2459
A benign liver tumor often occurs with prolonged use of hormonal medications and regular consumption of large doses of alcohol. The likelihood of a neoplasm increases if the patient has hepatitis C.
A benign tumor often forms in people who work in hazardous industries. Patients who constantly eat foods with large amounts of animal fats are also at risk.
Causes
The likelihood of pathology occurring increases under the influence of the following factors:
- Adverse habits;
- Hereditary predisposition;
- Abuse of fatty foods;
- Deficiency in the diet of foods with fiber: dishes made from corn grits, fruits, vegetables.
Causes of tumors
Unfortunately, it is not yet possible to name the exact reasons that contribute to the maturation of liver cells. But it is possible to identify those factors that contribute to the formation of benign and malignant tumors.
And so, the appearance of neoplasms can be facilitated by:
- long-term use of hormones;
- hereditary factor;
- bad habits (alcohol, drugs, smoking);
- spicy and fatty foods;
- hepatitis B and C;
- parasitic diseases;
- contact with harmful substances;
- history of thyrotoxic goiter and other diseases.
Symptoms
Usually there are no adverse symptoms until the benign tumor significantly increases in size.
The patient often has a feeling of heaviness in the liver. Aching pain often appears. The occurrence of discomfort is explained by the pressure of a benign tumor on the organs located near it. Patients often complain of nausea, vomiting, and a bitter taste in the mouth.
If the patient has a benign tumor, other symptoms may be observed:
- Increase in abdominal volume;
- Gastrointestinal bleeding;
- Deterioration of bile outflow;
- Fever;
- The appearance of signs of heart failure.

Benign tumors differ from malignant tumors in the following ways:
- The patient has no symptoms of intoxication: lethargy, loss of appetite, sudden weight loss;
- A blood test does not reveal the presence of relevant tumor markers;
- There is no sharp growth of the tumor.
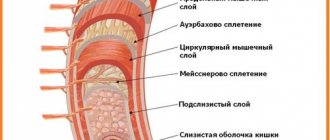
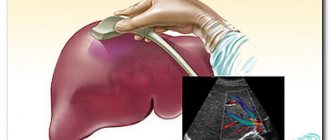
What a focal formation in the liver looks like on ultrasound
Focal liver damage is detected by ultrasound diagnostics. In a healthy person, the organ tissue is moderately hyperechoic, which is what the ultrasound diagnostician writes in the conclusion. If the structure is changed, the specialist sees hypoechoic formations in the liver on the monitor. Ultrasound allows you to analyze their density, size, and determine the presence of a capsule.

Hypervascular and hypovascular formation is an indicator of the number of blood vessels (there are many or few of them, respectively).
It can be benign in nature or formed from cancer cells - a biopsy followed by cytological examination helps differentiate them.
Types of neoplasms
There are different forms of tumors:
- Hemangioma. This tumor is formed from the vessels of the liver;
- Adenoma affecting the bile ducts. It consists of glandular cells;
- Fibroma formed from connective tissue;
- Hemangioendothelioma. The neoplasm consists of epithelial tissue lining the vascular walls.
There are various tumors of low-quality nature:
- Hepatocellular carcinoma. The neoplasm consists of parenchyma cells. Hepatocellular carcinoma is diagnosed more often than other low-grade liver tumors;
- Angiosarcoma, consisting of endothelial cells. The pathology is quite difficult to treat and often leads to death due to excessive hemorrhage;
- Hepatoblastoma. This tumor is usually diagnosed in pediatric patients under five years of age.
Tumors in children
Neoplasms in the gland in young patients are quite rare, but in 70% of cases they are malignant.
Liver cancer in children most often has 2 morphological categories:
- Hepatoblastoma. It develops from an embryonic pluripotent anlage at the stage of intrauterine development and is detected at 1 year of life. Most often it affects the right lobe of the gland and consists of one node. having no capsule, it freely grows into the liver tissue. This type of cancer is not recorded in adults.
- Hepatocarcinoma. It has a high rate of metastasis and has several nodular formations that rapidly grow into neighboring organs.
The reasons for their development have not been precisely established, but the following factors are assumed:
- Heredity.
- Gene mutations.
- Action of carcinogens during embryonic development.
The appearance of a liver tumor in children can be caused by hepatitis B, helminthic infestations, and hereditary malformations. Children whose mother took hormonal contraceptives for a long time or abused alcohol and drugs are at risk.
Treatment for cancer in a child depends on the stage of its development. The most favorable results are achieved by surgical intervention and further use of medications to stop the progression of the disease.
Liver fibroma in children develops in 40% of the total number of young patients with benign tumors. It is formed from connective tissue in the form of multiple foci.
Diagnostics
To detect benign tumors in the liver area, use:
- Magnetic resonance imaging. Using this method, the location of the tumor can be clarified. Thanks to magnetic resonance imaging, it is possible to find out at what distance from the stomach or gallbladder a benign neoplasm is located;
- Computed tomography;
- Scintigraphy. During this diagnostic procedure, iodine ions are introduced into the body, which gradually accumulate in the corresponding cells. Scintigraphy helps to obtain reliable information about the size of the tumor and the presence of metastases;
- Ultrasound examination of the liver. Using this method, the type and exact size of the tumor is determined;
- Liver puncture biopsy. This procedure is carried out under ultrasound control. The resulting material is delivered to the laboratory for further study under a microscope.
Treatment of liver cancer in women
Liver cancer is difficult to treat. It is considered resectable (subject to radical surgical treatment) only at stage 1, and also in a certain proportion of patients at stage 2. The tumor cannot be removed if:
- she is big;
- located close to large blood vessels;
- multiple oncological foci;
- there are metastases, including in nearby lymph nodes.
Then ablation, embolization, immunotherapy, targeted therapy and radiation therapy are performed. These methods help reduce tumors, increase life expectancy, and remove the main symptoms of the disease.
Take care of yourself, book a consultation now
Treatment
Appropriate medications can improve the patient's well-being. If discomfort occurs in the stomach area, take “Omez”, “Proxium”. The average duration of the course is two weeks.
If unpleasant sensations appear in the area of the right hypochondrium, “Nosh-pu”, “Baralgin” are used. Painkillers should be taken one tablet at a time. Frequency of application – three times a day. The duration of taking the medicine is determined individually.
For bloating, activated charcoal is often prescribed: one tablet of the drug per 1 kg of weight. A patient who has been diagnosed with a liver tumor is also prescribed hepatoprotectors. These medications help improve liver function. “Essentiale” should be taken 1 capsule twice a day.
In the presence of a benign tumor, vitamin and mineral complexes that have general strengthening properties are also taken. The drugs help improve immunity and improve the patient’s quality of life.
In some cases, taking medications that improve the functioning of the digestive organs is indicated. These medications contain special enzymes that facilitate the digestion of food.
Surgical intervention
If there is an increased risk of a benign tumor transforming into a malignant one, surgery is performed. Depending on the location and size of the tumor, the following is carried out:
- Marginal resection;
- Segmentectomy, which involves removing a separate segment of the liver;
- Lobectomy. During the operation, the corresponding lobe of the liver is excised;
- Hemihepatectomy;
- Removal of the cyst through endoscopic drainage.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies prevent further increase in benign neoplasm. They are recommended to be used under medical supervision.
You can use a tool consisting of the following components:
- 30 grams of potato flowers;
- 30 grams of wormwood root;
- 15 grams of calendula flowers.
- 15 grams of calamus root.
The recipe for preparing the product is as follows:
- All of the above components are crushed with a blender;
- 20 grams of medicinal mixture should be poured into 0.4 liters of boiling water;
- The product must be infused for five hours.

Drink 0.1 liter of drink three times a day. The infusion is taken approximately 20 minutes before meals.
If there is a benign tumor in the liver area, a product containing the following ingredients is used:
- 30 grams of elecampane root;
- 40 grams plantain leaves;
- 40 grams of agrimony leaves;
- 40 grams of immortelle flowers;
- 20 grams of celandine leaves;
- 30 grams of St. John's wort flowers.
A step-by-step recipe for preparing the infusion is given below:
- Plant materials are thoroughly crushed;
- A tablespoon of medicinal mixture is poured into 0.25 liters of boiling water;
- The product is infused for 25 minutes.
The daily dosage of the infusion is 0.3 l. The product is consumed approximately 60 minutes before meals.
If a patient has liver pathologies, there is often a feeling of heaviness in the stomach area and pain in the right hypochondrium. If there is no nausea, you can take a product made according to this recipe:
- 40 grams of pine branches and parsley leaves are placed in an enamel container;
- To these ingredients add three small lemons, which are first cut into neat slices;
- Gently pour 1 liter of olive oil into the resulting mixture;
- The product is kept on low heat for 30 minutes;
- After this, the drink is infused for 20 hours;
- Then the product is filtered through cheesecloth.

Drink 100 ml of medicinal decoction twice a day. The average course duration varies from two to three weeks.
You can take another effective remedy. To prepare it, 6 lemons are cut into 8 parts. Slices of citrus fruit are mixed into an enamel pan, into which 20 chopped figs are first added. Approximately 3 ml of alum purchased at the pharmacy is poured into the resulting mixture. Then add 10 grams of rhubarb root to the product. After this, wine vinegar is poured into an enamel container so that the liquid completely covers the contents of the container. The product is kept in a dry room for two days.
You need to eat 10 grams of the medicinal mixture three times a day. The drug is taken 20 minutes before meals. The average duration of the treatment course is ten days.
Diet
If you have a benign tumor in the liver area, you should eat the following foods:
- Raw vegetables;
- Dishes made from buckwheat and oatmeal;
- Vegetable stew;
- Dishes prepared from chicken fillet, veal, turkey;
- Milk;
- Fermented milk products with low fat content;
- Boiled eggs;
- Fruits;
- Tea;
- Fruit drinks.

Prohibited products include:
- Legumes;
- Peas;
- Dishes made from wheat cereals;
- High fat cream;
- Dishes from fatty poultry, pork;
- Smoked meats;
- Salty, fried foods;
- Sweet sparkling water;
- Chocolate products;
- Alcoholic drinks;
- Mayonnaise;
- Spicy seasonings.
What are the types of formations on the liver?
If a focal formation was detected during ultrasound diagnostics, you should not diagnose yourself and guess what it could be. It is better to listen to your doctor's advice.
Benign cysts include cysts of non-parasitic origin (single, multiple), as well as:
- nodular hyperplasia, hemangioma, adenoma, lipoma;
- hematomas of traumatic and postoperative origin.
Infectious foci are detected with abscess, echinococcosis, alveococcosis. Malignant formations are hepatocellular carcinoma, angioblastoma, hepatoblastoma.
Benign
Small lesions often do not make themselves felt. The altered areas are formed from epithelial tissue (adenoma), stromal tissue (nodular hyperplasia), blood vessels (hemangioma), and fat cells (lipoma).
Structural changes in the liver are detected by chance. It is possible to suspect their presence without instrumental examination. If the formation increases, pain occurs in the right lobe of the liver.
Hemangioma is characterized by a high level of vascularization (proliferation of the vascular network), that is, hypervascular. Cyst, adenoma, abscess are hypovascular formations of the liver. The approach to treating a benign structure is determined by its size, rate of increase and the danger of degeneration into a malignant form.
Adenoma and cystadenoma
Adenomas are formed from cells similar to normal liver cells. The lesions are single or multiple, located in groups, and have a capsule. Adenomas can progress rapidly, reaching a diameter of up to 20 cm. If intensive growth is observed, removal of the abnormal area is required.
Cystadenoma often occurs in women over 40 years of age. This is a single multi-chamber formation, the cavity of which is lined with cuboidal epithelial cells. Mucus accumulates inside the chambers, and papillomas may occur. Cystadenoma is prone to degeneration from a benign to a malignant form, so it must be removed immediately.
Hemangioma
The structure of the hemangioma is formed from venous elements. It grows slowly, does not metastasize, and does not spread to other organs. Regular monitoring of hemangioma is necessary due to the high risk of compression of the bile ducts and disruption of bile outflow, deterioration of blood supply to the liver when the vascular bed is blocked. Possible bleeding due to rupture of blood vessels. Transformation into cancer is rare.
Lipoma
Formed from fat cells. The diameter of a lipoma in the liver is rarely more than 5 cm. The risk of cancerous degeneration is low.
Liver hyperplasia
Hyperplasia is associated with a change in the lobulation of the organ. Pathology is often diagnosed in the right lobe of the liver. With the nodular form of hyperplasia, multiple nodules are found, the size of which is no more than 4 cm. The volume of the liver remains normal. Pathological areas grow slowly, do not spread to nearby organs, and respond well to treatment.
Cysts
The formations are congenital or occur against the background of inflammatory processes. Cysts have a capsule containing fluid inside. The color varies from transparent to brown-green (blood and bile are present). Multiple or single cysts are found both inside and on the surface of the liver. The size of the formations sometimes reaches 25 cm in diameter. Large ones are removed, small ones (up to 5 cm) are observed.
Hematoma
Occurs after injury or surgery for vascular damage. Ultrasound shows the accumulation of fluid and clots (during the formation of a cyst), a thick mass with a dense capsule, septa (a progressive cyst). Often the hematoma resolves on its own.
Infectious
Liver masses are often of infectious origin. An abscess occurs when pathogens invade the liver. Transmission of infection through blood, lymph or bile is possible when:
- cholecystitis, cholangitis;
- diverticulitis;
- duodenal ulcer;
- damage to the integrity of the intestine.
A person complains of pain on the right under the ribs and increasing weakness. Against the background of an abscess, fever and profuse sweating occur. With parasitic infestation (infection with echinococcus, alveococcus), cysts form. Echinococcosis formations do not appear for a long time. When the patient seeks help, the cyst may fill with a large volume of fluid (from 1.5 to 5 liters).
Multiple formations are formed during alveococcosis. The cysts are filled with thick white contents; when cut, they resemble cheese with holes. The diameter of the formation ranges from 1 to 30 cm. The cyst can grow beyond the liver and spread to nearby organs. Because of this, the pathology is called alveococcal cancer.
Malignant
A tumor in the liver may be malignant. It occurs directly in the tissues of the organ or is the result of the germination of metastases from other foci.
- Hepatocellular carcinoma develops very quickly and often causes death. Occurs mainly in men over 50 years of age.
- Angiosarcoma is also very aggressive in nature, occurring with equal frequency in women and men.
- Hepatoblastoma is diagnosed in children under one year of age. The formations look like nodes without a capsule.
Symptoms of a malignant tumor in the liver are yellowing of the skin and eyes, dark urine. A person quickly loses weight, feels weak, and has pain on the right side under the ribs.
Complications
If a patient has a benign liver tumor, the following consequences may be observed:
- Bleeding into the abdominal cavity;
- Rupture of a benign tumor. The main causes of this complication are injuries, high intra-abdominal pressure;
- The occurrence of severe anemia due to massive bleeding;
- Malignancy of the neoplasm. With this pathology, a transformation of a benign tumor into a malignant one is observed.

Symptoms of a benign liver tumor
A benign tumor that has not caused complications or has not reached a large size is asymptomatic. Usually the diagnosis is made by chance, during a routine ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs or when the patient consults a doctor for some other disease.
A number of nonspecific symptoms are possible, such as:
- nagging pain in the right hypochondrium and in the stomach area;
- decreased or complete lack of appetite;
- belching sour;
- heartburn;
- slight nausea;
- bloating;
- bowel disorder.
Due to the poor symptomatic picture of the disease, in order to distinguish a benign tumor in the liver from a malignant one, a number of signs are used:
- no history of malignant tumors;
- lack of rapid tumor growth;
- absence of metastases;
- normal levels of cancer markers in the blood;
- absence of symptoms of tumor intoxication (headache, fever, etc.).
Forecast
A patient with a benign liver tumor is advised to visit a hepatologist regularly.
If the neoplasm affects the biliary tract, it is removed with resection of a certain portion of the organ. Surgical intervention is also performed in the presence of cysts, the risk of rupture of which is quite high.
The prognosis is favorable in most cases. The likelihood of the neoplasm degenerating into a malignant tumor is quite low. Such a serious complication as intra-abdominal bleeding is quite rare.
Treatment and prognosis
In the initial stages of the disease, benign liver tumors are treated using medications. Systematic observation by an oncologist and examination of the intensity of development of the formation are mandatory.
Taking medications is aimed at improving digestive functions and relieving pain. The list of medications includes: hepatoprotectors, analgesics, adsorbents, enzymes to improve digestion. If indicated, surgical intervention is performed.
Treatment of liver cancer depends on the stage of development, the nature of the disease, and the person’s state of health. Oncology can be treated using the following methods:
- Surgical resection. It is carried out in the early stages of the disease when the size of the neoplasm is no more than 5 cm.
- Liver transplantation. The operation is performed at stages 1 and 2 of cancer and has a long rehabilitation period.
- Cryodestruction. Oncology is removed using liquid nitrogen, which has an ultra-low temperature.
- Radiation therapy using the CyberKnife radiosurgical system. Performed on patients with inoperable types of cancer.
- Radioembolization. Exposure of neoplasm to tiny polymers containing radioactive components.
- Injection of ethanol or acetic acid through a skin puncture into the cancer site.
- Systemic chemotherapy.
For benign neoplasms, such as fibroma, angioma, liver cyst, the prognosis is overwhelmingly favorable. How long patients with liver cancer live depends on the stage of the disease, the number of tumor nodes and the treatment performed. The most positive outcome for single cancerous lesions and their timely removal is survival in 50% of cases.
With the development of 2 or more lesions, the likelihood of death increases several times. Metastatic cancer in the final stages has a negative scenario; death can occur in 1.5-2 months.
Prevention
You can reduce the likelihood of tumors appearing in the liver area by following these recommendations:
- You need to lead a healthy lifestyle, regularly visit the fitness club;
- Nutrition should be rational. The diet should include foods enriched with fiber, vitamins and minerals;
- You should refrain from smoking, drinking alcoholic beverages, and attend preventive examinations annually;
- Hormonal medications should be taken under the supervision of a doctor.

© 2020 – 2020, . All rights reserved.
Rare symptoms
In addition to the main ones, there are less noticeable, but also quite characteristic signs of the disease that may appear before all others, these are:
- reddish tint of the palms (the so-called “liver palms” - this sign is recorded in patients with cirrhosis, hepatitis and liver cancer);
- “Drum fingers” - the patient’s fingers take on the appearance of drumsticks. This symptom does not matter if a person has had such fingers since birth.
Symptoms of liver cancer in some cases may manifest themselves in the form of gynecomastia - fat deposition in men according to the female type (in particular, enlargement of the mammary glands may be observed).
Liver cancer can occur at any age, but is more common in men over 45 years of age. Liver cancer is often associated with alcohol abuse and smoking. In children, the disease is diagnosed extremely rarely.
Treatment of liver cancer at stage 4 is palliative, since complete cure at this stage is difficult.
All stages of liver cancer - from symptoms to survival prognosis - are described in this article.
Treatment of liver cancer in Russia is sometimes in no way inferior to treatment in many other countries, since this pathology is dealt with by highly professional doctors with extensive experience in this field. More details here.
Symptoms in children can manifest themselves in a more pronounced and severe form: sometimes the disease occurs from birth. Small tumors can be removed in a timely manner, but if the tumor has invaded a large part of the organ, doctors are looking for other treatment options.
Source: rak.hvatit-bolet.ru