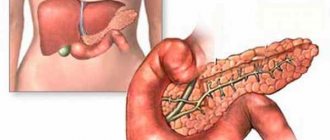
Many people have heard of the concept of nutmeg liver. This pathological condition is not a separate disease, such as cirrhosis, liver failure, cholecystitis, fatty hepatosis, etc.
Nutmeg liver is a condition that develops as a result of excessive blood supply to the liver due to impaired outflow of venous blood with intact or slightly reduced arterial inflow. In simple words, with this pathology, blood flows into the organ normally, but its outflow is very difficult.
The disease is treated symptomatically. The patient is prescribed drugs that help stop inflammatory processes, restore the integrity of liver cell membranes, have an antioxidant effect, dissolve blood clots and prevent blood clotting, as well as stabilize blood pressure and improve the flow of bile.
Let's take a closer look at the pathogenesis, symptoms and methods of treating nutmeg liver.
Is it possible to cure cirrhosis of the liver?
The destruction of hepatocytes - liver cells - is very dangerous, since these cells perform many functions. These cells take part in metabolic processes and secretory activity, and also counteract the effects of toxins.
Despite the fact that the process of tissue damage during the disease is irreversible , treatment is mandatory . Its goal is to improve the patient’s quality of life by preventing the development of complications and protecting the organ from further destruction.
Which doctor treats cirrhosis of the liver?
Initially, you should consult a general practitioner, but a more specialized specialist who prescribes treatment for liver diseases is a hepatologist . Also in such a situation, a gastroenterologist .
The treatment regimen will depend on the reason for which the pathology developed, for example, in the alcoholic form, alcohol must be excluded and therapy aimed at cleansing the body of toxins is carried out.
Is cirrhosis treated without diet?
Such patients must adhere to a diet, i.e. cirrhosis cannot be treated without following a diet . It is quite simple and excludes fatty, smoked, pickled and other foods that put increased stress on the liver. The main focus of the diet is to improve the health of the body. Read more about the diet.
Is it possible to cure cirrhosis without surgery?
Unfortunately, the disease leads to the development of complications . These include:
- bleeding from dilated veins of the esophagus (bloody vomiting occurs and can be fatal);
- portal hypertension of the hepatic portal vein;
- peritonitis , etc.
, liver failure develops . When complications develop, the surgeon's intervention becomes mandatory , and in some cases must be emergency, since the patient's life depends on it.
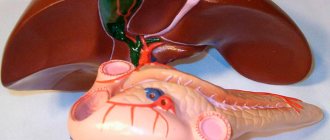
What happens to the gland
When the outflow of venous blood is disrupted, the central vein expands and becomes full of blood. Congestion spreads to the sinusoids, which also expand and compress the liver cells. Hepatocytes atrophy over time as their trophism is disrupted.
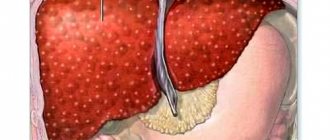
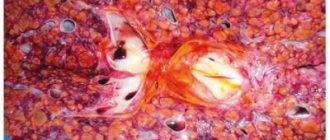
When describing the changes, experts note that the center of the lobule is red, and on the sides of the lobule, the liver cells suffer from fatty degeneration and become yellow-brown. The alternating yellow-brown and red colors give the organ a mottled appearance that resembles a nutmeg pattern.
Since during venous congestion the liver cells are compressed and a sufficient amount of nutrients and oxygen does not reach them, tissue swelling occurs, dystrophy and necrosis develop, and atrophic and sclerotic changes occur.
The proliferation of connective tissue occurs due to the fact that the state of chronic hypoxia leads to increased collagen synthesis by fibroblasts. Over time, connective tissue replaces the parenchyma, and induration (stagnant compaction) of tissues and organs develops.
Nutmeg liver causes the development of liver failure, which ultimately leads to sclerosis of the liver parenchyma (cirrhosis)
Nutmeg liver is manifested by hepatosplenomegaly, that is, the liver and spleen increase in size and become dense to the touch. The edges of the liver are rounded. When examining the tissue under a microscope, it is clear that only the central sections of the lobules are full-blooded, where the gland cells are destroyed, and on the periphery of the lobules the cells undergo degeneration.
The accumulation of blood in the center of the lobules is explained by the fact that stagnation processes primarily affect the hepatic veins, spread to the central and collecting veins, and then to the sinusoids. The latter expand, and only in the central and middle sections of the lobule, where they encounter resistance from the inflowing capillary branches of the hepatic artery, the pressure in which is stronger than in the sinusoids.
As the stagnant process progresses, hemorrhage occurs in the center of the lobules, liver cells undergo dystrophy and atrophy, and then die. Hepatocytes located on the periphery try to compensate for losses and hypertrophy, thereby becoming similar to centrilobular ones.
Fibrous tissue begins to grow in the gland; as a result, a basement membrane is formed in the sinusoids, which leads to even greater hypoxia and enhances atrophic and sclerotic changes in the gland. The developing insufficiency of the lymphatic system of the liver leads to the progression of congestive liver fibrosis.
When connective tissue grows, complete regeneration of hepatocytes does not occur, nodes form in them, deformation and changes in the structure of the organ occur. The so-called nutmeg cirrhosis of the liver develops; it is also called cardiac cirrhosis, since it often develops with chronic heart failure.
The cause of the development of nutmeg liver is heart failure.
Morphologically, three stages of changes that occur during venous hyperemia of the liver can be distinguished:
- nutmeg liver (liver tissue is yellow, and dilated dark red vessels are visible against its background);
- congestive fibrosis (the liver becomes dense due to the proliferation of fibrous tissue, foci of sclerosis appear);
- congestive cirrhosis (the surface of the gland is lumpy).
Treatment methods
The principles of treatment of liver cirrhosis require an integrated approach. It is necessary to solve the following problems :
- elimination of factors that provoked the disease;
- stopping the degeneration of tissue into fibrous;
- launch of compensatory processes;
- reducing the load on the veins of collateral blood flow;
- eliminating existing complications and preventing the development of new ones.
A visit to your doctor will help you figure out what measures to take to treat liver cirrhosis. Typically, the scheme includes the following components:
- taking medications;
- diet;
- physiotherapy;
- moderate physical activity.
If necessary, surgical treatment is performed, which involves a liver transplant .
Liver cirrhosis can be cured (correct existing symptoms) only if all doctor’s recommendations are followed. This is a complex disease, and if measures are not taken to support the functioning of the organ, the development of complications is inevitable. You can read about what happens in the last stage of cirrhosis here.
Patients who are faced with the disease at an early stage do not always think about how to treat cirrhosis of the liver. However, it must be said that if detected at an early stage, the prognosis is relatively favorable . In case of a disease caused by exposure to alcohol, if the consumption of alcoholic beverages is not excluded, rapid decompensation and the development of complications are observed.

SOS signals from the liver and gallbladder
Frequent signs of disorders and pathologies of the liver and gall bladder in the human body are a sour-bitter taste in the mouth; dry mouth or throat (although this symptom can also occur with other disorders in the body); nausea; yellowing of the sclera of the eyes and skin of the body; trembling of limbs, rapid heartbeat.
Subscribe to our INSTAGRAM account!
It is known that the liver is responsible for the condition of the tendons and muscle membranes, therefore, when its function decreases, they also lose their elasticity and weaken. Also, if there is a disturbance in the functioning of the liver, there is insomnia, many dreams in one night, and often disturbing ones. Since the peak activity of this organ occurs at 1.00-3.00 a.m., during pathological processes in it a person often wakes up at this time. Continuing the list of signs and symptoms that indicate pathology of the liver and gall bladder, I want to say that one of the common causes of headaches and dizziness is precisely spasms or inflammation in the gall bladder, as well as congestion in the liver.
Drug treatment of liver cirrhosis
Cirrhosis is associated with the degeneration of organ cells, so drugs for the treatment of cirrhosis include medications designed to protect hepatocytes . In addition to them, agents are used whose action is aimed at restoring and preventing the development of further cell destruction.
Essential phospholipids are designed to ensure normal metabolic processes and maintain the desired level of fats, carbohydrates and cholesterol. They are needed to reduce the level of collagen, which is involved in the process of replacing organ cells with liver tissue.
This category of drugs includes the following tablets for liver cirrhosis: Essentiale, Phosphonciale; Eslidin.
Lipotropics are drugs for liver cirrhosis that reduce the level of bad cholesterol and promote the breakdown of fats. From this category, Heptral, Betargin, Ornilatex are used.
The most important vitamins that need to be taken for liver diseases include: retinol, ascorbic acid, tocopherol, lipoic acid and cocarboxylase . In addition to them, you need to ensure that you take B vitamins, as well as rutin and vitamin D.
With liver dysfunction, the production of bile acid decreases, which affects the process of digesting food. is used to restore disrupted processes . Drugs in this group include: Ursonan, Ursodex, Ursorom .
Strengthening the immune system is another important factor in the fight against any disease. For this purpose, Vilozen, Zadaxin, Thymogen .
Drug treatment of liver cirrhosis also involves taking diuretics . This is due to the fact that a large amount of fluid accumulates in the abdominal cavity. Edema also appears on the upper and lower extremities and affects internal organs.
Micro and macro preparations are used for diagnosis. The microslide allows you to determine monolobular, multilobular and monomultilobular cirrhosis. Macropreparation - large nodular, small nodular and mixed cirrhosis. A microslide is a glass slide on which the object of study is placed. Macropreparation is used in cases where a microscope can be dispensed with.
Diagnosis of the hepatobiliary system

If you suspect nutmeg liver, you need to undergo differential diagnosis. First, anamnesis data is collected, all patient complaints are studied, and a physical examination is performed.
During palpation, the physician may detect thickening and enlargement of the liver, and the spleen is also enlarged. When pressing on the gland, the patient experiences discomfort or pain. To make an accurate diagnosis, you need to undergo laboratory and instrumental tests.
The patient is prescribed:
- Lipidogram. Helps determine the level of cholesterol fractions and identify lipid metabolism disorders.
- Proteinogram. Allows you to assess the state of protein metabolism.
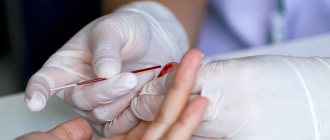
- General blood and urine analysis.
- Fecal occult blood test.
- Blood test for liver enzymes. A test for bile acids is also performed. These studies help determine whether the liver is coping with its functions.
- Biopsy. Liver tissue is collected using a needle, after which the sample is sent for histology.
- Ultrasound/CT/MRI of the liver. Instrumental studies make it possible to assess the structure and size of the liver, as well as identify abnormalities, areas of atrophy and necrosis.
To make an accurate diagnosis, you need to examine the cardiovascular system. To do this, it is recommended to undergo a chest x-ray, Doppler sonography of the heart and inferior vena cava, and an electrocardiogram.
Hepatoprotectors
Hepatoprotectors improve organ function. These include the following groups of drugs:
- herbal medicines;
- essential phospholipids;
- lipotropics;
- vitamins.
Most herbal preparations for the liver are based on milk thistle . This plant contains silymarin, a substance whose action is aimed at protecting organ cells from the effects of toxins and destruction.
One of the drugs in this category that is widely used is Legalon . In addition to strengthening the cell membrane and stimulating their work, Legalon relieves the inflammatory process and promotes tissue restoration.
This remedy can also be used as a preventive measure, as it reduces the load on the organ.
medications are also used :
- Karsil;
- Silymarin;
- Gepabene;
- Heptral.
At-risk groups
The disease is not yet a leader, but is already in the top five leading causes of death in people 40-55 years old. Every year, about 50 million people die worldwide due to viral cirrhosis. Cirrhosis is diagnosed much more often in men after 40 years of age, but can develop in patients of any age. Risk factors for the development of pathology are:
- people suffering from viral hepatitis B or C;
- abusing alcoholic beverages and suffering from alcohol dependence for 10 years or more;
- patients with venous stasis;
- heart disease at the stage of decompensation;
- people suffering from obesity, metabolic pathologies;
- poisoning with chemical, hepatotoxic substances;
- diseases of an autoimmune nature;
- pathologies of the hepatobiliary and endocrine systems;
- forced to take medications for a long time.
To prevent the development of the disease, doctors recommend paying close attention to your health, abstaining from alcohol and taking hepatotoxic drugs.
Herbal treatment
For cirrhosis, folk remedies .
When treating liver cirrhosis with herbs, it is useful to use milk thistle . The plant is characterized by regenerative properties, as it contains flavolignans.
To prepare medicinal tea, use the following recipe: the seeds and herbs of the plant are crushed, and both components are mixed in a teaspoon. The mixture is poured with a glass of boiling water and left for 15 minutes.
After straining, the product is ready for use. Take it one cup three times a day on an empty stomach before meals. When peppermint is added to tea, the effectiveness of the tea increases.
Treatment of liver cirrhosis at home can be carried out using garlic . Garlic is used to remove toxins from the body and also promotes tissue regeneration. It can be used in several ways:
- The clove is ground and mixed with a glass of kefir. This drink should be drunk every morning before meals.
- You can also use an infusion with garlic. To prepare it, 2 cloves are crushed, poured with a glass of boiling water and infused for 24 hours. Also take the product in the morning before meals. The duration of such treatment is 1-2 months.
You can find many folk recipes for cirrhosis. However, we must not forget that they are considered only as a supplement to the main methods of therapy prescribed by the doctor.
Liver cirrhosis is a dangerous disease for which it is simply unreasonable to choose treatment on your own. The sooner treatment is started, the greater the chance of avoiding complications.
How long do people live with cirrhosis?
If treatment is started on time, the factors leading to liver cirrhosis are promptly excluded and the process is in a well-compensated state, then fifty or more percent of people live more than 10 years. In severe conditions, the average life expectancy ranges around 3 years. The most unfavorable sign is hepatic encephalopathy. The duration for this pathology varies about 1 year.
With properly selected therapy, overall health and average life expectancy are significantly improved.
Specifics of the disease
Irreversible destruction of liver cells (hepatocytes), as well as the replacement of parenchyma with fibrous tissue provokes poisoning of the entire body, which leads to the death of the patient. Cirrhosis develops in several stages, each of which has its own characteristics. There are 4 stages of the disease:
- Compensation stage. This is the first stage of the development of the disease, in which an inflammatory process occurs, which is accompanied by necrosis (death) of hepatocytes. The patient has symptoms that are often ignored due to their non-specificity. For example, the patient is concerned about:
- weakness in the body;
- apathy;
- deterioration of concentration and memory;
- deterioration of appetite and sleep. Often this condition is explained by fatigue or vitamin deficiency and people do not seek help. Therefore, this stage gradually flows into the next.
increased fatigue;

Phases of development of liver cirrhosis
- increase in temperature indicators;
jaundice;
Stages of liver damage
- hepatic coma;
pulmonary pathologies;
- anemia;
leukopenia;