Common Diarrhea Factors
Common causes of green diarrhea in an adult are:
- eating food filled with caustic green dyes;
- the use of antibiotics that cause dysbacteriosis, as well as treatment with other drugs for a long time;
- excessive consumption of fresh vegetables, regardless of their color, can lead to watery, green-colored diarrhea;
- infection with bacteria due to consumption of poor-quality food, contaminated vegetables and fruits (in addition, there is mucus in the stool);
- internal bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract - feces come out along with blood;
- liver damage - due to the breakdown of red blood cells, diarrhea turns green (bilirubin is produced, which colors the stool).
The cause of dark green diarrhea in an adult may depend not only on these signs. Additional factors often indicate the course of a particular pathology; detection and subsequent treatment require a full diagnosis and testing.
What is diarrhea and what are its causes?
Diarrhea itself, or as it is commonly called, diarrhea, is not an independent pathology, but a symptom of a disease that has already arisen in the body. The reasons for its appearance, if there is pain in the liver area at the same time, are different, among them:
- infectious lesion - penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the hepatocellular region with the development of an acute inflammatory process;
- parasitic infestations - helminths, in the process of their vital activity, poison the small intestine with toxins with the development of diarrhea;
- oncological neoplasms in the liver area, which provoke digestive disorders and can become the root cause of persistent diarrhea;
- enzymopathies - the production of enzymes necessary for the proper absorption of nutrients occurs in a smaller volume and against this background problems with stool appear;
- circulatory failure in the right hypochondrium;
- drug poisoning - certain subgroups of drugs lead to disturbances in the activity of liver cells, simultaneously with the development of diarrhea;
- surgical interventions on intestinal loops undergone by the patient.
Experts talk about diarrhea when rectal emptying occurs more often than 1-2 times a day, and stool has a liquid consistency. They may additionally contain other inclusions - streaks of blood, clots of pus, or pieces of undigested food. A person’s well-being suffers from dehydration, rapid loss of beneficial microelements, severe pain in the abdomen - both the liver and the intestines themselves hurt.
Intestinal infection as the main factor
The most common cause of green diarrhea among adults and children is infection with bacteria that causes inflammation in the intestines. Microorganisms penetrate through infected products and dirty hands. Poisoning is accompanied by additional symptoms in 90% of cases:
- severe nausea and vomiting occurs, which can be profuse, restrained or one-time;
- acute pain and cramps develop in the abdomen;
- the person experiences severe weakness, dizziness;
- temperature can rise to 39 degrees;
- no appetite.
Penetrating into the digestive system, microbes cause inflammation, causing gastroenteritis, enteritis or colitis. With severe infection, duodenitis or gastritis may develop.
Rotaviruses and enteroviruses are the most common infections.
Fecal masses are excreted in large quantities, often accompanied by bloody spots if bleeding occurs or lesions of the mucous membrane form.
Green feces with a yellow tint - causes and treatment
Yellow-green diarrhea in most cases indicates the development of serious diseases or damage by strong pathogens. The most common cause is rotavirus infection.
It manifests itself not only with frequent and loose stools, but also with several very aggravating symptoms:
- Frequent profuse vomiting.
- Nausea.
- Weakness.
- A sharp increase in temperature.
- Chills.
- Cough.
- Runny nose.
Diarrhea and fever in an adult in this case are very dangerous due to rapid dehydration. All this can be treated with a group of drugs, after which a rehabilitation process is necessary.
Also, green, foamy, yellow-green stools may indicate the presence of quite severe gastrointestinal diseases.
These include:
- Gallbladder diseases.
- Hepatitis and other liver diseases.
- Pancreatitis.
- Ulcerative diseases.
- Gastritis.
All these conditions require serious treatment, often carried out in a hospital. But the sooner it is detected, the faster and more effective the treatment will be.
Important! Undigested bile often gives a yellowish tint to stool. In this case, the person feels strong wandering pains in the abdominal area. At this time, the digestion process is seriously disrupted, so it is necessary to urgently seek medical help.
Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
Internal bleeding is the most dangerous pathology that can cause green diarrhea in an adult. But there is one nuance: in this case, the feces become dark, almost black due to the mixing of iron with digested food. If oxidation is not complete, it remains green.
Useful information: What to do if diarrhea lasts a week
Green stool can be the cause of blood problems, not necessarily bleeding. Increased breakdown of red blood cells in the liver is one of the symptom factors. A similar thing happens if the pancreas does not produce enough enzymes to digest food.
Prevention
Prevention includes:
- Increasing fluid intake;
- Taking rehydrating medications;
- Spending at least two hours in the fresh air;
- Exclusion from the diet of low-quality food, exclusion of fast food, food containing dyes;
- Quitting alcohol and tobacco;
- Taking medications only as prescribed by a doctor;
- Maintaining hygiene;
Liquid green stool in an adult can occur in patients of all ages.
Diarrhea can be a consequence of taking various medications or the presence of infectious diseases. Therefore, when the first symptoms appear, you should contact a professional specialist.
Dysbacteriosis
Green diarrhea from dysbacteriosis most often occurs in children, but can appear in an adult. Factors in the development of dysbacteriosis are:
- a sharp change in immunity;
- use of antibiotics;
- intestinal infections;
- allergy;
- eating disorders.
Under the influence of these factors, pathogenic microflora develops in the intestines, overwhelming beneficial bacteria. As a result, the functioning of the body deteriorates.
Reasons for the formation of green stool in adults
Green or marshy stool appears in adults for various reasons. These are physiological reasons when feces are colored by natural green dyes, chemical compounds found in vitamins and medications, food additives, foods, and food coloring. Pathological causes include diseases.

Products that change the color of stool
Many foods influence the composition of fecal excretions of adults and adolescents. After their consumption, green feces are formed; the reason for this coloring of excrement is chlorophyll
.
This group includes:
- green onion feather;
- parsley;
- wild garlic;
- green peas;
- green beans;
- dill;
- broccoli;
- spinach;
- blueberry, serviceberry, blueberry;
- sea kale.
Why don’t “green poop” appear in all healthy people who eat fresh vegetables, berries and seasonings? The reason lies in the different course of metabolic processes in the body. The amount eaten is also of great importance.
The more food rich in chlorophyll and bright green pigments, the more green appears in the stool. The stool may be green (or swamp-colored) after eating red fish, beef, horse meat, and beans.

Greenish, gray-green, dark green fecal discharge often appears in people on strict vegetable diets. The meal kits of strict vegetarians and people who eat only raw fruits and vegetables are also loaded with greens, causing the color of the feces to change. This is often observed among lovers of carbonated drinks and confectionery products colored with food pigments.
Food colorings
Natural food colors are made from natural plant pigments and obtained by synthesis. There are several dyes that give creams, pasta, candies, jellies, drinks, marmalades, ice cream and other products a greenish tint (color).
Consumption of foods colored with pigments and special nutrition for athletes is one of the reasons for the formation of greenish-colored stool. Fecal discharge, colored with pigments, may acquire a greenish-yellow tint; it may be yellow in color. Due to the synthetic pigment, which is poorly decomposed in the liver, the color of poop can be similar to the color of kiwi.
HELP: High-quality products and food dyes, which cause excrement with a greenish tint, do not change its consistency. There is no putrefactive or other fetid or unpleasant odor during bowel movements
. The stool is moderately hard, thick, and formed.
Vitamins, dietary supplements and medicines
Manufacturers of medicines and supplements indicate in the instructions information about possible changes in the color of fecal matter when taking the drug. The list of drugs that cause greenish and green-black feces includes:
- drugs to combat iron deficiency anemia;
- vitamin complex products containing iron;
- medications to relieve constipation;
- iodine-containing drugs;
- biologically active food supplements containing iron, chlorophyll concentrate and iodine;
- seaweed food supplements;
- medications for the treatment of hyperacid gastritis, gastric and duodenal ulcers (Vicair, De-nol);
- antibiotics.
Diseases that cause green stool
If an adult does not eat food or dyes, and the stool turns greenish, this means that pathological processes are occurring in the body.
As a rule, other symptoms also manifest themselves with diseases. This means that the sick person requires treatment. The list of pathologies includes:
- Intestinal infectious diseases.
- Dysbacteriosis.
- Poisoning (including the toxic effects of alcohol).
- Recovery period after poisoning.
- Lactose or fructose intolerance.
- Stomach ulcer.
- Colitis.
- Intestinal neoplasms (benign and malignant).
- Enteritis.
- Celiac disease.
- Inflammatory process in the intestines.
- Diseases of the thyroid and pancreas, gall bladder.
- Hepatitis.
- Diabetes.
- Individual reaction to the product.
For different diseases, stool has a different consistency, smell, color, and inclusions. The frequency of bowel movements will vary. The development of the disease is indicated by the increasing severity of the condition and the worsening of symptoms, and the rapidity of development of the disease. By the coloring of the discharge, one can first suspect the presence of a particular disease.
Green stool with liquid consistency
Liquid, green-colored feces occur with intestinal infections - salmonellosis and dysentery. These infectious diseases are accompanied by a number of painful symptoms
. They begin quickly, from two to three hours to three days after bacteria enter the stomach, and lead to loss of water by the patient’s body.
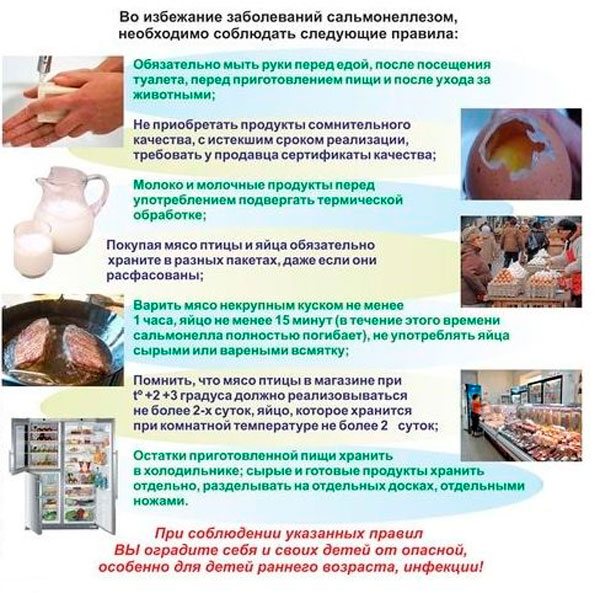
Salmonellosis is often severe. Typical signs of the disease:
- diarrhea up to ten times a day;
- abdominal pain (in the navel area);
- high temperature (up to 38-40 degrees);
- nausea and vomiting.
Feces with salmonellosis are liquid, foamy and watery, green lumps with mucus are visible in the discharge. Fecal matter resembles swamp mud
.
The smell of feces is pungent and unpleasant. On the 3rd day, diarrhea with blood in the form of streaks begins, causing the pain to intensify
. In some forms of the disease, in severe condition, a rash may appear, a decrease in blood pressure, and tachycardia, from which the patient’s condition sharply worsens.
Dysentery occurs with similar symptoms. Stools with this disease are frequent, but not very abundant.
.
The stool is yellow-brown mixed with green, or dark green. The fecal matter contains streaks of red blood, a lot of mucus, and possible pus
. With this disease, frequent ineffective urges, vomiting, and headaches are observed.

Liquid greenish stool is formed due to dysbacteriosis and enteritis. Similar feces are formed in some blood diseases.
Green thick stool and constipation
In some adults, stool changes color due to constipation. During this period, fecal discharge is difficult to pass; it resembles pellets and balls of green or gray color with greenery.
If the poop of infants turns green when changing their diet or introducing inappropriate complementary foods (due to the imperfection of the child’s digestive system), then in adults it is not easy to identify the cause of such changes. The patient needs to visit a local physician and gastroenterologist.
Before treating constipation, you need to undergo tests prescribed by your doctor. The cause of the malaise may be dysbacteriosis, taking medications that destroy bacterial flora, or constantly eating food colored with green pigments. A medical examination should not be postponed if constipation is accompanied by bloating, pain, or blood is visible in the feces.
Light green fecal matter
Light green excrement, brown feces “with greenery”, appears when taking certain antibacterial medications. It is not dangerous, but you should consult your doctor. The consistency of fecal discharge is thick and shaped. Due to the fact that the microflora dies, the excrement is almost odorless.

An alarming sign in this case is vomiting. If the patient has a fever or stomach pain, you should visit a doctor immediately.
Black and green chair
Dark, fairly well-formed stool occurs after taking activated carbon. But often black, black-green, dark green feces appear when there is bleeding in the walls of the intestines or stomach. The blood has time to clot by the time of defecation, as evidenced by the dark, almost black color of the feces.
The cause of bleeding is a burst vessel or neoplasm, which requires an immediate trip to the doctor, or even calling an ambulance. Intestinal bleeding is treated in the hospital.
Yellow-green stool
With pancreatitis, the stool is yellow-green or gray, it can be whitish or light yellow. Feces are liquid, they emit a pungent, fetid, nauseating odor
. After defecation, feces are poorly washed off, the surface of the discharge is smooth and shiny.
There is a lot of plant fiber in the feces, and fatty inclusions are observed. Fats in them appear due to a lack of lipase (digestive enzyme), which breaks down these compounds
. The amount of fat in feces increases if the patient eats a lot of fat-containing foods.
Rate this article:
- Poisoning:(
Girls, what to do if you are poisoned? I'm at week 11. I don’t think toxicosis has just woken up.
Yesterday it was bad all day. Whatever I don’t eat, I return (sorry for the details), even activated charcoal.
The cause of the poisoning ... - Poisoning
Last night (August 16-17) I had a terrible poisoning from glazed cheese (“Dairy Country”) from Hypo. Well, why the hell are they selling products to people, that’s some kind of horror.
Apparently already at the factory some rat had rolled around in the cottage cheese shop...
. - Poisoning
I thought I was giving birth at 37 weeks, girls. I sleep at night at 4 and I wake up and I feel terribly bad, the baby is shaking, I can’t sleep at all because of the heat. I went to the toilet, and my stomach tightened....
- Poisoning