area of the right lobe. |
| №7 | The boundaries of this section are the diaphragmatic contour, that is, it is located even lower than the previous segment. |
| №8 | This area is reed. Its surface meets the diaphragm and differs only slightly from it. |
The anatomy of the liver is of great importance in the activity of the organ. Between the segments there are membranes (a kind of border between segments that do not allow the spread of pathology), thanks to which the risk of complications is reduced.
What is the significance of segments in the study
Since the organ is divided into zones, doctors receive accurate results after performing a CT scan of the liver. The method allows for a thorough examination of the grooves, blood vessels and determines the location of the lesion. In addition, the study helps to detect various neoplasms in the gland.
Heavy, lengthy preparation for a CT scan of the liver is not required. The doctor must inform the patient in advance about all the risks, as well as contraindications, and warns that during the procedure you cannot move and sometimes you will have to hold your breath. If a CT scan of the liver is performed with contrast, the patient must first undergo an allergy test and a creatinine test.
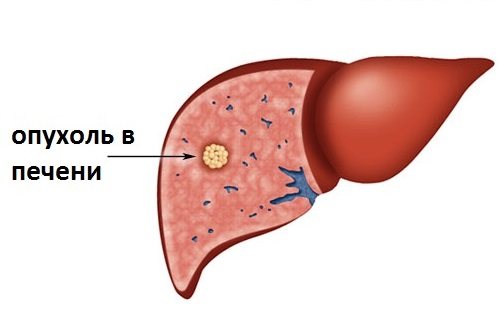
CT scan of the liver allows you to diagnose tumor formations in the organ
When conducting a study, doctors need to indicate the exact location of the pathology. All the vessels and grooves of the organ are visible on the screen of the CT machine. Thanks to the accuracy of the procedure, doctors should determine in which segment the disease is located, for example, a cyst, hemangioma.
The information content of the study and the quality of the resulting images depend on the amount of adipose tissue in the patient.
By scanning the liver by segment, you can determine the presence of the following diseases:
- Liver cysts. Upon examination, it is clear that they have clear boundaries. The density and their structure are uniform. Small cysts do not always have borders. Often they cannot even be differentiated from the liver. Therefore, doctors sometimes measure the density of the tumor to prove the presence of a cyst. They can develop in any segment of the liver.
- Echinococcal cysts. They have partitions, and their structure is multi-chamber. If the parasite dies, it is difficult to distinguish such a cyst from other formations. Most often these lesions affect the right lobe.
Before undergoing a CT scan of the liver with contrast, the patient must be tested for creatinine and allergens
- Benign neoplasms. They have clear darkened boundaries of a wavy structure. This formation is small in size. In addition, it grows quite slowly. Such pathologies include liver hemangioma, which on CT has a density of about +30 units. Typically, this neoplasm appears under the hepatic capsule. Liver adenoma on CT also shows low density.
- Cancer tumor. Such focal formations in the liver on CT look like shadows and have jagged edges. They quickly grow to large sizes, affecting any segments.
Liver adenoma on CT scan has low density
Increased echogenicity of the liver: what is it, causes, diagnosis
Echogenicity is the ability to reflect the ultrasound wave of the tissue being examined.
Using it, a specialist can determine the presence or absence of pathological processes. The speed of reflection of sound waves increases if the density is high, and vice versa. Increased indicators indicate the presence of fatty degeneration, hepatosis and other pathological processes.
Knowing about the causes of thickening of liver tissue and methods of treating this pathology, you can begin therapy in a timely manner and restore the functioning of one of the most important vital organs.
What is echogenicity
Patients undergoing diagnostic testing using ultrasound may hear about a technical term called echogenicity. This indicator usually indicates the degree and ability of tissues and organs to reflect sound waves during ultrasound.
An ultrasound machine displays an image on the screen that appears as a result of the transformation of sound waves reflected from the surface of the tissue being examined.
Using it, specialists can determine the presence or absence of changes in the structure of internal organs. Echogenicity can be normal, high or low.
Based on echogenicity indicators, a diagnosis is made about the presence of pathology or its absence.
By deciphering the liver ultrasound indicators, you can get a complete picture of all the conditions of the organ and diffuse changes in the parenchyma. The specialist can also detect fibrotic changes in the kidneys and pathological changes in other organs.
Increased echogenicity of the liver parenchyma means that changes are currently observed in the tissue of the organ. If the readings are higher than normal, the specialist will prescribe an additional examination to make a more accurate diagnosis.
Echogenicity values
Ultrasound can give an accurate picture of all changes in the tissue of the organ being examined. In addition, echogenicity demonstrates:
- tissue stiffness and liver size;
- characteristics of fabric uniformity;
- presence of scars, cracks, knots;
- changes in structure and the presence of neoplasms;
- pathological changes in the veins, vessels, bile ducts;
- enlarged lymph nodes.
Types of tissue echogenicity:
- Reduced. Indicates the presence of edema or an initial degree of inflammatory processes.
- Average. If the values are normal, a healthy liver is diagnosed.
- Increased. The hyperechoic structure of tissues indicates a disorder and the onset of pathological processes.
Experts also use the term “anechoic structure.” On the screen it appears as an area colored black. May serve as a basis for suspicion of an abscess or cyst in the gallbladder.
Causes of increased echogenicity
In normal condition, the cells of the organ are filled with a special fluid. With an increased echogenicity of the liver parenchyma, fatty layers in the tissue are visible on the ultrasound machine screen.
Due to pathological changes, the normal functioning of the organ is disrupted: this may indicate that the process of changes in the structure has already begun.
An increase in echogenicity indicators is observed with:
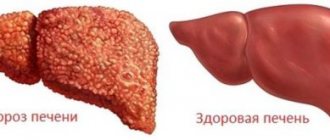
- Cirrhosis. When diagnosed, formation of connective tissue in the liver is observed. The surface of the parenchyma is covered with tubercles and has a heterogeneous structure. In the initial stages it is accompanied by hepatomegaly. In a more advanced form, it manifests itself as dystrophy and a sharp decrease in the size of the gland. The echo density of the tissue is increased, and the indicators increase depending on the proximity to the lesions.
- Chronic hepatitis. An increase in the size of the organ is observed on the device’s screen. The chronic course is characterized by an even, smooth surface structure. The increase in echo density is moderate.
- Dystrophy and hepatosis. On the monitor screen, the specialist observes a pathological change in the normal pattern of blood vessels, the enlargement of the organ is moderate. The echo density index increases in the direction from the replacement fat cells to the hepatocytes.
- Purulent processes or abscess. In the early stages, the purulent cavity is characterized by reduced echogenicity. The indicator increases as the area of inflammation spreads.
- Chronic form of cholangitis. The signal intensity comes from the affected areas, hyperechogenicity is observed.
The screen of the ultrasound machine reflects a noticeable increase in echo density in case of parasitic diseases and echogenic formations. Hemangioma is characterized by a clear contour of the picture, a heterogeneous or uniform structure. In the presence of a disease such as adenoma, echogenicity is significantly higher than normal. The contours of the formation are lumpy, uneven, the structure of the organ tissue is homogeneous.
The echodensity of the liver tissue can increase with a sudden change in weight, as well as diabetes mellitus and after an overdose of medications. Particular attention is paid to high echogenicity in pancreatitis. In this case, there is a simultaneous increase in the parameters of both the liver and pancreas.
The focal form is observed in such serious diseases as cirrhosis, steatosis and tumor formations. In this case, the specialist should prescribe an additional, more extensive examination of the gland.
Symptoms of diseases
In all cases, when, during the diagnosis of internal organs, increased indicators of echogenicity of the liver parenchyma are detected, the doctor prescribes additional studies. Sometimes this indicator can be provoked by natural processes, therefore, to make an accurate diagnosis, the patient is prescribed additional tests.
The symptoms of disorders also help to distinguish pathological changes in the functioning of the liver from natural processes.
Characteristic symptoms:
- the main sign of the disorder is pain in the liver area (under the ribs on the right side);
- discomfort, nausea or frequent vomiting after eating (sometimes for no reason);
- jaundice;
- itching;
- swelling;
- redness of the skin on the palms;
- hormonal disbalance;
- sudden weight gain;
- loss of appetite, insomnia, irritability.
Upon detailed examination by a specialist, an enlargement or deformation of the liver is observed. In general urine and blood tests, an increase in the concentration of fats and glucose is diagnosed.
Disruption of the cardiovascular system, along with general symptoms, also gives the doctor a reason to prescribe an additional ultrasound of the liver.
Diagnostic methods
Healthy liver tissue has a fine mesh uniform echostructure. Anatomical state of the organ: weight approximately 1200 -1500 g, color – dark red.
Pathological changes lead to weight gain almost doubling: the shade changes to a darker, closer to brown. The most accurate method for diagnosing liver disorders is ultrasound. Using scanning, you can determine the onset of inflammatory processes and see neoplasms (tumors or cysts) in the initial stages.
Ultrasound is one of the first diagnostic methods prescribed to a patient. If the results indicate that the echo density of the liver tissue is increased, additional diagnostic methods are prescribed:
- Conversation between the doctor and the patient and collection of anamnesis. The medical history includes all the symptoms that the patient has. In addition, the specialist examines the skin, mucous membranes of the eyes and mouth. Palpation is used to check for enlargement or possible deformation of the organ. If there are signs of pathological disorders, the doctor prescribes additional tests.
- Biochemical analysis of the patient's blood. Laboratory tests help determine the level of bile pigment, glucose and liver enzymes. Using this analysis, you can also determine markers of hepatitis and HIV.
- Instrumental research. To determine the localization of hyperechoic formations, computed tomography and MRI are prescribed.
- Biopsy. This diagnostic method is used to identify oncological and tumor formations. It is also used to determine cirrhotic changes in the gland.
The final diagnosis is made only after a comprehensive examination of the patient.
Based on the totality of tests, ultrasound and medical examination, as well as the patient’s complaints and severe symptoms, some studies may not be prescribed. If the results show discrepancies and inaccuracies, a biopsy (sampling of liver tissue fragments) under ultrasound guidance is prescribed.
Treatment
The main goal of treating hyperechogenicity is the complete elimination of the disease that provoked disturbances in the functioning of the gland. Complex therapy includes improving the functioning of the digestive system and individual organs, as well as restoring the functionality of hepatocytes. Treatment consists of a special diet and medications. Recommended diet:
- milk and water porridges;
- soups with water or vegetable broth (without tomatoes).
The therapeutic diet is based on the principle of healthy eating. All harmful foods and dishes made from them are excluded from the diet. Food must be warm (no higher than 50°C), but not cold. The menu is made up of permitted products, and carbohydrates must be at least 350 g per day. The consumption of protein foods should be reduced to 70-80 g per day.
Prohibited use:
- muffins, white bread, pastries with cream;
- lard, fatty fish and meat;
- smoked meats, hot seasonings, legumes;
- canned foods;
- black tea, coffee, cocoa, alcohol and carbonated drinks.
The diet is based on minimizing the load on the gland. During treatment, you must strictly follow all the advice of nutritionists and count the calories you eat.
For an adult, the daily norm is 2500 kcal. The diet should be fractional, divided into 5-6 meals at intervals of 3-4 hours.
The amount of water consumed without gas is at least two liters.
Healthy foods:
- Cabbage. Contains a large amount of vitamins. Has antitumor and antioxidant effects. It is a natural liver stimulant.
- Millet. Recommended for preparing porridges and decoctions. It is a good source of magnesium, vitamin B3 and potassium. The gluten-free product contains a large amount of fiber and reduces the load on the liver.
- Potato. Vegetable juice has a beneficial effect on muscles and liver cells. Used to cleanse and restore the organ.
Depending on the symptoms, various medications are prescribed. Pain syndromes are relieved with antispasmodics. Congestion in the hepatic ducts is removed by choleretic agents.
Congestion in the abdominal cavity and swelling are removed with diuretics. To restore liver tissue and normalize the functioning of the organ, it is recommended to take vitamin complexes and hepatoprotectors.
When a diagnosis of cirrhosis and hepatitis of any type is made, therapy is prescribed on an individual basis.
Important! Self-medication with medications is prohibited. Antibiotics, antivirals and antihistamines can cause complications and side effects.
Prevention
A properly designed menu and a balanced diet help reduce the risk of developing liver pathologies. To maintain the functioning of the digestive system, you should eat only natural foods without dyes or preservatives.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7Cf7ER-AL3E
Alcohol and medications pose a particular danger to liver cells.
In addition, it is advisable to regularly clean the organ and arrange fasting days. In folk medicine there are several simple but effective recipes that will help reduce the load on the gland.
Folk remedies
- Tansy has a choleretic effect and has a beneficial effect on organ cells. Recommended for restoring basic liver functions. The decoction is indicated for use in cases of alcoholism, cirrhosis, hepatitis, and in the treatment of infant jaundice .
dried flowers (2 tablespoons ) into a liter of water and cook over low heat for 25 minutes. Leave the strained broth for 1 hour. Take 1/2 cup three times a day every 6 hours. - Liver cleansing .
Preparation lasts 5 days, for this you need to include only cereals, vegetables and fruits in your diet. After unloading, you need to do an enema. After 2-3 hours, the liver warms up: to do this, apply a hot heating pad to the liver area under the rib. It is advisable to carry out the procedure in the evening before bedtime. - Herbal cleansing. Pour 1 tablespoon of immortelle flowers and corn silk into a saucepan, pour boiling water (1 cup) and bring to a boil. Infuse the resulting decoction for an hour, strain and drink warm on an empty stomach. An hour after taking the product, warm the liver with a heating pad.
Any traditional medicine can be used only after consultation with your doctor. Otherwise, complications are likely.
© 2020 – 2020, MedPechen.ru. All rights reserved.
Source: https://MedPechen.ru/exogennost-pecheni-povyshena.html