The appearance of a rash due to dysbacteriosis in adults can be explained by a fairly simple fact - this type of disease has a close relationship with an allergic reaction. The occurrence of a large number of allergic diseases will occur due to changes in the microflora of the digestive system.
Dysbacteriosis, which is caused by an allergen entering the intestinal cavity, will have symptoms such as hives, spots, rashes on various areas of the skin, for example, on the hands.
Causes of rashes due to dysbacteriosis
A rash on the face, hands, spots and other skin manifestations of dysbiosis may appear due to various factors:
- The patient is constantly taking antibiotics.
- Previous infection in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Occurs together with dysbiosis of pancreatitis, gastritis, ulcers and gallbladder diseases.
- Poor nutrition, too much consumption of flour, spicy, fatty foods. The rash can also be caused by a lack of fermented milk products and plant products in the diet.
- Problems with the immune system.
Pathogenesis of rash due to dysbacteriosis
How can a rash appear on the face due to dysbacteriosis? The intestinal cavity contains beneficial microorganisms in constant quantities, which ensure the normal condition of the intestinal mucosa, which affects the digestion of food and the extraction of useful substances from it. When dysbiosis occurs, pathogenic bacteria begin to synthesize toxins that enter the bloodstream and have an adverse effect on human organs. Thus, with severe intoxication of the body by secretions of pathogenic bacteria, the condition of the skin is disturbed, that is, rashes appear, because it bears the greatest burden on removing metabolic products.
With dysbacteriosis, increased activity of the sweat and sebaceous glands first begins. The skin begins to dull, becomes oily, an invisible rash appears, and the smell of sweat becomes sharp and unpleasant. When the glands can no longer fight pathogenic bacteria, all skin pores begin to be involved in the process, especially in the most delicate places: folds, perineum, limbs. Thus, with dysbacteriosis, a rash appears on the face and hands. These areas are the thinnest and most sensitive, and cannot quickly get rid of a large amount of toxins, and thus the inflammatory process begins, manifested in the form of a rash. Infection begins quite quickly, and hives and spots appear.
Skin rashes due to dysbacteriosis
An allergic reaction to dysbacteriosis, manifested by a rash on the skin, is predominantly acute, that is, after a few hours, urticaria may appear. In addition, along with them, mild symptoms of an allergic reaction begin to appear - itching, Quincke's edema, bronchospasms, and low blood pressure.
Also, symptoms of the onset of the development of the inflammatory process due to dysbacteriosis are the appearance of pimples, mostly painful and having a red tint. In addition, the appearance of a rash on the face due to dysbacteriosis will be accompanied by peeling of the skin, that is, signs of vitamin deficiency.
Can dysbiosis cause allergies?
Internal healthy microflora normally protects the body from harmful microorganisms.
A disturbance in the number of beneficial bifidobacteria and lactobacilli leads to negative changes in the intestinal microflora. May cause allergies. Dysbacteriosis and allergies can occur in parallel, or they can be interconnected. Intestinal dysbiosis manifests itself in many symptoms. Sometimes a person treats manifestations without suspecting that the root cause is located on a different plane. The connection is successfully corrected with well-chosen therapy.
Within the individual, all organs and systems are in stability - a state of homeostasis. An imbalance in the ratio of pathogenic bacteria to beneficial bacteria leads to dysbacteriosis. A skin reaction may occur. There are symptoms visible on the body.
Disorders in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract are explained by the presence of toxins that are released when there is a large accumulation of harmful microorganisms. Corrected by taking antibacterial agents. The intestinal immune system suffers. To protect the intestinal mucosa, additional medications are taken.
In case of allergic dysbacteriosis, treatment is adjusted. Toxic agents enter the blood and spread throughout the body. This activates humoral immune cells. The immune system begins to release counteragents that affect the toxin.
There are a large number of agents. They remain in the blood. The available antibodies are nonspecific. A foreign substance in the bloodstream is perceived as an agent. Signs of allergies appear. It is difficult to treat a manifestation caused by impaired intestinal microflora.
Manifestations of allergies for this reason are different. The first signs are found on the skin: a rash appears, redness, and dermatitis develops. In rare moments, burning and itching sensations may occur. In some cases, dysbiosis manifests itself only in allergic reactions. In this case, there is no disruption in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
To determine the exact cause, the doctor's experience plays an important role. Eliminating symptoms does not eliminate what caused the disease. It continues to progress.
Diagnosis of allergies due to dysbacteriosis
To clarify the causes of the reaction in both adults and children, blood and stool tests are prescribed. A general blood test will provide information about the presence of an allergic reaction in the body. A stool examination will show the composition of the intestinal microflora.
To differentiate the diagnosis and indicate the cause of the disorder, the doctor prescribes a one-time dose of an antihistamine, the onset of action of which is short in time. If the result is positive, indicating a connection between allergies and dysbiosis, complex therapy is recommended.
Diagnostic methods at the current stage of development of medicine can determine the likelihood of bacteria releasing allergenic substances into the blood.
Serological testing or genetic PCR test refers to the above mentioned:
- The genetic method is highly accurate. Shows the likelihood of microorganisms acting under unfavorable environmental conditions. Determines a way to protect cells from the effects of medications. Conducted in a minimum time interval. It has an advantage over bacteriological research.
- Identification of general and specific diseases. The number of pathogens present in the blood serum is calculated. The colorimetric and radiometric form of the immunological indicator is used. Used when a specific allergen is suspected. The only downside is the length of time. The analysis is prepared within 7 days. It is necessary to donate venous blood.
Consequences
The disease rarely goes away without complications and consequences. The prolonged presence and movement of antibodies through the bloodstream causes persistent allergic reactions that are difficult to correct.
Allergies caused by dysbacteriosis in children are especially dangerous. The presence of antibodies affects the growth rate, immune development and digestive system of the baby.
The number of microbes increases. Skin rashes can be caused by certain foods. The child is diagnosed with allergy status.
In the absence of an imbalance in microorganisms, the foods consumed would not cause a reaction.
If the cause of an allergy is due to an unequal balance of bacteria in the gastrointestinal tract, the immune system is subject to high stress. Despite the complexity of treatment, it is necessary to restore balance. Normal and healthy microflora protects the intestines.
Medicine has developed effective ways to combat allergic reactions. Medications can relieve symptoms. For a while the person becomes comfortable.
A provocative therapy method involves the deliberate introduction of an allergen with low activity. When it enters the body, the production of antibodies begins. Stable complexes arise.
After the formation of connections with accelerated kidney function, the substances are excreted in the urine. The synthesis of the resulting formations continues, but not so actively.
Using this method will allow you to cope with allergies in a few steps.
In adults, the immune system is formed. It can prevent the formation of allergies due to pathogenic microbes. The presence of dysbacteriosis in an adult provokes increased immune function. Aimed at combating agents, the body’s overall defense weakens. The incidence of the disease is progressive.
There is an inverse relationship. Allergies cause dysbiosis. The cause is a violation of the intestinal barrier. The amount of undigested allergy pathogens in the bloodstream increases.
Symptoms become:
- Swelling in the nasal cavity.
- Redness of the eyes and eyelids. Feeling of a foreign body in the conjunctival zone.
- Having difficulty breathing. Bronchial spasms are noted. Breathing becomes wheezing. The occurrence of shortness of breath.
- The patient notes pain in the ears and decreased hearing.
- Rashes, hives and eczema appear on the skin.
- Headaches rarely occur.
- Digestion is disrupted. In some cases, there is an increase in body temperature.
Treatment
Medication therapy is carried out in limited quantities. Drugs may block the action of agents. There is no reaction at the cellular level. Allergy symptoms may be reduced, but dysbiosis is not cured. Long-term use of the products is not recommended.
Increasing doses of histamine develop resistance. The susceptibility to allergies is reduced. To prevent allergies from becoming chronic, the doctor selects a treatment method that has a prolonged effect.
This is especially true if allergies occur during pregnancy. The selection of a medicinal product takes into account the risk of exposure to the fetus. Allergies due to dysbacteriosis are not a rare phenomenon, which makes it possible to suspect the disease if there is no effect from the therapy.
The use of beneficial bacteria helps restore microflora.
The information on our website is provided by qualified doctors and is for informational purposes only. Don't self-medicate! Be sure to consult a specialist!
Rumyantsev V. G. Experience 34 years.
Gastroenterologist, professor, doctor of medical sciences. Prescribes diagnostics and carries out treatment. Expert of the group for the study of inflammatory diseases. Author of more than 300 scientific papers.
to the doctor We recommend: What is the peculiarity of the diet for enterocolitis in children and adults?
Source: //gastrot.ru/kishechnik/disbakterioz-i-allergiya
Formation of infant microflora and possible risks
In the womb, the fetus has no contact with any bacteria, which the mother’s body takes care of; all nutrients enter through the bloodstream. When a baby is born, he comes from an absolutely sterile environment into a world full of various microbes, which almost immediately begin to populate his body.
The baby's intestines are partially filled with microbes during childbirth. But these microbes are not enough. It is believed that when applied to the mother’s belly, her skin partially gives up its microflora, thereby protecting the newborn from the initial colonization of “foreign” microbes.
Feeding newborns in the first days is especially important. After the first meal, the intestines become the habitat of a huge number of microorganisms. In general, the formation of intestinal microflora takes several months after birth.
At the same time, children experience transient dysbacteriosis, which does not require treatment. Due to negative factors, the balance between beneficial and pathogenic organisms may be disrupted, which is caused by several factors:
- Lack of breastfeeding or no milk at all, which means you have to switch to formula too early. Unlike breast milk, they are less conducive to the normal formation of microflora.
- Taking antimicrobial drugs, which kill beneficial bifidobacteria and lactobacilli. Even if antibiotics were prescribed to the mother, the baby also has a risk of developing dysbiosis.
- Introducing complementary foods ahead of time. Up to six months, infants are not able to digest solid food, so the inclusion of “adult” foods in the diet can significantly disrupt digestion.
- Intestinal infections that inflame the mucous membrane, this entails the growth of pathogenic bacteria.
- Food allergies. Allergens lead to damage to the cells of the gastrointestinal tract, thereby disrupting the functioning.
- Poor nutrition, unsanitary conditions and other factors that weaken the immune system.
Types and causes of rashes in children
One of the most common is a colorless rash. It signals an allergic reaction to an irritant. Parents need to pay attention to the child’s diet and remove allergens from there.
An allergic rash can also appear due to:
- substances in the medications taken by the child;
- flower pollen;
- inhalation of dust;
- contact with synthetic fabric.
If a colorless rash appears only on the forehead of an infant, this indicates lactose deficiency. At the same time, the baby’s stool becomes green, and weight gain is poor. To solve the problem, the mother must exclude sweets from the diet. With proper breastfeeding, an enzyme will be produced that will heal the child.
There is a rash that looks like goosebumps. She may appear briefly and then disappear. The point is improper care of the baby. If the room is cold, the child may freeze, which leads to the appearance of a rash.
If the goosebumps do not go away for a long time, then their presence is the cause of one of the pathologies:
The red rash is a symptom of about 100 diseases. It may indicate meningococcal infection. The rash appears within 24 hours of infection. Rashes on the child’s skin may occur on the second day. The later the rash appears after the onset of pain, the milder the disease progresses.
Features of the rash:
- have a purple-blue color;
- different sizes;
- spread at high speed;
- are localized mainly in the hips, buttocks and lower abdomen.
Intoxication allergic rash looks similar to burns received from nettles. It is often localized on the baby’s chin and cheeks, but can also appear in other areas.
In appearance, the rashes look like scaly spots. Because of them, the child looks feverish.
If the allergic poisoning is severe or the allergen is consumed regularly, the rash may develop into a scab or weep. Skin rashes in an infant may appear due to the mother's poor diet.

Often a reaction is observed if the mother’s diet contains:
- red fish;
- citrus fruit;
- tomatoes;
- nuts;
- veal meat;
- whole milk.
If a child develops a red rash, these foods should be excluded during breastfeeding. Feeding formula may cause allergies due to the proteins it contains. If the rash gets worse, you need to change the brand of baby food. Allergies can occur if complementary feeding is incorrect or started too early.
A small rash that appears in infants may indicate neonatal cephalic pustulosis. This is a harmless and non-contagious disease. Appears in 20-30% of children. The cause of the rash is the growth of yeast bacteria on the body.
Some clinical symptoms
Symptoms of dysbiosis may differ depending on the cause that caused the condition. In general, the following manifestations occur:
- Problems with the baby's stool, it becomes: liquid, irregular, “wrong” color, and there is also a strong odor or mucus.
- Flatulence and pain associated with it.
- Regurgitation more than usual.
- Deterioration of appetite, manifested by refusal of breastfeeding or formula.
- Slight weight gain.
- Skin rashes. Due to the lack of beneficial bacteria, in addition to the rash, the skin becomes dry and flaky. There is usually no itching.
- Restless behavior, poor sleep.
- Heat.
There are several stages of dysbiosis:
- The first is characterized by: loss of appetite, poor weight gain, change in stool, mild flatulence.
- During the second stage, the following are observed: restlessness due to abdominal pain caused by gases, the presence of mucus in the stool, constipation and diarrhea.
- The third is manifested by the following symptoms: weakness, weight loss or loss, slight increase in temperature, nausea, anemia.
- A severe degree of the disease is also possible, and the following are observed: a strong increase in temperature, very frequent bowel movements, more than ten times a day, weight loss.
Symptoms often develop progressively, so it is important to start therapy as soon as possible.
Associated symptoms
Rashes due to dysbacteriosis in a child are accompanied by additional symptoms. They may appear before the rash. These signs include:
- flatulence;
- frequent and severe abdominal pain;
- unpleasant odor in the mouth;
- excessive salivation;
- anxiety and tearfulness;
- dry skin;
- allergic dermatitis;
- thrush;
- prolonged diarrhea;
- vomiting reflex;
- lack of appetite;
- poor weight gain.

The baby's fecal matter contains foreign impurities in the form of mucus and blood. Foamy inclusions are also possible. The urge to defecate can occur up to 12 times a day.
It is worth noting that in infancy, children have yellowish stools. The consistency of feces resembles sour cream. After feeding, the baby spits up. Then bloating and excessive gas formation appear.
The baby's skin begins to fade. An oily sheen appears. There is a high risk of stomatitis on the mucous membranes. Diarrhea lasts at least 2-4 days. The baby sleeps poorly and often cries and refuses to feed. The skin around the anal sphincter begins to turn red.
From this video you can find out why allergies can occur with dysbacteriosis and how to treat it:
Treatment
In the treatment of dysbiosis, breastfeeding is especially important in the first year of a child’s life, especially when it comes to problems with microflora. If this is not possible, preference should be given to adapted mixtures rich in protective factors, for example: fermented milk, containing live bacteria, with prebiotics, etc.
It is not recommended to select mixtures yourself. You must first consult with your pediatrician.
The basis of treatment is drugs that eliminate an excess of pathogenic flora. They are prescribed only after receiving test results, otherwise it is unlikely that it will be possible to select an effective drug.
Next, taking pre- and probiotics is important. They will populate the intestines with healthy flora and create all the necessary conditions for its growth. In addition, you need to take a vitamin complex.
The body of a small child who has just been born is highly susceptible to negative factors. Sometimes children develop dysbacteriosis, one of the symptoms of which is a skin rash.
There are several reasons for this phenomenon; it is necessary to identify it and begin treatment as soon as possible. As soon as the baby's microflora is restored, all symptoms, including rashes, should go away.
In the modern world, symptoms of dysbiosis can appear in anyone - women, men, adults and children. The reason for this phenomenon is the frantic pace of life, in which it is difficult to adhere to a healthy lifestyle and proper diet. Let's not forget that the current environment and quality of products leaves much to be desired.
begin , sharp pain in the abdomen, problematic digestion - this is dysbacteriosis . Symptoms and causes in adult women have a number of features.
Is intestinal dysbiosis the cause of allergic diseases?
pageDisbacteriosis
Allergies due to dysbiosis in adults occur due to changes in the intestinal microflora. Through disruption of the tissue barrier in the intestines, allergens enter the bloodstream. The reaction is characterized by general and local inflammatory foci.
Features of manifestations of dysbacteriosis
Toxic elements released by bacteria seep into the circulatory system. Cellular and humoral immunity is activated. Antibodies released by the immune system eliminate toxic elements. But in large quantities they continue to circulate in the blood.
IgE immunoglobulins are the main type of antibodies that act as protection against toxic elements. They react to any foreign body that appears in the blood and cause skin rashes. In such a situation, it is difficult to identify the factor that provoked the syndrome of bacterial overgrowth in the intestines.
When turning to an allergist for help, the patient receives treatment aimed at eliminating the symptoms, but does not eliminate the cause of the disease.
Clinical picture:
- skin redness;
- dermatitis;
- rashes.
Tingling and itching are rare symptoms of an allergic reaction. If the microflora in the intestines is disrupted, disorders of the gastrointestinal tract may not appear. For such purposes, accurate diagnostics will be required.
Symptoms of allergies due to dysbacteriosis are:
- Swelling of the nasal mucosa.
- The patient feels pain in the eye area.
- The whites of the eyes become red.
- Whistling breathing occurs, the patient has difficulty taking a breath, and an asthmatic spasm appears.
- Loss of hearing, pain in the ear canals.
- A rash, irritation, and small red spots appear on the skin.
- Rarely has a headache.
In adult patients, anaphylaxis may occur.
Allergy due to dysbacteriosis in a small child is closely related to a violation of the intestinal microflora. Dermatitis and rashes in a child have something in common with dysbacteriosis. Rash in newborns occurs as a result of an immune barrier to allergens.
The development of a baby’s immunity takes up to 7 years. The weakening of protective functions is manifested in a strong response to the pathogen. The result is destruction of tissues and body systems.
The mucous membrane of the digestive organs takes the brunt of the attack. Negative changes occur in the absorption of food and local mucosal immunity, toxins seep into the child’s blood.
The result is a persistent reaction of the body that turns into an allergy.
Conclusion - intestinal dysbiosis can be a cause of allergic diseases. Often, for the purpose of therapy to eliminate reactions, the doctor prescribes drugs that normalize the intestinal microflora.
Diagnosis of allergic dysbiosis
Diagnosis is carried out in the following stages:
If it is not possible to determine the reaction factor, a general stool analysis will be required. It will help indicate the number of beneficial bacteria in the stomach.
- A general blood test will determine the presence of a toxin in the bloodstream that causes rash and swelling.
- A one-time use of drugs that block histamine receptors will help determine the presence of allergenic factors after a few hours. If the relationship between the two diseases is confirmed, complex treatment is prescribed.
- A genetic test (PCR) will help identify bacterial activity and highlight allergenic toxicity. Fast and accurate method.
- The scratch test is determined by introducing the allergen into the thickness of the skin of the forearm or back using an intradermal injection. The result in the presence of allergies is local redness of the skin or the appearance of hives after 30 minutes. Economical, simple, optimal way to perform diagnostics. Has complications: hypersensitivity to the injected substance, develops 6 hours after administration, duration of exposure to the element is 24 hours; the emergence of a new type of allergic reaction as a consequence.
- Determination of the total and specific IgE levels contained in the patient’s serum. It is carried out thanks to colorimetric and radiometric analysis.
Diagnostic methods are determined by the doctor based on the etiology of the disease.
Loading …
Therapy methods
Allergies due to severe dysbiosis require the following medications:
- Solution for injections "Adrenaline".
- Antihistamines.
- "Sodium cromoglycate."
The substances reduce the manifestation of allergy symptoms and disruption of digestive functions due to pathologies of microflora in the intestines in adult patients. But you should not use it for a long period. In case of anaphylaxis, use as an “ambulance”.
Rashes due to microflora disorders are treated with “Histamine”, increasing the dose.
Medicines are selected taking into account individual sensitivity to the components. A test for inhibition of normal leukocyte emigration with drugs for dysbacteriosis will help determine this.
To avoid chronic pathologies, the following measures will be required:
- Follow the diet prescribed by a nutritionist.
- Take probiotics or prebiotics (Linex, Hilak Forte, Baktisubtil).
Take medications under the supervision of a doctor.
Therapy for dysbiosis and allergies in infants is determined by a specialist. You can avoid a negative reaction by adhering to the following points:
- Determine the appropriate diet for the mother if she is breastfeeding.
- Eliminate potential external allergens.
- Temporarily stop bathing your baby in herbal baths.
- Apply external effects on the skin using Bepanten cream, and eliminate internal infections with Smecta powder. Give plenty of fluids throughout the day.
- Beneficial bacteria for the baby's intestines come from breast milk. They fight pathogenic microorganisms, providing lasting immunity. When artificial feeding, give preference to adapted formulas.
- Mom shouldn't worry about anything. Stress is passed on to the child. If the baby’s behavior is normal, you should not run to the doctor the first time the baby cries.
- Maintain room temperature at +18-19°C. At this temperature, the skin is able to breathe, the child sweats less.
- Provide natural humidity in the room using damp towels or a humidifier.
According to mothers, good products for bathing children are “Oilatum” and “A-derma”.
For preventive purposes, mother and child can take the drug “Likopid”. Use probiotics during lactation.
Possible complications
With a systematic allergic response, an adult patient develops anaphylaxis, which provokes complications:
- decreased blood pressure;
- swelling;
- severe skin rashes;
- bronchospasm;
- to whom.
Sometimes the disease can lead to death.
Dysbacteriosis is dangerous if the child is allergic. Excessive synthesis of toxins leads to a constant response from the body. Children may experience digestive system disorders related to intestinal flora. The baby may develop:
- diseases of the rectum;
- allergy status to certain foods, other antigenic forms.
Untimely treatment of the disease leads to a decrease in the functioning of the baby’s immune system.
Accurate and timely diagnosis of allergies due to dysbiosis helps determine the optimal therapeutic treatment and eliminate the cause of the pathology. A diet on the recommendation of a nutritionist, a comfortable temperature in the house for the baby will help prevent the onset of the disease.
Smecta prevents the absorption of toxins, and Bepanten prevents minor skin rashes. When treating dysbiosis, experts recommend taking medications aimed at eliminating the cause of the disease - prebiotics and probiotics.
The article has been approved by the editors Link to main publication
articles:
(2 5,00 of 5) Loading...
Source: //toxikos.ru/disbakterioz/i-allergiya
Dysbacteriosis, symptoms from the reproductive organs
In the vast majority of cases, the appearance of dysbiosis in adult women is due to the development of vaginal dysbiosis.
In order not to trigger the disease, pay attention to these symptoms in time:
- copious vaginal discharge;
- change in color and consistency of discharge;
- sharp, unpleasant odor of discharge;
- insufficient lubrication during sexual intercourse;
- noticeable dryness of the genitals.
There are two types of vaginal dysbiosis. We present their comparative characteristics in the table.
| View | Pathogens | Symptoms of dysbiosis in adult women | Treatment |
| Bacterial vaginosis | Bacteria and germs | burning; | Drugs that kill bacteria, topical antibiotics |
| itching; | |||
| the discharge has a grayish tint; | |||
| the discharge has a putrid fishy odor | |||
| Vaginal candidiasis | Fungi of the genus Candida | itching, burning sensation; | Antifungal agents, extended spectrum antibiotics |
| the smell of the discharge is extremely unpleasant; | |||
| the discharge looks like curd mass, sour cream; | |||
| discharge is excessively strong; | |||
| painful itching. |
Doctors recommend treating these diseases for both partners!
A man can be a hidden carrier of the disease, and a woman will be re-infected from him.
Also, the disease can go from a silent form to an acute one. Then the partner will experience a number of unpleasant symptoms: itching of the intimate organs, painful urination, white discharge from the penis.
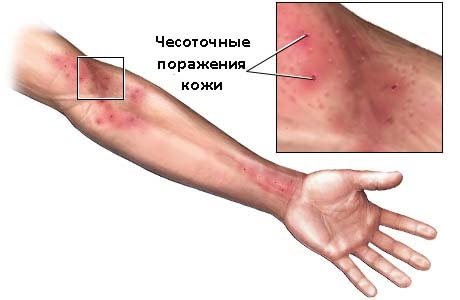
For scabies
Scabies is a contagious parasitic disease. The causative agent is the scabies mite. One of the main properties of the disease is itching, which becomes more intense at night. Paired nodular-bubble formation is formed in areas where mites are located. Primary rashes look like small erythematous papules. Over time, they can acquire a vesicular or lemphigoid appearance.
For children under 3 years of age, the drug can be used under the watchful supervision of a doctor:
- Day 1: the medicine is rubbed all over the child’s skin below the navel level;
- Day 2: rub the product into the skin above the navel;
- further application alternates.
Allergic reactions
Not long ago, scientists discovered that dysbiosis is one of the causes of allergies. This is not surprising, because with dysbacteriosis, the body’s protective functions are weakened.
It becomes vulnerable to bacteria and microbes. Cells become more sensitive, and this provokes allergic reactions.
For example, these:
- runny nose;
- cough;
- swelling of the nasopharynx;
- redness and tearing of the eyes;
- headache;
- skin rash.
According to another version, allergies appear due to impaired permeability of the intestinal walls. Because of this, allergens can easily penetrate into the body.
Interesting fact! Some people mistakenly believe that they are allergic to the smoke from burning tobacco.
After all, it causes them to develop coughing, lacrimation, wheezing, and difficulty breathing. However, this opinion is wrong. Allergens cannot survive in a smoking cigarette. Allergies are caused by contact with tobacco , for example, when an allergic person picks up a cigarette or an object where it recently lay.
Once in the blood, antigens cause an aggressive immune reaction, which underlies the development of various allergic diseases.
The most common allergic diseases that can be caused by dysbacteriosis are:
Allergic rash: treatment features
A good medicine is Gistan in capsules. The basis is made up of extracts of medicinal herbs and a complex of vitamins. The drug regulates immune and metabolic processes, and under its action allergy symptoms are relieved.
The medicine cleanses the body of harmful substances. The drug is approved for children from 14 years of age. During the day, take 1 capsule orally with meals. The maximum course of treatment is 20 days.
Available in 3 forms:
Depending on age, the dosage differs:
- 1-12 months: 1/4 tablet (6.5 mg) 2-3 times a day. Grind the product into powder and mix with baby food.
- 1-6 years: 1/4 tablet 3 times a day or half a tablet 2 times.
- 6-14 years: half a tablet 2-3 times a day.
The drug has analogues:
Among folk remedies, mumiyo solution is considered effective. The substance is dissolved in a ratio of 1 g per 100 mg of boiled water. The resulting solution should be lubricated on areas of skin with rashes.
Mumiyo solution is also taken internally, but in a lower concentration. 2 tsp is enough. mix the above solution with 100 mg of pure water. It is allowed to take the medicine orally no more than once a day in the morning. Duration of treatment – 20 days. If the rash occurs in a child under 5 years of age, the concentration of mumiyo should be reduced by 2 times (1 tsp of a 1/100 solution with 100 mg of pure water).
Symptoms of drug-induced dysbiosis in adult women
Corresponding symptoms in women may appear due to the treatment of any diseases with medications, especially broad-spectrum antibiotics.
These medications are too aggressive. Once in the body, they destroy the beneficial intestinal microflora along with pathogenic microorganisms.
The causes of drug-induced dysbiosis may be the inappropriate use of antibiotics, poor quality of drugs, incorrect dosage, or incorrect regimen.
Symptoms of this type of dysbiosis are as follows:
- constipation or, conversely, diarrhea;
- flatulence;
- rumbling in the stomach;
- belching;
- itching of the anus;
- Sometimes the genitals may be affected. Then there is discharge, itching of the genitals, painful urination;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- sharp pain in the intestines after eating.
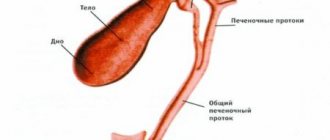
Intestinal dysbiosis
Up to 500 species of different microorganisms are found in the human intestine. Their total weight is more than 1 kg. The microbial community is considered a separate, vital organ of the human body (microbiome).
The normal functioning of the human body is due to bifidobacteria, lactobacilli, enterococci, Escherichia coli and bacteriodes, which account for 99% of the normal intestinal microflora. 1% are representatives of opportunistic flora: clostridia, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, staphylococci, Proteus, etc.
Bifidobacteria and lactobacilli, intestinal and acidophilus bacilli, enterococci are the basis of the human intestinal microflora. The composition of this group of bacteria is always constant, numerous and performing basic functions.
Rice. 2. The total area of the intestine (its internal surface) is approximately 200 m2. It contains up to 500 species of various microorganisms.
The intestinal microflora changes during treatment with antibiotics, immunosuppressants, and diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. The intestinal microbiome is affected by harmful environmental factors. During a person's life, the intestinal microflora undergoes qualitative and quantitative changes. It changes with age. Microflora depends on the nature of nutrition and lifestyle, climatic conditions of the region of residence, and the time of year.
Changes in the intestinal microflora do not go unnoticed for humans. Sometimes they are latent (asymptomatic). In other cases - with pronounced symptoms of an already developed disease, which are caused by the appearance of secretory diarrhea. As the permeability of the intestinal wall increases, toxins and allergens begin to enter the bloodstream, contributing to the development of food allergies. Superinfection often leads to the development of sepsis.
Rice. 3. Sectional view of the wall of the small intestine. Computer visualization.
Dysbacteriosis of the small intestine
- Dysbiosis of the small intestine develops with an excessive intake of microbes due to the lack of hydrochloric acid and a number of enzymes in the digestive juice of the stomach. Food is poorly digested. The processes of bacterial decay are started.
- Dysbiosis of the small intestine develops as a result of impaired function of the valve, which is located in the ileocecal angle. This valve prevents microbes from entering the small intestine.
- Dysbiosis of the small intestine develops with disturbances in absorption processes, immunodeficiency diseases and intestinal obstructions.
Enzymes produced by intestinal microflora take part in the process of breaking down bile acids. Secondary bile acids are reabsorbed, and a small amount (5 - 15%) is excreted in the feces. Secondary bile acids are involved in the formation and movement of feces, preventing their dehydration.
If there are too many bacteria in the intestines, then bile acids begin to break down prematurely, which leads to secretory diarrhea (diarrhea) and steatorrhea (excretion of increased amounts of fat). The absorption of fat-soluble vitamins is impaired, and cholelithiasis often develops.
With the participation of bifido-, lacto-, enterobacteria and E. coli, vitamins K, C, group B (B1, B2, B5, B6, B7, B9 and B12), folic and nicotinic acids are synthesized.
Toxins and waste products of pathogenic bacteria (phenols, amines) bind vitamin B12.
Intestinal microflora promotes normal trophism of the intestinal mucosa, thereby reducing the penetration of various food antigens, toxins, viruses and microbes into the blood.
The waste products of pathogenic bacteria and their toxins damage the epithelial lining of the small intestine. Microvilli are destroyed, their height decreases, and the crypts deepen.
Rice. 4. Histological preparation of the intestinal wall.
Dysbacteriosis and vitamin deficiency
Nowadays, people, trying to lead a healthy lifestyle, have learned to eat a balanced diet. They consume proteins, fats, carbohydrates in the correct ratio and quantity. Despite this, many suffer from vitamin deficiency.
The problem is that modern technologies process food so much that they do not give vitamins and microelements a chance to remain in it. Also, people who consume normal amounts of vitamins may suffer from vitamin deficiency. The cause is intestinal dysbiosis.
The absorption of nutrients, vitamins, and microelements directly depends on the intestines. Dysbiosis prevents the intestines from functioning normally. Therefore, vitamin deficiency and dysbacteriosis often go together .
No matter how expensive and high-quality preparations with vitamins a person consumes, the body has no chance to absorb them until the dysbiosis is cured.
Mono-diets can provoke dysbiosis
Symptoms appear more often in adult women, because they are the biggest fans of extreme weight loss methods.
Strict restriction in food provokes an imbalance in the intestines, as well as a lack of vitamins and beneficial microelements. To avoid this situation, you need to consume probiotics and fermented milk products on diet days.
Symptoms of vitamin deficiency against the background of dysbacteriosis can manifest themselves in the following:
- skin problems;
- hair loss;
- nausea, vomiting;
- lack of appetite;
- decreased immunity;
- sensitivity, tooth decay;
- rapid weight loss;
- decreased mental activity;
- diarrhea;
- pain in the limbs.
If you have these symptoms, you need to take care of your intestinal microflora.
- Introduce coarse fibers, cereals, bran bread, fruits, vegetables, and dairy products into the diet;
- Limit the consumption of sugar, white bread, baked goods, sweet drinks, and alcohol.
- Do not eat food that contains preservatives, dyes, or flavors.
- Take probiotics and vitamins regularly.
- Eat regularly.
- Eat only freshly prepared food.
Rashes in a child
The intestinal microflora in young children is still in the formative stage, so children are at risk for the development of dysbacteriosis. With this pathology, the number of beneficial lactobacilli and bifidobacteria in the intestines is reduced, against the background of which opportunistic and pathogenic pathogens are activated. With dysbacteriosis, a baby may develop rashes on the skin in the first days of life.
Causes
The risk of dysbacteriosis in children, which may be accompanied by skin rashes, increases with:
- Refusal to breastfeed.
- Early transition to artificial formulas.
- The mother is taking hormonal or antibacterial medications.
- Treating a child with antibiotics.
- Insufficient synthesis of digestive enzymes (may be normal or pathological).
- Physiological immaturity.
- Development of a variety of diseases.
- Injuries that occurred during birth.
- Infectious diseases in the mother, mastitis, etc.
Sometimes the cause of dysbiosis and rashes in infants is a combination of several factors.
A rash can appear for completely different reasons that have nothing to do with the composition of the intestinal microflora. An experienced doctor can make an accurate diagnosis.
Symptoms
The rash that appears against the background of dysbacteriosis has the appearance of allergic rashes. Doctors associate its appearance with an increase in sensitization of the body. Visually, the rash may look like:
- Areas of redness on the skin.
- Small red rash.
- Peeling.
- Red spots merging with each other.
- Weeping areas, etc.
Why is dysbiosis dangerous if left untreated?
Intestinal dysfunction can lead to a number of consequences and complications:
- chronic fatigue;
- joint pain;
- waking up at night due to a feeling of heat (cause of liver dysfunction);
- various skin diseases;
- decreased libido;
The manifestation of vaginosis and candidiasis is a complication of dysbiosis; these symptoms appear in adult women
- avitaminosis;
- gout;
- conjunctivitis;
- fungi on the nails;
- psychological problems (depression, anger, irritation);
- sepsis;
- peritonitis;
- inflammation of the large and small intestine;
- sudden weight loss;
- anemia;
- allergic manifestations.
Treatment options
Treatment of allergy symptoms consists of the use of medications of different groups:
- Antihistamines. Eliminate symptoms, prevent the development of severe complications, and promote rapid recovery. These drugs include: Tavegil, Claritin, Loratidine, Fenistil; Citrine. Use strictly as prescribed by a doctor.

- Enterosorbents. Removes toxins and waste from the body. Used when signs of an allergic reaction develop. The use of activated carbon and Enterol will be effective.

- Glucocorticosteroid ointments and moisturizing creams. Used to eliminate symptoms that appear on the skin. Eliminate rash, itching, peeling, and dryness faster. Products such as Lokoid, Aquaderm, Bepanten are effective.

Drug therapy is necessary for the development of moderate and severe stages. When the allergen cannot be identified for a long time, the patient is prescribed a strict diet and immunotherapy. Treatment of dysbiosis with drugs begins with the development of the second stage. The initial development of pathology does not require drug therapy; it is enough to balance the daily diet and adhere to a nutritional schedule. The following drugs are prescribed for treatment:
- probiotics;
- prebiotics;
- bacteria and live strains;
- bacteriophages;
- immunostimulants;
- enzymes;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- antibacterial drugs.

Restoration of intestinal microflora is long-term and requires complex treatment. It is important to pay attention to nutrition. During the period of drug therapy, it should be complete, vitamin, and dietary. Eating unhealthy foods can cause allergies.
Young children, especially infants, often experience dysbacteriosis and allergies. The reason lies in a weakened immune system and an underdeveloped digestive system. They are susceptible to infection with staphylococcus, salmonella, and E. coli, so it is important to monitor the quality of the products consumed.
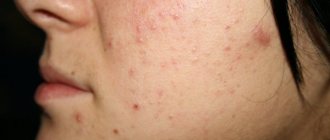
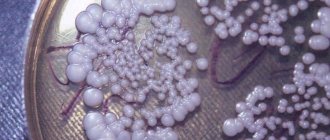
Dysbacteriosis in infants: photos, symptoms, infant feces with dysbacteriosis, skin rashes, rash
Dysbacteriosis appears in infants quite often, and many doctors do not consider it a diagnosis at all. Symptoms of dysbiosis in a baby only signal a decrease in beneficial microflora, which is easy to correct if you notice signs of intestinal disorder in time.
Symptoms of dysbiosis in infants
Dysbacteriosis in infants (photo 1) is characterized by a certain set of signs by which doctors accurately determine bacterial imbalance. Dysbiosis is a more correct name for a stomach disorder, but most people prefer to use the familiar term. Symptoms of dysbiosis in infants are as follows:
- the child feels heaviness in the stomach, children cry from pain and become restless;
- children suffer from flatulence, the accumulation of gases provokes pain;
- a typical sign of a microflora disorder is stool disorder;
- atypical stool mixed with undigested food;
- frequent regurgitation in large volumes;
- skin rashes, atopic dermatitis, diaper rash;
- brittle nails, hair loss on the scalp and increased fragility;
- dirty white coating on the surface of the tongue, different from milky coating after feeding;
- the appearance of bad breath;
- decreased appetite, whims before feeding.
Baby feces with dysbacteriosis
Feces in a baby with dysbacteriosis (photo 2) have characteristic signs. First of all, like stool in an adult, the consistency of stool changes.
If normally a child’s stool has a dense structure, then dysbiosis in infants provokes a change in the nature of the bowel movements - they have a liquid appearance, and undigested grains of food are noticeable in the stool itself.
This could be curdled milk or particles of complementary foods that are clearly visible on the diaper.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ODYoiqZ5iv0
The color of stool also changes when an infant has dysbiosis - depending on the severity of the disorder and the food taken, the color of stool can be dirty green or yellowish.
The color of stool in adults is approximately the same, but darker due to the presence of food of a different nature. At the same time, stool with dysbacteriosis in infants has a liquid consistency and includes light mucous strands, and the stool itself may bubble.
This is clearly noticeable if the child has recently used the potty or diaper.
Externally, stool may be similar in color to stool during pancreatitis, when the disease becomes acute. It is also worth noting that the stool of a newborn acquires a characteristic pungent odor with sourness.
If dysbacteriosis is suspected, the feces of a newborn are collected and sent to the laboratory for testing.
Skin rashes due to dysbacteriosis
Dysbacteriosis in children and adults has a close connection with skin rashes. Rashes in infants with exacerbation of dysbacteriosis will give a clear reaction on the skin. Therefore, rashes in adults and children can be treated symptomatically, focusing on intestinal problems.
Skin rashes due to dysbacteriosis (photo 3) appear when the body is intoxicated with toxins that are formed during the process of fermentation and putrefaction of intestinal contents. Toxic substances from the intestines, which are richly supplied with blood vessels, enter the blood and are distributed throughout the body.
Dysbacteriosis in a child and an adult provokes a protective reaction of the body, the work of the sebaceous and sweat glands is activated, which try to remove toxins from the blood. In this case, a rash appears on the skin; with dysbacteriosis in children and adults, it has typical signs of irritation and an allergic reaction.
Dysbacteriosis typically manifests itself on the face - the skin becomes duller, and the sebaceous glands actively secrete fatty lubricant. A small rash appears in infants due to dysbacteriosis; in adults, when the glands are clogged with fatty contents, pustules appear. Dysbacteriosis is most noticeable in a newborn on the face, in the folds of the skin, and on the hands.
If you do not properly care for the skin of newborns and children, then children's dermatitis worsens, and the allergic process covers increasingly larger areas. Rashes in a child when the allergic component intensifies are accompanied by itching, burning, and swelling.
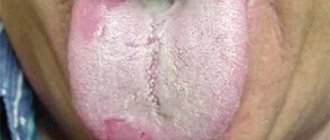
Dysbacteriosis of the oral cavity
Dysbacteriosis of the oral cavity (photo 4) manifests itself in various forms of dysbiosis. Dysbacteriosis in infants and adults is characterized by an increase in pathogenic microflora in the oral cavity compared to a healthy one. Dysbacteriosis on the tongue and oral cavity goes through several stages:
- Dysbiotic shift is a slightly increased amount of pathogenic microflora, externally the overall composition of the handicap does not suffer, so visual manifestations at this stage are practically not noticeable. Dysbacteriosis at the beginning of the pathological process looks like whitish patches in the corners of the mouth;
- In the subcompensated form, dysbiosis of the oral cavity provokes a whitish coating, and when the test is taken, a shift in 2-3 indicators of flora representatives is noted. Plaque can be noticed on the teeth, and the mouth becomes dry and the gums begin to bleed;
- In the monoculture form, lactobacilli are displaced. With intestinal dysbiosis, the tongue changes its color and acquires a dirty yellow tint, and an unpleasant sour odor appears from the mouth. Inflammation of the tonsils occurs, teeth and gums suffer;
- In the fourth, decompensated stage, yeast-like fungi settle in the oral cavity; they affect not only the tongue, but also coat the walls of the mouth and palate.
Intestinal dysbiosis should not be a concern - this condition can be easily corrected if you add beneficial microflora to the patient, which will quickly suppress pathogenic microorganisms and restore normal balance in the digestive organs.
Gallery of photos of dysbacteriosis
(: 4, average: 4.00 out of 5) VKontakte What disease has/has been bothering you lately:
- 20 – 17% of all
- 15 – 13% of all
- Candidiasis (thrush) 12%, 14 14 – 12% of all
- 10 – 9% of all
- Osteochondrosis 6%, 7 7 – 6% of all
- 6 – 5% of all
- 6 – 5% of all
- Diabetes mellitus 4%, 5 5 – 4% of all
- 5 – 4% of all
- 4 votes – 3% of all
- 4 votes – 3% of all
- 4 votes – 3% of all
- 4 votes – 3% of all
- 3 votes – 3% of all
- 2 votes – 2% of all
- 2 votes – 2% of all
- 2 votes – 2% of all
- 1 vote – 1% of all
- 1 vote – 1% of all
- Plantar fasciitis* 1%, 1 vote1 vote – 1% of all
- 1 vote – 1% of all
- 0 – 0% of all
Which specialist have you consulted recently?
- Gynecologist 27%, 19 19 – 27% of all
- 10 – 14% of all
- Dermatologist 11%, 8 8 – 11% of all
- 6 – 8% of all
- 6 – 8% of all
- Endocrinologist 7%, 5 5 – 7% of all
- 4 votes – 6% of all
- 4 votes – 6% of all
- 3 votes – 4% of all
- Otolaryngologist (ENT) 3%, 2 votes2 votes – 3% of all
- Ophthalmologist (ophthalmologist) 1%, 1 vote1 vote – 1% of all
- 1 vote – 1% of all
- Gastroenterologist 1%, 1 vote1 vote – 1% of all
- Physiotherapist 1%, 1 vote1 vote – 1% of all
- Radiologist 0%, 0 0 – 0% of all