Why does sour vomiting occur and how to treat it?
Vomiting of acidic contents is a fairly common symptom of diseases of the digestive tract. Its appearance and intensification is characteristic of gastric pathology.
Causes
The main diseases that provoke its appearance are:
- Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum.
- Zollinger-Ellison syndrome.
- Chronic gastritis.
- Pyloric stenosis in the stage of decompensation.
- Bacterial and viral diseases.
All of these diseases, with the exception of pyloric stenosis, occur with an increase in the production of gastric juice, which leads to an increase in acidity in the lumen of the stomach.
Vomiting itself is a complex reflex act that is controlled by the medulla oblongata. Typically, vomiting refers to the eruption of gastric contents into the oral or nasal cavity.
It should not be confused with nausea, since nausea is a prerequisite for the gag reflex and is usually regarded as a state of discomfort in the abdominal cavity.
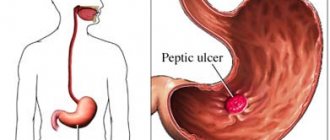
Vomiting due to peptic ulcer
A stomach ulcer can be localized in any part of the stomach. Its development is due to two interdependent mechanisms.
The first of them is protective, under the influence of negative factors (hot food, large pieces, exposure to Helicobacter) provokes a decrease in the synthesis of protective mucus that envelops the surface of the gastric mucosa.
The second mechanism, an increase in acidity, depends on the same factors that lead to a decrease in protective properties. As a result, there is an increase in the acidity of gastric juice due to increased secretion of hydrochloric acid.
The so-called irritable stomach syndrome develops, which leads to stimulation of autonomic nerve fibers, irritation of the vomiting center, transmission of nerve impulses to the diaphragm and abdominal muscles and subsequently to vomiting. A characteristic feature of vomiting in peptic ulcers is sour contents, and vomiting itself does not bring relief. It appears almost immediately after eating (up to 10 minutes).
Vomiting with pyloric stenosis and chronic gastritis
Pyloric stenosis is characterized by a narrowing of the outlet leading from the stomach to the duodenum. Because of this, a mechanical barrier arises during the evacuation of gastric contents from its cavity. Waves of reverse peristalsis begin to form, which promotes the flow of digested food and gastric juice in the opposite direction.
Vomit may contain undigested food components, but most often they are of a liquid consistency. If this symptom appears, consultation with a surgeon is necessary, since the condition is somewhat life-threatening.
Chronic gastritis with hypersecretion is a chronic inflammation of the cells of the gastric mucosa, accompanied by increased acid production by parietal cells (in medicine it is more often known as chronic gastritis type B or gastritis associated with Helicobacter pylori).
This disease is accompanied by prolonged hunger pain. Vomiting with acid develops. Most often it manifests itself at night and usually brings some relief after removing the contents of the stomach. It worries patients for a long time and requires long-term observation and competent therapy.
Vomiting in infectious diseases
The most common cause of sour vomiting is food poisoning. The reason for their development is the penetration of microorganisms into food products, the formation of certain metabolites and poisoning by these substances when consuming food.
Most PTI are characterized by rapid development of symptoms (within a few hours) and its rapid progression: initially there is nausea, which is subsequently accompanied by vomiting.
The vomit is watery, with large quantities of liquid, which is formed due to damage by the microorganism to the initial parts of the small intestine, disruption of the natural physiological processes occurring in the superficial cells of the mucous membrane and increased excretion of intracellular and intravascular fluid.
Vomiting is repeated several times until the gastric contents are completely evacuated, which includes microbial toxins and brings significant relief.
Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
With this disease, a tumor develops in the pancreas, which produces large amounts of gastrin, a natural stimulator of gastric secretion.
With its increased amount, the content of hydrochloric acid also increases. The mechanism of vomiting is the same as during the development of gastric ulcer.
Vomiting cannot be controlled with antiemetic drugs and requires surgical intervention.
In addition to diseases of the digestive tract, vomiting can also occur with diseases of other organs.
Most often it occurs with traumatic brain injuries (repeated several times and does not bring visible relief), severe cerebral strokes.
Sour vomiting may indicate a decrease in stomach tone and excessive overeating (such vomiting is considered physiological and does not require the intervention of qualified specialists).
What to do if these symptoms develop?
All of the above diseases require thorough instrumental and laboratory examination. It is necessary to determine the cause of vomiting and eliminate it.
Most often, a cure can be achieved with the help of competent correction of the diet and the preparation of a proper diet.
Patients with peptic ulcer disease are strictly prohibited from eating spicy, salty, or smoked foods, since these foods not only provoke vomiting, but also contribute to the progression of the spread of the ulcer and its perforation or malignancy.
Such patients are under the supervision of gastroenterologists, and if symptoms of perforation of the ulcer or bleeding from it appear, they are transferred to surgical wards or intensive care units for qualified treatment and restoration of body functions.
Zollinger-Ellison syndrome and pyloric stenosis must be treated only in specialized surgical and oncology departments, since the only way to eliminate the cause of vomiting is surgery (tumor removal for pancreatic adenoma and reconstructive surgery for stenosis).
Food toxic infections are treated in the departments of infectious diseases hospitals and in most cases do not require specialized drug treatment. All measures come down to gastric lavage, the use of adsorbents (activated carbon) and the administration of enemas. Usually these measures are enough for a complete cure.
Chronic gastritis is treated conservatively, and drug therapy is reduced to the use of antibiotics, to which the Helicobacter bacterium is sensitive; gastroprotectors to protect the mucous membrane from the effects of aggressive factors of gastric juice, as well as antacids - medications that help neutralize excessive amounts of hydrochloric acid.
It is important to remember that with the appearance of vomiting that has a sour taste, you must immediately consult a doctor to establish an accurate diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Source: https://zavorota.ru/kishechnik/rvota-kislym.html
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
The occurrence of fecal vomiting in a person is provoked by severe diseases with a high incidence of multiple organ failure and the risk of death, for which emergency medical care is indicated. To save the patient's life, it is critical to quickly determine why the disorder began. You cannot self-medicate, take antiemetics or painkillers, which can blur the clinical picture until the doctor arrives.
Conservative therapy
Drug therapy is prescribed regardless of the cause of vomiting of intestinal contents. Treatment is aimed at restoring circulating blood volume and electrolyte disturbances, reducing endogenous intoxication, and preparing the patient for surgery. To eliminate the expansion of intestinal loops, decompression is additionally performed by nasointestinal intubation. For fecal vomiting use:
- Infusion solutions
. Massive infusions of saline solutions (isotonic NaCl, Ringer's) are necessary for rehydration and replenishment of blood volume. For a stable effect, the drugs are combined with plasma-substituting colloidal solutions - rheopolyglucin, dextrans. - Antibiotics
. The reasons for the development of fecal vomiting often also lead to intestinal infarction and the addition of a bacterial infection. Therefore, to prevent it, broad-spectrum antibiotics are used in high therapeutic dosages. - Analgesics
. To eliminate severe pain, narcotic drugs are indicated and administered to prepare the patient for surgery. For the purpose of premedication, tranquilizers with sedative and weak analgesic effects are also recommended.
Surgery
If intestinal obstruction is diagnosed, laparotomy is usually performed, followed by exploration of the abdominal organs, dissection of adhesions, resection or elimination of the volvulus. Operations for peritonitis include revision, sanitation and other manipulations. If a non-viable section of the intestine is identified, it is resected and an anastomosis is formed. In case of a serious and threatening condition of the patient, they are limited to a colostomy with future surgery to restore the continuity of the intestinal tract.
Vomiting of acid and bile (alcohol and food poisoning) - causes and treatment methods
Category: Food poisoning
Vomiting acid signals the occurrence of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Occurs rarely or regularly. When contacting a gastroenterologist, pathologies such as ulcers and gastritis are identified, but the formation of other diseases is possible.
Causes of vomiting
Acid vomiting occurs for a variety of reasons. Popular ones include: infections, gastritis, gastric and duodenal ulcers, narrowing of the pyloric lumen and Zollinger-Ellison syndrome (pancreatic tumor).
These diseases are accompanied by a strong secretion of gastric juice, which causes the urge to vomit, which comes out along with the vomit. Experts identify causes that are not related to the development of gastrointestinal pathologies.
Other reasons:
- traumatic brain injury;
- concussion and cerebral stroke.
Excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages and overeating leads to vomiting, which does not require special treatment. In case of brain diseases, the patient must be urgently hospitalized.
Vomiting due to ulcer
An ulcer appears on the walls of the stomach or in the duodenum. Under normal conditions, the human stomach is protected by a mucous substance that coats the walls of the organ and prevents close contact with the organ's secretions.
With improper nutrition, the mucous membrane of the organ is destroyed. The walls become vulnerable to the acid produced. In places where the mucous layer is smaller, an ulcer appears, causing vomiting of hydrochloric acid along with the remains of undigested food.
This happens after a meal. The painful sensation lasts for a long time. High acidity of the stomach can provoke pathology.
Vomiting with gastritis
The presence of bile in the vomit indicates improper functioning of the pylorus and bile entering the stomach. Due to the spasm, an obstruction appears that prevents food from passing normally through the gastrointestinal tract. Consequently, food mixed with gastric juice and bile comes out, leading to bitter vomiting. Pathology appears due to the presence of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, poisoning or infections.
With chronic gastritis with increased secretion of gastric juice, severe heartburn, vomiting, and severe pain appear. The disease manifests itself at night when there is no food in the digestive organs. After the vomit is released, the patient experiences slight relief, but the symptoms reappear.
For infectious diseases
A common cause of sour vomiting is the formation of a food infection that develops due to the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms. Symptoms of caused intoxication appear rapidly: attacks of nausea, vomiting with sour contents, chills, fever, diarrhea.
Appears due to the release of excessive amounts of mucus to eliminate pathogenic microflora, which disrupts the stable functioning of the organ. This leads to excessive secretion of gastric secretions, increasing the acidity of the organ.
Vomiting during pregnancy
Acid vomiting during pregnancy can occur in early and late stages. The main reason is hormonal imbalance and active secretion of gastric juice.
Pathology manifests itself when the diet is disturbed, when there are long periods of lack of food.
When hungry, the walls of the stomach contract, producing hydrochloric acid, which becomes a sign of nausea and vomiting.
During pregnancy, a woman's organs are subjected to severe stress, which leads to their dysfunction. If you have liver disease, you may experience dark brown vomiting, the whites of your eyes and skin become yellowish, and discomfort appears in the abdominal area. Acid vomiting during pregnancy can occur with appendicitis, severe heartburn, and duodenostasis.
Diagnostics
Before prescribing drug therapy, the doctor must identify the cause of vomiting. The gastrointestinal system is diagnosed first.
Examination methods:
- ultrasound examination of the digestive organs;
- X-ray of the stomach;
- gastroscopy;
- blood and urine tests;
- magnetic resonance and computed tomography in special cases.
After diagnosis, treatment is prescribed. To improve the condition, sometimes it is enough to follow the correct regimen and therapeutic nutrition.
Treatment methods for vomiting
What should you do first with a sick person? If acid vomiting occurs, the patient must be placed in a horizontal position. The place where the patient is located should be comfortable and spacious so that the person can turn over at the right time.
Place a container for vomit nearby. If the patient is very weak, it is necessary to turn him on his side to prevent choking on vomit.
After an attack, give warm liquid and rinse the mouth. It is allowed to replace boiled water with disinfectants: a weak solution of potassium permanganate or baking soda. To prevent the gag reflex, it is recommended that the patient put 2-3 drops of mint drops on the tongue or give an ice cube.
Medicines
Depending on the cause of acid vomiting, the doctor chooses medications to relieve unpleasant symptoms. In case of infectious pathologies or overdose, sorbents are used that quickly remove the remaining toxins from the body.
Popular means:
- Polysorb. The drug is diluted in warm water and taken throughout the day, dividing the dose for an adult or a child into 4-5 doses 60 minutes before meals. For adults, the daily dosage of the drug is up to 20 grams, for children up to 8-10 grams.
- Enterodesis. Dilute 5 grams of the drug in ½ glass of water. Take 2 hours before meals three times a day.
- Activated carbon is used based on the patient's weight. For 10 kg, take 1 tablet with a dosage of 250 mg.
- Enterosgel. Dilute 22 grams of gel in 100 ml of warm, boiled water. Drink 1 hour before meals. The drink is taken up to 3 times a day.
You will like the article: “ Pills for nausea and vomiting for children in case of poisoning .”
To normalize the water-salt balance in the body, saline solution is used, which is administered intravenously. To relieve pain, use the painkiller Papaverine tablets. Almagel and Vikalin will help reduce acidity.
What to eat and what to exclude
In addition to treatment, doctors prescribe therapeutic (dietary) nutrition. Be sure to remove spicy, salty, sour, pickled and sweet foods from your usual diet. Fried foods, smoked foods and fatty foods are also prohibited.
Principles of dietary nutrition:
- heat treatment of food - steam, cooking, stewing (without oil);
- Allowed vegetables are potatoes, cucumbers, cabbage. Legumes are prohibited;
- Among the dishes you can eat liquid porridges, soups, chicken, omelettes, casseroles;
- what is allowed to drink: freshly squeezed juice from sweet fruits, herbal teas, casseroles and homemade yogurt;
- You should not eat fresh bread. Dried or stale is allowed.
Food should be warm. Portions of 200 grams, but every three hours. Coffee and alcoholic beverages are also prohibited from being included in the diet. Sometimes after drinking alcohol a person experiences an attack and a deterioration in his general condition.
Consequences and prevention
In the process of regular vomiting, there is a loss of moisture in the body, with which useful substances are released, which leads to an imbalance in vitamin balance. The inability to eat food leads to exhaustion of the body.
Negative consequences include an increased risk of damage to the walls of the digestive system. The described reactions of the body can lead to death or impaired functioning of internal organs.
In order to prevent the occurrence of consequences, it is recommended to promptly consult doctors for help, as well as organize proper nutrition. Be sure to follow the rules of personal hygiene and carefully process vegetables and fruits before consumption. Pay attention to the appearance, taste, smell and expiration date of products.
: how to reduce acid in the body
Source: https://otravlen.info/pishhevye/rvota-kislotoj.html
Vomiting feces (black, white, green) with fecal odor
Some situations will require outside help from a specialist, since a late response can lead to detrimental health consequences.
A similar situation would be vomiting with feces, which cannot be treated with home remedies.
Moreover, these symptoms can be characterized as the last stages of an advanced disease, which will also require the help of a specialist for diagnosis and the prescription of a treatment course.
Vomiting with feces usually occurs with distal intestinal obstruction, then fecal impurities are contained in the vomit and the vomit itself has a characteristic fecal odor. The main reason why vomiting with feces occurs is that fecal matter cannot move into the anus, resulting in vomiting feces, because.
Kalou simply has nowhere else to go. It is important to remember that if a person vomits feces or if the vomit contains fecal matter, you should call an ambulance as soon as possible.
It is important to remember that intestinal obstruction is not only a threat to human health, but also a direct threat to human life.
Next, we consider in detail the main causes of vomiting with feces and other painful symptoms.
Fecaloid vomiting
Similar symptoms are inherent in a disease such as intestinal obstruction. Also in this case, there may be a slight bowel movement with persistent heaviness in the abdominal area and weakness.
If obstruction occurs in the upper part of the intestine, a similar symptom will be expressed repeatedly. In addition, an external examination will make it possible to clearly distinguish the stomach against the background and even hear its “work” in the form of rumbling. Intestinal bloating that will be clearly visible is called Wahl's syndrome.
If such symptoms and intestinal bloating with vomiting feces occur, you should immediately seek help from a specialist.
In case of pain and such a syndrome, it is recommended not to wait for a doctor, but to call an ambulance, as this may even require surgery.
Such symptoms may even indicate the last stage of intestinal cancer, which even surgery cannot cure.
Vomiting with black feces
In this situation, not only black feces are released, but the vomit itself has a bloody tint, which indicates internal bleeding in one of the sections of the gastrointestinal tract.
Vomit with a brown color indicates that bleeding has formed in the stomach, and the stool itself can have a different color, including black.
Also, blood clots may be present in the vomit in such a situation.
Internal bleeding, the source of which is the duodenum, will be accompanied by melena. Any type of vomiting with black feces, first of all, will be a sign of internal bleeding and will require calling an ambulance.
Vomiting blood and feces
With internal open or hidden bleeding in any of the departments and organs of the gastrointestinal tract, vomiting will be accompanied not only by feces, but also by blood clots. However, in such a situation, vomiting will not be the most important symptom and not even always characteristic. Vomiting and the appearance of blood in it can be caused by open gastritis or an ulcer.
If blood is found not inside, but on the surface of the stool, the cause is a hemorrhoidal fissure. The reason for vomiting is intoxication, as well as prolonged constipation and the movement of large and hard masses of feces.
Vomiting with white feces
These symptoms will also be accompanied by general weakness and deterioration of the condition, indicating hepatitis disease. Similar symptoms can appear at any age. Also, such symptoms occur with tumors or stones in the bile ducts. In such a situation, it will be important to pay attention to the level of bilirubin and undergo examination.
Vomiting with green stool
The occurrence of vomiting with green feces is a consequence of one of the many diseases. In addition, such vomiting may even occur due to intolerance to drugs or foods and a reaction to taking vitamin complexes.
Also on this list that causes similar symptoms are Corn's disease, celiac disease, ulcers, diabetes, lactose intolerance and much more.
Long-term manifestation of symptoms will require specialist supervision and a series of studies.
Vomit with fecal odor
In this situation, the most likely cause is intestinal obstruction. This problem is also evidence of possible future health consequences, which may even require surgical operations. In any situation where feces or its smell appears in the vomit, you should immediately contact a specialist.
Source: https://evestart.ru/rvota-kalom-chernym-belye-zelenym-s-zapaxom-kala.html
Causes of vomiting with high acidity
If the digestive system is upset, it can vomit acid due to diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Causes
Common pathologies:
- chronic gastritis;
- viral, bacterial infections;
- Zollinger-Ellison syndrome;
- stomach or duodenal ulcer;
- pyloric stenosis.
These pathologies lead to increased production of gastric juice, which increases the level of acidity. When reflex vomiting occurs, its contents are expelled by the body.
For ulcers
An ulcer can develop in any part of the organ. Its development is associated with several mechanisms.
The first is protective, which arises due to the impact of negative factors on the organ: hot food, large undigested pieces of food, the presence of Helicobacter bacteria.
They lead to a reduction in the protective layer that envelops the inner surface of the stomach. Another mechanism is an increase in acidity, which occurs for similar reasons due to increased production of hydrochloric acid.
Irritable stomach syndrome is observed, which provokes an impact on the nerve fibers and leads to an eruption. Vomiting with an ulcer does not require relief, appears after eating and contains acid.
For gastritis or pyloric stenosis
There is a narrowing of the outlet leading from the stomach to the duodenum. Because of this, a mechanical barrier appears to the passage of stomach contents through the gastrointestinal tract. Then the digested food mixed with gastric juice moves in the opposite direction, which leads to vomiting. They often have a liquid consistency.
The disease poses a threat to the patient's life and requires urgent treatment.
Chronic gastritis, accompanied by hypersecretion, is an inflammation of the gastric mucosa when excessive acid formation occurs in the parietal cells.
The disease is manifested by vomiting with acid and prolonged pain. Appears at night, when there is no food in the stomach to digest.
After the eruption, short-term relief occurs, and symptoms return.
Treatment
To establish the cause, a comprehensive instrumental and laboratory examination of the gastrointestinal tract is carried out:
- blood analysis;
- Ultrasound of the gastrointestinal tract;
- radiography;
- Analysis of urine.
If necessary, MRI and CT scans of the abdominal organs are prescribed.
Often, to eliminate the cause of acid vomiting, it is enough to normalize the diet by prescribing the correct diet.
In patients with ulcers, heavy foods are excluded from the diet:
- spicy;
- salty;
- smoked.
It is difficult to digest, because the level of acidity of gastric juice increases. Vomiting is provoked due to the progression of the ulcer or the development of malignant tumors. Patients with prerequisites for this should undergo regular medical examinations and, if signs of an ulcer or internal bleeding are detected, are treated in intensive care or surgery.
In cases of Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome and pyloric stenosis, surgery is required. During this procedure, the formation is removed or reconstructive surgery is performed if stenosis is present.
For foodborne infections, medications are used for treatment. Absorbents to remove residual toxins:
- Polysorb – 6-12 g per day, divided into 3-4 times, drink one hour before meals, no more than 20 g per day;
- Enterosgel – dilute 22.5 g of gel in 100 ml of water and drink 3 times a day 1-2 hours before meals;
- Enterodes – 1 sachet, 5 g, diluted in 100 ml of water and consumed 3 times a day 1-2 hours after meals;
- activated carbon – 2-3 tablets of 250 mg per day.
To prevent dehydration, the administration of infusion drugs and saline is prescribed.
To relieve pain, painkillers are prescribed:
- Papaverine – 2 tablets 3-4 times a day.
Antacids are used to reduce acidity:
- Almagel – 1-3 dosage spoons 3-4 times a day 30 minutes before meals;
- Vikalin – crush 1-2 tablets and add to 50 ml of water, take after meals 3 times a day.
If acid vomiting occurs, it is important to immediately go to the hospital for diagnosis and treatment. Such a symptom indicates the development of serious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and requires urgent measures.
Source: https://orvote.ru/vidy/kislotoj.html
Vomiting feces
Treatment of the disease begins with conservative therapy methods. Initially, to stop vomiting, the patient is prescribed complete rest, as well as abstaining from food for a while. A nasogastric tube is inserted into the stomach through the nose to help empty its contents. This way stops vomiting.
Medicines
During the treatment, intravenous administration of drugs (anesthetics, antispasmodics, antiemetics) and solutions is performed. Prozerin is also used - it is injected under the skin to stimulate intestinal motility.
Prozerin must be injected under the skin 1-2 times a day. 1 ml of 0.05% solution. The maximum single dose is 0.002 g, but no more than 0.006 g can be administered per day.
Side effects of the drug: severe sweating, hypersalivation, digestive disorders, dizziness and headaches, pollakiuria, blurred vision, twitching of the tongue muscles and skeletal muscles.
The drug is contraindicated in hyperkinesis, epilepsy, angina and bradycardia, as well as in severe atherosclerosis and bronchial asthma.
Sodium chloride solution 0.9% is used for severe loss of extracellular fluid (observed with incessant vomiting), intestinal obstruction, as well as hyponatremia and hypochloremia, combined with dehydration, and as a detoxification drug. Contraindicated in acidosis, hypernatremia and hyperkalemia, pulmonary and cerebral edema, extracellular hyperhydration, acute left ventricular failure. Side effects include hyperhydration, acidosis, and hypokalemia.
Traditional treatment
Beetroot can be used as a folk remedy for treating fecal vomiting due to intestinal obstruction. The tincture is prepared as follows: boil water (5 l) in a saucepan, peel 0.5 kg of beets, and add them to the water.
Leave to boil for 45 minutes, then leave to infuse for 3 hours. Next, you need to strain the tincture, add 150 g of sugar, as well as yeast (1 tsp).
Leave the resulting drink to sit for a day, and then drink without restrictions at any time and in any quantities.
Bowel obstruction is also treated with enemas using butter and milk. You can make an enema mixture in the following way: heat 100 g of milk and melt 20 g of ghee in it.
Pour the resulting medicine into an enema, and then use it to inject the patient into the anus. Next, you need to lie on your left side for some time (so that the medicine passes into the intestines as deeply as possible).
A similar procedure should be carried out before bedtime (2 hours before) for 3 days.
Herbal treatment
Herbal treatment also helps to cope with the manifestations of the disease.
An effective recipe is one that uses sand sedge and St. John's wort.
To make the medicine, you need to take 100 g of sedge, as well as 70 g of St. John's wort, chop them finely and pour them into a thermos (the volume of the thermos should hold at least 3 glasses of water (600-650 g)).
Next, you need to let the herbs brew overnight, and strain the tincture the next morning. The medicine should be taken before meals four times a day for 1 week. A single dose should be ¾ cup. (approximately 175-180 g).
Fennel can also be used to treat intestinal blockage. This recipe is usually used for children. The decoction is made as follows: 0.5 tsp.
pour fennel into a cup, pour boiling water over it, cover and leave for 15-20 minutes. Drinking drinks with fennel helps improve intestinal motility.
An alternative option is to use fennel tea bags - this is a more convenient method.
Homeopathy
The homeopathic drug Conium is prescribed for fecal vomiting or weak peristalsis. It is used under the tongue until completely absorbed - 8 granules per one-time dose, 5 doses of the medicine must be taken per day. The treatment course usually lasts 8 weeks. If necessary, it can be re-appointed.
Contraindications to taking the drug include individual hypersensitivity to any constituent substance, during pregnancy and lactation, with kidney disease and severe epilepsy, as well as in children under 18 years of age. Conium should be used with caution in people with hypotension. Side effects include rare manifestations of dermatitis or allergies. In case of overdose, a strong decrease in blood pressure is possible.
Surgical treatment
Surgical treatment of intestinal blockage is carried out under general anesthesia (endotracheal anesthesia is used through intubation with the additional use of muscle relaxants).
The presence of such a pathology involves making a median incision in the abdominal cavity (its anterior wall) - the so-called wide median laparotomy.
This incision is needed for a full examination of the organs from the inside in order to identify the cause of intestinal blockage. Once the cause is determined, appropriate surgical procedures are performed.
Obstruction can be eliminated using different methods - it depends on the degree of changes that have occurred in the strangulated area of the intestine, the etiology of the disease, as well as the general condition of the patient. The following procedures are most often performed:
- During inversion, detorsion occurs;
- In case of intussusception, a process of disinvagination is carried out;
- If adhesive obstruction is observed, dissection of the adhesions is performed;
- If gallstone blockage due to an obstructing stone is observed, an intestinal opening is performed to remove this obstruction;
- The nonviable part of the intestine or the part that is affected by the tumor is completely removed.
Before the operation, the legs are wrapped with an elastic bandage to prevent the risk of blood clots forming in the veins of the legs.
Source: https://worldwantedperfume.com/rvota-kalom/
What are the reasons for a pronounced sour taste when vomiting?
Sour vomiting has various causes. A diagnosis can only be made through comprehensive diagnostics. Tests can only be taken at a medical institution with a doctor’s prescription. It is impossible to make a diagnosis on your own.
Typically, the causes of sour vomiting are due to disruption of the functioning of the digestive system. It is strictly forbidden to ignore the sign, since untimely treatment leads to complications.
The symptom is common and is observed in many patients.
The causes of vomiting with a sour taste are most often associated with pathologies of the digestive system.
Gag reflex with gastric ulcers
An ulcer of the digestive organ can be localized in any part of it. The disease must be diagnosed on time, as it often leads to complications. The pathology occurs only in a chronic form. Sour vomiting bothers the patient regularly.
When the digestive organ is ulcerated, the balance between the aggressive and protective environment is disrupted. The balance is destroyed and the formation of a peptic ulcer occurs.
The pathology can be secondary and form against the background of gastritis or erosive damage. In this case, the symptoms of the additional disease will be erased. The patient will not realize for a long period of time that one disorder has developed into another, more serious one.
The disease has specific symptoms and provoking factors, which are listed in the table.
| Root causes of ulcers | Violations can be caused by:
|
| Symptoms of pathology | General signs of pathology include:
|
Ulcers are divided into types depending on the location of the lesion. The clinical picture present depends on the location. A painful sensation in the abdomen appears immediately after eating. The symptom disappears after a few hours. The patient has not only nausea, but also sour belching. The patient refuses to eat. Body weight rapidly begins to decline.
With a gastric ulcer, the patient experiences sour vomiting, heartburn and belching
Vomiting due to stenosis
Stenosis of the pylorus of the stomach is a complication of peptic ulcer of the digestive organ. In the presence of pathology, a narrowing of the lumen occurs. The passage of food through the gastrointestinal tract becomes significantly more difficult.
The disorder can only be acquired and occurs mainly in adulthood. With stenosis, food is not able to enter the intestinal tract in full. If treatment is not started in a timely manner, malignant cells may form.
Vomiting acid is not uncommon with this disease. The pathology occurs in three stages. The third stage is the most dangerous. There is a high risk of dehydration. The gag reflex is rapid. The condition does not provide relief. The masses have a fetid odor and the remains of undigested food.
Gastric pyloric stenosis prevents the normal flow of food into the intestines
The first stage of the disease is the mildest. Can be treated without any problems. The patient begins to complain of belching that has a sour taste. After eating, there is a feeling of fullness in the stomach. From time to time the condition improves slightly.
The first stage of the disease is characterized by the rare appearance of sour vomiting. The removal of masses from the digestive system does not provide relief. The patient's condition is satisfactory.
The second stage of the disease is characterized by a constant feeling of fullness in the abdominal cavity. In addition, there is belching and periodic abdominal pain. Body weight begins to actively decrease. I feel the sound of sand in my stomach.
The main cause of the disorder is a scar consisting of connective tissue. Its formation occurs during the healing of an ulcerative lesion.
Sour vomiting in infectious diseases
Infectious diseases are a large group of diseases that have a distinctive feature - all pathologies are provoked by pathogenic microorganisms. The causative agents may be:
- fungi;
- viruses;
- bacteria;
- protozoa.
All infectious diseases have a similar clinical picture. The main features include:
- significant loss of strength;
- sour gag reflex;
- muscle pain;
- chills;
- body aches;
Sour vomiting can be caused by the presence of pathogenic microorganisms in the gastrointestinal tract
- increased body temperature;
- painful sensation in the joints;
- dysfunction of the intestinal tract, which manifests itself in the form of diarrhea;
- difficulty breathing;
- runny nose;
- skin rashes;
- insomnia;
- painful sensation in the throat.
The patient may have one symptom or all at once. This directly depends on the diagnosis and individual characteristics.
Regardless of the type of pathology, the disease is always accompanied by severe headache, increased temperature and sour vomiting.
At the first stages of the course of the deviation, only general signs are observed. And only over time specific manifestations are formed.
Infectious diseases always have an acute course. The intensity of manifestations is constantly increasing.
From the video you will learn how to get rid of the sour taste in the mouth:
Causes
The intestines can be clogged with gallstones and fecal stones, foreign bodies, tumors, as well as an accumulation of helminths. The cause of obstruction can also be a violation of peristalsis: spasms or excessive relaxation of the organ. In these cases, feces cannot move further through the intestines, accumulate and are released along with vomiting. In this case, dehydration of the body develops.
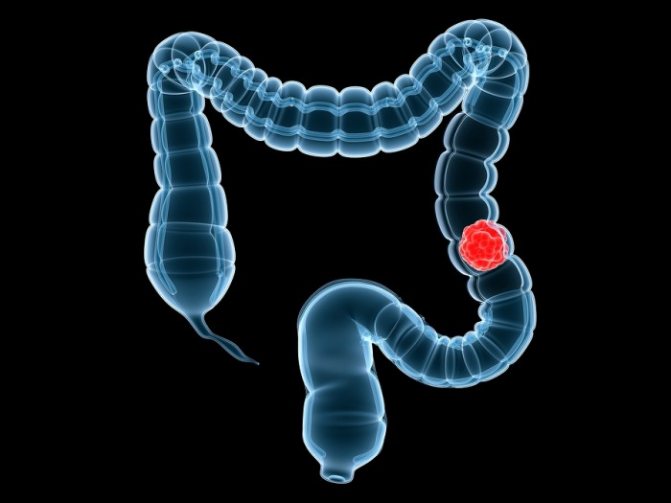
Intestinal obstruction is the main cause of fecal vomiting. A symptom of pathology is also a significant decrease in bowel movements. This is a serious condition that requires immediate medical attention. Complications of intestinal obstruction can include peritonitis, sepsis and intoxication of the body.
Another cause of vomiting feces is a fistula in the gastrointestinal tract. In this case, an anastomosis is formed between the stomach and colon. As a result, feces enter the upper gastrointestinal tract and are released in vomit.
Mechanism of nausea
In the medulla oblongata of each person’s brain there is a special center, which experts call the emetic center. It is he who receives weak signals from neurons and provokes the onset of nausea or vomiting. Even just memories of unpleasant phenomena or products can cause excitation of corticobulbar afferent neurons, which in turn activate the vomiting center. At the command of this center, the following changes occur in the human body:
- The tone of the stomach decreases.
- Peristalsis sharply decreases or completely stops.
- The tone of the duodenum and small intestine increases sharply.
When a person exhales, a sharp contraction of the abdominal muscles occurs; when inhaling, all the muscles of the diaphragm and abdominal cavity also become very tense, and the oxidized contents of the gastric cavity are released into the esophagus. When such contractions become prolonged, vomiting develops.
What is the difference between nausea and vomiting

Nausea and vomiting most often complement each other and are symptoms of many diseases. These could be problems with the digestive system, brain, infectious diseases, allergic reactions and other health problems. These two phenomena appear reflexively and are completely beyond human regulation. Some people consider nausea and vomiting to be one unpleasant condition, while the two phenomena differ from each other.
What happens in the body during nausea?
The answer is provided by emetology (the science that studies nausea and vomiting). In the human medulla oblongata there is a center that experts call vomiting. It receives signals from neurons and, when irritated, causes nausea or vomiting. Some mentions of unpleasant things or events excite corticobulbar afferent neurons, activating the vomiting center. On his command:
- The tone of the stomach decreases.
- Peristalsis sharply slows down or stops altogether.
- The tone of the duodenum and jejunum increases.
During exhalation, the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall sharply contract; when inhaling, the diaphragm and respiratory muscles also contract strongly, and the acidic contents of the stomach are thrown into the esophagus. If the contractions are strong and prolonged, vomiting develops.