The gallbladder is actively involved in the functioning of the digestive system. It accumulates bile in its cavity and sends it to the duodenum. A disabled gallbladder is an organ that, for a number of reasons, cannot perform its functions.
Related articles:
How to tubage the gallbladder using mineral water Treatment of gallstones with folk remedies Causes of bile stagnation in the gallbladder - how to treat it What are gall bladder stones - symptoms and treatment Use of medications after gallbladder removal
Disconnected gallbladder syndrome indicates that the organ is not functioning, and therefore is completely useless for the human body. In addition, a non-functioning bladder becomes a source of infection, since pus can accumulate in it instead of bile. According to ICD 10, this condition can be coded K82 and K83, R93.2.
What does pathology mean?
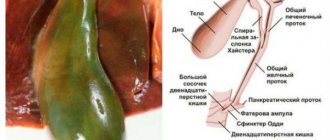
To understand what the concept in question means, you need to understand how the gallbladder works in humans. The function of this organ is to receive and secrete bile.
It is important to know!
The concept of “disabled gallbladder” was first used by radiologists. During the examination of patients using X-rays using contrast, a dye liquid stains the bladder and bile ducts. This allows you to clearly see the organs on an x-ray and assess their condition.
If the gall bladder is not visible on the x-ray, that is, remains invisible, then it is called “disabled”.
If an X-ray contrast study reveals that the bladder is “disconnected,” then doctors can assume:
- Violation of organ function.
- Disorders of the bile formation system in the liver.
- Technical errors that led to insufficient amounts of contrast entering the bile.
If a patient is diagnosed with a non-functioning gallbladder, then a more specific reason for its shutdown is determined using ultrasound.
Clinical manifestations
Quite often, this pathology is a complication of a condition such as cholelithiasis. The following are signs of a disabled bubble:
- sudden appearance of pain in the area of the right hypochondrium;
- excessive accumulation of gases in the small and large intestines, accompanied by a feeling of bloating;
- the occurrence of heartburn;
- specific unpleasant taste in the mouth;
- disorders of the digestive process;
- signs of an attack of hepatic colic (they appear only if there is complete obstruction of the excretory duct).
In the absence of adequate treatment, a strong inflammatory process develops in the area of the gallbladder, which can lead to perforation of the organ wall. In this case, all the accumulated purulent fluid freely enters the abdominal cavity and initiates the development of peritonitis. Thus, if the gallbladder is disabled, it can threaten not only health, but also life.

With an exacerbation of cholelithiasis (GSD), the patient develops mechanical jaundice. In this case, the skin has a jaundiced tint, feces are almost completely discolored (acholia), and urine has a rich dark color. In parallel, symptoms such as severe skin itching and increased body temperature occur. After an attack, all existing symptoms can almost completely regress.
Important! If there are no stones, then the disabled gallbladder may not manifest itself in any way and the disease is asymptomatic for quite a long time. Moreover, in some cases, this pathological condition does not indicate a complete shutdown of the organ, but its temporary dysfunction.
Causes
The main causes of pathology are:
- Complete filling of the organ with stones.
- Blockage of the duct.
The consequences of a disabled gallbladder are quite serious, since there is a possibility of inflammation and rupture of the organ.
It is important to know!
When an organ is filled with stones or its duct is blocked, the internal walls and the bladder itself are greatly modified, the mucous membrane disappears, and the walls become covered with scars.
As a result of the destruction of muscle tissue, atony of the gallbladder develops.
The following diseases can be the causes of the pathology:
- Cholecystitis.
- Flakes or stones in the gall bladder.
- Shriveled gallbladder.
- Limescale deposits on its inner walls.
- Cholelithiasis.
- Dyskinesia or obstruction of the ducts.
- Cholecystectomy.
Many people don't know what gallbladder flakes are? Flakes, or biliary sludge, are formed as a result of prolonged stagnation of bile and are characterized by the appearance of cholesterol crystals, bilirubin pigments and calcium salts in the cavity of the organ and its ducts. Over time, the flakes can harden and turn into stones. Sludge also often causes the development of cholelithiasis.
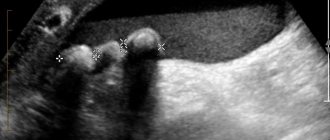
The gallbladder is contracted - ultrasound results
When interpreting the results, doctors are guided by standard indicators. The length of the organ should not exceed 8 cm, width - 3 cm. In normal condition, the diameters of the hepatic ducts are no wider than 5 mm, the gallbladder - 6 mm.
Deviation from the norm is considered to be:
- reduction in the size of the organ, thickening of the walls and the formation of bends on them, indicating chronic cholecystitis;
- blurred contours, as in acute inflammation, accumulation of exudate;
- the presence of cholesterol in the submucosal layer of the wall in the form of polyps (cholestorosis);
- epithelial abnormalities.
If the gallbladder is somewhat contracted, the doctor identifies changes in neighboring organs. If the outflow of biological fluid is poor, biliary dyskinesia is diagnosed, and if the cystic duct is obstructed, dropsy is diagnosed. Its quality and composition change if clots, grains of sand, or stones appear.
What does it mean
JP leads to dysfunction of the smooth muscles of the walls, the sphincter of Oddi - circular muscles that regulate the intensity of contraction. In this case, no organic changes occur. We are talking about a violation of the movement of bile, which leads to:
- to difficulty or rapid outflow;
- the problem of breaking down hard-to-digest fats in the small intestine;
- inflammation of the ducts;
- gallstone disease.
Treatment
It is important to know what measures should be taken if the bile ducts are clogged, the symptoms and treatment of which pathology should be considered, and what the consequences of such a condition may be.
- When the blockage of the ducts is caused by a stone, doctors may try to push it with a catheter into the cavity of the bladder. If this is successful, the patient will be prescribed a drug containing ursodeoxycholic acid, which helps dissolve the stones.
- If hypotonic dyskinesia occurs, then appropriate medications, for example, magnesia, are used to stimulate contraction of the gallbladder walls.
- In cases where the gallbladder is an atonic, wrinkled and shapeless organ, completely covered with scars, its surgical removal will be required.
What to do if your gallbladder is disabled?
For diagnosis, you should undergo a complex examination - cholecystography, since ultrasound does not provide a complete picture of the pathology. The doctor must find out the reason why the gall bladder is turned off, and then decide what to do. There is no point in preserving an organ if it is clogged with stones, deformed, or has a lot of scars and adhesions. Such an organ will never work again, so an operation is performed - abdominal or laparoscopic cholecystectomy to remove the gallbladder.
If the cystic duct is blocked by a stone, you can try to push it back using special tools. Drugs are often prescribed that can dissolve stones, but they do not always help. Reduced organ tone is stimulated with medication, and, as a rule, the effect is positive. In case of pathology, it is mandatory to prescribe a diet in accordance with available medical recommendations. Diet is also urgently needed for patients after surgery to remove an organ.
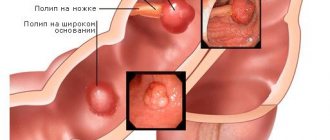
Polyp formation
Such neoplasms can appear on the walls of the intestines, stomach, gallbladder or any other organ. The danger is that they can become malignant in the future.
The main factors for the occurrence of polyposis: genetic predisposition, diagnosed biliary dyskinesia, complications arising from the development of infection or inflammatory process. A common cause of pathology is impaired metabolism (in particular, lipid metabolism).
When is invasive intervention required? If the doctor has diagnosed adenomatous polyps (due to the high probability of their transformation into an oncological tumor) or if they are located in dangerous places. For example, close to the ducts or in the narrow neck of the gallbladder.
If the size of the formations is less than 10 mm, drug treatment is prescribed. If more than 10 mm, the surgeon cuts them out.
The difficulty of diagnosing polyposis at an early stage is the absence of pronounced specific symptoms. The patient may periodically experience nausea, loss of appetite, and signs of flatulence. Pain in the right hypochondrium, characteristic of other gallbladder diseases, is usually absent.
Conclusions and recommendations
There are many reasons why gallbladder removal is prescribed. To avoid this, it is advisable to adhere to the following preventive measures:
- do not overeat;
- limit the consumption of fatty, smoked, spicy, sweet, salty and high-calorie foods, as well as fast food;
- Avoid stress (physical and emotional) if possible;
- lead an active lifestyle, play sports;
- do not use strict diets. Fasting is possible only for medicinal purposes for a short period and only after consulting a doctor and passing the necessary tests;
- undergo regular medical examinations. This is the only way to identify a number of diseases in the initial stages.
If you suspect problems with this organ, it is recommended to consult a doctor and undergo an examination. If the pathology is detected early, it can be treated without the need to remove the gallbladder.
If the patient refuses to undergo surgery, the result will be serious complications and the spread of the inflammatory process to nearby organs. After invasive intervention, people return to normal life, often without even noticing the changes. However, you must follow all medical recommendations and adhere to a special diet. The diet is not too strict, it only limits the consumption of animal fats, since such lipids are difficult to digest by the body, and strong alcoholic beverages.
Thus, the main causes of diseases include poor nutrition, hormonal imbalances, pathologies in the nervous system, and frequent stress. These factors provoke impaired motility of the organ, which leads to the formation of gallstones or oncology. It is important to identify the disease in a timely manner and, if necessary, perform a cholecystectomy. Otherwise, serious health problems and even death may occur.
Preparing for an MRI of the gallbladder

Preparatory measures include following a diet 4-5 days before diagnosis, excluding from the diet foods that contribute to stagnation of bile or its excessive production :
- fatty meats and fish;
- legumes;
- raw vegetables, herbs and fruits;
- mayonnaise, margarine;
- spices and marinades;
- canned food;
- milk and its derivatives;
- yeast-containing baked goods;
- confectionery products, etc.
Alcohol, strong coffee and tea are prohibited. You must appear for an MRI of the gallbladder on an empty stomach; your last meal should be no later than 6-12 hours before. Smoking contributes to organ contraction and unreliable results. For patients suffering from flatulence and constipation, the possibility of cleansing the intestines with an enema or taking medications (antispasmodics, sorbents) should be checked with the doctor who referred for diagnosis.
Cholesterosis
The disease is characterized by increased cholesterol levels in the body due to impaired lipid metabolism. As a result, the substance is deposited on the walls of the gallbladder, and it stops functioning properly.
The motility of the organ in a normal state ensures the absorption of some of the cholesterol. However, as pathology develops, it does not leave the bladder wall. The bile thickens, as a result of which stones can be deposited. If they block the ducts, the person experiences severe stabbing pain and requires urgent hospitalization.
Only the attending physician, after carrying out all laboratory tests and hardware diagnostics, can say in which cases it is possible to remove an organ and why this is required in each specific situation.
The occurrence of cholesterosis is often caused by poor nutrition, physical and psycho-emotional stress, and pathologies of the peripheral nervous system. Often patients are interested in whether it is necessary to remove the bladder due to cholesterosis. If it proceeds in a normal form, drug therapy will be sufficient, but if cholelithiasis becomes complicated or polyps appear, surgery must be performed. If timely intervention is not carried out, the result may be death due to blockage of the ducts by stones.
Consequences and prevention
If therapy is not carried out, organ dysfunction leads to inflammation, the formation of pus and its spread into the abdominal cavity - peritonitis. Large stones can cause the bladder to burst. This condition is life-threatening.
If removal has been performed, you must follow a diet, eat often and in small portions. In the absence of a storage organ, bile is constantly present in the intestines in small quantities. During fasting, it irritates the intestinal walls, and when eating difficult-to-digest foods, it becomes insufficient.
To prevent gallbladder diseases, it is recommended to follow a diet that excludes alcohol and heavy foods. If the outflow of bile is difficult, take choleretic drugs (magnesia, sorbitol, plant extracts - immortelle, rose hips, barberry) provided that there are no stones in the bladder.
Chronic cholecystitis
This type of disease is characterized by periodic changes in phases of remission and exacerbation. The first period is characterized by an improvement in the condition and the absence of signs of the disease, and the second - by the manifestation of symptoms of acute cholecystitis. Remission can last quite a long time. Exacerbation most often occurs when the prescribed diet is violated.
The symptoms of this type of pathology are similar to the clinical picture of the acute form. Yellowing of the skin and sclera of the eyes is often observed. Sometimes the symptoms are supplemented by itching of the skin.
The main causes of the disease: poor nutrition (abundance of high-calorie and fatty foods in the diet), pathogenic or parasitic organisms, infection with a virus. These factors lead to bile stagnation, which can result in the formation of stones in the bladder.
In the absence of stones, drug treatment is usually effective. Otherwise, invasive surgery will be required to remove the gallbladder to prevent serious complications.
Therapeutic diet
Nutritional therapy is always recommended in combination with other means and methods against this disease. The diet has the following features:

Eat often, in small portions (up to 300 g).- Do not fry dishes, but boil, stew, steam.
- Consume more plant foods, less animal fats.
- Do not forget about choleretic products, especially vegetable and fruit juices.
- Season vegetables with vegetable oil to stimulate bile drainage.
- Eat more foods with vitamin C.
- In the acute phase of the disease, eat only liquid, semi-liquid food, and pureed foods.
- Reduce the amount of salt and sugar in your diet.
- Drink at least 3 liters of fluid per day.
There are foods that the diet completely prohibits from eating when the gallbladder is disabled. These include beef fat, lard, lamb fat, as they are too heavy to digest, as well as ketchup, mayonnaise, marinades, and mustard. In the initial period after the operation, the menu is meager and mainly vegetarian (vegetables and fruits with an abundance of essential oils are also prohibited - radish, rhubarb, onions, garlic, and the like). Then throughout your life you should limit the amount of mushrooms, high-calorie foods, fatty fish, fried and spicy foods.
The patient can eat dried bread, jelly and compotes, fermented milk foods, eggs (sometimes only without yolks), and soups without frying in low-fat broth. Semi-viscous porridges are useful - buckwheat, oatmeal, barley, baked fruits and vegetables. But you can only eat ripe fruits - watermelons, melons, apples, pears and others. Sour, unripe fruits are prohibited for consumption. Not everyone can eat cabbage and legumes, which increase gas formation and irritate the mucous membrane of the gallbladder. We must also not forget that diet, despite its importance, will never cure the disease completely, so if necessary, you will still have to decide on surgery or conservative treatment.
The “disabled gallbladder” condition means that for some reason it is not functioning. This happens when it is impossible to fill with bile, deformation and loss of contractility. This means that the disabled gallbladder falls out of the process of digesting food, but at any moment it can make itself felt with pain and inflammation. Bile passes directly from the liver to the intestines, without accumulating anywhere, which impairs digestion.