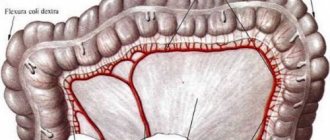
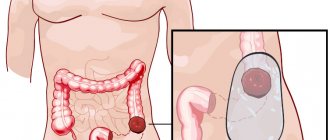
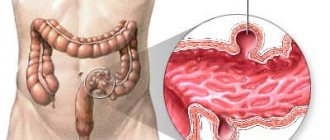
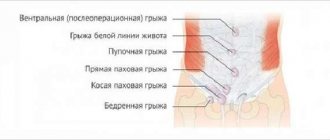
Diverticulosis, or diverticular disease, is a disease characterized by the formation of pouch-like protrusions of the colon wall of a congenital or acquired nature, called diverticula (from the Latin diverticulum - road to the side). Congenital, or true, diverticula are formed during embryonic development due to disorders of histogenesis. Acquired (false) diverticula occur as a result of protrusion of the intestinal mucosa through defects in the muscular layer.
The muscular layer of the intestine is most poorly expressed between the longitudinal muscle bands (taenia), so it is here that diverticula most often form. They are often localized where blood vessels enter the intestinal wall. The reasons that contribute to the occurrence of diverticula are inflammatory processes in the intestine, weakening its wall, and an increase in intraluminal pressure (constipation). Diverticula have a neck 3-5 mm long and a body with a diameter of 0.5-1.5 cm. In terms of frequency, they occupy first place among diverticula of other parts of the gastrointestinal tract.
True and false diverticula
As noted above, a distinction is made between true, or congenital, and false, or acquired, diverticula. Structurally, true diverticula are formed by all layers of the colon wall. In contrast, false diverticula are devoid of a muscular layer and are hernia-like protrusions of the mucous and submucosal layer. Congenital diverticula are usually single and are found in the right half of the colon. Most diverticula occur in adults and are acquired. The location of diverticula in relation to the circumference of the intestine is quite characteristic.
They never penetrate taenia. Most of them occur on the lateral walls of the intestine between the mesenteric and two antimesenteric taenia. A diverticulum consists of a narrow neck passing through the muscular layer of the intestine and an expanded body located outside the muscular layer.
Apples

A remedy made from green apples and wheat germ helps prevent inflammation of the diverticulum. The drug is aimed at cleansing the intestines and enhancing the protective properties of the mucous membrane. For preparation you will need:
- Take sprouted wheat and green apples in equal quantities.
- The wheat needs to be crushed, the apples must be peeled and cored, and ground in a blender.
- Mix the ingredients.
- During breakfast for a month you need to eat 300 grams of apple-wheat porridge.
- Take a break for 28 days, then take the course again, and so on throughout your life.
According to reviews, treating diverticulitis with a folk remedy made from apples is very tasty! Some write that they didn’t take breaks, and it didn’t get any worse!
We talked about the most effective, judging by reviews, folk remedies for the treatment of intestinal diverticulosis. But we remind you once again that before using even the most harmless drug, you need to consult a doctor.
Predisposing factors and pathogenesis
Diverticula were first identified by Morgagni in 1700. Colon diverticulosis often occurs in people over the age of 40, and the disease becomes more common with age. The bulk of patients (up to 80%) are people over 60 years of age. Diverticulosis often occurs in countries where the population consumes waste-free foods and large amounts of refined carbohydrates. Almost 80% of patients have multiple diverticula. Any part of the colon is affected, but the most common (68% of cases) is the sigmoid.
Read also Causes of malabsorption syndrome
For the formation of diverticula, in addition to these factors, impaired intestinal motility and increased intraintestinal pressure (intestinal hypertension) are important. In the occurrence of increased pressure in the intestine, the process of segmentation plays an important role, which normally contributes to the portioned movement of feces through the intestines. Intraintestinal pressure in closed segmentations and spasms of cavities can increase 10 times or more compared to normal. As a result of a prolonged spastic state, significant thickening of the muscles of the intestinal wall occurs.
Subsequently, a hernial protrusion of the mucous membrane occurs through weak areas of the muscular layer of the colon. As the diverticulum enlarges, its wall becomes depleted and the mucosa atrophies. Stagnant feces in the diverticulum cause the formation of erosions, ulcers, and the development of an inflammatory process (diverticulitis).
Products for treatment
There is no officially proven effect from the use of traditional medicine for intestinal diverticulum. Experiments with health can cause more harm than treatment agreed with a doctor.
Due to stagnation of feces in the intestines and difficulties during bowel movements, an inflammatory process occurs. To ensure the normalization of peristalsis, people recommend using green apples and sprouted wheat grains. The course lasts up to 30 days. Then there is a break.

Oatmeal jelly brings a noticeable effect in the treatment of diverticulosis. Use it warm during the day. Preparing oatmeal jelly takes a lot of time. You should avoid eating processed or ground oatmeal.
Psyllium seeds contain a large amount of fiber. The main reason for the development of diverticula is the human diet, which contains a small amount of plant fiber. The presence of this substance enhances the motility of the organ.
The amount of fiber in plantain seeds exceeds the content of certain types of cereals. The scheme for using seeds is as follows:
- The product is filled with liquid (kefir, yogurt, juice).
- After the composition is prepared, you must immediately consume it in small sips.
- After half an hour, the patient drinks a glass of water.
The peculiarity of taking the seeds is that they enter the large intestine already in an enlarged form. A stimulus is generated to increase peristalsis of the organ. It is allowed to take the drink until the manifestations of the pathology are completely eliminated. It is allowed to treat the disease with a folk remedy in the absence of concomitant diseases.
Flax is one of the traditional medicines. It has a positive effect on the digestive system. Seeds and oil are used in folk remedies therapy.
The oil is consumed on an empty stomach in the morning. Throughout the day, the mucous membrane of the organ is protected. The effect of using the seeds is similar to that of plantain seeds. Diverticulosis is treated with swollen seeds.

Bran contains a large amount of fiber and nutrients. The product must be introduced into the diet gradually. The scheme for introducing bran is discussed with the attending physician. The specialist takes into account the patient’s weight, age and characteristics of the course of the disease. Bran can be mixed with fermented milk products and act as a side dish. There is a restriction when consuming the product (a tablespoon of bran).
Symptoms of diverticulosis, diverticulitis
There are 4 clinical variants of colon diverticulosis.
- asymptomatic diverticulosis;
- chronic diverticulitis;
- acute diverticulitis;
- complicated diverticulitis.
Asymptomatic diverticulosis is characterized by a long latent course. Patients make no complaints. The diagnosis of the disease is confirmed by instrumental examination as an accidental finding.
Chronic diverticulitis is manifested by mild nagging pain or discomfort in the left half of the abdomen, flatulence (increased gas production), discharge of mucus and blood from the anus, unstable stool (diarrhea-constipation), and a feeling of incomplete emptying of the rectum during bowel movements.
Acute diverticulitis occurs in approximately 20% of patients with diverticulosis. It manifests itself as sudden severe pain in the left half of the abdomen, stool retention, increased body temperature, increased heart rate, leukocytosis, muscle tension in the anterior abdominal wall, local symptoms of peritoneal irritation, etc.
Read also Diarrhea (diarrhea) - causes, symptoms, treatment
Acute diverticulitis can cause a number of complications: peri-intestinal abscess, internal fistula (enterovesical, sigmoid-uterine, sigmoid-vaginal, rectal bleeding, often profuse, requiring surgical intervention).
Diverticula of the right half of the colon are much less common. They, as a rule, are true, solitary, and not prone to recurrence and perforation. When these diverticula become inflamed, acute pain is observed in the lower abdomen or throughout the entire abdomen, which after some time is localized in the right iliac region. Nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, constipation or diarrhea may also occur. An objective examination reveals muscle tension in the right iliac region. Body temperature rises, leukocytosis is observed in the peripheral blood. Clinically, such cases are very difficult to distinguish from acute appendicitis. Inflamed cecal diverticula usually form so-called inflammatory tumors, which are difficult to distinguish from cecal cancer even during surgery.
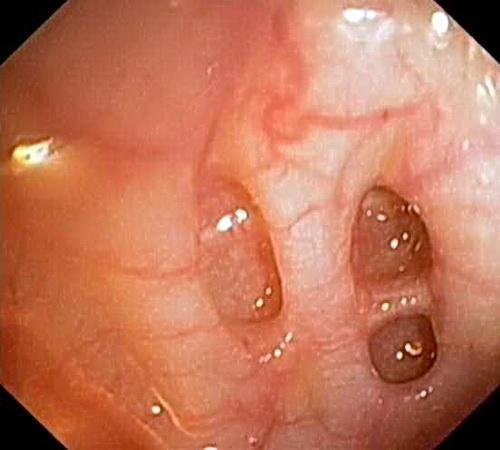
Complications of diverticulitis
1. Against the background of diverticulitis, perforation of the diverticulum into the free abdominal cavity can occur (in 2-27%) with the development of peritonitis. When perforation occurs in the retroperitoneal tissue, phlegmon develops. When perforation occurs in the tissue located between the layers of the intestinal mesentery, a paracolic abscess develops.
2. Another complication of diverticulitis is the formation of abscesses in the closed cavity of the diverticulum. When an abscess breaks into the abdominal cavity, peritonitis develops, and into a hollow organ - an internal fistula.
3. Long-term diverticulitis leads to the occurrence of adhesions, which often results in the development of intestinal obstruction.
4. Bleeding (from arrosion of the arterial trunk located at the neck of the diverticulum) occurs in 3-5% of patients with diverticulosis. Bleeding occurs suddenly, is often profuse and is manifested by general (weakness, dizziness, pallor, tachycardia, etc.) and local (admixture of altered blood in the stool) phenomena. Up to 30% of patients with bleeding are subject to surgical treatment. Before surgery, it is necessary to know exactly the location of the source of bleeding, for which colonoscopy is used.
Read also Colon cancer - signs, diagnostic methods
Rules for treatment with folk remedies
Colon diverticulosis affects the functioning of the entire digestive system. The use of traditional methods is aimed at normalizing the activity of the damaged organ and minimizing symptomatic manifestations. The goals are to strengthen intestinal motility and normalize the patient’s stool.
The main point is to coordinate the use of alternative medicine with the doctor. The use of some herbs and plant parts may have the opposite effect and cause harm.
The rules for using traditional medicine recipes are:
- Prohibition on independently changing the ingredients, dose or time of treatment. The above is strictly agreed with the attending physician.
- The cooking instructions must be strictly followed.
- The quality of the products from which the composition will be prepared should not raise doubts or complaints.
- Confidence that no component of the prepared product will cause allergic reactions.
- Treatment is stopped immediately if there are signs of deterioration in health, changes in the color or condition of the skin and other signs of intolerance.
Diagnosis of diverticulosis
The diagnosis of colon diverticula is made on the basis of anamnesis, clinical picture and radiological data. X-ray examination using a barium enema and subsequent contrast is of primary importance in the diagnosis of diverticulosis. During irrigoscopy, diverticula are revealed as a rounded depot of barium suspension extending beyond the intestine. With double contrast, the remaining tightly filled diverticula are clearly visible against the background of the CO relief. With fistulas, narrow passages are identified that are located outside the intestinal lumen and communicate with its lumen.

Choosing surgery for diverticulosis
The optimal operation is considered to be a one-stage resection of the affected area of the intestine. It is considered advisable to combine these operations with colon myotomy, which leads to a decrease in intraluminal pressure. In case of bleeding, surgical treatment consists of suturing the bleeding vessel and intussusception of the diverticulum into the intestinal lumen or resection of a section of intestine. The mortality rate during emergency operations reaches 20%. The use of the latter is considered acceptable in complicated forms of diverticulitis (free or covered perforation without symptoms of severe peritonitis, internal and external fistulas), when it is possible to connect the unchanged ends of the colon.
If an unreliable anastomosis is suspected, a discharge fistula should be placed on the transverse colon. In the presence of an abscess, severe inflammatory changes in the intestinal wall, or acute intestinal obstruction, a two-stage surgical intervention is indicated (Hartmann's operation or resection with removal of both ends of the intestine in the first stage and restoration of intestinal patency in the second).
In case of profuse bleeding, the most radical operation is considered to be subtotal colectomy with immediate or delayed ileorectal anastomosis.