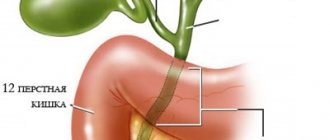
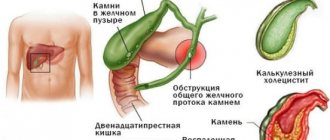
What is gallbladder cholesterosis
A continuous process occurs in the human body - the exchange of organic compounds of fats and fat-like substances in cells. This is called "lipid metabolism". Its violation leads to the concentration of cholesterol in various tissues of the body. When cholesterol accumulates in the gallbladder, this condition is called “cholesterosis.” Deposition of lipids and cholesterol develops in the form of fatty protrusions on the wall of the organ.
Cholesterosis of the gallbladder walls is more common in the age group of 20-40 years, and women are more susceptible to it. Compared to other biliary disorders, cholesterosis is quite rare. This is due to the fact that the pathology is not so easy to diagnose, and it does not manifest itself in all cases.
Cholesterosis is considered as a separate disease or as a stage of cholelithiasis. Most often, inflammation (cholecystitis) does not accompany the deposition of cholesterol in the walls of the bladder, but is its complication.
Are there risk factors?
Despite the fact that it has not yet been possible to find out exactly how cholesterosis of the gallbladder walls develops, doctors have identified several main risk factors:
- First, it is worth mentioning dyslipidemia. This condition is associated with disruption of normal lipid metabolism. In most cases, the disease is caused by eating too much fatty food.
- Gallbladder cholesterosis is often diagnosed in patients with hypothyroidism due to a decrease in the amount of hormones synthesized by the thyroid gland.
- Risk factors also include diabetes mellitus.
- Some experts associate cholesterosis with abdominal obesity.
- The disease can also develop against the background of non-alcoholic fatty liver.
- The so-called bacterial overgrowth syndrome, in which a change in the quantitative composition of the intestinal microflora is observed, is also considered potentially dangerous.
- Naturally, risk factors include diseases of the digestive tract, including cholelithiasis, gastritis, pancreatitis, intestinal lesions, etc.
Modern classification
Cholesterosis has its own classification depending on several criteria.
According to the accompanying sign - stone deposition:
- acalculous - the most common type of cholesterosis;
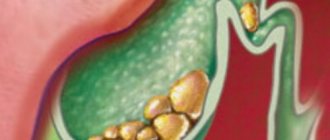
- with cholelithiasis - with the simultaneous formation of cholesterol stones.
It is this criterion that determines the method of treatment.
25% of patients with gallbladder cholesterosis have no symptoms of the disease.
According to the form of the disease:
- Polypoid cholesterosis. The polypous form is characterized by the formation of polyps - benign formations that can grow into the lumen of the bladder. The polypous type of disease, depending on the number of polyps, is divided into single and multiple.
- Focal cholesterosis. Characterized by the formation of cholesterol plaques that are not connected to each other.
- Diffuse cholesterosis. It is represented by deposits that are evenly distributed along the wall of the gallbladder or concentrated into a dense network.
- Total cholesterosis. Deposits affect the entire area of the organ wall.
According to the degree of organ dysfunction:
- minor gall dysfunction;
- moderate dysfunction (up to 50%);
- severe dysfunction (up to 90%);
- non-functioning organ.
According to changes that can be detected under a microscope, there is an asymptomatic (hidden) form and a form in combination with additional changes:
- with tumors of various types;
- with a growth of connective or fatty tissue around the bubble;
- with the growth of pseudoglandular structures.
Diet
Gallbladder cholesterosis requires exclusion from the diet of hot seasonings, fatty meat dishes, alcohol and sweet products. These foods require large amounts of bile.
The emphasis can be on seafood. They do not require a large amount of bile to digest them. Marine fish, such as cod, are especially useful. It contains a large amount of lyotropic substances.
It is recommended to focus on vegetables in raw, boiled and stewed form. These can be various salads, side dishes and independent dishes. Salads made from fresh vegetables with vegetable oil are useful as snacks. You can eat:
- fruit salads,
- vinaigrettes,
- squash caviar,
- jellied fish.
Milk sausage, ham and mild cheese can be consumed in small quantities.
The main condition is compliance with the regime. You should eat in small portions, but often. All food should be warm and fresh. Your diet should not focus on cream, full-fat milk, fermented baked milk, sour cream and salty fatty cheese.
Reasons and mechanism of formation
The main cause of cholesterosis is the failure of the fat metabolism system in the body, which is why the walls of the bladder begin to accumulate the product of lipid metabolism - cholesterol. This leads to a weakening of their contractile function.
The following factors are prerequisites for the development of cholesterosis:
- diabetes mellitus is a pathology of the pancreas associated with poor absorption of glucose due to a deficiency of the hormone insulin;
- hypothyroidism - weakened thyroid function (insufficient production of hormones);
- dyslipidemia - an imbalance of fat metabolism that develops as a result of excessive consumption of fatty foods;
- fatty liver is a pathology characterized by excessive deposition of fat metabolic products in the liver;
- bacterial overgrowth syndrome (SIBO) - the proliferation of pathogenic (bacterial) microflora in the intestines;
- abdominal obesity - fat deposition occurs in several organs of the abdominal region;
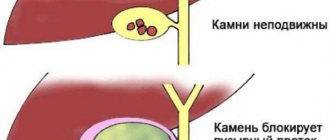
- cholelithiasis - the formation of stones in the cavity of the bladder;
- dysfunction of the circulatory and lymphatic systems;
- weakening of the evacuation and motor function of the gallbladder walls.
Lipids are transported into the gallbladder by bile. In normal condition, the healthy walls of the bladder partially absorb cholesterol, a third of which goes into the serosa, and then into the blood and lymph flow. The remaining two parts of the three cholesterol enter the gallbladder without being absorbed by their walls. Violation of this process or an increased amount of cholesterol leads to cholesterosis.
However, an increased level of this substance in the body does not always mean the presence of bile pathology. And vice versa - cholesterosis can occur even with normal cholesterol levels.
Treatment tactics
Previously, cholesterosis of the gallbladder walls was considered a disease that was not amenable to conservative therapy, so treatment was reduced to the only option - removal of the gallbladder. In modern gastroenterology, thanks to high-precision diagnostic methods, cholesterosis is detected at stages that can be successfully treated with drug therapy. Many doctors adhere to a wait-and-see approach - adjusting the patient’s diet and monitoring the condition of the organ using ultrasound. But similar tactics are used for focal cholesterosis with isolated cholesterol deposits.
Drug treatment is selected individually, taking into account the form of damage to the walls of the gallbladder, the preservation of its contractile function and the general condition of the patient. Groups of drugs used in drug therapy:
- antispasmodics and analgesics to relieve pain in biliary colic (Riabal, Drotaverine);
- medications to improve gallbladder motility and optimize the composition of bile (Magnesia, Ursohol, Gepabene), over a long course - at least six months;
- enzymes to improve the functioning of the digestive tract and the absorption of nutrients (Mezim, Creon);
- antimicrobial agents are indicated only in case of infection.
Surgical treatment of cholesterosis is carried out if there are indications:
- lack of positive dynamics from drug therapy;
- negative dynamics of the condition of the gallbladder according to the results of sonography (growth of polyps, increase in the area of cholesterol plaques);
- decrease in gall motility to 30% or less;
- development of purulent cholecystitis;
- formation of stones in the organ cavity and ducts;
- frequent relapses.
Surgical treatment of cholesterosis is carried out by complete excision of the organ - cholecystectomy. In modern surgery, cholecystectomy is performed using a low-traumatic, minimally invasive method - laparoscopic.
Clinical manifestations and possible complications
Cholesterosis most often does not manifest itself with specific symptoms, and experts are still debating whether its clinical picture is independent. Often the disease is detected in an advanced form by ultrasound diagnostics.
Signs of cholesterosis are similar to symptoms of other bladder disorders:
- Pain. They occur after eating fried, spicy foods, alcohol, smoked foods and spread to the hypochondrium on the right side. They can hit the back, lower back, and even under the right arm. They are increasing or constant, sharp or aching in nature, and can also be spasmodic.
- Nausea. Her attacks occur mainly after eating, especially fatty, spicy or fried food.
- Bitterness in the mouth. Along with dryness, this symptom most often occurs in the morning.
- Stool disorder. Constipation alternates with diarrhea.
- Yellowness of the skin is rarely observed.
- In the advanced stage, malaise and weakness are possible.
In the absence of proper treatment and proper nutrition, complications of cholesterosis may occur:
- atherosclerosis (deposition of cholesterol in blood vessels);
- inflammation of the gall bladder - cholecystitis;
- deposition of stones in the bladder;
- malabsorption syndrome - impaired absorption of nutrients;
- weight loss and other pathologies.
Symptoms
This disease very often occurs without visible signs and is practically invisible in the early stages. If cholesterosis begins to progress or worsen, you may notice the following manifestations of the disease:
- Pain in the right upper abdomen, spreading to the back, arms or shoulder blades.
- Nausea and vomiting, worse after eating fatty foods.
- Bitterness in the mouth, dryness in the morning.
- Constant constipation or diarrhea.
- Weakness, dizziness, high sweating.
If cholesterosis is accompanied by inflammation of the walls of the gallbladder, then there may also be an increase in temperature, up to 39-40 degrees.
Methods for diagnosing the disease
The main methods for identifying and confirming gall pathology are ultrasound and radiography. A gastroenterologist deals with diseases of the biliary and other organs of the digestive system.
- Before identifying gallbladder cholesterosis by ultrasound, a specialist analyzes complaints, accompanying symptoms, existing diseases, similar pathologies in relatives, the patient’s lifestyle and diet.
- Next, the doctor conducts an examination, during which he checks for obesity, signs of impaired fat metabolism (yellowish fatty deposits on the skin), and palpates the abdomen and hypochondrium on the right side.
- An ultrasound of the peritoneum is performed with a detailed examination of the biliary and bile ducts. A decrease in bladder function can often be assessed by ultrasound with a special intake of high-fat breakfasts.
- Dynamic cholescintigraphy, which involves the study of contractions of the gallbladder and the release of bile through sequential X-ray imaging.
Some laboratory tests are prescribed as additional diagnostics:
- clinical and biochemical blood tests;
- study of the blood lipid spectrum (to study the state of lipid metabolism in the body, increase cholesterol levels);
- general urine analysis;
- stool analysis to detect protozoa and worms;
- coprogram - examination of stool for the presence of large amounts of undigested fats and pieces of food.
The right diet is the key to a quick recovery
A proper diet is extremely important for patients diagnosed with gallbladder cholesterosis. The diet in this case is selected individually, but there are some generally accepted recommendations. To begin with, the patient is transferred to fractional meals - food must be consumed often, but in small portions.

Naturally, you should exclude fatty meats and fish, as well as lard and fried foods from your diet. It is also worth limiting the amount of spices and hot spices. Prohibited foods include fresh baked goods, ice cream, spinach, sorrel, processed foods, alcoholic beverages and black coffee.
The diet should consist of cereals, boiled lean meat and fish, vegetable soups, non-acidic vegetables and fruits (fiber is extremely important for the normal functioning of the digestive tract). Vitamin therapy will have a positive effect on health - patients are advised to periodically take multivitamin complexes.
How to get rid of the problem
If the disease was detected at an early stage, then a wait-and-see approach is used to begin with. For six months, a specialist monitors the condition and functioning of the gallbladder, based on which he selects a method and treatment regimen. Treatment for cholesterosis can be surgery or medication in combination with a special diet.
If the patient develops severe symptoms of cholesterosis, gallstones, cholestasis, then surgical intervention is indicated.
Surgery to remove the gallbladder is a last resort: it is used in advanced stages or complications of the disease.
Drugs from the pharmacy
The main purpose of using medications in the treatment of cholesterosis is to reduce cholesterol in bile and have a choleretic effect. To solve these problems, drugs such as Cholenzym and Allochol are prescribed.
Bile acid can be used to reduce cholesterol levels in the bile.
To restore lipid metabolism and reduce the content of bad cholesterol in the body, the doctor may prescribe:
- Drugs whose active ingredients bind bile acids and promote their excretion from the body. Due to the resulting bile deficiency, the liver begins to produce bile acids from cholesterol. Such drugs include Cholestyramine, Colestipol.
- Products with nicotinic acid that help eliminate excess fatty acids. These include Acipimox, Enduracin.
- Drugs aimed at removing cholesterol along with bile (Probucol).
- Medicines that improve the properties of bile and the quality of the bile wall, so that it can prevent the sedimentation of cholesterol. Among such drugs: Ursosan, Ursofalk and others.
Tubazh
Tubing of the gallbladder is carried out only as prescribed by a doctor and under his supervision. The procedure is carried out using a substance that has a choleretic effect. This could be Essentuki or Borjomi mineral water, sorbitol or magnesium sulfate. The liquid is drunk in small sips in a volume of 200-300 ml for 20-30 minutes. At this time, a heating pad with warm water is applied to the liver area. If the procedure is carried out correctly, the feces during subsequent bowel movements should have a yellow-green tint.
Diet food
Diet for gallbladder cholesterosis is a prerequisite for effective treatment. It involves eating food in fractions (a little, but often). The disease requires adherence to dietary table number 5, which excludes baked goods, fatty fish and meat, coffee, fried foods and many other foods. The diet should be supplemented with plant foods containing dietary fiber (whole grain cereals, bran). Along with healthy food, it is necessary to take vitamins E, K, A, D, iron, B12.
Is it possible to use folk recipes?
Treatment with folk remedies can be used as an additional measure to the main treatment of cholesterosis and must be agreed with a doctor. Beetroot juice, infusion of dandelion roots, infusion of St. John's wort and immortelle, and strawberry tea help well with the disease.
The role of nutrition in recovery
First of all, with cholesterosis it is necessary to change the number of meals. Meals should become fractional. All food should be chewed slowly. Small portions eaten 5 times a day will help the body cope with the burden on the digestive system. You can't eat before going to bed. In order not to go to bed on an empty stomach, it is recommended to drink a glass of kefir, milk or compote without sugar.
Prohibited Products
The diet of a patient with gallbladder cholesterosis is sharply limited. Fatty, spicy foods, sweet pastries, spinach, and fast food products are strictly prohibited. The diet for gallbladder cholesterosis should include only lean meats and fish. The way all products are processed should be changed. Abandoning frying, you need to bake, boil and stew food.
What is included in the diet
With a disease such as cholesterosis of the gallbladder wall, it is necessary to introduce fermented milk products into the daily menu, which will help normalize the intestinal microflora. Any fresh seafood is good for the patient’s body, as well as fiber: fruits, vegetables. For meat, choose chicken, turkey and veal instead of fatty pork to ensure a balanced and complete diet.
Traditional treatment is often long-term and requires changes in diet and daily routine.
You also cannot do without using folk remedies. Small polyps and stones may disappear completely with this therapy; they do not have to be removed surgically. The traditional method of treatment successfully helps to get rid of stagnation of bile and stones in the organ, but only under the strict supervision of a specialist. Changing your lifestyle, taking the necessary medications every day and regular consultations with a gastroenterologist will definitely give positive results.
How to behave after treatment
If cholesterosis was detected in time and treated without surgery, special attention should be paid to maintaining the functioning of the digestive system and, in particular, the gallbladder. You should avoid excessive stress, stress, and eat right.

The disease does not provoke severe changes in the functioning of the gallbladder and is often asymptomatic, so cholesterosis is characterized by a favorable prognosis.
In your diet you need to minimize fried, fatty and spicy foods, alcohol, and stop smoking. It is necessary to regularly take vitamin complexes, carry out diagnostics and control cholesterol levels. Despite the fact that the gall bladder is not a vital organ, its dysfunctions, which occur due to cholesterosis, affect digestion and human well-being.
Treatment
The widespread use of high-precision ultrasound diagnostics has helped improve the follow-up of patients with cholesterosis. The data obtained showed that the long-term presence of cholesterol polyps often does not lead to morphological degeneration of their structure. This is a prerequisite for adopting a wait-and-see approach in the management of patients with CHD.
The main guidelines for managing patients with cholesterosis are:
- long-term lipid-correcting therapy based on ursodeoxycholic acid,
- long-term ultrasound observation,
- surgical cholecystectomy if rapid growth, neoplasms, or concerns about the presence of a malignant process are detected.
Typically, control ultrasounds to assess the dynamics of the bladder wall and the nature of its contents are carried out every six months. Detection of negative dynamics, consisting in an increase in the number of polyps, as well as their size, may lead to the need for surgery. If ultrasound indicators do not exclude a malignant process, or conservative treatment for six months or a year does not produce results, then this may be an indication for cholecystectomy. In addition, monitoring of the patient's lipid characteristics is recommended:
- total cholesterol,
- low density lipoproteins,
- triglycerides,
- high density lipoproteins.
Conservative treatment of cholesterol accumulation in the gallbladder is based on diet, recommendations for changing dietary habits and developing correct eating behavior to treat this disease. Careful monitoring of body weight and eliminating bad habits is recommended. Patients are usually prescribed fractional meals within a given caloric content. It is necessary to introduce into the diet foods rich in fiber, vegetable fats, and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids.