Factors in the development of gastrointestinal spasm
An illness in which symptoms of an attack of gallstone disease may appear occurs for various reasons.
One of the risk factors is female gender. Statistics show that representatives of the fair half of humanity develop this disease much more often than men. Another equally important risk factor is age. Gallstones are found in many people after 60 years of age. Obesity plays a significant role in increasing the incidence of cholelithiasis. Overweight people produce bile that is oversaturated with cholesterol. Another very significant factor is pregnancy. In pregnant women, estrogen levels increase. Because of this, the secretion of cholesterol into bile increases.
Other risk factors that cause gallstone disease (attack) are:
- rapid and significant reduction in body weight;
- diabetes;
- parenteral nutrition;
- diseases of the small intestine;
- taking oral contraceptives.
According to medical statistics, in most adult patients, an attack occurs due to the formation of stones that disrupt the outflow of liver secretions (bile). In 90% of cases, the cause of biliary colic in adolescents and young children is a disorder of the functionality of the gallbladder.
Most often, an attack of gallstones is provoked by cholelithiasis
. According to doctors, most often biliary colic occurs due to a violation of the excretion of bile. This disorder occurs as a result of blockage of the ducts, spasm of the bile ducts, and the movement of a large stone through the neck of the gallbladder.
The severity of symptoms depends on the location of the spasm, since different parts of the bile ducts react to pain differently. Moderate pain occurs in the area of the cervical duct, where it merges with the body of the gallbladder. When the ducts spasm, sharp pain appears, as they are more sensitive. As a rule, sphincter spasm occurs due to stress, excessive physical exertion, nutritional deficiencies, and regular alcohol consumption.

A reflex spasm occurs when a large stone enters the duct. For this reason, the blood supply to this area deteriorates, the outflow of bile is disrupted or stops. As a result, the sections located above the blockage expand, the contractile function of the duct increases and sharp pain occurs. Due to a violation of the outflow of liver secretions, cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder) develops, and an infection occurs.
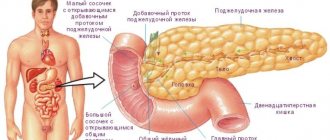
Gallbladder diseases
- Cholelithiasis. Gallstones are formed due to an increase in the concentration of cholesterol in the liver secretion, impaired contraction of the gallbladder, its ducts, and biliary hypertension. According to statistics, the risk group for cholelithiasis includes women over 40 years of age with fair skin and hair after pregnancy and who are overweight, as well as older men who abuse alcohol and have an unhealthy diet.
- Violation of the contraction of the gallbladder, as well as the bile ducts, occurs due to poor nutrition and frequent stress.
- Cholecystitis often develops against the background of cholelithiasis. There are stones in the organ that irritate its walls, provoke an increase in bile pressure, infection and an inflammatory process. In 10% of cases, acalculous cholecystitis develops, then inflammation is provoked by bacteria, parasites, an allergic reaction, diseases of the digestive organs (pancreatitis, hepatitis), etc.
- Cholangitis (inflammation of the bile ducts) occurs against the background of pathologies in which, due to infection or mechanical trauma by stones, the tissue of the bile ducts is replaced by fibrous tissue.
- Parasitic infections often provoke inflammatory processes.
- Oncological diseases. According to medical statistics, 80% of patients with chronic inflammation of the gallbladder and its ducts develop cancer. In this case, tumor cells quickly spread to other organs.
An attack of gastrointestinal tract can be triggered by appendicitis, colitis (inflammation of the colon), or ulcer. In addition, the likelihood of biliary colic increases after gallstone removal. Pain on the right under the ribs after surgery occurs due to digestive disorders, changes in the concentration of bile and its entry into the duodenum.
Diagnostics
During the initial examination of the patient, the doctor examines his medical history and family history. Be sure to palpate the gallbladder and its ducts: a feeling of discomfort and pain indicates the presence of the disease.
To make a diagnosis, the patient is prescribed the following procedures:
- Ultrasound examination of internal organs.
- Urine and blood tests with mandatory indication of bilirubin, duodenal compounds, cholesterol, alpha-amylase, fats.
- Stool analysis (to identify elements of undigested food in it).
- Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (examination of the inner layers of the esophagus, surfaces of the stomach and duodenum).
- Cholangiopancreatography (examination of the bile ducts with a duodenofibroscope).
- MRI and CT of internal organs.
Such an extensive list of examinations is explained by the difficulty of making an accurate diagnosis due to the specificity of the symptoms of cholelithiasis.
Causes of an attack of cholelithiasis
Problems associated with the formation of gallstones are quite common. The causes of an attack may be:
- sedentary lifestyle;
- poor and/or irregular diet;
- eating large amounts of fatty foods;
- chronic diseases of the pancreas;
- systematic nervous overstrain and/or nervous stress.
All these factors can lead to salt deposits and the formation of stones of various sizes.
As a rule, the disease can occur in people after forty years of age, but recently it has begun to occur very often among young people. At the initial stages of salt deposition in the gallbladder, there are practically no painful sensations or cramps, only slight bloating is present.
People who suffer from cholecystitis should undergo timely treatment from a specialist. To prevent an attack of hepatic colic from occurring in a person, it is recommended to follow all doctor’s recommendations and eliminate conditions that provoke spasms and the advancement of stones.
The very first cause of this disease is poor nutrition. It doesn't have to be just eating the wrong foods. These include frequent fasting, which causes stagnation of bile in the organs, and frequent overeating, which place a heavy burden on the body, in particular on the organs of the digestive system. Frequent consumption of excessively fatty, fried, spicy and pickled foods leads to disruptions in the food digestion system.
The main predisposing factors in the development of a crisis state include:
- Diseases of inflammatory origin, regardless of form - acute or chronic.
- Helminthic infestations and parasitic lesions.
- Constant overeating, frequent consumption of spicy, fatty, fried foods, and alcoholic beverages.
- Frequent psycho-emotional stress, depression, prolonged stay in a traumatic situation.
- Past acute respiratory viral diseases and colds, infections of the oropharynx and nasopharynx (tonsillitis, pharyngitis, laryngitis, tonsillitis, sinusitis, sinusitis).
- Infectious mononucleosis or adenovirus.
Living in unfavorable environmental conditions and genetic predisposition can cause the development of gallstone disease. Such factors provoke disturbances in the normal functioning of the gallbladder.
Causes and essence of attacks

For what reasons does an attack occur? You may not feel the gallbladder before it. At the moment of the attack, pain begins in the area where the organ is located (in the right hypochondrium).
Doctors say they are caused by:
- Physical exercise. Lifting heavy objects or changing body position most often causes an attack. A long stay of the body in an inclined position also leads to a shift of the conglomerate.
- The patient is in a stressful state. It provokes spasms of the gall muscles. By contracting, the walls of the organ push out the accumulated stones.
- Drinking large amounts of liquid. Its excess leads to dilution of bile. Having become more fluid, the secretion picks up the stones, carrying them to the ducts, like grains of sand.
- The presence of a viral infection in the body. In this case, an attack of cholelithiasis is caused by a general weakening of the immune system and inflammatory processes.
- Violation of the recommended diet. The patient's condition worsens when eating fatty or fried foods. Alcoholic drinks can also cause seizures.
An attack of cholelithiasis is a condition when a stone begins to move in the patient’s ducts. This is due to increased bile flow or spasms. In order not to provoke them, patients should not eat foods that activate the gastrointestinal tract and liver. Any pressure on the organ also leads to colic.
An attack when gallstone disease is diagnosed is observed in pregnant women in the third trimester. During this period, the fetus puts pressure on the internal organs, interfering with the normal movement of bile.
How does the disease manifest itself?
Some people have stones in their gallbladder, but patients do not have any complaints. This form of the disease is called asymptomatic (latent). Experts consider it as a period of cholelithiasis, because, according to statistics, after about 10 or 15 years, 30-50% of people experience symptoms of the disease and complications.
Another form of cholelithiasis is dyspeptic. Sick people complain of functional disorders of the gastrointestinal tract. The following symptoms are observed (they usually occur after eating, especially if fried, fatty, spicy foods, or alcoholic drinks have been consumed):
- feeling of heaviness in the epigastrium and right hypochondrium;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- heartburn;
- excessive accumulation of gases in the intestines;
- unstable chair.
Gallstone disease is a pathological process of stone formation in the gall bladder and bile ducts. Gallstone disease can be asymptomatic for a certain period of time. In such cases, the patient learns about the existence of stone deposits during an abdominal ultrasound, which may be performed for a completely different reason.
For example, an incidental finding during an ultrasound may be an echogenic suspension in the gallbladder, from which, under unfavorable circumstances, stones will later form.
In other cases, the first symptom of gallstones is biliary colic. The main manifestation of biliary colic is severe paroxysmal (paroxysmal) pain in the right hypochondrium. The pain can reach the right shoulder blade and also move to the spine. A painful attack occurs due to a stone blocking the flow of bile. Colic lasts from a few minutes to several hours, after which it gradually goes away.
Associated symptoms may include:
- nausea,
- uncontrollable vomiting,
- bloating,
- subjectively felt interruptions in the functioning of the heart.
The diagnosis of cholelithiasis is based on a typical clinical picture: biliary colic with nausea and vomiting. Jaundice, itching, discoloration of urine and feces are additional symptoms indicating the origin of the pain.
Performing instrumental studies, such as abdominal ultrasound (sometimes abdominal radiography), can confirm the diagnosis and accurately determine the location of the stones. In the diagnosis of gallbladder diseases, laboratory tests are used (transaminases, GGT, alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin concentrations divided into fractions).
For more information about how to detect the disease in time, whether it is necessary to remove the gallbladder if stones are present, and how to avoid complications, read the article about cholelithiasis.
Also read answers to questions about gallstones that our expert hepatologist often asks. Your question may already be answered!
Signs of a gallstone attack
According to statistics, in 70% of patients, cholelithiasis develops without symptoms, and it is detected only by ultrasound of the abdominal cavity. Only in the remaining 30% of cases does paroxysmal pain occur.
Signs that determine that this is an attack of gallbladder disease:

- gagging;
- yellow tint of the skin and mucous membranes;
- itching all over the body;
- temperature increase;
- urine becomes darker;
- pain in the liver area, that is, in the right hypochondrium.
Pain during an attack is always accompanied by nausea, which feels similar to food poisoning. In case of serious complications, vomiting does not improve the condition of the body. Jaundice is considered an invariable sign of cholelithiasis. It is what gives the skin a yellow tint, contributes to the discoloration of feces and the appearance of a dark tint in the urine.
The temperature can rise to a maximum of 38 ºC. If the attack is accompanied by chills and fever, this indicates the development of a purulent process. In this case, hospitalization is absolutely necessary. In an inpatient setting, the patient is given antispasmodics and sent for examination.
In extremely serious conditions, antibiotics are prescribed and detoxification therapy is used. If the process progresses, then surgery is prescribed. It follows that the main sign of the development of an attack of cholelithiasis is acute, stabbing pain.
What to do if you have an attack of gallstones
For cholelithiasis, treatment depends on what stage the disease is currently in. In the advanced stage of the pathology, in which acute attacks and severe pain occur, no independent treatment methods, especially with the help of alternative medicine, should be present.
Otherwise, a person risks not only his own health, but also his life. It is important to react to the situation correctly. Typically, biliary disease is accompanied by the presence of stones in the organ or in its ducts. The symptoms that appeared indicate that over time the stone began to move during an attack, causing blockage of bile in the bile ducts. If the attack does not stop within a few minutes, you must follow the following algorithm of actions:
- At the first sign of an attack, you should take a horizontal position. In this situation, you cannot bend over.
- Next you should take vasodilators and antispasmodics. This way the movement of the stone will become more intense, and it will move much faster and easier.
- Next, you need to use a heating pad, placing it on the sore spot. Under no circumstances should it be hot, just slightly warm. You can also place a hot heating pad on your feet, this will help the blood vessels expand quickly.
- For pain, it is recommended to take a hot bath. This procedure should not last more than 15 minutes.
- At the same time, you should drink little by little, but often, especially if nausea is present. A large amount of heated water will prevent vomiting. If a person does everything right, such events are usually enough.
- If you have chills, a hot bath can help get rid of it, or you can cover yourself with a warm blanket.
Drug therapy
Therapy takes place at the level of prescribing by a doctor and taking the necessary medications:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce inflammation in the gallbladder;
- antipyretic and painkillers;
- Opioids are prescribed if pain medications do not relieve pain.

Physiotherapeutic
The method is used when the size of the formed stone is no more than 1 cm or when several small stones are detected. Doctors recommend resorting to crushing or dissolving stones. However, with such therapy, in 50% of cases, pain in the gallbladder returns again.
Crushing stones in the pancreas
Surgical method of treating the disease
An operation is prescribed if the size of the formed stones exceeds 1 cm. Here, both the classical method of removal and manipulation can be carried out using laparoscopy.
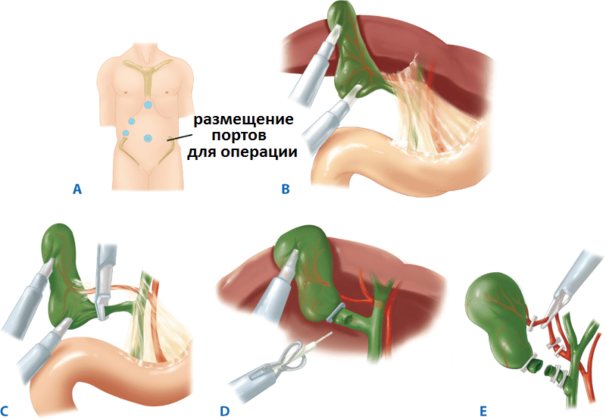
Progress of laparoscopy of the gallbladder
Sanitary resort option
The patient is prescribed a certain regime of physical activity, and treatment with mineral waters and oxygen baths is prescribed. Fresh air and a calm environment promote recovery.
Sanitary resort treatment
Why is biliary colic dangerous?
- Call an ambulance - call “033” (from a landline phone - “03”).
- Calm the patient, place him in bed on his right side, place a container for vomit on the floor next to his head. If possible, place a heating pad on your feet.
- Give antispasmodics in a large dose with a small amount of water - drotaverine ("no-spa") 6 tablets of 40 mg, papaverine 8 tablets of 40 mg.
- In the absence of antispasmodics - nitroglycerin under the tongue, 2-4 tablets.
- If there are irritating or distracting agents (Vietnamese balm, menovazin, pepper patch, capsicum, capsicum tincture, etc.), apply to the area of the right hypochondrium and under the left mammary gland (left nipple in men).
- 15 minutes after the antispasmodics, if help has not arrived, give an analgesic - ketorolac or pentalgin.
There are indications for surgery during the interictal period. In case of cholelithiasis, surgery is considered necessary if there are stones in the gallbladder with a diameter of more than 1 cm. Surgical treatment is possible using the classical method or the most common method today: using laparoscopy.
Gallstones. Scheme. View in full size
The danger of biliary colic, in addition to its painful nature for the patient, lies in the possibility of developing life-threatening complications:
- acute pancreatitis and pancreatic necrosis,
- perforation or rupture of the gallbladder with the development of peritonitis,
- cardiac ischemic attack.
The cause of pancreatic necrosis in biliary colic is a blockage of the outflow of pancreatic secretion (“juice”) from the pancreas:
- Blockage of the outflow occurs due to the fact that the gallbladder and pancreas have a common opening into the lumen of the duodenum. The occurrence of a mechanical obstruction to the movement of bile leads to an increase in the synthesis of the hormone cholecystokinin (previously called pancreozymin).
- Cholecystokinin enhances contractions of the gallbladder in order to increase pressure in the ducts to overcome the obstruction to the outflow of bile. At the same time, cholecystokinin enhances the secretory activity of the pancreas.
- When the duct is blocked by a stone, increased contractions of the gallbladder lead to increased swelling and spasm, which leads to blockage of the outflow of pancreatic juice.
- Pancreatic juice contains enzymes that break down fats (lipase), proteins (trypsin and chymotrypsin), and carbohydrates (amylase). Pancreatic cells under normal conditions produce inhibitors of these enzymes in order to avoid self-digestion. When the outflow is disrupted, the pancreatic tissue quickly swells, the synthesis of inhibitors decreases, and the concentration of enzymes in the immediate vicinity of the organ cells increases significantly. The action and concentration of inhibitors becomes insufficient for the organ’s self-defense - and membrane lysis begins, and then necrosis of pancreatic cells begins.
- Necrotic areas of pancreatic tissue uncontrollably release the supply of synthesized enzymes, which further accelerates the process. A large number of proteolytic enzymes appear in the blood, which has a systemic effect: it destroys antibodies and inhibits blood clotting. In the absence of emergency assistance, death occurs within a few hours.
Perforation or rupture of the gallbladder is a consequence of the mechanical action of stones on the wall of the organ in conditions of increased intravesical bile pressure. The entry of stones and bile into the abdominal cavity quickly infects it against the background of mechanical and chemical irritation of the peritoneum. Death from peritonitis occurs within one to several days.
An ischemic attack, up to the development of myocardial infarction, is caused reflexively due to spasm of the coronary vessels: due to the fact that the heart and gallbladder have a common innervation through the vagus nerve. Often gallstone disease, as a manifestation of cholesterol disease, is accompanied by atherosclerosis and the development of cholesterol plaques in blood vessels, including the coronary arteries. Even a slight spasm of the coronary arteries in conditions of a decrease in their internal lumen leads to a deterioration in the blood supply to the heart and myocardial ischemia.
It is important that coronary heart disease itself can provoke biliary colic, so the differential diagnosis of these conditions presents certain difficulties even for experienced clinicians.
Asymptomatic and dyspeptic forms of cholelithiasis are not the only ones. Experts also distinguish hepatic (biliary) colic. This is the most common clinical form of the disease. It is detected in 75% of sick people suffering from cholelithiasis.
Hepatic (biliary) colic is characterized by sudden and periodically recurring symptoms of an attack of cholelithiasis. In some patients, they occur due to poor diet and physical activity. In other people, provoking factors cannot be identified. The attacks begin at night, during sleep.
The appearance of hepatic colic is a clear symptom of the development of cholelithiasis. This sign has the following properties:
- the attack is acute, it is localized on the right, where the liver is located;
- pain can radiate to the back;
- the main symptom is visual swelling of the peritoneum;
- sometimes the temperature fluctuates - a person gets chills and then gets a fever;
- often an exacerbation is accompanied by a disorder of the digestive system;
- there is a heartbeat disorder.
After torturing the patient for about half an hour, the sharp pain begins to gradually subside, becoming aching. When it is impossible to anesthetize it, after a couple of hours it completely subsides on its own.
If there is only one symptom, it is impossible to judge the formation of stones, but their combination indicates the need to urgently rush to the clinic.
How to relieve an attack of gallstone disease
First aid for an attack of gallstone disease is to relieve pain in the gallbladder and get rid of the main symptoms, to prevent the development of complications of gallstone disease. How to relieve an attack of gallstone disease at home:
- In order to quickly independently relieve an attack of cholelithiasis and relieve pain during spasm, the bile ducts must be provided with rest. This will prevent further movement or sticking of the stone in the ducts,
- First aid for gallstones is to stop eating any food, drink plenty of fluids,
- take an anesthetic and vasodilator,
- put a warm heating pad on your feet to dilate the blood vessels and ensure the outflow of bile,
- If possible, take a hot bath, this will help the stones pass faster.
Next, you should call an ambulance. You do not need to use any painkillers on your own, without a doctor’s permission, especially several times a day. If the patient’s condition does not improve an hour after taking the medicine, be sure to call emergency help. Otherwise, untimely contact with specialists can lead to dangerous consequences not only for health, but also for life.
Duration and frequency of attacks
Pain in people suffering from cholelithiasis occurs suddenly. The duration of the attack can range from 15 minutes to 8 hours. Sometimes the pain continues for 12 hours. This happens with the development of acute cholecystitis. When the attack of the disease passes, the pain disappears. All that remains is an unpleasant sensation in the abdominal area.
The frequency of attacks during the disease varies from person to person. In some sick people, symptoms of biliary colic may occur every day, in others - once a week, in others - once a month. It is extremely rare to have just one pain attack.
First aid
Acute pain during an attack requires immediate relief. The spasm can be so sharp that the person cannot move normally and constantly tries to find a normal position to soothe the pain. You cannot do without the help of a specialist in the acute stage of the disease. Before the doctor arrives, you can do the following to help relieve pain at home:
- Do not make sudden movements or bend over, as this will increase the pain. Free yourself from tight clothing and lie on your right side.
- Taking a painkiller will help reduce the sensitivity and sharp pain that occurs when stones move through the ducts. People who suffer from cardiovascular diseases need to take sedatives and vasodilators. This will help relieve pressure and tension, since the spasm during an attack is quite strong and the heart needs support.
- Place a warm heating pad on your feet. If you don't have a heating pad, even a hot water bottle will do. This will also help dilate blood vessels.
- Apply heat to the area that is the source of the spasm. This will help block the pain during an attack or alleviate it a little.
- In acute attacks of cholelithiasis, painkillers can be administered intramuscularly, which will help relieve the attack of pain.
- With this method, the medicine will better spread throughout the body and relieve spasm.
- A warm bath may also be an alternative. You need to take a warm bath and lie down for a while so that the whole body warms up well and the blood vessels dilate. After this, lie down in bed and apply cold to the site of inflammation, which will help block the pain.
- When a small stone moves, the attack does not last long and does not cause acute spasms. You just need to lie down on the bed, the pain goes away after 20 minutes.
High body temperature
However, an acute attack will not allow you to remain idle, so it is better to immediately take the necessary measures. You should not wait for the attack to end quickly.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YS-xQH5QjDs
Most often, the attack is accompanied by fever and high temperature. High fever should be combated with cold compresses or rubbing. It is necessary to contact an ambulance and not wait for the next attack.
If you experience symptoms of a gallstone attack, you should urgently call a doctor. Before the specialist arrives, the patient should be given first aid:
- ensure rest (bed rest is recommended);
- give a heating pad (it must be placed on the right hypochondrium);
- suggest taking a warm bath.
At the time of an attack of cholelithiasis, it is allowed to give medications: antispasmodics (“Drotaverine”, “No-shpa”) in combination with analgesics (“Spazmalgon”, “Baralgin”). You can wait for the doctor to arrive. The specialist will tell you how to relieve an attack and administer the necessary medications in a certain dose:
- “No-shpu” (intramuscular 2 ml);
- “Papaverine”, 2% (intramuscular 2 ml);
- “Baralgin” (intravenously 5 ml);
- “Atropine”, 0.1% (subcutaneous 1 ml).
Other dangerous conditions may be hidden behind the symptoms of an attack of gallstone disease. To confirm the diagnosis, you will need to do a detailed blood test, ultrasound or fluoroscopy. If indicated, specialists will perform the following activities:
- cleaning the bile ducts;
- surgical removal of existing stones and gallbladder.
Everyone should know what to do on their own during an attack of chronic cholelithiasis. If the attack starts suddenly, emergency measures must be taken. First aid consists of lying down, providing room for your legs to rest.
When the patient is at home, you should call relatives, asking them for help. They need to come because vomiting is likely, a significant increase in the attack, when painkillers are not able to help. In such a situation, you will have to call an ambulance.
To relieve pain, you should take any of the following medications:
- No-shpa;
- Papaverine;
- Drotaverine;
- any antispasmodic.
When visiting a clinic, the doctor warns you in advance about the need to have a painkiller with you in case of an attack. Some doctors recommend that patients take a bath during an attack. It should contain water that is pleasant to the skin (temperature 37–39°). You should not stay in the bath for a long time; ten minutes of relaxation is enough.
Then you need to move to bed, preventing the warmed body from cooling down. An alternative heating method that improves vascular activity is a heating pad applied to the lower extremities. The person should be wrapped up as much as possible, since warmth is extremely beneficial for gall bladder problems.
To prevent dehydration, you need to drink more fluids. Mineral water, always non-carbonated, is suitable. You cannot draw water from the tap. Serious attacks last a maximum of half an hour, after which you are allowed to get up and continue with daily activities.
When the attack drags on, the situation is serious and a doctor’s consultation is required. Be sure to call an ambulance.
Important! The earlier a gallstone is detected, the more promising the treatment is, which does not involve surgery.
Symptoms of an attack of cholelithiasis
The doctor is obliged to warn the patient that a single attack, even with timely medical care, will not be the only one. It is important for the patient to know what to do during an attack of gallstone disease, as well as after it.
In the future, the attacks will recur and the condition will worsen. Complex therapy is necessary, but the main thing is that the person himself must change his diet to reduce the load on the liver. In extreme cases, when the disease is advanced and the doctor cannot provide effective assistance using conservative methods, a decision is made to perform an operation - cholecystectomy (removal of the gallbladder).
First aid
If the patient experiences an attack of pain in the right abdomen, which only gets worse, as well as all the typical symptoms of cholelithiasis, take the following first aid measures:
- Bed rest. You cannot get up until the attack stops.
- Starvation. It is prohibited to eat until you have fully recovered from the attack.
- When the temperature rises, cover with a blanket.
- If the pain does not increase, but does not go away, an ice pack is placed on the stomach, and in no case a heating pad.
- You need to drink water, especially if you feel nauseous. It should be warm.
- Monitor the condition as the patient may lose consciousness. In this case, urgent hospitalization is necessary.
On your own, before seeing a doctor or an ambulance, you can take a pill or give an injection of an antispasmodic: Drotaverine, Papaverine, Mebeverine in a minimal dosage. This will help relieve acute pain.
It is important to understand that these medications do not help the stone pass. If the stone remains in the duct and blocks it, the patient will only be helped in a clinical setting.
Help in hospital
Relieve pain with injections of Papaverine or Dibazol. No-Shpu or Eufillin is administered intramuscularly. Analgesics are used as auxiliary painkillers.
If these medications do not help, a potent drug is administered, for example, Tramal, Atropine, etc. If vomiting does not stop, use Cerucal. To replenish fluid losses, a drink based on a solution of Regidron or Citroglucosolan is prescribed.
Tsrukal Tramal
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YS-xQH5QjDs
Injections are a last resort treatment and are not used once the vomiting and pain stop. In this case, preference is given to tablet drugs. If swallowing is difficult, medications are administered by enema, for example, a combination of Analgin, Eufillion and belladonna.
If all the measures taken do not produce a tangible result, the doctor considers the need for surgery. Laparascopic cholecystectomy is indicated for stones larger than 1 cm in diameter. In this case, small punctures are made in the abdominal cavity and the organ is resected through them.
Proper nutrition
The main cause of an attack of the disease is an unbalanced diet, the presence of a large amount of fats and fried foods in the diet. After the attack is stopped, you can eat for the first time only after 12 hours. Let's say vegetable broth or compote without sugar. Only after a day can you return to a nutritious diet.
The recommended diet after an attack 100% excludes:
- pickled canned food, salted and pickled vegetables and fruits;
- sausages and smoked meats;
- pasta;
- baked goods;
fatty and fried;
- legumes;
- hot spices and herbs, as well as vegetables (onions, radishes, radishes, horseradish, etc.);
- alcohol.
The most useful foods after an attack of gallstone disease:
- cereal-based soups: rice, oatmeal, semolina;
- porridge, boiled or steamed in water;
- boiled vegetables and baked fruits;
- chicken and fish only boiled or steamed;
- crackers, stale bread;
- kefir, ayran, whey, matsoni, yogurt - without sugar.
It is allowed to return to the usual eating schedule 8-9 months after the attack. It is recommended to completely avoid eating spicy food, as it provokes cramps.
The first symptom of an attack of cholelithiasis is biliary colic. The condition may appear at night or 1-1.5 hours after eating. Belching and abdominal distension are not typical for colic. Common signs of an attack include:
- Sharp, and then wave-like pain in the right hypochondrium, which spreads to the epigastrium. The pain can radiate to the thoracic spine, neck, between the shoulder blades, and under the right shoulder blade. The attacks last from several minutes to several hours.
- Increased body temperature (usually no higher than 38°C).
- Bloating, nausea, vomiting that does not bring relief.
- Decreased blood pressure, changes in heart rate, hyperhidrosis.
- Shallow breathing, pain when deep breathing.
The patient may “throw around” in bed in search of a comfortable position. Colic disappears on its own if the stone enters the intestines. It also goes away after taking antispasmodics.
If there is no improvement within 6 hours, it may cause acute cholecystitis. A body temperature above 38°C may indicate an inflammatory process in the gallbladder, cholangitis and pancreatitis. If treatment is not started, fever develops, and in later stages, jaundice.
Hardening of the abdomen is life-threatening. These symptoms indicate rupture of the gallbladder and inflammation of the peritoneum. In such a situation, the patient needs emergency medical care.
A patient with biliary colic should seek emergency medical attention as immediate surgery may be required. So, what to do if an attack of cholelithiasis occurs:
- stop eating;
- put the patient in a comfortable bed, cover him with a blanket;
- give the patient an antispasmodic drug, for example, “Drotaverine”, “Mebeverine”, “Papaverine”;
The patient's relatives need to constantly monitor his condition until the ambulance arrives.
The patient is strictly forbidden to take a hot bath, warm up the right hypochondrium, or take choleretic drugs. Such actions can only harm him, since the symptoms that arise may indicate another disease in which heating is dangerous.
Help in hospital
In a medical setting, pain is controlled with intravenous painkillers. Papaverine and Pethidine are administered intramuscularly. Infusion therapy allows you to quickly relieve pain in which the patient cannot adequately respond and cannot bear it.
Before prescribing any treatment, the doctor conducts an examination. Ultrasound and radiography are prescribed. Such procedures help determine the structure, size and location of stones. Blood is drawn and urine is given. Only after this the doctor prescribes appropriate therapy. It is important to provide rest to the body; the patient must remain in bed.
After two days, if relief does not occur, the doctor considers the advisability of laparoscopic surgery. If the size of the stones exceeds one centimeter, surgical treatment is prescribed.
Nutrition rules
The key reason for exacerbation of an attack of gallstone disease is an unbalanced diet. After consuming a large amount of fried, fatty foods, or alcoholic beverages, an attack of biliary colic may occur. After the attack has stopped, you should not eat food for another 12 hours. After this, you are allowed to eat light vegetable broth, drink compote or herbal decoction.
After a day, the diet can be expanded by adding porridge with water, meat broth, boiled fish or boiled poultry, non-acidic fruits and vegetables. Mineral water and alkaline drinking are recommended. You should not eat fried and fatty foods, baked goods, pasta, sausages, smoked meats, pickles, pickled foods, sweets, chocolate, and alcoholic beverages. Meals should be fractional, the number of meals should be at least five per day, two to three hours should pass between meals.
If drug treatment does not bring the desired result, the doctor prescribes radical stone removal. But in most cases, with a correctly prescribed therapeutic algorithm, surgery can be avoided. In the future, you need to maintain proper nutrition, lead a healthy lifestyle, and introduce feasible physical activity into your life.
To avoid an attack of gastrointestinal tract, the patient must follow a diet. It is recommended to eat foods that contain minimal amounts of fat and cholesterol. Your daily diet should be supplemented with fiber-rich foods.

Improper diet provokes biliary colic
The patient should eat more fresh vegetables, fruits, wholemeal bread, brown rice, and bran. In addition, meat and fish (low-fat varieties), and fermented milk products with low fat content are not contraindicated. It is recommended to cook oatmeal, rice, semolina porridge, and soups in vegetable broth. You should also include cold-pressed vegetable oils in your menu. It is better to eat warm foods and drinks.
Some foods increase the likelihood of cholelithiasis and biliary colic:
- fatty, fried, spicy foods;
- whole milk and products made from it;
- alcohol, soda;
- coffee, tea, cocoa;
- red meat.
Compliance with nutritional rules will not help dissolve existing stones, however, by changing the diet, unpleasant symptoms are alleviated, and attacks of gastrointestinal tract occur less frequently.
It is important to know that with biliary colic you cannot sharply limit the number of calories. If the patient is overweight, he should reduce it gradually (no more than 1 kg in 7 days). If after changing your diet rules the pain does not disappear, then you need to visit a doctor.
An attack of cholelithiasis, the symptoms of which are known to every gastroenterologist, is familiar firsthand to many people. However, not everyone thinks about prevention. Changing your daily menu will greatly help in preventing attacks of gallstone disease.
First, you should avoid refractory fats. Due to insufficient bile supply, the activity of a special enzyme, lipase, decreases. This, in turn, leads to a deterioration in the breakdown and absorption of fats. People feel pain, cramping, and bloating. Only butter and vegetable oils are allowed.
Secondly, you should exclude rye bread, mushrooms, peas, beans, nuts, millet, chocolates, coffee, cocoa, and pastry from your menu. These products cause aggravation, because their digestion requires tension in the enzyme systems of the human body.
Prevention
A single gallstone attack is a warning and reminder of the need to take care of your health. To protect yourself from recurrence, it is enough to follow a number of preventive measures. The demands become extremely important after an attack. Eg:
- You should fast for 12 hours after the onset of pain;
- then they move on to drinking rosehip decoction, eating soups prepared with fresh vegetables;
- on the third day after inflammation, cereals boiled in water, cottage cheese (necessarily low-fat), milk (low-fat), broths with lean meat, bread (rye), fresh vegetables and fruits are returned to the diet - eliminating the sour taste;
- With great caution, after an attack occurs, river fish, turkey meat, and chicken (without skin) should be added to food. Discuss with your doctor the possibility of a therapeutic course of taking mineral water.
The diet, developed by nutritionists solely to prevent new attacks of gallstone disease, is accompanied by a list of prohibited foods:
- pasta (even the highest grade);
- sausage;
- spinach;
- dairy products with high fat content;
- dishes subject to heat treatment, in addition to boiling and steaming;
- forget about seasonings, pickled and highly salted foods;
- coffee;
- alcohol.
It is required to adhere to a diet during an attack and after it. The diet helps reduce the load on the gallbladder and the processing system as a whole. Take care of your diet, it is not difficult and does not require much effort.