Zenker's diverticulum is located in the region of the pharyngoesophageal junction. It is one of the types of esophageal diseases. It is a protrusion of the esophagus in the form of a pouch. The main signs of the disease are bad breath, frequent belching, difficulty swallowing and a dry cough. As the disease develops, the formation of a soft, round-shaped structure becomes noticeable on the patient’s neck, which changes size when eating food.
To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor performs an examination. Esophagoscopy and x-ray examination of the esophagus with a contrast agent will provide the necessary information about the condition of the organ.
If the diagnosis is confirmed, it is recommended to eat foods in fractions and rinse at the end of meals.
If a person seeks help late, an endoscopic or open diverticulectomy is prescribed.
Reasons for education
Esophageal diverticula can be congenital or acquired. In the first case, the formation appears due to weakening of the muscular walls of the organ.
The development of this process can be facilitated by the presence of bad habits of the expectant mother when carrying a child, depressive or stressful situations, and premature birth.
In the second case, disorders occur due to the transfer of pathological processes in the organs of the digestive system, chronic forms of these diseases, such as:
- Tuberculosis of the lymph nodes.
- Esophagitis.
- A consequence of reflux esophagitis (when the organ is irritated by the acidic environment of gastric juice).
- The presence of fungal infections in the organ.
- Esophagospasm (a disease of the esophagus affecting the nervous and muscular systems).
- Damage to the mucous membrane of an organ due to burns or medications. This leads to traumatic narrowing of the organ.
This list includes the individual characteristics of the body, heredity, genetic predisposition, and age-related changes.
If several causes are detected, the disease develops faster and more rapidly.
Diseases of the esophagus
Bifurcation diverticula are classified as tractional, the rest are classified as pulsational, see Diverticum disease. A diverticulum of the cervical esophagus occurs as a result of weakness of the posterior wall of the pharyngoesophageal junction (Lymer's triangle) on the one hand and dyskinesia of the cricopharyngeal muscle on the other. The most likely cause is considered to be a lack of coordination of the contractile activity of the cricopharyngeal muscle, which acts as the upper esophageal sphincter. As a result of premature contraction of the upper sphincter, an increase in pressure occurs, and the mucous membrane of the Kimian triangle protrudes, forming a diverticulum. This is a sac-like protrusion of the mucous membrane of the esophagus located above the area of the cricopharyngeus muscle, forming first on its posterior wall and then moving to the sides. Quite often, a saccular diverticulum filled with food masses causes external compression and obstruction of the esophagus.
Symptoms
After esophageal diverticula form, the patient begins to experience unpleasant symptoms and discomfort.
How are they expressed:
- Incoming food does not pass well through the esophagus, causing dysphagia.
- When swallowing food, the patient experiences pain.
- Infants experience frequent regurgitation.
- In adult patients, frequent belching and unpleasant odor from the mouth are noted.
- Presence of dry cough and tickling.
As the disease progresses, the patient experiences significant changes in his voice; it becomes hoarse and hoarse.
There is rapid weight loss. It is impossible to fully eat meals.
This process is accompanied by suffocation, redness of the skin on the face, and the patient may choke when swallowing food.
With a rapid increase in the size of the formation, the following signs are noted:
- Severe pain is felt in the chest area. Based on this feature, it is easy to confuse the pathology with a disease of the heart muscle.
- Frequent belching. During this process, undigested parts of food are released along with air.
- When swallowing, a gurgling sound is felt.
- Coughing attacks that bother you even during sleep.
- There is an increase in body temperature.
If the sacs form in the lower part of the organ, a disturbance in the rhythm of the heart muscle may occur.
Medical practice test
Medical practice GOS. Test on medical practice Topic Diseases of the esophagus. Test topics. Human anatomy 2. Pathological anatomy 3. Normal physiology 4. Pathophysiology 5.
Biology 6. Microbiology 7. General and clinical immunology 8. Medical and biological physics 9. General and bioorganic chemistry Biochemistry Pharmacology Military and extreme medicine Forensic medicine Hygiene and fundamentals of human ecology Public health and healthcare Biomedical ethics Philosophy Jurisprudence Pulmonology Gastroenterology and hepatology Nephrology Hematology Endocrinology Propaedeutics of internal diseases Rheumatic diseases Polyclinic therapy and medical and social examination Phthisiopulmonology Nervous diseases Psychiatry, narcology and medical psychology Radiation diagnostics and radiation therapy Pediatrics Dermatovenerology History of the Military Medical Academy Occupational diseases Military field therapy Infectious diseases Clinical pharmacology History of the Fatherland, cultural studies, political science, sociology and economics History of medicine Histology, cytology and embryology Cardiology Anesthesiology and resuscitation Diseases of the thyroid gland Breast diseases Diseases of the heart and blood vessels General surgery Diseases of the lungs and pleura Hernia of the diaphragm and abdominal wall Diseases of the esophagus Diseases of the stomach and duodenum Diseases of the intestine Diseases of the rectum Diseases of the biliary tract and liver Diseases of the pancreas Outpatient surgery Dentistry and maxillofacial surgery Traumatology and orthopedics Urology Military field surgery Pediatric surgery Otorhinolaryngology Ophthalmology Operative surgery and topographic anatomy Obstetrics What clinical signs are found in benign neoplasms of the esophagus?
Choose the correct combination of answers:. What complications are possible with scar post-burn stricture of the esophagus in the long-term period: a chronic esophagitis; b bleeding; in esophageal cancer; d esophageal polyposis; d perforation of the esophagus; e regurgitation. What research method is indicated to identify esophageal diverticulum?
What research methods are the most informative for diagnosing benign neoplasms of the esophagus? What tests should be ordered if esophageal cancer is suspected? What method is used to treat benign tumors of the esophagus: a extirpation of the esophagus; b enucleation of an esophageal tumor; c resection of a segment of the esophagus; d radiation therapy; d chemotherapy.
Indications for surgery for esophageal diverticulum should be considered: a diverticula with a contrast suspension delay of less than 2 minutes. Which of the following clinical signs are characteristic of cardiospasm?
A 20-year-old patient mistakenly took a caustic soda solution about 3 months ago. Currently, rapidly progressing dysphagia has developed. X-ray reveals a cicatricial stricture of the middle third of the esophagus. Its diameter does not exceed mm. Treatment indicated:. Which of the listed methods of treating cardiospasm should be used in case of persistent and long-term course of the disease?
A 58-year-old patient develops painful heartburn and regurgitation of eaten food due to constant intense pain in the chest. Pain often radiates to the interscapular space and left shoulder. The ECG shows minor changes in the myocardium. Which study would you prefer? The patient complains of increased salivation, a scratching sensation in the throat, awkwardness when swallowing, and cough.
Periodically, after starting to eat, dysphagia and swelling in the neck appear. Sometimes, in order to swallow food, you have to take forced positions, while gurgling sounds are heard, and the swelling disappears. Your diagnosis: A 47-year-old patient is emotionally labile, has satisfactory nutrition, and complains of dysphagia, heartburn and chest pain, which is more pronounced with emotional stress. Substernal pain lasts from several minutes to an hour, radiates to the jaw, back, pain occurs at night, when walking towards a cold wind.
Nitroglycerin reduces pain; after belching or after drinking soda, the pain also decreases. There is no pathology on the ECG. X-ray of the esophagus is also without pathology. A 55-year-old patient suffering from liver cirrhosis was admitted to the surgical department with moderate bleeding from esophageal varices. The patient has been ill for about 3 years, complaining of difficulty passing food, regurgitation once a day, and periodic chest pain.
The patient is somewhat undernourished, blood tests are within normal limits. For what types of cardiospasm is surgical treatment indicated?
Diagnostics
When the first signs of the disease appear, you must immediately contact a specialist.
An experienced doctor will carefully examine the clinical picture, carry out all the necessary diagnostic methods, and prescribe the correct treatment.
Additionally, you will need to undergo laboratory tests of blood, urine, and stool.
The doctor can detect abnormalities by palpating the patient during an examination of the cervical spine.
Characteristic protrusions with a soft consistency will protrude on the neck. When the formations are compressed, they noticeably decrease in size.
X-ray of the esophageal cavity allows us to establish the presence and location of the sacs.
Also, using this method, you can find out their size and the presence of pathological changes. These include oncological tumors, fistulas, and polyps.
Plain radiography and computed tomography of the sternum can clarify many details when pathology is detected.
Thanks to the images obtained as a result of the study, large diverticula can be seen. They will look like formations filled with liquid and air.
Thanks to esophagoscopy, it is possible to examine the cavity of the formation itself. The method allows you to detect the presence of ulcerative lesions of the mucous membranes, identify the appearance of bleeding, tumor neoplasms, and analyze endoscopic biopsies.
Due to the high risk of damage to organ diverticula, this technique is performed with extreme caution.
Esophageal manometry allows you to study esophageal motility. Differential diagnostics are also carried out.
It is necessary for heart diseases, the presence of a hernia in the esophageal opening of the diaphragm, cysts, and malignant neoplasms.
Quiz with answers: “Diseases of the esophagus”
What clinical signs are found in benign neoplasms of the esophagus a dysphagia b weight loss c sensation of a foreign body in the esophagus d heartburn d aching pain in the epigastric region e putrefactive breath hiccups Select the correct combination of answers:. What complications are possible with scar post-burn stricture of the esophagus in the long-term period: a chronic esophagitis b bleeding c esophageal cancer d esophageal polyposis d esophageal perforation f regurgitation Select the correct combination of answers:. What research method is indicated for identifying esophageal diverticulum? a X-ray examination b mediastinoscopy c electrokymography d esophagomanometry e ultrasound. Which research methods are the most informative for diagnosing benign neoplasms of the esophagus a X-ray examination b esophagomanometry c echography d esophago-ionometry d esophagoscopy Select the correct combination of answers:. What studies should be ordered if esophageal cancer is suspected: a esophagomanometry b esophagoscopy with biopsy c X-ray examination of the esophagus and stomach d electrokymographic study of the esophagus d computed tomography Select the correct combination of answers:. Which method is used to treat benign tumors of the esophagus: a extirpation of the esophagus b enucleation of a tumor of the esophagus c resection of a segment of the esophagus d radiation therapy d chemotherapy Choose the correct combination of answers:.
Treatment
After a detailed study of the clinical picture, laboratory tests and a detailed examination of the patient, a diagnosis is made and treatment is prescribed.
Treatment of esophageal diverticulum directly depends on the degree of development of the disease and the size of the formation.
For small diverticula (up to 2 cm), therapy is carried out using non-surgical methods.
For these purposes, conservative therapy is used. The doctor prescribes medications that can reduce the acidity of gastric juice. If the formation is large, surgery is required.
Conservative therapy
Conservative treatment requires taking medications to reduce the acidity of gastric juice.
Be sure to follow a balanced diet. It is necessary to carry out all preventive measures aimed at preventing the development of possible complications.
What needs to be observed:
- Special dietary food. Provide exceptionally healthy and healthy nutrition. They give preference to fruits, vegetables, cereals, lean meats and fish, which must be thoroughly boiled. This measure will prevent the formation of injuries. As a heat treatment, preference is given to boiling, stewing, light baking, and steaming. Avoid spicy, overly salty, fried, fatty foods.
- Provide the patient with a drinking regime. The daily fluid intake should be 1.5-2 liters. Purified still water is used as a liquid.
- To treat the inflammatory process, it is necessary to rinse with antiseptic solutions.
Additionally, it is important to walk more in the fresh air and give up all bad habits that have a detrimental effect on the condition of the entire body.
You need to avoid overeating and get rid of the bad habit of eating before going to bed.
In some cases, drug therapy may not be effective. This can be facilitated by the individual characteristics of the body and concomitant diseases.
Application of devices
The use of laser and electrocoagulation gives positive results in the treatment of this disorder.
With their help, it is possible not only to prevent the development of multiple formations, but also to restore the structure of the surface layer of the mucous membrane.
The use of a laser in a medical facility, where professionals and masters of their craft work, gives amazing results.
This technology is not suitable for all patients because it is expensive.
Surgery
In cases where conservative methods of therapy have not brought the desired result, the esophageal diverticulum is removed.
This measure is extremely necessary in cases where there is a risk of developing serious complications that can lead to death.
Excision of an esophageal diverticulum is carried out in case of acute pain, bleeding, fistulas, violation of the integrity of the organ, and other accompanying diseases.
Removal of an esophageal diverticulum is performed under general anesthesia. The convex part is excised and a suture is applied.
Surgery is performed through the neck or thoracic region, depending on the location of the formation.
Excision of an esophageal diverticulum must be justified; this procedure should be carried out only after a detailed diagnosis, taking into account the individual characteristics of the body.
If the size of the bag is small, surgical intervention is not required. For these purposes, intussusception is used.
The technique involves no need for removal. For these purposes, the bag is turned inside out into the cavity of the esophageal organ, after which the esophageal wall is sutured.
The diagnosis and treatment method must be established exclusively by the attending physician after diagnosis and a detailed study of the clinical picture of the disease.
Folk recipes
The use of alternative therapies can also bring positive results.
They should be used in practice only after consultation with the attending physician and after his permission.
This therapy cannot be used as a primary therapy. It is used in conjunction with traditional methods, observing special dietary nutrition and regimen.
Which recipes are most effective:
- Flax oil. You will need flax seeds in the amount of 200 grams. They are thoroughly ground to a powder. The resulting dry mixture is poured with vegetable oil (you can use olive or sunflower oil). Send the medicine to infuse in a dark place, after covering it tightly with a lid for 30 days. The medicine relieves inflammation, heals damage, stimulates the body's immune defense.
- Bran. You will need to take 2 tablespoons of bran, poured with boiling water in the amount of 0.5 cups. This mixture is infused for 20 minutes. This medicine has a beneficial effect on all organs of the digestive system.
- Chamomile decoction. Medicinal chamomile has many positive qualities. It actively relieves the inflammatory process, relieves pain, relieves irritation, and promotes rapid healing of injuries. The broth is prepared for washing. For these purposes, pour 1 tablespoon of dry plant with 1 glass of boiling water. The resulting mixture is infused, after which it is carefully filtered.
Any of the traditional medicines presented can have a positive effect only if the patient has no contraindications.
Operation
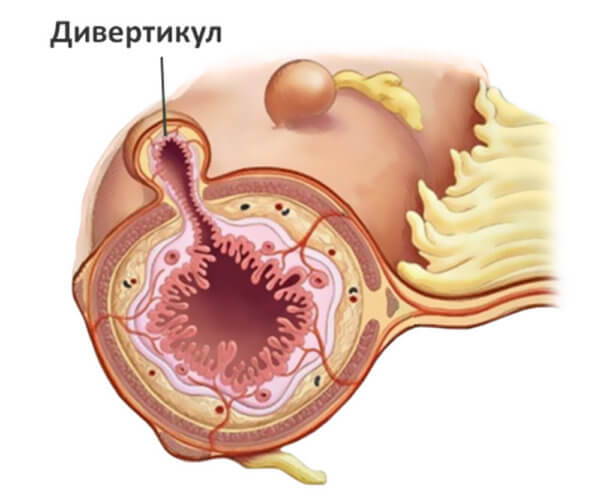
To remove Zenker's diverticulum, a simultaneous diverticulectomy is performed. The operation is carried out as follows:
- An incision is made along the anterior edge of the sternocleidomastoid muscle.
- The tissue is dissected layer by layer, large vessels are pushed back until the thyroid gland is reached.
- The left lobe of the thyroid gland must be removed to the right; if necessary, it will have to be resected.
- After this, diverticulosis becomes visible. It is necessary to carefully examine the location of the diverticulum.
- U-shaped silk sutures or clamps are placed on its neck, after which the bag is cut off. The diverticular protrusion is not cut off at the very wall of the esophagus, but a little further from it, otherwise the lumen of the esophagus may narrow. But you also shouldn’t leave too much, lest a relapse occurs.
- Finally, after the diverticulum is removed and the mucosa is closed, sutures are placed on the muscles. As a rule, the wound is closed tightly, but if it is infected, drainage should be left.
After surgery, you should not eat for two days. Many surgeons recommend feeding the patient liquid food using a tube also on the third or fourth day after surgery. Then you can start taking semi-liquid foods and gradually expand your diet.
There are also operations during which the diverticulum is not removed. Instead, it is invaginated into the wall or lumen of the esophagus, after which the muscle covering over it is sutured. A diverticulum that has undergone intussusception atrophies over time. Such operations are performed only in cases where the diverticulum is small and its wall consists of mucous membrane. This technique is safer, since during its implementation the lumen of the esophagus is not opened.
Other operations are also performed: relocation of the diverticular sac and diverticulopexy. Both operations cannot be considered a complete solution to the problem and are now practically not performed anywhere, so we will not talk about them in detail.
There is an endoscopic technique aimed at splitting the septum between the diverticular sac and the esophagus, but this method has a couple of problems: descending mediastinitis can develop, and during the operation there is a possibility of damaging important vessels.
Complications
If pouches are detected during a diagnostic examination, immediate treatment is required in order to prevent further development of pathology and serious complications.
What consequences can develop in the absence of correct and timely treatment:
- Multiple aphthous and erosive lesions can form on the walls of the esophagus. The formation of ulcerative lesions may be observed, which is also one of the unpleasant complications.
- Bleeding often occurs, which must be stopped urgently.
- Lack of treatment leads to destruction of the walls of the esophageal organ.
- In the absence of therapy, these formations can degenerate into malignant neoplasms.
- Possible formation of a pulmonary abscess.
- Polyps may form.
- Aspiration pneumonia may develop. This condition is characterized by the spread of the inflammatory process to the respiratory system.
Diverticulitis is considered one of the most common complications of the pathology.
This is the name for the presence of an inflammatory process in formations due to damage by pathological microorganisms. This can be facilitated by accumulations of food debris and rotting processes.
To prevent this complication, regular visits to the doctor and diagnostics are required on a regular basis or when the first unpleasant signs appear.
If these recommendations are followed, the disease can be prevented in the early stages.
Your IP address is blocked.
A 22-year-old patient mistakenly took a solution of caustic soda about 3 months ago. Currently, rapidly progressing dysphagia has developed. X-ray reveals a cicatricial stricture of the middle third of the esophagus. Its diameter does not exceed mm. A 56-year-old patient develops painful heartburn and regurgitation of eaten food due to constant intense pain in the chest. Pain often radiates to the interscapular space and left shoulder. The ECG shows minor changes in the myocardium. The patient complains of increased salivation, a scratching sensation in the throat, awkwardness when swallowing, and cough. Periodically, after starting to eat, dysphagia and swelling in the neck appear.
Diverticulosis is a protrusion of the walls of a certain organ that is affected by pathology. An esophageal diverticulum, accordingly, is a deformation of the esophageal walls. The size of the abnormal enlargement may vary depending on the individual and the nature of the disease. Symptoms of diverticulosis depend on the size of the tumor and its location, which are determined at the stage of diagnosing the disease. The size of the esophageal diverticulum reaches such a level that palpation of the formation is possible, and the inflammation will be visually distinguishable.
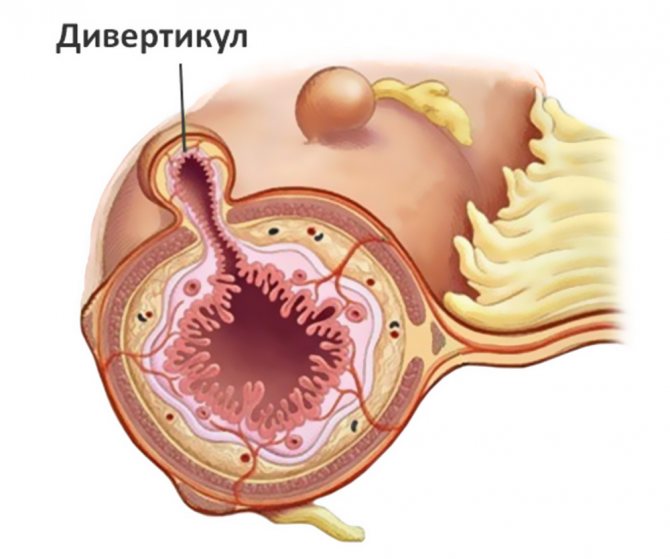
Protrusion of the walls of the esophagus, depending on its size, can be diagnosed with high probability.
Prevention
In addition to therapeutic methods of influencing pathology, there are special prevention methods that can prevent the development of the disease. What is included in these recommendations:
- Be sure to chew food slowly and thoroughly while eating. You should not eat quickly and absorb poorly chewed pieces of food.
- The temperature of the food consumed should be approximately room temperature. Excessively hot or cold food can have a negative effect on both the esophagus itself and other organs of the gastrointestinal tract.
- You need to eat slowly, taking a sitting position. Avoid eating while walking or standing.
- If disturbances in the functioning of the digestive system are detected, immediate treatment is required to avoid serious consequences.
- It is required to maintain the integrity of the esophagus from various types of injuries.
- Be sure to follow all recommendations of a gastroenterologist and nutritionist.
If the pathology is detected in time and all measures to eliminate it are taken immediately, the prognosis for recovery will be favorable.
Refusal to follow a dietary diet, abuse of bad habits and refusal of treatment can have serious consequences.
The appearance of the first unpleasant symptoms and discomfort in the esophagus should be a serious reason to consult a doctor. You cannot self-medicate.