It happens, it happens that a person can suddenly catch some kind of infection or virus, which is why he develops a fever, weakness, and belching air with an unpleasant odor. It is important to determine the cause in time, since such symptoms indicate the development of a serious disease.
Belching with fever and general malaise often portends a number of gastrointestinal diseases.
Causes
The causes of belching are divided into physiological and pathological.

Physiological factors:
- rapid absorption of food, swallowing huge portions and talking, resulting in overeating;
- unbalanced and unhealthy diet;
- outdoor games immediately after meals and during meals;
- wearing tight clothes.
Belching in a child after eating may also have a pathological basis:
- problems with the gastrointestinal tract, gastritis or dysbiosis, all kinds of disorders;
- inflammatory processes in the pancreas;
- inflammatory processes in the liver that occur against the background of a viral disease.
Along with belching, other symptoms of disease appear: nausea, pain in the stomach, bloating.
An unfavorable environment can also cause problems for the baby: toxic poisoning, high humidity in the home, tobacco smoke. Constant belching can occur due to frequent use of chewing gum, carbonated drinks, and due to gum or dental disease.
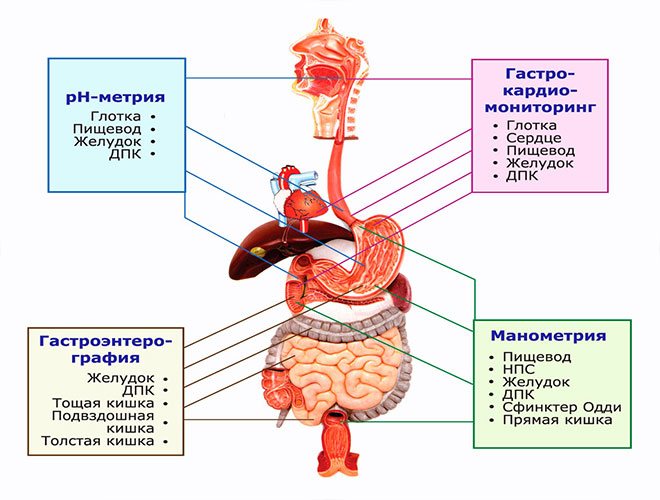
Diagnostics
It is impossible to independently identify the causes of heartburn. For this reason, if one or more symptoms appear, you should seek help from specialists. Before prescribing laboratory and instrumental measures, the doctor must:
- study the medical history and life history of a small patient - this will help identify possible factors in the formation of heartburn;
- carry out a thorough physical examination, interview parents about the time of the first complaints and the intensity of their manifestation.
Only after this is done:
- clinical and biochemical studies of blood, urine and feces;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- tests to determine the acidity of gastric juice and the presence of Helicobacter pylori.
If necessary, the following additional examination methods are prescribed:
- radiography;
- endoscopic examination of the mucous membrane of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum.
After studying all the examination results, the doctor will be able to identify the causes of heartburn in children, and also create an individual treatment strategy.
Vomit
A very dangerous condition if a child’s belching is accompanied by vomiting and suffers from heartburn. This may be evidence that a gastric ulcer is developing, perhaps, insufficient motor function in the digestive organs.

Such processes can appear against the background of constant mental stress in a child, which even parents do not know about.
Causes and signs of heartburn in infants.
Heartburn in a child is a burning sensation in the chest caused by the reverse movement of the liquid contents of the stomach, followed by reflux into the esophagus. Doctors call the process of retrograde entry of acidic gastric contents into the esophageal tube reflux.
Until 3 months of age, reflux in children is considered a normal physiological phenomenon. The baby's stomach is small and spherical. Digestion and movement of food into the intestines is slow. The esophageal sphincter muscles are not developed enough to provide full closure function. Minor overeating is accompanied by regurgitation.
When the process goes beyond the normal limits, the baby develops heartburn. Parents notice the following signs:
- profuse regurgitation, the stream of vomit looks like a fountain;
- the child cries, arching his back;
- poor daytime and night sleep;
- sour smell from the mouth;
- breast or bottle refusal;
- crying and restlessness after eating;
- lag behind the norms of height and weight;
- cough, tickling, burping through the nose;
- digestive disorders - constipation, loose foamy stools, flatulence.

In breastfed children, digestive system defects are diagnosed 50% less often than in formula-fed newborns. Alarming symptoms indicating heartburn are caused by serious health problems in the baby:
- chronic hypoxia during fetal development due to difficult pregnancy and childbirth;
- damage to the cervical and thoracic vertebrae during childbirth, which leads to disruption of the innervation of the esophagus and stomach, inhibition of their functions;
- congenital obstruction of the esophagus, stomach, intestines, decreased motility and peristalsis;
- diaphragmatic hernia, when part of the stomach is displaced through the opening of the diaphragm into the chest cavity;
- acute infectious gastritis, ulcers, enteritis;
- genetic metabolic abnormalities – cystic fibrosis, diabetes;
- severe intrauterine pathologies of the brain, lungs, kidneys, liver, and other organs.
Consistently frequent sour belching in a baby can cause throat diseases, asthma, and even cause sudden death in newborns.
Taste
If belching after eating has a sour aftertaste, then 99% of the time there are problems with the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, or more precisely with the valve that separates the stomach itself from the esophagus. If symptoms appear several hours after eating, then most likely the child has gastritis or bulbitis.
The hydrogen sulfide smell that accompanies belching in a child may indicate that there are problems with the mucous membrane or stenosis is developing, there are disturbances in the microflora of the stomach, and perhaps there are neoplasms of malignant origin.
A rotten smell may occur after eating canned foods or certain fruits and vegetables that are high in protein. As a rule, the consumption of such products is accompanied by diarrhea and decreased acidity. This condition is typical for sick children who have undergone a long course of antibacterial therapy.
Treatment
If your child experiences heartburn or other symptoms, it is imperative that you contact your pediatrician. It is the pediatrician who can tell you what to do in case of such manifestations. Self-medication can be dangerous.
However, parents are interested in the question: what can be done to alleviate the child’s condition before being examined by a doctor? There is only one answer - give the child still water to drink.
Medical recommendations for neutralizing heartburn in children include the use of several methods:
- compliance with the rules of proper nutrition and sleep;
- medicinally;
- use of traditional medicine;
- if conservative treatment is ineffective, surgical intervention is indicated.
Recommendations for proper nutrition include the following measures:
- a child under one year of age should be fed in an upright position;
- It is allowed to put the baby down after eating only after belching air;
- Sleeping in a prone position is prohibited. It is recommended to place the child on his back, with the head slightly higher than the body and slightly turned to the side;
- Children over three years old must be fed frequently and in small portions. The last meal is allowed 45 minutes before bedtime;
- adherence to dietary nutrition involves the exclusion or reduction of foods that may cause heartburn if consumed, namely: anything fried, spicy, sour juices, carbonated drinks, chocolate, citrus fruits, fruits that are plentiful in the summer - tomatoes, radishes, peppers, etc.;
- preparing dishes using the most gentle methods, namely steaming, stewing and boiling;
- Parents should ensure that the child does not overeat and chews food thoroughly.

Recommended sleeping position for heartburn
The diet menu for heartburn includes enriching the diet with products such as:
- boiled potatoes;
- carrots, beets and cabbage;
- cereals, in particular buckwheat, rice and oatmeal;
- fruits, except sour ones;
- dairy and fermented milk products;
- dietary varieties of meat and fish;
- boiled eggs or as a steam omelet.
If you have heartburn, your doctor may prescribe medications that, when taken, will alleviate the patient’s general condition:
- antacids - to reduce the acidity of gastric juice;
- prokinetics – to normalize the process of food movement through the gastrointestinal tract;
- antispasmodics;
- proton pump inhibitors and H2-histamine blockers - to reduce the secretion of hydrochloric acid in the stomach.
In addition, good results can be achieved using traditional medicine recipes, which involve the use of:
- milk;
- freshly squeezed potato juice;
- walnuts or almonds;
- decoctions of calendula and chamomile, rose hips.
Characteristics for different ages
- Up to 1 year. Belching and regurgitation are normal at this age. As a rule, after 8 months everything gradually improves, and the baby burps less and less.
- Up to 2 years. Most often it is a consequence of mental disorders; most likely, the child grows up in constant nervous tension, the parents argue, the child is afraid. Vomiting and increased body temperature may occur.
- Up to 3 years. As a rule, it is a consequence of pathological disorders associated with the respiratory tract and gastrointestinal diseases.
- Up to 4 years. At this age, the child has unstable emotions, he constantly tries to violate the daily routine and diet. In this case, parents need to take walks with the baby more often and not forget about daytime sleep.
- Up to 5 years. Attacks of hiccups may indicate that the child is fed too often fatty foods, chocolates and carbonated drinks.
Interesting! What does belching with the smell of acetone indicate?
In most cases, burping in a child is just a consequence of poor nutrition. Naturally, it is necessary to undergo all recommended medical examinations, but still you should not indulge your baby and buy him “harmful” food products.
What to do?
If a person develops symptoms such as belching, fever, abdominal pain, this may be a consequence of diseases in the body, which can be very diverse. Most often, such symptoms are caused by food poisoning, which is dangerous for both adults and small children. In case of poisoning, the body becomes dehydrated, the water balance is disturbed, the body loses fluid, which causes further complications. Before the ambulance arrives, you can try to rinse your stomach with a weak solution of potassium permanganate and drink 8-10 tablets of activated carbon. In case of food poisoning, a course of antibiotics and adsorbing drugs is most often prescribed. In addition to everything, the doctor will recommend taking probiotics and following a therapeutic diet that will help overcome the disease.
With diseases of the stomach and cancer, the body temperature may also increase and symptoms such as abdominal pain, severe heartburn, bloating, and belching with an unpleasant odor may appear. In such a situation, it is better not to self-medicate, but to consult a doctor. To begin with, he will recommend going on a therapeutic diet for 2-3 weeks, which excludes junk food, alcohol, and cigarettes. If no improvement has occurred during this time, the doctor will order a full examination of the gastrointestinal tract and, based on the results obtained, prescribe a course of treatment.
Why does putrefactive aerophagia occur?
The main cause of foul-smelling belching is hydrogen sulfide, a gas that is released after the tract breaks down sulfur-containing proteins in food. Aerophagia during the neonatal period and one year is caused by several factors:
- imperfection of internal organs;
- psychosomatic disorders;
- functional disorders.
Deviations change the outflow of bile and contribute to its entry into the stomach. Additional symptoms of belching with rotten eggs are nausea, pain in the right hypochondrium, diarrhea, and vomiting.
Many factors cause pathological aerophagia, but they are all associated with putrefactive processes in the digestive system. They develop against the background of altered gastric motility and slow synthesis of digestive enzymes. Food masses stagnate in the stomach, and sulfur-containing proteins rot with the release of hydrogen sulfide.
At an older age, for example, at 5–6 years old, the release of rotten belching occurs under the influence of functional states:
- enteritis;
- duodenitis;
- Crohn's disease;
- pyloric stenosis;
- gastritis with low acidity;
- biliary dyskinesia;
- allergies to certain foods;
- pancreatitis with enzyme deficiency.
At 3 years old, a child’s body is often attacked by intestinal infections. Therefore, burps of rotten eggs can be released after infection with Giardia, Salmonella and other intestinal parasites.
Hiccups and belching
Prolonged hiccups coupled with regurgitation cause obvious discomfort to the child. Symptoms usually appear after eating dry food or overeating. In this case, the burp has a rotten, bitter or sour taste. Also leading to pathology is aerophagia - frequent involuntary swallowing of air while eating.
If belching occurs regularly along with hiccups, problems with a number of body systems can be suspected:
- intestines;
- gastrointestinal tract;
- liver;
- gall;
- of cardio-vascular system.
To reduce the risk of developing serious diseases, it is advisable to take your child to a gastroenterologist or pediatrician.
Hiccups themselves are a convulsive contraction of the diaphragm, during which a sharp involuntary inhalation occurs, followed by protrusion of the abdomen. It occurs not only due to nutritional problems - hiccups are caused by hypothermia, prolonged stress or severe stress.
Heartburn as a dangerous symptom in newborns
In most cases, heartburn in newborn babies occurs due to underdevelopment of the digestive system. In this case, the unpleasant phenomena gradually decrease and, over time, disappear with time. Sometimes heartburn can be associated with increased stomach acidity and other problems. They can lead to complications such as:
- anemia;
- pneumonia;
- chronic cough;
- inflammatory diseases of the respiratory system, as well as the ears and sinuses;
- developmental delay