Appendicitis is an inflammation of the appendix, the name given to a small appendage of the cecum, which can lead to serious health problems. That is why many people have a question: where is appendicitis located in a person and how does it hurt? Appendicitis is one of the most common pathologies of the abdominal organs, which can occur in any person, regardless of age and gender. Inflammation of the appendix can manifest itself in different ways, depending on the form and stage of the inflammatory process.
The disease is an inflammatory process that affects a small appendage of the cecum, which is called the appendix. This pathology requires immediate treatment, since the lack of urgent treatment measures can lead to the most dire consequences, including the death of a person.
The appendix is a small worm-shaped appendage, 7-9 cm long , which is an appendage of the cecum. The appendix is located directly in the initial part of the large intestine and performs extremely important functions:
- Takes an active part in the process of producing intestinal juice, which is necessary for complete digestion of food.
- An equally important function of the appendix is the synthesis of lymphoid cells, which are “responsible” for the level of activity of the immune system.
- Helps restore normal intestinal microflora after infectious diseases.
Inflammation of the appendix can lead to serious consequences for the body, so treatment should not be delayed under any circumstances.
What is the appendix for?
For a long time, the appendix was recognized as a kind of mistake of nature or a vestige of the evolutionary process.
For a long time, doctors and scientists could not determine its purpose, since it does not have much effect on the digestive system—very little juice collects in it. However, recently it was proven that the appendix is part of the immune system, as it contains lymphoid cells. And it is necessary to know which side of appendicitis is on, because when symptoms appear - in both women and men - the disease can develop very quickly.
It has been proven that without an appendix, people are more susceptible to certain diseases, and it is for this reason that modern doctors do not remove it without good reason. The operation is prescribed only if the appendix threatens to burst in the very near future.
On which side does appendicitis occur?
There are several options for the location of the appendix. All of them are the norm, and only isolated cases are considered a deviation.
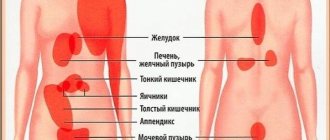
In most cases, the appendix is located slightly below the junction of the ileum and the cecum. Externally, it is below the ribs, if you point your hand slightly towards the navel.
The pelvic location of the appendix occurs periodically. This option is more common in women. Appendicitis is located behind the stomach, so pain can occur from different sides.
The apex of the appendix is usually directed downward, but modern medicine knows cases when the apex “looks” upward. This location is called subhepatic. An ultrasound is performed to determine the location of the organ.
Left or right?
Traditional localization is on the right. On the left are “mirror” people, but there are quite a few such people on the planet. The usual location of the appendix is on the abdominal side, but in approximately 30% of patients the appendix is close to the back.
If we are talking about which side the stomach hurts on, then the answer is ambiguous. The standard course of the disease is accompanied by pain in the right side, but pain can also radiate to the stomach, back, or left side. Women sometimes have pain in the groin or lower abdomen. During pregnancy, the localization of pain is higher because the appendix moves slightly upward.
Nutrition after surgery
- in the first 12 hours the patient is not allowed to eat, after which he can have rice water, fruit jelly,
- over the next 2 days, the menu expands to low-fat chicken broth, mashed potatoes, vegetable puree (pumpkin, zucchini), unsweetened natural yogurt, pureed chicken meat,
- Over the next days, you can have liquid soups, unleavened cereals, adhere to the principles of fractional nutrition, and eat in small portions.
If you know which side a person’s appendicitis is on, you can determine the inflammation by seeking help in a timely manner. You can read reviews on this topic or write your opinion on the forum.
Description of the disease
Inflammation of the appendix is usually acute. The result of the disease is the accumulation of pus, which is not able to freely exit the appendix due to its narrowness. The appendix becomes inflamed and enlarges, becoming painful. The result of this process is the rupture of the appendage and the release of pus from it. This in turn leads to inflammation of the peritoneum (acute peritonitis), sepsis or abscesses, which carry a risk of death.
The most severe complication is pylephlebitis. This is an inflammatory process of the portal vein, leading to severe liver damage and having a particularly high probability of death.
The disease progresses very quickly and rarely lasts more than 4 days, very rarely - more than a week. Cases of spontaneous healing of appendicitis are rare; sometimes the formation of a protective infiltrate around the inflamed appendix is possible, but such a formation can also lead to an abscess. Therefore, this disease requires medical attention; with timely treatment, the prognosis is favorable.
Sometimes there are patients with chronic appendicitis, which is characterized by emerging and receding symptoms that are common in acute appendicitis. The likelihood of developing the disease in the acute form is approximately 100 times higher than in the chronic form. As a rule, with this form there is no need for surgical treatment.
Acute appendicitis can be catarrhal (simple) or destructive, carrying a risk of complications. Simple appendicitis without adequate treatment almost always develops into destructive appendicitis.
Appendicitis has the following main stages:
- Catarrhal.
- Phlegmonous.
- Gangrenous.
- Perforated.
Features of structure and location
The appendix is located at the back of the cecum, three centimeters from its junction with the small intestine. It is covered on all sides by the peritoneum. For most people, its length reaches 9 cm and width from 10 to 20 mm. In some cases, the lumen from the cecum into the appendix may become overgrown. This often happens in older people. This process causes inflammation in the organ, which is an indication for removal. The inflammatory process in medicine is classified as appendicitis. The condition is very dangerous for humans and requires urgent medical attention, hospitalization and surgery. Otherwise, the disease can cause death. The location of the appendix is also influenced by the location of the cecum. Thus, the following types of appendix location are distinguished:
- lateral;
- medial;
- ascending;
- descending (this arrangement occurs in half of all people).
Important!
The internal structure of the appendix is a mucous membrane containing a large amount of lymphoid tissue. Very similar to the anatomical structure of the large intestine.
Causes
The reasons for the development of appendicitis have not been reliably established, but scientists agree that there is no single reason for the appearance of this disease that is universal for all patients.
As a rule, appendicitis is provoked by a blockage of the entrance of the appendix to the rectum. The blockage itself, in turn, may have its own reasons - for example, inflammation may be caused by foreign bodies or fecal stones entering the appendix. Also, blockage can be caused by adhesions, which are a consequence of enteritis or cholecystitis and provoke compression of the upper part of the appendix.
Bacteria - Escherichia coli, enterococci, streptococci and staphylococci - also play a great role in the development of appendicitis. Most often, both of these factors are combined. The formation of stagnation of the contents of the appendix weakens its local immunity, which facilitates the introduction of pathogenic bacteria into its mucosa.
In addition, there is an opinion that the main cause of appendicitis is spasm of the vessels that supply blood to the appendix. Another likely cause is trauma to the abdomen, leading to displacement or damage to the appendix.
Factors that contribute to the disease include poor intestinal motility, a tendency to constipation, lack of plant fiber in the diet, overeating, a number of infectious pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, and the presence of parasites. Also, the appearance of the disease can be influenced by hereditary factors, suppression of the immune system due to stress, bad habits, and lack of microelements and vitamins.
There is also an increased incidence of the disease in pregnant women - this is explained by displacement of the appendix, provoked by an enlarged uterus. Some pathological processes occurring in the uterus can transfer the source of inflammation from it to the appendix.
Symptoms
The main symptom of appendicitis is pain. Initially, the pain is transient; the pain may be weak and aching. It gradually intensifies, appearing more often and for a longer time.
The intensity of pain depends on the stage at which the inflammatory process is located. When spreading to the deep layers of the appendix, the pain manifests itself in the right part of the abdominal region and becomes permanent. It can only be suppressed temporarily with the use of painkillers.
The last, most dangerous form of the disease is accompanied by acute pain, which prevents you from walking, relieving yourself, touching your stomach, drinking or eating.
Appendicitis in adults
In addition to pain, adults also experience additional symptoms, including:
- loss or decreased appetite;
- periodic nausea and vomiting;
- chills;
- difficulty with bowel movements;
- inability to pass gas;
- false and quite painful urge to defecate;
- elevated temperature – up to 40°C.
If a person experiences at least some of these symptoms, then he needs to urgently contact a medical facility. You should not wait for the body to heal itself. Timely assistance can save lives.
Appendicitis in children
Young children themselves cannot explain what worries them, so parents must pay special attention to their child’s behavior.
You should sound the alarm if your child:
- does not allow you to touch your stomach;
- became moody or lethargic;
- refuses even his favorite dishes;
- Cries constantly for no apparent reason;
- tends to lie on his side and presses his legs to his stomach.
At the age of up to 3 years, pain in children is localized lower and is accompanied by vomiting and bloating. Older children experience pain in the right side of the abdominal cavity, in the same place as in adults. When the child moves, the discomfort increases, so he tries to move less.
An ambulance must be called even if there is a vague suspicion of inflammation of the appendix. If, in addition to other symptoms, there is an increase in body temperature to 38-40°C, then it is important to immediately consult a specialist. The appendix may rupture, which can have serious consequences.
Atypical forms
There are also several atypical forms of appendicitis, when the symptoms differ from the usual:
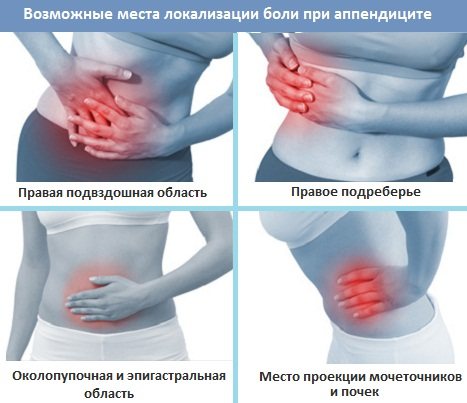
- Emypyema. This is a form of the disease with a slow development, it is characterized by the absence of Kocher's sign and the appearance of pain immediately in the iliac region.
- Retrocecal. Accompanied by mild signs of inflammation of the peritoneum and loose stools. Pain often spreads to the lower back, while radiating to the hip area.
- Left-handed. The disease in this form has a standard clinical picture, but pain is noted in the left iliac region.
- Pelvic. This form is more common in women. There is a slight increase in body temperature, dysuria, and pain radiating to the navel area.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis at home does not guarantee an accurate result, but it will allow us to assume whether appendicitis is possible in principle.
First of all, you need to touch your stomach. You need to press and evaluate its density. Inflammation of the appendix manifests itself as acute pain if you press on the right side of the abdomen or bloating if the abdomen is elastic and hard to such an extent that when pressing, the finger cannot even go a little deeper into the body.
Diagnostic measures
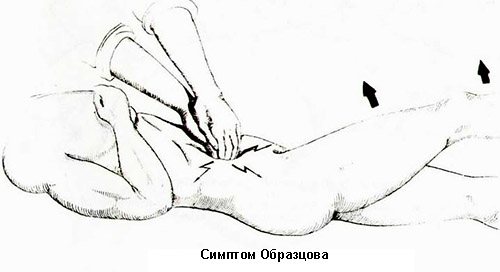
Diagnosis is carried out primarily through palpation and visual inspection. The main symptoms include a tense abdomen and pain in the lower right part, but these methods are not always effective enough.
Diagnostic methods such as computed tomography, MRI and ultrasound, urine and blood tests are also used. When reviewing blood test results, you should pay attention to an increased level of white blood cells (leukocytosis). A laparoscopic diagnostic examination may also be performed through an opening in the abdomen.
Appendicitis or not?
It should be borne in mind that recognizing the disease can be somewhat difficult, since the signs of acute appendicitis are many similar to other gastrointestinal diseases.
These include pancreatitis, acute gastroenteritis, ulcers (especially perforation), renal or intestinal colic, rupture or stretching of the abdominal muscles, inflammatory processes of the uterus. Therefore, it is important to differentiate appendicitis from other diseases that usually do not require immediate surgical intervention.
The symptoms of appendicitis are similar to viral gastroenteritis.
The difference between them lies in the source of pain. With gastroenteritis, the pain appears widespread and its source cannot be found. With appendicitis, the pain is localized in the area of the appendix, and it is from there that the discomfort comes.
There are many other diseases that are characterized by abdominal pain. Appendicitis can be excluded only in a state where there is no vomiting, nausea, fever, or loss of appetite. If your stomach hurts for more than 3 days, you should consult a doctor.
Stages of development of appendicitis
photo: stages of appendicitis
Catarrhal stage
The catarrhal stage lasts the first 10-12 hours and is manifested by dull, mild pain in the iliac region and around the umbilical ring. Nausea, one-time vomiting, frequent urge to urinate, loose frequent stools, and a gradual increase in body temperature above 37 degrees are possible. General weakness, dry mouth with white skin appears, pain becomes more pronounced, more paroxysmal.
This is the best time for surgery. On examination, softness of the abdominal cavity is observed; when palpating the right area, the patient experiences increased pain.
Phlegmonous stage
Soreness manifests itself in the lower abdomen. Intoxication of the body becomes pronounced (constant nausea, diarrhea, possible vomiting). Body temperature becomes low (below 36 degrees). The swelling is very noticeable, and pain on percussion increases.
Gangrenous stage
Gangrenous appendicitis is the penultimate stage of acute purulent appendicitis, in which necrosis of the wall of the intestinal appendix develops. The consequences of such a disease are very dangerous, especially for children: a perforation of the wall and a breakthrough of pus into the abdominal cavity may occur. The symptoms of gangrene of appendicitis differ markedly from other types of this disease, so it is especially important to promptly assess the danger and consult a doctor to immediately begin comprehensive treatment.
Perforated stage
The perforated stage appears at the end of the third day. Acute, throbbing pain becomes cramping and sometimes radiates to the intestines. Frequent vomiting, a brown coating appears on the tongue, the temperature rises to a critical level. Intestinal peristalsis does not work, laxatives do not help. Peritonitis (blood infection due to a ruptured appendix) may develop. The pain is paroxysmal, severe, sometimes radiating to the lumbar region. It is strictly forbidden to endure for a long time; delay can result in death.
The time frame for the stages of the disease is arbitrary. In each case, the development of the disease proceeds differently (both a sharp course and a less pronounced, hidden one).
The only solution is surgical removal of the inflamed appendicular process.
Other manifestations that, together with pain, indicate appendicitis:
- Lost appetite.
- Vomiting is not constant, 1-2 times.
- Bloating.
- Fever, temperature up to 38 °C.
With these signs you need to consult a doctor.
Absolutely forbidden!
Before being examined by a doctor, you should not take painkillers or any other medications or give an enema. Due to self-medication, the symptoms of appendicitis may change.
How to quickly check whether there is appendicitis or not
"fetal position" for appendicitis
To determine the disease, the hospital does a blood test, urine test, and may conduct an ultrasound or other examinations. But first you will be examined by a surgeon. He will feel your stomach and make a diagnosis. You cannot put pressure on your stomach yourself, as this can lead to rupture of the organ.
Simple techniques will help you recognize appendicitis
Tests that you can carry out yourself, but keep in mind that self-diagnosis must be carried out very carefully:
- Cough. When coughing, the pain on the right will intensify.
- Curl up ( fetal position ) on your right side. In this case, the pain should subside.
- Turn on your left side and stretch your legs. With appendicitis, the pain will become more severe.
- Apply gentle pressure with your palm to the area of your abdomen where it hurts the most. Hold your hand here for 5-10 seconds. The pain will ease slightly. Now remove your hand. If pain appears at this moment, this is a sign of acute appendicitis.
When you need to act urgently
There are a number of symptoms that indicate complications:
- Increasing abdominal pain.
- Vomit.
- Weakness, lethargy, cold sweat.
- Frequent heartbeat.
- Pallor.
- Temperature above 38 °C.
Frequent cases in medical practice of non-typical location of the appendix in humans
The frequency of cases where the appendix is located variable (atypically) in relation to the cecum:
- descending location of the appendix (pelvic): 50% of cases,
- lateral: 20% of cases,
- medial: 20% of cases,
- posterior (retrocecal): 10% of cases
- ascending (subhepatic): rarely,
- anterior (ventral): rarely,
See photo of appendix location
Video: How to distinguish appendicitis from other abdominal pain
Treatment
Since the symptoms of appendicitis are similar to a number of other diseases, the attending physician will conduct a careful examination of the abdomen, prescribe diagnostics and tests. Treatment is carried out only when the diagnosis is confirmed.
Appendectomy
Unfortunately, there is only one successful way to combat this common disease. This is an appendectomy - an operation during which surgeons cut out the appendix. Most modern specialists prefer to remove this organ through another surgical intervention - using laparoscopy.
After open surgery, the patient is left with a large scar, but it allows the appendix to be removed very quickly. This procedure is often performed in emergency cases, if there is no time for diagnosis and examination of the insides.
Appendectomy is not a complex operation, and after the anesthesia wears off, the patient can stand, sit, or even walk. It is also worth noting that it is recommended to limit stress on the body during the next month after surgery.
During the recovery period, you need to do dressings, take antibiotics, and undergo prescribed procedures. If necessary, the doctor prescribes painkillers.
In addition, the patient is prescribed a diet. He is allowed to eat non-solid food; it is not recommended to eat flour, citrus fruits, sweet, salty, spicy and fatty foods. Cigarettes and alcohol are prohibited.
Laparoscopy
Laparoscopy for appendicitis is a modern operation that allows you to remove the appendix with minimal damage. This type of intervention leaves only small scars, and painful sensations disappear faster, reducing the length of stay in the hospital.
The point of laparoscopy is to create several small incisions, rather than one large one. The abdomen is explored through these incisions, making a quick operation inconvenient.
The recovery period differs from standard surgery in that it does not require a special diet, you are discharged from the hospital earlier, and recovery after laparoscopy is faster.
What does appendicitis look like on an ultrasound?
Normally, the appendix during ultrasound examination looks like a hollow tube consisting of several layers with a diameter of up to 6 mm. When inflamed, the walls of the organ thicken, and it looks like a curved, fluid-filled tube. Free fluid is also detected in the abdominal cavity, which confirms the inflammatory process. Ultrasound not only helps to confirm or refute appendicitis, the method also determines other possible causes of the patient’s complaints.
Computed tomography allows you to get photos of appendicitis and possible complications. This method allows for layer-by-layer photography of the human body. If the diagnosis of appendicitis is refuted, CT allows one to determine the cause of the patient’s complaints.