The liver is the most important organ responsible for the chemical processes of all substances entering the body. Hepatocytes remove toxins, stabilize metabolism, and carry out complete storage of nutrients.
Some pathologies impair liver function.
The organ takes on many blows that come from the outside. It is affected by alcohol, tobacco, poor diet, and disruption of the daily routine. Some pathologies impair the functioning of the organ. Is a liver cyst dangerous? What complications can it cause?
Description
A cyst is a benign formation. A dark green liquid accumulates inside the capsule. Its consistency resembles jelly. It includes cholesterol, bilirubin, mucin, fibrin, epithelial cells. If hemorrhage occurs, hemorrhagic fluid appears, and when infected, a purulent secretion is formed. The course of the pathology depends on the internal contents.
A dark green liquid accumulates inside the capsule.
Liver cysts are diagnosed in middle-aged people (30-50 years old). The capsule is formed on the surface, in shallow layers or inside. The right and left lobe and segments are affected. The diameter depends on the intensity of tissue formation and can reach 25 cm. Liver cysts are often diagnosed with cirrhosis, polycystic kidney disease, and tumors of other organs.
Concept and disease code according to ICD-10
A liver cyst is a general concept that implies the presence of a cavity filled with fluid or secretion. A cyst can occur on any part of the liver, and can be located on the surface or inside the organ.
Its size can range from a few millimeters to several centimeters. For a long time, the cyst does not manifest itself in any way, so it is usually diagnosed by chance, or at a later stage. Most often, cysts form in women aged 40-50 years.
According to ICD-10, liver cysts belong to the class “Other specified liver diseases” with disease code K76.8.
Classification
Tumors are divided into:
- purchased;
- true;
- parasitic;
- non-parasitic.
Echinococcal
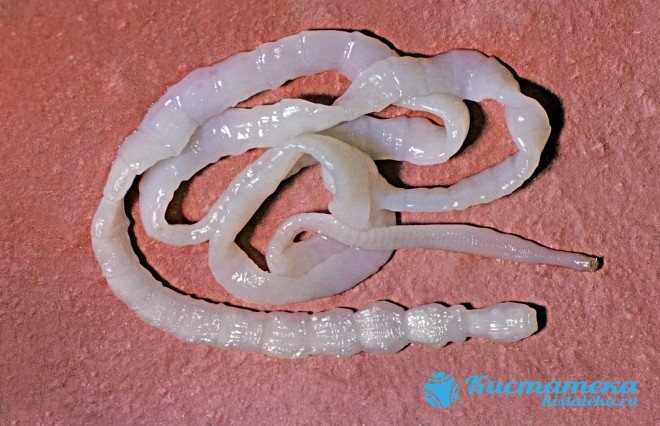

Formed when a tapeworm larva invades. In the hydatid cyst of the liver, the parasite develops from 1 to 20 years. The larvae mature, and as they develop into adults, they migrate to the small intestine. There they enter the sexually mature stage, in which they are able to reproduce. Liver cystosis with echinococcus is transmitted through household contact with animals. The capsule has impressive dimensions, its weight reaches 100 grams. Lack of treatment leads to rupture of blood vessels and bile ducts.
Solitary
This type refers to a simple liver cyst. A capsule with spherical walls gradually forms. It has no partitions or legs and is located singly. The borders of a non-parasitic liver cyst are thin and capable of accumulating large amounts of fluid. When the capsule grows more than 5 cm, pressure begins on the liver. It causes discomfort to the patient. In case of solitary liver tumor, a complete examination will be required, since it is difficult to clarify the diagnosis. This is due to the thin walls of the capsule.
Small
Small multi-chamber cavities often form after trauma. Tumors contain pus or blood and are found to be of parasitic origin. Formation occurs due to a limited necrotic process. The dead cells are closed by a capsule, in the cavity of which the parasite develops. As it grows, the substance acquires a chocolate hue. Almost 40% of cysts with an amoebic process are infected with microbes. E. coli is actively developing, and the liquid acquires a yellow-green tint with a fecal odor. Tumor rupture threatens the health and life of the patient.
Multiple
Such capsules in the liver are of a non-parasitic hereditary nature.
Such capsules in the liver are of a non-parasitic hereditary nature. This is a rare disease, occurring in 1 patient in 100,000 people. The pathology is usually detected after 40 years of age and is often found in women. As you grow older, the number of cysts increases sharply, and disturbances appear in other organs. Symptoms become pronounced with the development of complications - rupture of the cyst walls, bacterial infection, hemorrhage.
Diet for liver cyst disease
In addition to taking medications and medical procedures, a person with a liver cyst should remember that in the conditions of his disease it is extremely important to follow a diet and proper nutrition.
- Nutrition for liver tumors should be dosed. That is, 3 meals for a healthy person, for a person with a tumor should be divided by 4-5. At the same time, portions of such fractional meals should be reduced in size and strictly adhere to calorie limits.
- All foods that are eaten by a person with a tumor on the liver should not be fried or too fatty. As a rule, dishes in a diet for a sick person are steamed or boiled.
- It is important to remember that under conditions of constriction, the stomach may be more difficult and take longer to digest food. To help him and make his work easier, food should be thoroughly chopped and food that is too hard or tough should not be consumed.
- When dieting, it is important to remember fluids. A person with a liver tumor should drink at least 2 liters of pure water per day. Water helps break down and digest food faster and helps cleanse liver tissue.
- While you should drink a lot of fluids for liver cysts, you need to remember that it should not contain gases or flavorings. All carbonated drinks lead to flatulence and intestinal dysfunction. A liver tumor already provokes complications in the intestines. Mineral waters will only worsen the symptoms and cause pain in the abdomen.
- For a person with a liver tumor, it is especially important to get the maximum amount of vitamins and microelements from food. Therefore, the diet should include the maximum amount of vegetables, fruits, lean fish and seafood.
Causes
The formation of the capsule is influenced by many factors:
- genetic predisposition;
- taking certain medications (hormonal drugs);
- mechanical damage to the liver (intense sports, injuries);
- infection with parasites (through contact with sick animals).
In adults and children
Age does not affect the development of cysts. It can be formed equally in both children and adults. The only difference is that the child does not always show complaints, which complicates the diagnosis. It negatively affects the functioning of the liver, and with complications it becomes a health hazard. At the first symptoms, it is necessary to undergo diagnostics for further treatment.
Symptoms
A cyst in the left lobe of the liver appears suddenly when it reaches an impressive size. Small tumors up to 2 cm do not appear for a long time. The first signs are noticeable after the cyst has enlarged by more than 5 cm. The most severe course is observed in polycystic disease, when the abdominal wall is subjected to strong compression. Often the symptoms are not pronounced and are nonspecific. They can be confused with manifestations of other pathologies. The symptoms of cysts in the right lobe of the liver are similar.
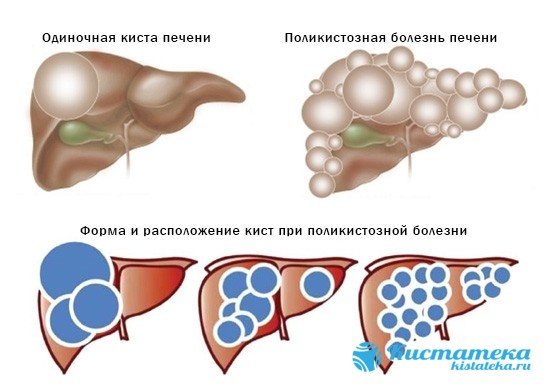
The most severe course is observed in polycystic disease, when the abdominal wall is subjected to severe compression.
The patient may experience:
- nausea after eating, vomiting or belching;
- bloating becomes pathological;
- there is a feeling of heaviness in the liver area after physical exertion;
- increased sweating;
- sleep and appetite disturbances;
- shortness of breath during intense walking or running;
- increase in body temperature up to 37 degrees;
- pallor and yellowness of the skin;
- significant loss of body weight;
- enlargement of the right hypochondrium.
A dangerous symptom is peritonitis when the capsule ruptures. The contents reach the abdominal wall, become infected and damage the tissues. Despite the ability to grow, cystic liver tumors rarely degenerate into a malignant formation.
With complications, acute abdominal pain appears that does not subside for several hours. The first sign of peritonitis is weakness, decreased blood pressure and pallor. Polycystic disease is characterized by deterioration of liver function due to the replacement of normal tissue with numerous capsules.
TYPES OF LIVER CYSTS
Doctors distinguish several types of cysts depending on their origin and development.
First of all, tumors are divided according to their origin:
- True cysts are of congenital origin and are limited by a special lining of the epithelium;
- False cysts appear throughout a person’s life due to injury or inflammation.
Neoplasms are distinguished according to their structure:
- A simple cyst or monocyst is a single formation without any complex structure;
- A multilocular cyst is a single tumor, which is internally divided by septa;
- Polycystic or polycystic – several different small tumors. They can be grouped in one area of the organ or distributed throughout its entire volume. May have the same or different content.
Another classification of cysts is based on their interaction with the liver itself. Tumors are classified according to this type:
- Parasitic - occurs when an organ is damaged by various kinds of parasites - worms, helminths and others;
- Non-parasitic - occur due to other reasons: injury or inflammation.
Diagnostic methods
Most often, pathology is discovered by chance when the patient undergoes an ultrasound scan. To clarify the diagnosis, more in-depth studies are used.
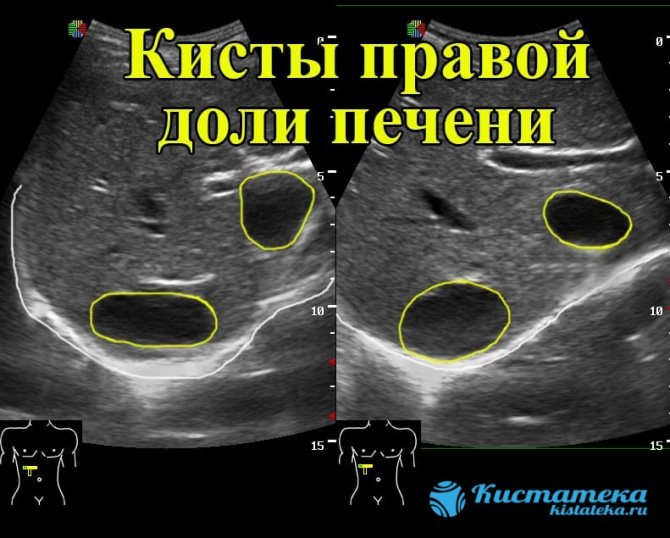
Most often, pathology is discovered by chance when the patient undergoes an ultrasound scan.
These include:
- computed tomography (allows you to determine the structure of the cavity);
- puncture of the cyst (puncture of the capsule and collection of contents for further histological examination);
- angiography with the introduction of a contrast agent (determination of liver vascular tone).
Treatment
What should I do to make the cyst on the liver resolve? In practice, two types of treatment are used - medication and surgery. If the cavity is within 3 cm, does not progress, and does not manifest symptoms, such a patient is observed by a gastroenterologist or hepatologist.
Medicines

Medicines are used for symptomatic treatment. Hepatoprotectors restore damaged tissue and promote cell renewal in a short time. Taking such medications should be regular and continuous. The most popular are Phosphogliv, Gepabene, Essentiale and Darsil.
Symptomatic treatment is aimed at relieving spasm and pain. For this, No-shpa, Diclofenac, Renalgan and other antispasmodics and analgesics are used. You can quickly stop a liver attack with injections.
Operation
Surgical treatment is necessary for bleeding, rupture and suppuration of the cavity. Be sure to remove capsules whose size exceeds 6 cm. Indications for surgery will be compression of the bile ducts, impaired bile excretion and portal hypertension.
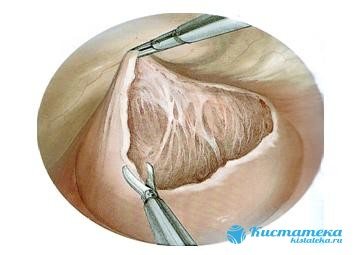
The most common operation to remove a tumor is resection.
The most common operation to remove a tumor is resection. A gentle method can also be used, where the walls of the cyst are excised. Surgical intervention is performed laparoscopically, which significantly reduces the risk of tissue injury.
For small cysts and no bacterial infection, sclerotherapy is suitable. The method is based on sealing the cyst walls.
The most complex operation is liver transplantation, which is performed with polyacid and complete replacement of liver cells with fibrous tissue.
Diet
After the operation, the patient adheres to a gentle diet. Foods that put a strain on the digestive tract are excluded from the diet, as they complicate food processing. It is necessary to give up spices, fried foods, smoked meats, flour products, pickles, sweet creams and alcohol. Sugary carbonated drinks and pasteurized juices have a negative impact on the liver.
Malignant tumors
During laparoscopic examination of the abdominal cavity, material is collected, which is subsequently sent for histology. In addition, laparoscopy makes it possible to examine surrounding organs, which is necessary to determine the extent of the malignant process.
The morphological structure of the tumor can only be determined using histological analysis.
It is not always possible to use the puncture technique under ultrasound guidance, since the material can be collected from the unaffected part of the organ. In most cases, the pathology is diagnosed at a late stage, when the tumor is considered inoperable and metastasis is observed.
It is not always possible to suspect a malignant lesion using ultrasound examination, since it may have the same echogenicity as normal gland tissues. Only computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging make it possible to more accurately establish the localization of the lesion, assess its size, density, and relationship with surrounding tissues.
When using elastography, as well as elastometry, the information content of ultrasound increases significantly. An important part of the diagnosis is the assessment of blood flow in the tumor.
A malignant lesion can be of primary or secondary origin. In the first case, malignant transformation of cells occurs directly in the liver. As for the secondary process, the gland is affected by metastases from the main tumor, which may be located in another organ. Often the liver is affected secondarily.
Among the types of cancer it is worth highlighting:
- hepatocellular carcinoma, which is characterized by rapid progression and high mortality. The risk group is the male part of the population after 50 years of age;
- angiosarcoma, which is also characterized by high aggressiveness;
- hepatoblastoma - manifested by nodes without a capsule, yellowish tint. Pathology is diagnosed in infants.
Symptomatically, the malignant process manifests itself:
- severe malaise;
- icteric syndrome (yellowing of the skin, mucous membranes, darkening of urine and discoloration of feces);
- rapid loss of body weight;
- pain syndrome in the area of the right hypochondrium;
- dyspeptic disorders (nausea, vomiting and flatulence);
- lack of appetite.
On palpation, the gland is felt as a dense, lumpy, painful formation. Therapeutic tactics depend on the stage of the oncological process and the morphology of the tumor. If the formation is considered operable, it is removed.

Treatment of liver tumors is based on:
- type of disease;
- stages of the pathological process;
- functional state of the gland;
- general condition of the patient (presence of allergic reactions and concomitant pathologies);
- the risk of complications (this applies to cases where the formation affects large vessels, intestines and diaphragm).
A feature of the malignant process is the rapid growth of the tumor, metastasis, germination into surrounding organs, inhibition of organ functions and often an unfavorable outcome due to late diagnosis and aggressiveness of the tumor.
Prognosis and prevention
Can a cyst disappear on its own? In some cases, the tumor does not grow. For a long time her presence is not detected. But even without further progression, parasitic cysts cannot go away on their own. Traditional medicine recipes are also weakly effective.
What can be done to resolve a solitary liver cyst? To do this, you must take medications prescribed by your doctor. It is recommended to use pharmaceutical herbs that have an antitumor effect only with the consent of the attending physician.
Thanks to radical treatment, the risk of relapse is reduced to zero. With multiple cysts and lack of treatment, the tissue degenerates, which leads to liver failure.
To prevent liver disorders, it is necessary to undergo an ultrasound in a timely manner. It will help to identify deviations early.