Regular bowel movements are essential for the body. It ensures the removal of toxins and toxic substances. Obtaining energy for life support is associated with the supply of necessary substances with food. In addition, the quality of food is partly responsible for the cleansing process.
Atonic constipation is one of the types of impaired excretion of feces. We are not talking about a one-time delay, but long-term defecation failures, which cause patients not only inconvenience, but real suffering. A healthy person should have stool every day or every two days, but not after three or more days.
There are many types of constipation. They can be caused by:
- entry into the large intestine of insufficiently “processed” food residue at previous stages in diseases of the stomach, duodenum, liver and gallbladder, pancreas;
- diseases of the intestine itself with damage to secretory function, disruption of microflora;
- failure of peristalsis (a special type of contraction of the longitudinal and transverse muscle fibers of the intestine), when either muscle spasm or complete relaxation occurs;
- a mechanical obstacle to the movement of feces due to intestinal obstruction (for example, with tumors).
The atonic type of constipation is associated with the inability of the intestinal muscles to provide contractile function.
What factors ensure normal peristalsis?
Violation of intestinal contractile activity can occur due to pathology of the intestinal wall, affecting the nerve endings, against the background of a failure of the nervous regulation processes that ensure proper peristalsis.
The autonomic part of the nervous system is responsible for normal intestinal motility, which does not obey the will of the person. It independently controls internal organs through the transmission of impulses along the sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves.
The anatomy of the muscle wall distinguishes two layers of fibers: on the outside with a longitudinal direction, on the inside - circular or ring-shaped.
In the large intestine, 3 powerful ribbons are formed from longitudinal fibers
Intestinal peristalsis is ensured by a sequential change of sympathetic and parasympathetic signals that cause spasm and muscle relaxation through the release of the mediator acetylcholine. Several waves are constantly moving through the intestines.
Excessive accumulation of this substance contributes to spastic muscle contraction. The process intensifies under stress and hard work. On the contrary, with rapid utilization or lack of mediator, the muscles come to a relaxed state.
In a healthy person, both types of signals are balanced and aimed at performing the function of cleansing the intestines through the evacuation of feces. It is known that stress and physical inactivity have a significant impact on the disruption of innervation. This mechanism plays a decisive role in the pathogenesis of atonic constipation.
Another “irritant” of intestinal contraction is food. Peristalsis increases reflexively when the wall is exposed to coarse residues and undigested fiber, but decreases if easily digestible substances are supplied, which are almost completely absorbed into the blood.
With peristalsis, secretions from higher organs (bile, pancreatic juice) are delivered to the intestine. Sufficient motility is important to ensure the quality of food digestion.
Description
Colitis is the most common gastrointestinal disease. Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the large intestine becomes a consequence of the influence of external factors that have entered the internal organs of a person - viruses, bacteria, in addition, endogenous processes can become the cause.
You should not try to cope with the disease on your own, since antispasmodics and laxative enemas will show short-term results, and then only worsen the situation, the intestines will stop contracting on their own. Therefore, treatment should be carried out as prescribed by a doctor.
Causes and risk factors
The causes of an atonic state of the intestines can be any factors that cause disruption of normal peristalsis. These include:
- lack of sufficient physical activity (need for prolonged bed rest, paresis and paralysis, laziness);
- a monotonous diet of flour products, meat, fatty foods without enough vegetables and fruits is a common cause of atony in obesity;
- insufficient water consumption or drinking water with a high calcium content, significant fluid loss in the heat, with sweat, vomiting (more typical for a child);
- chronic diseases of the intestines and digestive organs, especially with ulcerative and erosive lesions of the mucous layer;
- abuse of cleansing enemas and laxatives depletes the nerve endings in the intestinal wall, leading to loss of muscle tone;
- nutritional dystrophy due to fasting is accompanied by a sharp loss of energy, atonic constipation is one of the problems of people during the recovery period after a long absence of food, and accompanies attempts to lose weight;
- endocrine diseases caused by decreased function of the pituitary gland, ovaries, and thyroid gland (especially in menopausal women and men) affect the nervous system and disrupt intestinal motility;
- The physiological state of pregnancy is close to endocrine problems; atonic constipation can take a long course and not stop after childbirth;
- in older people, muscle atrophy is important;
- increased mental and emotional stress;
- toxic effect of certain medications, consequences of poisoning with toxic substances;
- complication after intestinal surgery, infectious diseases (dysentery).

Long breaks in meals, attempts at fasting in order to lose weight, eating “on the go” lead to the opposite effect
Prevention
How to prevent the occurrence of atonic colitis? To avoid problems with bowel movements, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- To live an active lifestyle. Low mobility leads to a serious deterioration in intestinal motility.
- Do gymnastics regularly to strengthen your abdominal muscles.
- Do not overuse flour. spicy and fried foods.
- If you are over the age of 55, visit a gastroenterologist regularly.
Following these measures will help avoid intestinal problems.
Symptoms of atonic constipation
The accumulation of feces in the large intestine stretches the intestine and puts pressure on neighboring organs. Therefore, patients complain of rare bowel movements, the need to push hard, and take a special “squatting” position.
There is a feeling of fullness in the abdomen, dull pain along the intestines, in the right hypochondrium. After emptying, rocky hardness of the stool, pain in the rectum, an admixture of blood on the surface of the stool caused by hemorrhoidal bleeding are noted, local pain appears in the rectum due to cracks.
Low intestinal motility impairs liver function. Unremoved toxic substances remain in the blood. Excessive load during a long course of the disease leads to the manifestation of signs of intoxication:
- loss of appetite;
- headaches occur;
- worries about weakness, nausea;
- the temperature often rises to small numbers;
- the person becomes irritable and sleeps poorly;
- Women are characterized by tearfulness;
- increased hair loss;
- the condition of the skin worsens (dryness, itching, wrinkles on the face, pale or jaundiced tint, acne appear);
- mental disorders are possible (weakened memory, suspicion, outbursts of aggression), the mood depends entirely on how the patient went to the toilet.
Forms of colitis
The course of colitis occurs in 2 forms. Determining an accurate diagnosis is difficult due to the similarity of symptoms, and in order to establish the degree of development, you will need to undergo a number of clinical and laboratory tests.
The forms of the disease are as follows:
- Chronic – children and people over 45 years of age are susceptible to the disease. Characterized by prolonged constipation, which can appear and suddenly disappear for a while. There is an inflammatory process in the colon.
- Acute – the risk group includes older people. One-time difficulty defecating. This form is easier to eliminate than the chronic form. And most often there is no repetition.

To clarify the diagnosis, the patient must describe the symptoms in detail.
How does intestinal atony manifest in a child?
The problem of intestinal atony can occur in an infant. It is believed that up to three months the main reason is the imperfection of the digestive system. Normal bowel movements should occur 1–2 times a day, in newborns up to 8 times.
Age-related anatomical features of children are poor development of the muscular layers of the intestine, the sigmoid part of the colon has strong tortuosity, and reduced secretion of the digestive organs.
There is a complete dependence on the quality of nutrition (mother's milk), the reaction to the introduced complementary foods, as well as the great importance of adherence to the regime, environmental conditions and conditions, fear, irritation of parents, and other mental influences.

When defecation is delayed, the child becomes irritable, often cries, is capricious, and refuses to eat.
The cause of constipation in a child can be a helminthic infection. In this case, rashes appear on the skin, the baby scratches the anus area (if the helminth is pinworms), and rumbling is heard in the swollen abdomen. The attention of parents and the observation of a local pediatrician will help solve the problem.
Symptoms
The main symptom of atonic colitis is problems with bowel movements. Patients suffer from constant constipation. This is accompanied by a feeling of heaviness in the abdominal cavity, flatulence, and pain.

Patients may not have bowel movements for 3 days or more. In this case, patients do not feel the urge to defecate. In severe cases, fecal stones form, which have to be removed mechanically.
Diagnostics
To make a correct diagnosis, the doctor should learn to listen to the patient’s complaints and obtain the necessary information from them. It should be borne in mind that people with constipation always examine stool and are able to describe their condition for a long time.
With atonic constipation, when it is possible to achieve emptying, the denser part of the stool comes out first (patients talk about “stones”), and then the soft consistency. It is necessary to find out the person’s nutritional type and the characteristics of their professional activities. It is important to find out how the patient eats at work.
In a situation with constipation, it is always necessary to exclude a mechanical factor - polyps, intestinal tumors, adhesive obstruction. In men, symptoms may be caused by a tumor of the bladder or prostate. In women, adhesions are formed by chronic inflammatory diseases of the uterus and appendages, and previous cesarean sections.
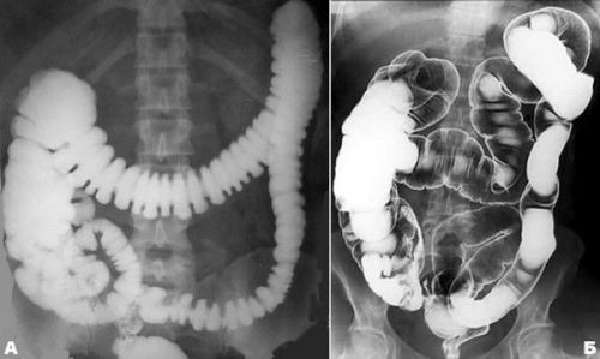
The X-ray diagnostic method using a barium suspension and subsequent examination of its progress through the intestines, as well as irrigoscopy (administration of contrast with an enema) continues to be used in clinics
The patient is recommended to undergo tests:
- general clinical and biochemical blood tests to check the functional state of the liver and pancreas, for cancer markers;
- urine;
- feces for scatology, worm eggs (the doctor will definitely prescribe it for the child);
- women are referred to a gynecologist, men need a digital examination of the prostate;
- fibrogastroscopy - will allow you to check the stomach and identify secretion disorders;
- Colonoscopy - insertion of an optical probe into the rectum to examine almost the entire large intestine - is necessary to rule out suspicion of tumor growth and identify intestinal diseases that cause constipation.
Treatment of atonic constipation with exercise and diet
Before treating constipation with medications, your doctor will advise you to pay attention to your lifestyle (adequate movement) and adjust your diet. Patients with atony need to start every morning with exercises for the abdominals and intestines.
It will be useful to alternately pull your knees to your chest in a lying position, “scissors” at an angle to the floor of 45 degrees or lower, twisting while lifting your torso up, as well as throwing your legs behind your head.
It is recommended to carry out a breathing exercise: sharply drawing in the abdomen, holding it for several seconds while inhaling, and pushing it out as much as possible while exhaling.
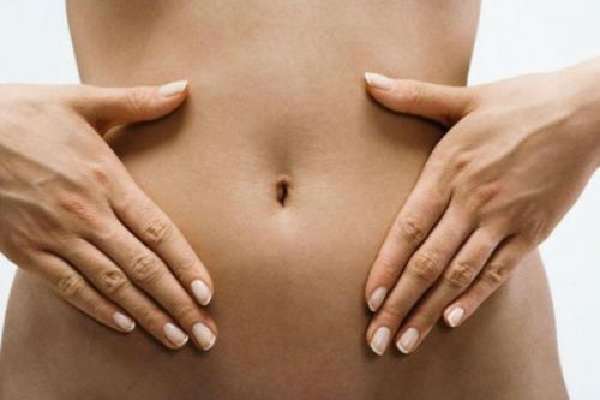

Self-massage of the abdomen - carried out clockwise using pressing movements, followed by soft deep immersion of the fingers and sharp removal
Walking is a natural reflex stimulator of the intestines. All the necessary muscles are involved in the process. Therefore, patients are recommended to spend more time walking, and be sure to walk part of the way to work.
Basic nutritional requirements:
- the frequency of meals should be 5–6 times a day;
- Long breaks and overeating are unacceptable;
- The sandwich method of eating is excluded; at work you need to adapt to heating food you brought with you or visiting the canteen.
It is necessary to limit:
- culinary products, cakes, sweets;
- fried and smoked meat products;
- coffee up to 1 cup per day;
- It is better to exclude beer and alcohol;
- sparkling water;
- hot sauces, lard, mayonnaise.
Preferences should be given to:
- cottage cheese;
- kefir and fermented baked milk;
- buckwheat porridge;
- boiled lean meat and fish;
- vegetable salads, casseroles;
- seafood;
- fresh fruit;
- rye and “Doctor” bread with bran.
It is recommended to include pureed vegetables and pureed fruits in your baby’s intestinal menu.
Drug treatment
If diet and exercise do not bring relief, the doctor prescribes special medications to stimulate the intestines. They are part of a large group of anticholinesterase drugs, all of which promote the accumulation of acetylcholine and thus restore motor function.
Itomed - used for vomiting, nausea, heartburn. Not recommended for pregnant and lactating women, children under 16 years of age, if there is a suspected mechanical obstruction or bleeding in the intestines, or if there is lactase deficiency.
Negative symptoms include:
- allergic reactions;
- salivation;
- suppression of leukocyte and platelet synthesis;
- hand tremors;
- gynecomastia in men;
- headache;
- jaundice.
Other drugs in the group do not differ in negative effects from Itomed:
- Ganaton,
- Motilium,
- Coordinax,
- Montana,
- Prozerin.
They are supplemented by Peristil, which can cause cardiac arrhythmias and requires caution in elderly patients. Kalimin 60 N is contraindicated for urolithiasis and bronchial asthma. Negative effects include constriction of the pupils, nausea, bradycardia, vomiting and increased secretion in the bronchi.
As we can see, such pathogenetic therapy turns out to be too dangerous for outpatient treatment, especially for elderly patients with various chronic diseases.
Therefore, gastroenterologists recommend using laxatives to empty the intestines. Available in tablets, drops, nutritional supplements, and rectal suppositories. It is better to use them at night.
A negative property is that the body gets used to one medicine. Lack of effectiveness with long-term use. Some drugs can cause too much irritation of the intestinal mucosa, promote further inflammation, and disrupt the bacterial flora.
The patient is recommended to alternate between different types of laxatives:
- Phenolphthalein,
- Izaman,
- Izafenin,
- Regulax,
- Lizalak,
- Bisad,
- Weakened
- Slabicap,
- Phytolax,
- Guttalax.

Long-term use of laxatives leads to a “lazy bowel” condition. Rectal glycerin suppositories are administered once. After 20 minutes, due to irritation of the rectum, the urge to go to the toilet appears. Suppositories should not be used for exacerbation of hemorrhoids and inflammation of the rectum.
To reduce dependence on laxatives, physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed to stimulate the intestines. Circular and Charcot showers, electrophoresis on the intestinal area with a solution of calcium chloride and Proserin, and diadynamic currents on the abdominal muscles are recommended.
A positive effect is expected from subaquatic baths with a water temperature of 33–34 degrees (for a stimulating effect) and underwater massage.
Treatment with enemas
Enemas for intestinal atony differ in purpose:
- Cleansing - carried out with a quantity of liquid of 1-2 liters, you can add decoctions of plants with anti-inflammatory effects (chamomile, calendula), apple cider vinegar. Emptying of the large intestine occurs immediately.
- Oil - the therapeutic effect is to soften the stool, improve movement through the intestines, the volume is 150-200 ml, it is necessary that the temperature of the solution approaches 38-39 degrees. Before the oil enema, cleansing is carried out. It is best to do the procedure before bed. Defecation should be expected after 8–10 hours.
- Hypertonic - half a glass of warm water contains a tablespoon of salt, mix the solution well, the action is based on irritation of the intestinal mucosa and nerve receptors. The enema volume is no more than 100 ml.

Contraindications to the method include any signs of suspected “acute abdomen”, appendicitis, intestinal obstruction, intestinal bleeding and the presence of rectal fissures, paraproctitis, acute hemorrhoids.