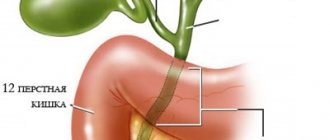
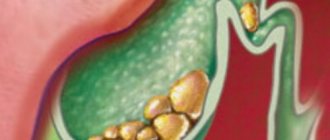
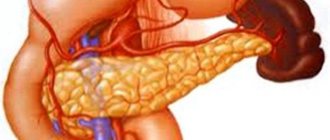
Suspension in the gallbladder: causes, diagnosis, treatment
Gallbladder diseases are extremely common among people who lead a sedentary lifestyle, resort to eating unhealthy foods, and drinking too much alcohol. When the body is clogged with cholesterol, a suspension is first deposited in the gallbladder. Subsequently, the formed substances crystallize, causing the formation of so-called sand and stones. Let's find out how to treat the gallbladder and what to do to avoid health problems.
Symptoms of the disease
- Sudden loss of appetite.
- The occurrence of painful sensations of varying intensity in the area of the right hypochondrium, paroxysmal or constant tingling, which intensifies after eating.
- Periodic nausea.
- Vomiting, in which thick bile is noticeable.
- Heartburn.
- Constipation, diarrhea and their alternation.
Types and composition of suspended matter
At the initial stage of development of the disease, a putty-like suspension is formed in the gallbladder, presented in the form of clots, the presence of which is noticeable only during an ultrasound examination. Later, a fine suspension is formed, which is characterized by movement in the gallbladder when the body position changes. The latter consists of undissolved proteins, cholesterol, calcium salts and their combinations.
According to the composition, a suspension is isolated in the gallbladder with a predominance of bilirubin, calcium or fats. Based on the mechanism of occurrence, secondary and primary impurities are distinguished. Some are deposited as a result of the development of cholelithiasis, inflammation of the pancreas. Others act as an independent phenomenon in which there are no other pathologies.
Reasons for the formation of suspended matter
Why is suspension deposited in the gallbladder?
Sudden weight loss and limited consumption of foods containing fatty acids have a negative impact on free outflow. Surgery on the organs of the gastrointestinal tract can cause malfunction of the gallbladder. In addition to this, there may be a need to take a lot of medications containing calcium.
One of the common causes of stagnation of substances in the gallbladder is sickle cell anemia of tissues. The disease is hereditary in nature and consists of modifications of hemoglobin proteins in the blood. As the disease develops, the functions of this component are disrupted, which leads to difficulty in transporting oxygen to healthy cells of the internal organs.
Among other things, sand in the gallbladder can form as a result of:
- bone marrow transplantation, organ transplantation;
- development of cholesterosis in persons suffering from hepatitis;
- liver cirrhosis;
- treatment of hydrocele of the gallbladder;
- long-term parenteral nutrition.
The risk group also includes diabetics, people with a genetic predisposition to obesity, and people who lead a sedentary lifestyle. As practice shows, most cases of the formation of an abundance of suspension in the gallbladder occur in elderly women aged 50-60 years who do not eat properly.
Diagnostics
Several diagnostic procedures can be used to detect sand in the gallbladder. First of all, the gastroenterologist interviews the patient, finds out the first symptoms, and determines the area of localization of unpleasant sensations. Then laboratory tests are carried out, the results of which make it possible to determine the level of cholesterol, bilirubin and protein in the blood.
As for the most common outpatient diagnostic methods, it is worth noting:
- Ultrasound examination makes it possible to detect the smallest flakes of substances stagnant in the gallbladder and determine their density.
- Magnetic resonance imaging can detect pathological changes in the tissues of the gallbladder and liver.
- Duodenal intubation is aimed at obtaining bile samples to determine its composition.
Diet for suspension in the gallbladder
The majority of dietary programs, when suspended matter is detected in the gallbladder, require a reduction in the amount of fatty foods consumed. The following products are gradually excluded from the diet: meat of large animals, mayonnaise, all kinds of sauces, cream, eggs. Minimize the preparation of cereal-based dishes.
At the same time, the diet for suspension in the gall bladder allows you to consume fresh fruits and vegetables, berry juices, coffee and tea, jelly, compotes, wheat and rye bread, butter and vegetable oil, fermented milk products (cottage cheese, hard cheese, sour cream).
Timely detection of a suspension in the gall bladder before the formation of so-called sand is a reason to exclude soups with fatty broths, lard, baked goods, canned food, smoked meats, ice cream, chocolate, and alcohol from the menu.
Suspension in the gallbladder: treatment
First of all, when a suspension is detected, drug therapy is prescribed. Here drugs containing ursodeoxycholic acid are used. This substance helps to liquefy bile and activate metabolic processes in the body.
During therapy, one cannot do without antispasmodics, which are intended to eliminate pain. If the presented treatment methods do not give the expected results, they resort to radical solutions, in particular surgery.
Traditional medicine methods
How to treat the gallbladder using traditional methods? Such therapy, in addition to the diet prescribed by a specialist, involves the use of herbal remedies. Tinctures based on wormwood, St. John's wort, rose hips, beets, and strawberry leaves allow you to remove stagnant bile from the body. To eliminate inflammatory processes, it is recommended to consume fresh cabbage and dill seeds.
Possible consequences of bile stagnation
In the absence of timely proper treatment, acute pancreatitis may develop against the background of stagnant processes in the gallbladder area. Often the consequence of a disorder in the body is cholecystitis, which leads to tissue inflammation.
To avoid the above manifestations, it is worth maintaining normal body weight. It is necessary to abandon the regular use of strict diets aimed at sudden weight loss. You should also prevent diseases such as cirrhosis and hepatitis, which often result in the formation of a suspension in the gallbladder.
It is recommended to be careful when choosing medications. Before taking medications, you should carefully study the side effects, consult a doctor and, if possible, reduce the use of chemicals in general.
Finally
To eliminate congestion in the gallbladder, it is necessary to resort to complex treatment. Here, the physical and age characteristics of the body, the speed of metabolic processes, and the degree of development of pathology must be taken into account. Usually, to stop the formation of suspension, dilute its concentration and stabilize the functioning of organs, several months of eating according to an established diet along with taking medications are sufficient.
Authorized Products
The diet for the presence of sand in the gallbladder includes:
- Vegetable/cereal soups based on vegetable broth (vegetarian cabbage soup and borscht, beetroot soup, milk soups).
- Dried wheat bread, dry biscuits, savory pastries with fish, boiled pasta.
- Beef, chicken fillet, lean young lamb, rabbit meat.
- Low-fat types of white river/sea fish, seafood.
- Dairy/fermented milk products (low-fat whole milk, mild low-fat cheese, curdled milk, kefir, fermented baked milk, low-fat cottage cheese and lazy dumplings, casseroles, puddings prepared on its basis).
- Chicken eggs soft-boiled/in the form of an omelet.
- Cereals, especially oatmeal and buckwheat.
- Raw, stewed and boiled vegetables, vegetable salads with vegetable oil, non-acidic sauerkraut, green pea puree, squash caviar, vinaigrette, garden herbs.
- Butter and vegetable oil, which are allowed to be added only to ready-made dishes.
- As snacks - doctor's sausage, low-fat ham, herring, stuffed fish, boiled fish/meat.
- For dessert - non-acidic fruits/berries, marshmallows, dried fruits, marmalade.
- Drinks include vegetable/fruit and berry juices, rosehip infusion, black/green tea, still mineral water, wheat bran infusion.
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
| eggplant | 1,2 | 0,1 | 4,5 | 24 |
| squash caviar | 1,2 | 7,0 | 7,4 | 97 |
| zucchini | 0,6 | 0,3 | 4,6 | 24 |
| cabbage | 1,8 | 0,1 | 4,7 | 27 |
| broccoli | 3,0 | 0,4 | 5,2 | 28 |
| carrot | 1,3 | 0,1 | 6,9 | 32 |
| cucumbers | 0,8 | 0,1 | 2,8 | 15 |
| salad pepper | 1,3 | 0,0 | 5,3 | 27 |
| parsley | 3,7 | 0,4 | 7,6 | 47 |
| iceberg lettuce | 0,9 | 0,1 | 1,8 | 14 |
| tomatoes | 0,6 | 0,2 | 4,2 | 20 |
| pumpkin | 1,3 | 0,3 | 7,7 | 28 |
| dill | 2,5 | 0,5 | 6,3 | 38 |
| bananas | 1,5 | 0,2 | 21,8 | 95 |
| apples | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 47 |
| nuts | 15,0 | 40,0 | 20,0 | 500 |
| raisin | 2,9 | 0,6 | 66,0 | 264 |
| dried apricots | 5,2 | 0,3 | 51,0 | 215 |
| almond | 18,6 | 57,7 | 16,2 | 645 |
| hazelnut | 16,1 | 66,9 | 9,9 | 704 |
| prunes | 2,3 | 0,7 | 57,5 | 231 |
| buckwheat | 4,5 | 2,3 | 25,0 | 132 |
| oatmeal | 3,2 | 4,1 | 14,2 | 102 |
| pearl barley porridge | 3,1 | 0,4 | 22,2 | 109 |
| rice | 6,7 | 0,7 | 78,9 | 344 |
| pasta | 10,4 | 1,1 | 69,7 | 337 |
| pancakes | 6,1 | 12,3 | 26,0 | 233 |
| bran bread | 7,5 | 1,3 | 45,2 | 227 |
| whole grain bread | 10,1 | 2,3 | 57,1 | 295 |
| marshmallows | 0,8 | 0,0 | 78,5 | 304 |
| fruit and berry marmalade | 0,4 | 0,0 | 76,6 | 293 |
| kefir 1.5% | 3,3 | 1,5 | 3,6 | 41 |
| Ryazhenka | 2,8 | 4,0 | 4,2 | 67 |
| cottage cheese 1% | 16,3 | 1,0 | 1,3 | 79 |
| beef | 18,9 | 19,4 | 0,0 | 187 |
| rabbit | 21,0 | 8,0 | 0,0 | 156 |
| boiled diet sausage | 12,1 | 13,5 | 0,0 | 170 |
| boiled milk sausage | 11,7 | 22,8 | 0,0 | 252 |
| milk sausages | 12,3 | 25,3 | 0,0 | 277 |
| boiled chicken breast | 29,8 | 1,8 | 0,5 | 137 |
| boiled chicken drumstick | 27,0 | 5,6 | 0,0 | 158 |
| boiled turkey fillet | 25,0 | 1,0 | — | 130 |
| omelette | 9,6 | 15,4 | 1,9 | 184 |
| soft-boiled chicken eggs | 12,8 | 11,6 | 0,8 | 159 |
| flounder | 16,5 | 1,8 | 0,0 | 83 |
| pollock | 15,9 | 0,9 | 0,0 | 72 |
| cod | 17,7 | 0,7 | — | 78 |
| hake | 16,6 | 2,2 | 0,0 | 86 |
| butter | 0,5 | 82,5 | 0,8 | 748 |
| olive oil | 0,0 | 99,8 | 0,0 | 898 |
| sunflower oil | 0,0 | 99,9 | 0,0 | 899 |
| mineral water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| green tea | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| carrot juice | 1,1 | 0,1 | 6,4 | 28 |
| pumpkin juice | 0,0 | 0,0 | 9,0 | 38 |
| rose hip juice | 0,1 | 0,0 | 17,6 | 70 |
| * data is per 100 g of product |
Suspension (thick mass) in the gallbladder: causes

More than 30% of the population suffers from cholelithiasis, which is characterized by a collection of stones in the gall bladder. The process of stone formation can be stopped in the early stages of the disease, but not all people promptly seek help from specialists and, as a result, bring the health of their body to the limit.
Gallstones cannot always be removed through medication, so most patients are referred for surgery to remove the gallbladder. To prevent this, we recommend starting the fight against stone formation at the first appearance of a bile suspension, a concentrated bile mass, which may include small grains of sand or stones.
A suspension in the gallbladder is a thick mass formed as a result of certain disturbances between bile particles, which precipitate and thus change the structure of the mucous membrane of the organ. These disorders can occur for a number of reasons and, as a rule, are accompanied by characteristic symptoms, against the background of which a person can determine the beginning of an unpleasant process in the digestive system.
Reasons for the formation of suspended matter
Occurring disturbances in the biliary system contribute to the accumulation of bile sediment. This stagnation is accompanied by the formation of a bile suspension, and the process itself is called sludge syndrome, which can occur in every adult for a number of specific reasons. Sometimes this process is detected in minor children, but most often women over 40 years of age are exposed to the formation of a suspension.
The bile suspension contains cholesterol crystals, calcium salts and protein. In each patient, this mass can form in different proportions in relation to each other, and the presence of a suspension can be determined using an ultrasound examination of the gallbladder. This formation is considered the beginning of gallstone disease, the process of which can be stopped by using special medications to prevent the development of gallstones.
Symptoms of sludge syndrome
This disease does not manifest itself in any way for quite a long time and is diagnosed, as a rule, unexpectedly during an ultrasound scan.
However, patients may be bothered by the following symptoms:
- pain of varying intensity under the rib on the right (pulling, dull, cramping, pulling and others);
- an adult and a child may experience a decrease in appetite and an aversion to any food;
- attacks of nausea (mainly during the daytime);
- vomiting, sometimes bile may be present in the vomit (vomiting usually occurs after eating);
- heartburn;
- unstable stool (diarrhea alternates with constipation);
Based on how sludge syndrome develops, it is divided into groups:
- Primary syndrome. The disease occurs on its own, without characteristic symptoms.
- Secondary syndrome. The disease can be caused by the consequences of pancreatitis or other diseases related to the functions of the pancreas.
The composition of the suspension in the gallbladder can be as follows:
- Microlithiasis is a suspension in the form of small inclusions, cholesterol crystals, salts, mainly potassium, and protein formations. Detected by ultrasound (a change in the patient’s position causes sediment to move).
- Clots of bile resembling putty.
- A combination of the first and second forms (clots plus microlithiasis).
Symptoms in adults and children are identical. Therefore, treatment of all categories of the population is carried out in the same ways and methods. Care must be taken in selecting treatment for children, especially younger ones.
Ultrasound revealed slight congestion in the gallbladder!
Elena Kondrashova
Pupil (116), closed 3 years ago
what to do? Help. Full description - The gallbladder is not enlarged in size, curved, the wall is 2 mm not thickened, the echogenicity of the wall is normal, medium echogenicity, the contents are not homogeneous - an echogenic suspension is determined in a small amount, finely dispersed when the patient is positioned on the left side, the shaking effect shifts. Choledok-4.3mm is not expanded, the wall of the choledok is not thickened. Portal vein 10.2 is not dilated. Linear blood flow velocity is normal
Added 3 years ago
and I lost my appetite, constant panic and sometimes feel sick. worries in general
Lyubava
Enlightened (36007) 3 years ago
You need to get rid of the echogenic suspension in the gallbladder. Pebbles can also stick together if you do nothing. I think that you need to remove the bile from the bladder, otherwise stones will form there, and you will even have to have surgery. To remove bile, use: follow diet No. 5 with the exception of fatty, fried and smoked foods. Meals should be regular, at the same time, every 3–3.5 hours, 4–5 times a day! This is necessary so that the bubble reflex is formed for a while and it contracts better. From sweets, exclude chocolate, cream products (cakes, pastries), add sour cream little by little to dishes, only baked pies (in the oven). Eat yesterday’s baked goods, porridge and biscuits as much as you want. In treatment: drugs that increase the contractility of the gallbladder: motilium (or motilak, or ganaton) 1 tablet 3 times a day 30 minutes before meals for 1 month. And choleretic: olemethine 1 caps 3 days after meals - 2 weeks, then - tanacechol 2 tablets 3 days 2 weeks. You can contact your local doctor for prescriptions. HERBS: rosehip, calendula, mint, immortelle, oats, corn silk, etc. alternate for 7 days, sorbitol 1 teaspoon 3 days 1 month (add to herbs). PROBE-LESS TUBAGES: 1 time per week in the morning on an empty stomach, take 400 ml of herbal decoction or mineral water at 40 degrees Celsius with the addition of 25% -40 ml of magnesia or 3 tablespoons of sorbitol with top, lie on your right side for 2 hours with a warm heating pad, for a course - 6 -8 procedures. This treatment can be repeated as needed. Repeat the ultrasound after treatment (after 4 months).
Honey Bee
Oracle (66371) 3 years ago
AND? Question? What's the problem? What do you want, surgery or cutting off the head?
Natalia Shmer
Enlightened (24417) 3 years ago
An ultrasound is for you to think about proper nutrition and a healthy lifestyle.
Alexei
Artificial Intelligence (448098) 3 years ago
How is your cholesterol? Do you often consume eggs, liver, kidneys, carp fish, animal oils, meat with fat? They did a blood test.
Well, if there is a predisposition, then monitor the level in the blood, do an MRI of the bile, liver, kidneys, urinary tract, to see if there are literally any stones. I consider the brain to be the most dangerous organ on the list; excess cholesterol and pressure surges will of course lead to a stroke, but they live without gallstones.
The suspension is small crystals of concentrated bile, which are formed as a result of a violation of the motor function of the biliary tract . Pathology can be detected by ultrasound or x-ray examination. Whether it is necessary to get rid of the suspension in the gallbladder and what consequences its presence leads to, we will look into it further.
Reasons for the formation of suspension in the gallbladder

A disruption in the structure of bile leads to the formation of a suspension (slange). Being a homogeneous liquid, it contains solid particles of cholesterol, which are formed under the influence of acid and pectin. Under the influence of certain factors, the bile thickens and thickens, and, finally, an echogenic sediment precipitates. This process is considered the initial stage of gallstone disease.
A newborn baby may have physiological jaundice and, as a result, the formation of a suspension. At the same time, bilirubin is produced in increased quantities. With artificial feeding, incorrect and untimely introduction of complementary foods, the risk of pathology increases.
In older children, the phenomenon may appear due to stress, disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, insufficient replenishment of the body with microelements, as well as insufficient consumption of choleretic products of natural origin.
Now let's specify the causes of the pathology. They may be:
- Nervous breakdowns, frequent stressful situations;
- Sedentary, sedentary lifestyle;
- Cholesterol metabolism disorder;
- Stagnation of bile;
- Eating fried, smoked high-calorie foods, fast food, and baked goods;
- Inflammations of an infectious nature;
- The development of diseases such as liver cirrhosis, diabetes mellitus, hepatitis, pancreatitis, pancreatic pathologies;
- Pregnancy and especially in severe cases;
- Frequent use of contraceptives and other calcium-based medications, some antibiotics;
- Alcohol abuse;
- Frequent use of strict diets and associated sudden weight loss.
There are also some factors that increase the risk of developing the disease. These include:
- Being female, there is a particular risk during pregnancy;
- Heredity;
- Overweight person.

A lack of silicon in the body can also lead to the appearance of suspension in the gallbladder. In this case, the problem is solved more simply by simply prescribing medications that increase its level in the body. These can be multivitamin complexes or appropriate dietary supplements.
The person himself can determine the deficiency and to do this, just look at his nails. If they are brittle, it means there is not enough of this element in the body.
If a suspension in the gallbladder is detected in time, the process of stone formation can be stopped, and therefore gallstone disease can be prevented.
Causes
The formation of flakes occurs for a number of reasons, due to which structural changes in the formed juice begin to occur. Initially, bile is secreted by the liver; it is viscous in consistency and contains acids, pigments, phospholipids, cholesterol, salts and some other compounds.
When the balance of these substances, in particular cholesterol, is disturbed, clots and subsequently solid particles are formed. Doctors call this sediment biliary sludge.
If provoking factors continue to act, measures to normalize cholesterol levels are not taken, then the compounds begin to crystallize, turn into sand and, as a result, into cholelithiasis. Such reactions are diagnosed in both adults and children.
Main provoking factors
It is difficult to identify clear reasons that provoked pathological processes inside the gallbladder; more often they are combined phenomena. However, most cases are diagnosed due to the following circumstances:
- Diseases of the liver, gall bladder, blockage of ducts. The formation of sand becomes a consequence of many dysfunctions of these systems, the diagnosis is added to the already actively developing pathologies.
- A sharp change in diet, prolonged restriction of certain foods. Weight loss, deficiency of fats and some other compounds leads to a disruption of natural metabolic processes in the body, including the outflow of digestive fluid.
- Long-term use of antibiotics, hormonal drugs, medications.
- Abuse of harmful foods and alcohol.
- Organ transplantation.
- Hereditary predisposition. This mainly concerns ailments affecting digestive functions.
- Anomalies of acquired, congenital type.
- Surgery that caused tissue damage, such as stone removal.
- Diabetes.
- Changes in biological reactions in the body associated with age, pregnancy, menopause, decreased immunity, and increased physical activity.
The above reasons are common, but not the only ones. A more precise origin of gallstone dysfunction can be determined by a specialist after diagnostic measures.
Signs and symptoms
There are practically no obvious symptoms at the onset of the disease, but by listening to the signals of your body, you can recognize the pathology.
So, signs of the formation of suspension in the gallbladder are:
- a feeling of heaviness and pain in the right hypochondrium (may differ in nature - paroxysmal or constant);
- stomach discomfort;
- nausea and vomiting, for example, after eating fatty fried foods. Such food requires increased production of bile, and if this does not happen, then the listed symptoms appear;
- bitterness in the mouth,
- the formation of a yellow coating on the surface of the tongue.
- stool disorders - diarrhea, constipation, flatulence, bloating (When poorly digested food enters the intestines, it causes irritation, which in turn leads to problems with defecation).
Possible consequences of bile stagnation
In the absence of timely proper treatment, acute pancreatitis may develop against the background of stagnant processes in the gallbladder area. Often the consequence of a disorder in the body is cholecystitis, which leads to tissue inflammation.
To avoid the above manifestations, it is worth maintaining normal body weight. It is necessary to abandon the regular use of strict diets aimed at sudden weight loss. You should also prevent diseases such as cirrhosis and hepatitis, which often result in the formation of a suspension in the gallbladder.
It is recommended to be careful when choosing medications. Before taking medications, you should carefully study the side effects, consult a doctor and, if possible, reduce the use of chemicals in general.
Types of suspension in the gallbladder
According to the etiology, chemical composition and ultrasound data, the sling is classified into types:
- Echo-heterogeneous bile with clots - single high-density nodes are recorded in the area of the posterior wall of the organ. This is an echogenic suspension detected by ultrasound;
- Hyperechoic formations do not provide an acoustic shadow and are detected only during an ultrasound examination, and only when the patient’s body position changes. These include fine suspension consisting of protein, cholesterol, calcium salts;
- Putty-like bile - characterized by the presence of putty-like clots moving in the space of the organ.
Diagnosis of the disease
If a patient detects the mentioned symptoms, he should immediately seek help from a doctor. During the first examination, the doctor collects anamnesis, analyzes the identified symptoms, the presence of other pathologies, and palpates the abdomen.
Laboratory tests help determine the development of the first disease that caused the formation of suspensions (for example, increased levels of cholesterol, salts, bilirubin, etc.).
An ultrasound is required during the examination. It is thanks to this study that the doctor can determine the presence of sediment in the organ and the formation of a pathological process. If the causes of the disease cannot be immediately determined, then the patient needs to undergo tomography and duodenal intubation.
The diagnosis is made based on a history and the results of a number of studies:
- laboratory testing of blood and urine: determination of the content of liver enzymes, cholesterol, total protein and bilirubin;
- Ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity allows you to detect suspension and sediment in the gallbladder, visually determine the number of suspended particles and assess the general condition of the gallbladder;
- magnetic resonance imaging shows pathological changes in the tissues of the gallbladder and liver;
- duodenal intubation and taking a bile sample for laboratory testing.
Treatment options
Depending on the diagnostic results, treatment is prescribed. All methods must be selected taking into account:
- age;
- physical characteristics of the patient’s body;
- given diagnosis.
First of all, doctors recommend a therapeutic diet (table No. 5). The nutrition system requires adherence to the following principles:

Frequent meals in small portions.- Exclusion from the diet of fatty, fried, smoked and salty foods.
- Eating eggs is unacceptable; mayonnaise; cream; various sauces flavored with seasonings; alcohol; chocolate; soups with fatty broth; ice cream; baking.
- Limiting the consumption of cereals;
- The introduction of fresh fruits and vegetables, jelly, fermented milk products, vegetable and butter, wheat and rye bread into the diet is encouraged.
A strict diet is followed for up to six months.
Drug therapy for suspension in the gallbladder
- Ursosan and Ursofalk are used to improve the quality of bile. Treatment is long-term, up to several months;
- Drugs such as Mebeverine, Niospam, Aprofen are used to restore the functionality of the gastrointestinal tract;
- The physicochemical properties of bile are normalized with the help of Rezalut Pro, Allochol, Galstena, which can reduce the concentration of cholesterol;
- Prebiotics are recommended for restoring the gastrointestinal microflora - Linex, Bifidumbacterin.
Treatment of the disease
Biliary sludge can be treated in different ways, including surgery, as well as folk remedies. In general, surgery is not required in most cases. The exception is patients who experience frequent recurrent attacks, in simple terms - abdominal pain. In other cases, doctors recommend conservative methods of therapy (use of various forms of analgesics) and normalization of nutrition.
Folk remedies (herbal medicine) can not only treat this disease, but also prevent the syndrome of the formation of suspensions in the gallbladder and ducts.
Naturally, all treatment should be started only after consultation with a doctor. Self-medication is strictly not recommended, so as not to aggravate the problem.
In this case, folk remedies and methods refer to treatment using decoctions of various herbs that have a choleretic effect, as well as anti-inflammatory herbs.
Basically, treatment with traditional methods and means is carried out in courses (2-3 months) twice a year.
Excellent medicinal decoctions are obtained from the roots and fruits of rose hips and strawberries. Doctors also recommend more often eating the juice of fresh and sauerkraut, beets, drinking lemon water and infusions made from St. John's wort, wormwood, corn silk, and dill seeds.
As a result of the use of traditional medicine, it is possible to minimize or completely get rid of suspensions in the gallbladder over the course of several courses (everything is purely individual and depends on the stage of the disease).
It is necessary to exclude most foods containing fats from the diet, while carbohydrate and protein foods can be left unchanged. You also need to remove fried foods and foods rich in fiber from your diet.
A similar syndrome in a child often occurs against the background of physiological jaundice (the level of free bilirubin increases at this time). The reason most often is artificial feeding of the child, as well as untimely introduction of new types of complementary foods. In older children, the disease can occur due to stress, disturbances in the functioning of the digestive system, when an insufficient amount of choleretic products enters the body.
Treatment of such children should be carried out with comprehensive therapeutic measures aimed at maintaining and restoring intestinal microflora and stabilizing the normal functioning of the gallbladder (correcting the outflow of bile).
Herbal medicine can be safely used as an additional therapy to the main type of treatment prescribed by a doctor. Before starting any methods of therapy, it is always necessary to clarify the diagnosis, and for this it is useful, even, or rather, necessary, to carry out diagnostics using ultrasound.
We recommend reading:
pechen1.ru
Folk remedies for treating suspension
In folk medicine, both herbal medicine recipes and mineral water are effectively used against suspended matter. But such treatment must be agreed upon with a gastroenterologist - only he can tell you what specifically will benefit you and what is contraindicated for you.
Mineral water has choleretic properties and is used for drinking and tubing. The famous mineral waters of Borjomi and Essentuki have healing properties.
Therapeutic drinking is carried out according to the following scheme:
- Half an hour before breakfast, drink half a liter of water heated to forty degrees in a water bath;
- Throughout the day, drink another half liter - always before meals and always warmed up.
According to this scheme, you drink water for a week, then take a two-week break and drink water again for a week.
Tubage with mineral water is carried out according to the rules:
- The procedure must begin at six o'clock in the morning - this is the time when the liver begins to work;
- Drink the prepared water, after releasing the gases from it;
- Lie on a heating pad on your right side, bending your right leg;
- You need to lie down for two hours;
- After the end of time you can eat;
- According to the doctor’s recommendations, you can do a cleansing enema before tubing;
- The procedure is done every other day for ten days.
Attention! Tubage is prohibited for gallstones.
3 ways to carry out tubage:

On an empty stomach, drink a glass of hot medicinal water of Essentuki with two tablespoons of sorbitol added to it. Drink slowly in small sips on an empty stomach. After a while, drink another glass of mineral water, then another. This procedure must be carried out twice a week for one month.- Drink a glass of warm water with the addition of one tablespoon of honey on an empty stomach. Lie on your right side, placing a heating pad under the gallbladder area. You need to lie down for one and a half to two hours. Probing will allow you to remove the suspension in the gallbladder.
- On an empty stomach, drink a glass of Borjomi type mineral water with one tablespoon of magnesium sulfate added to it. You need to drink in small sips. Don't forget to put a heating pad under your right side. A sign indicating the effectiveness of the procedure will be a slight tingling sensation in the side, followed by mushy stool.
As for treating suspension with herbs, you can use a recipe for wild strawberry infusion. The berry is rich in silicon, and this element is very important for preventing the appearance of sludge.
During flowering, prepare strawberry twigs and roots. The infusion is prepared in this way: several branches, after breaking, are brewed in a thermos, like regular tea, for about two hours. For a tablespoon of twigs you need two cups of boiling water.
Good health to you!

The appearance of some pathologies in the body may not directly cause any inconvenience or problems. But, in the process of their development, they can cause dangerous diseases.
What is suspension?
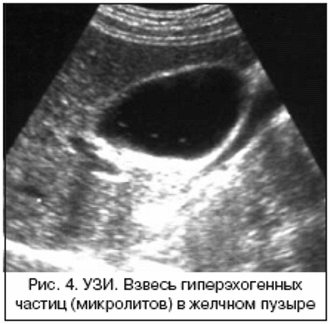
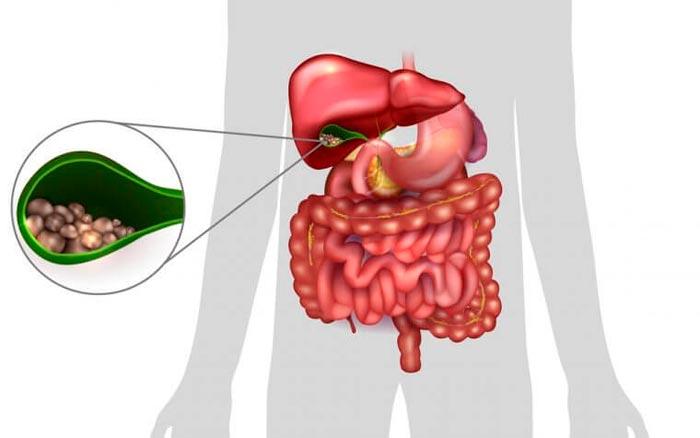
This is what a suspension in the gallbladder looks like on an ultrasound
An ultrasound examination of the gallbladder often reveals a suspension in its cavity. The suspension is thickened bile or a substance consisting of cholesterol crystals, bilirubin-containing pigments, and calcium salts.
Detection of suspension may indicate a disorder of the motor functions of the biliary tract. In the future, the disorder may develop into cholelithiasis or calculous cholecystitis.
Often the first detection of suspension occurs during a routine examination.
Types of bile heterogeneity
The composition of the suspension can be of the following types:
- microlithiasis, consisting of 4-5 mm foreign bodies that are detected during a change in body position;
- components of stagnant bile;
- heterogeneous, when microlithiasis is associated with stagnant bile.
Foreign crystals in suspension may consist of:
- cholesterol crystals in a liquid state;
- calcium salts in the combination of protein with parts of epithelial cells (the mixture of calcium salts with protein and epithelium is one of the most common causes of the formation of suspension);
- sludge of components of stagnant bile.
Etiopathogenesis
A thick sediment in the gallbladder is formed as a result of stagnation of bile - cholestasis, changes in its composition - dyscholia, and the development of inflammation - cholecystitis. These are the main etiopathogenetic factors of the syndrome, occurring in the following pathological and physiological conditions:
- Cirrhosis of the liver,
- Obstruction of the bile duct with a stone,
- Pancreatitis,
- Decreased immunity
- Sharp and rapid weight loss caused by stress or long-term diets,
- Surgeries on the intestines or stomach,
- Long-term treatment with antibiotics and cytostatics, taking calcium supplements, contraceptives and lipolytics,
- Anemia,
- Internal organ transplantation,
- Long-term parenteral nutrition
- Viral kidney inflammation
- Alcohol intoxication of the body,
- Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus,
- Psycho-emotional stress,
- Abuse of salty, fatty and fried foods,
- Bad habits - drinking alcohol, smoking, sedentary work,
- Genetic burden and congenital anomalies,
- Chronic diseases of internal organs, manipulations and operations,
- Pregnancy, menopause, physical inactivity.
In healthy people, bile components are in a colloidal state. When the ratio of bile acids to cholesterol changes, the latter precipitates and crystallizes. Thickening and stagnation of bile contributes to infection of the gallbladder by hematogenous, lymphogenous or ascending routes. Inflammation of the organ is accompanied by thickening of its walls and disruption of the dynamics of emptying, which leads to evacuation dysfunction and stagnation of bile.
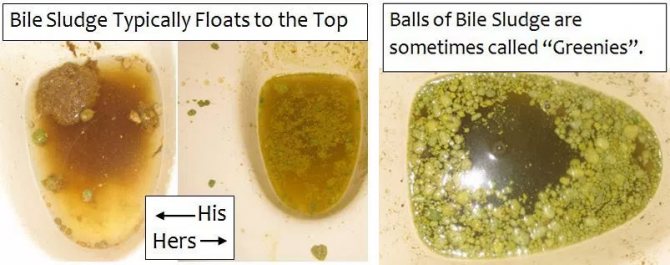
examples of biliary sludge
Sludge syndrome usually develops in women over 55 years of age, who are overweight and have a hereditary predisposition, who neglect proper nutrition and consumption of healthy foods - vegetables, fruits, and cereals.
In young children, the formation of sediment in bile is associated with an increase in the level of free bilirubin, which is observed with physiological jaundice, inability to breastfeed, and early introduction of complementary foods. In older children, the development of the syndrome is usually associated with a stress factor, severe gastrointestinal dysfunction, a lack of microelements in the blood and choleretic products in the diet.
Under the influence of the etiological factor, hypertonicity of the sphincter of Oddi and hypotension of the gallbladder muscles occur.
Pathogenetic links of sludge syndrome:
- Excessive cholesterol content in bile,
- Formation of large conglomerates from cholesterol crystals,
- Their deposition on the walls of the gallbladder and damage to the organ,
- Gradual enlargement of stones.
Biliary sludge in the gallbladder is a suspension inhomogeneous in composition, signaling the onset of gallstone disease.
Reasons for the appearance of suspended matter
Among the main reasons leading to the formation of suspended matter are the following:
- impaired cholesterol metabolism, which develops as a result of lack of optimal physical activity and excessive consumption of fatty, high-calorie foods and fast food.
- the period of the third trimester of pregnancy, when intra-abdominal pressure increases, leading to stagnation of bile;
- taking contraceptive medications that affect the structure of bile;
- a sharp decrease in fat intake, which results in a violation of dynamic function, an increase in the tone of the sphincter of Oddi and provokes stagnation of bile.
- excess calcium in the body caused by taking calcium-containing medications;
- alcoholism, drug addiction, causing irreversible processes in the gastrointestinal tract.
- operations in the abdominal cavity.
Strengthens and provokes the development of the disease: diabetes mellitus, hepatitis, excess weight, cirrhosis of the liver.
Possible complications
The development of complications of the disease is characterized by the following stages:
- oversaturation of bile with cholesterol;
- dysfunction of the mobile balance of pro- and antinucleating factors;
- factors of nucleation and precipitation of cholesterol components;
- the combination of crystals into microlites and their subsequent enlargement.
The presence of echogenic suspension can lead to complications: acute pancreatitis, bile stagnation, biliary colic, inflammatory process in the biliary tract, cholecystitis.
Symptoms of the presence of suspended matter

Suspension can lead to the formation of gallstones
There are two diametrically opposed opinions on the presence of suspension in medicine.
Some doctors believe that this problem, as a transit condition, does not require special intervention, others believe that the presence of suspension is the beginning of the development of gallstone disease. The optimal point of view is that suspension in the gallbladder is a reversible phenomenon, but in the absence of appropriate treatment it leads to serious complications.
The presence of suspension can be judged by the presence of intense pain, difficult and painful digestion. These symptoms are characteristic in 80% of cases and only in 20% of cases the presence of the suspension is not particularly felt by the patient.
Signs of the presence of suspension are somewhat different from the symptoms of cholelithiasis:
- the suspension can move through the bile ducts without much difficulty, so pain can be felt in different places;
- in the presence of suspension, the contractile function of the gallbladder suffers much less, so the suspension can be periodically excreted, causing pain.
- The pain can be intense, paroxysmal, lasting from a minute to 3-4 hours, the pain periodically returns, is localized in one area or spreads throughout the entire abdominal cavity.
Types and composition of suspended matter
At the initial stage of development of the disease, a putty-like suspension is formed in the gallbladder, presented in the form of clots, the presence of which is noticeable only during an ultrasound examination. Later, a fine suspension is formed, which is characterized by movement in the gallbladder when the body position changes. The latter consists of undissolved proteins, cholesterol, calcium salts and their combinations.
According to the composition, a suspension is isolated in the gallbladder with a predominance of bilirubin, calcium or fats. Based on the mechanism of occurrence, secondary and primary impurities are distinguished. Some are deposited as a result of the development of cholelithiasis, inflammation of the pancreas. Others act as an independent phenomenon in which there are no other pathologies.
Diagnostics
It is important to diagnose the disease as early as possible in order to avoid transformation into more severe forms of cholecystitis or cholelithiasis. Diagnosis is carried out as follows:
- examination of complaints: are there pains in the abdominal area, how are they located;
- study of the patient’s living conditions: what medications he took, whether there are diseases of the digestive system, liver diseases, bad habits (alcoholism, drug addiction).
- external examination of the patient, determination of pain in the abdominal cavity upon palpation;
- study of the results of a general analysis of urine and blood;
- study of the results of a biochemical blood test to determine enzyme changes in the liver, study of total protein, bilirubin, cholesterol, etc.
- use of instrumental diagnostic methods
The main method of instrumental diagnostics is ultrasound, through which pathologies of bile consistency and the presence of foreign bodies are determined.
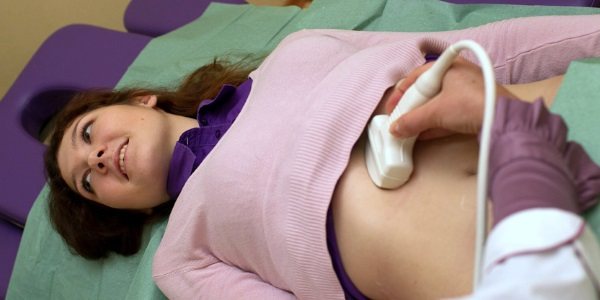
Detection of suspension usually occurs after an ultrasound scan
Duodenal intubation is used when it is necessary to obtain bile for microscopic examination for the presence of clots and foreign bodies. Computed tomography reveals abnormal changes in the liver and gallbladder.
Causes of biliary sludge
Violation of the composition of bile occurs against the background of other pathological processes and related therapeutic measures. The main risk group is people suffering from liver and gallbladder diseases. All pathologies that affect the excretion of bile from the body pose a threat to normal secretion. Pancreatitis, diabetes mellitus, sickle anemia, and gastrointestinal diseases in any case have a negative effect on the composition of bile.
The treatment regimen for the underlying disease, the patient’s age, and lifestyle, in turn, determine the development of biliary sludge. Despite the vague clinical picture, gastroenterologists identify three reasons for which a sediment forms in the bile with a probability of up to 80%.
Cholecystitis
Chronic inflammation of the gallbladder is characterized by mild symptoms and a long course. This means that a person may not be aware of the presence of the disease for many years. For this, cholecystitis gradually corrodes the walls of the gallbladder. Normal tissue is replaced by connective tissue, as a result of which the organ thickens, losing its functionality. Slow metabolic processes promote sediment formation. It is noteworthy that sludge completely disappears during the period of remission.
Pregnancy
Every fifth expectant mother develops biliary sludge. The growing uterus puts pressure on the gallbladder and its ducts. In this state, it is difficult to maintain natural functionality, so the secretion of bile slows down somewhat. The disease is asymptomatic and rarely causes discomfort to a woman. After childbirth, the organ is restored and the sediment is excreted naturally.
Regular diets for weight loss
In pursuit of ideal forms, women (and men) resort to radical measures. Strict diets and hunger strikes are becoming the norm. The lack of basic vitamins, nutrients and microelements negatively affects all internal organs. The gallbladder is the first to suffer. Motor functions slow down, stagnant processes form, and a smooth sediment appears. If you stop in time and balance your diet, the functions of the bile ducts will be restored on their own.
Treatment
Treatment is carried out in accordance with three schemes, depending on the complexity of the disease:
- Minor disorders that do not cause severe pain are eliminated by prescribing corrective diet No. 5. Fatty, fried, spicy foods, some types of vegetables, mushrooms, cocoa, and chocolate are excluded from the diet. The use of medications is aimed at eliminating the root cause of the disease.
- Most patients are prescribed conservative treatment. Medicines are used to thin the consistency of bile and eliminate stagnation.
- Surgery is prescribed for more serious complications, such as cholecystectomy, laparoscopy, extracorporeal lithotripsy.
Prevention

The main thing in prevention is proper nutrition. If you have a tendency towards such pathologies, you can try following diet No. 5
Prevention of the formation of a gallbladder involves, first of all, diet. The main element of gallstones is cholesterol, so it is necessary to limit its consumption, especially in older age.
You should minimize or completely eliminate the consumption of such products as:
- fat meat;
- offal (liver, kidneys);
- milk porridge;
- flour products;
- egg yolks.
To prevent the disease, you need to increase your consumption of foods with vitamin A (bran, carrots, celery, spinach), and drink more alkaline mineral water.
Herbal infusions thin bile and counteract the formation of sand and stones: barberry roots, peppermint, rose hips. Infusions are brewed in accordance with the dosage indicated on the package. Take 3-4 times a day for two weeks, one or two glasses.