Intestinal adenoma is a dangerous type of neoplasm. These are polyps that are localized in different parts of the digestive organ. The pathology needs to be treated as it often causes cancer. Rectal carcinoma transforms from benign mucous membranes and can quickly lead to patient decline.
Pathology often causes cancer.
Development mechanism
A benign lump looks like a polyp and is a growth on the tissues of the mucous membranes. It consists of epithelial cells and often has a thin stalk that is attached to the intestine. Typically, this type of thickening slowly increases in size and rarely exceeds 1 cm in diameter. If this happens, the probability of transformation of benign cells into malignant ones increases several times.
It is a growth on the tissues of the mucous membranes.
Polyps are constantly injured when digested food remains pass through the digestive tract. Therefore, they worsen a person’s condition and reduce immunity. If the neoplasm reaches a large size, it also makes it difficult for the passage of feces, which provokes constipation.
Classification
Depending on the progression of dysplasia, which is characteristic of all tubular adenomas, three degrees are distinguished:
- Weakly expressed;
- Moderate;
- Heavy.
Tubular adenoma of the colon with mild dysplasia is characterized by slight thickening of the epithelial layer and splitting of the basal layer. There is an inflammatory reaction due to the mitotic activity of cells. Microscopy reveals nuclear hypochromia and an increased ratio of nucleus to cytoplasm.
Tubular adenoma of the colon with moderate dysplasia is characterized by polymorphism (cells acquire different shapes and sizes) of epithelial cells and the process of proliferation. The basal layer of cells is blurred and indistinct.
With severe dysplasia, the nuclei under the microscope change to hyperchromic. All cells have even more modified shapes and sizes. Changed cells make up more than half of all epithelial cells.
There is also high-grade and low-grade dysplasia. Poorly differentiated dysplasia is a precancerous condition and inexperienced pathologists in some cases can confuse it with a malignant process.
Depending on the number of formations, the following are distinguished:
- Single;
- Multiple;
- Diffuse.
Causes
Doctors have not established the exact reasons why papillary adenoma of the colon or small intestine occurs. Risk factors have been identified that increase the likelihood of developing pathology:
- hereditary factor. If one of the parents has developed polyps at least once, the risk that they will appear in the child is several times higher. If there were many tumors (polyposis), then in most cases the children will be given the same diagnosis;
- unhealthy diet, which is dominated by fatty foods and lacks vegetables and fruits;

Poor nutrition. - Drinking alcohol and smoking cigarettes increases the risk;
- living in an unfavorable environmental environment, working in hazardous production;
- excess weight and sedentary lifestyle;
- hormonal disorders, diabetes, etc.;

Diabetics are at risk. - foci of inflammation in the organs of the gastrointestinal tract, in which the mucous membranes become irritated;
- removal of the gallbladder;
- damage by bacterial infections;
- cancerous lesions of the mammary glands.
Onions in the fight against adenoma
Folk remedies for prostate adenoma are natural products that do not contain chemicals, so the risk of side effects is practically reduced to 0.
But each person has his own individual body, which reacts differently to products.
Sometimes vegetables and fruits provoke the development of allergies or problems with intestinal function. Therefore, before using any folk recipe, the patient must undergo diagnostics and consult with a specialist.
So, in the treatment of adenoma with folk remedies, a male product – onions – is often used. This is a strong antiseptic that works great even if you simply take the bulb before bed. This was proven by P. D. Dvoyakovsky (a famous physician). He argued that the following ingredients should be prepared for therapy:
Therapy should last 90 days. During this period, the patient should alternate days of nutrition in the following order:
- On the first day, consume the onion in the evening.
- On the second day, eat 0.5 cups of raw, peeled sunflower seeds.
- On the third day, eat nuts (150 g) before bed.
To increase the effectiveness and quickly eliminate prostate adenoma in men, treatment with folk remedies should be accompanied by giving up bad habits (smoking, drinking alcoholic beverages). Even ordinary beer provokes the growth of tumor cells. Onions inhibit the development of tumor growth, and seeds and nuts weaken the negative impact on the entire body.
You can try another remedy: take equal amounts of green onion feathers and dried birch leaves and mix. Pour 2 tbsp into a separate container. l. mixture and add just boiled water (0.5 l). The broth should steep for 1 hour, but the container must be wrapped in a warm towel.
After this step, the liquid should be strained. Drink warm medicinal liquid twice a day, 0.5 cups after lunch.
It is useful to mix onions with honey, so it is worth taking a closer look at another effective tincture recipe. You will need onion peels (1 cup). Place it in a colander and rinse under running water. Place in a container and add water (500 mg). Place the pan over low heat and boil, leave to simmer for 7 minutes. Then the container must be removed and left for 40 minutes. The finished liquid is filtered and mixed with 3 tbsp. l. honey
The course of treatment is 5 days. Every day, 3 times a day, the patient should drink 0.5 cups of tincture. Then there should be a break (5 days), after which the patient is given salt wraps: pour salt (0.2 kg) into water (2 liters), soak a cloth in the solution, wring it out and wrap the area for 2 hours.
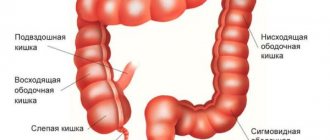
Localization and danger
Neoplasms appear in different parts of the digestive organ. An adenoma of the colon, small intestine, and rectum often forms.
Small intestine
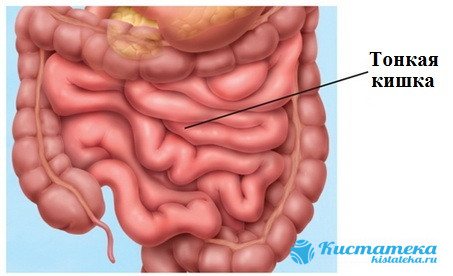
This section of the digestive organ is the longest. Polyps rarely form here. In total, they make up no more than 3–4 percent of all cases. The compaction does not bother the patient until it increases to 1.5 - 2 cm in diameter. When this happens, it becomes very painful.
Rectum
Adenoma in the rectum is a more dangerous type of formation. Its tissues often transform into malignant ones. This happens even when the thickening has increased slightly. A cystic formation with a diameter of 1 cm or more provokes unpleasant symptoms. Intestinal obstruction occurs and a focus of inflammation develops.
Colon adenoma - what is it?
An adenoma in the large intestine appears in one of its three sections, for example, in the blind (although less often). This type of neoplasm also has a tendency to transform benign cells into malignant ones.
Therefore, it is important to diagnose the pathology in a timely manner. Unfortunately, patients often ignore the problem and go to the hospital at a later stage. If done earlier, there is a chance of preventing the development of colon carcinoma.
In 10–15% of all cases, the tumor degenerates into malignant. It depends on its type. In this case, size does not matter. Even small polyps pose a serious threat.
Intestinal adenoma treatment with folk remedies
A benign polypous formation that appears on the walls of the intestine is called intestinal adenoma.
The pathology occurs independently and becomes a consequence of other diseases of the digestive system - ulcers, gastritis. Very often the disease takes on a more dangerous form and turns into cancer (carcinoma).
Any type of intestinal adenoma is equally dangerous and disease prevention measures must be taken throughout life, and in cases of occurrence, treatment must be started immediately.
It is believed that a small formation measuring up to 10 mm does not pose a major health risk. A polyp larger than 10 mm in size becomes cancerous in 10% of cases. The severity of the pathology and symptoms depend on the form the tumor has taken. Most often, the disease manifests itself after fifty years.
The following types of pathology are distinguished:
- tubular;
- villous;
- tubular-villous;
- serrated
Any of these types of polyps can occur in different sections of the large intestine. Most often, the site of localization is the rectum and sigmoid colon; less often, polyps grow in the area of the cecum. The rest of the region accounts for 11% to 18%.
At the same time, a large number of papillomas may appear in one area, and gradually with age and the development of the disease, the number of neoplasms increases.
This phenomenon becomes a precursor to colon polyp and cancer, which is why doctors recommend not delaying treatment.
Tubular adenoma of the intestine
The growth grows to a size of about 1 cm, has clear boundaries, a strong base, appears crimson, and is soft. Outwardly it resembles a branching glandular structure bounded by connective tissue.
This type of pathology is called adenomatous polyp; the larger the formation, the higher the risk of cancer. Rarely, tubular adenoma reaches a size of more than 3 cm.
In this case, the body has a lobed structure, rises on a stalk, and has a dark crimson hue.
Villous
Intestinal adenoma, which has a villous structure, is a body of fibrous villi (narrow, wide, thick, short). Depending on the form of attachment to the site of localization, the neoplasm can be creeping or pedunculated.
The creeping body has a wide base and practically does not rise upward. Pedicled adenomas can grow up to 3 cm and are attached to a thick or thin base. Most often, centimeter polyps occur, with a diameter of up to 2 cm; in 10% of patients they grow more than 3 cm.
The formation consists of fibromuscular tissue and blood vessels.
Tubular-villous
When a tubular intestinal adenoma is distinguished by a large proportion of villi (more than 25%), it begins to be classified as a tubular-villous type, called a tubulovillous polyp, in this case the villi can be from 25% to 75%. The tumor is large (more than 2 cm in diameter), can be on a thin stalk or placed on a flat, wide base.
Serrated
The profile of the epithelium and the surface of the formation is characterized by fine serration. The surface layers are distinguished by dysplasia; the complexity of the patient’s condition and the danger of the pathology depend on the degree of their change. Serrated intestinal adenoma can take different sizes and have a large diameter.
Intestinal adenoma symptoms
Most often, as soon as polyps begin to form, the patient does not feel any negative symptoms. In this case, the pathology is discovered by chance, during examination for another disease. Once an intestinal adenoma is diagnosed, treatment begins immediately. A tumor larger than 20 mm is already making itself felt, characterized by the following manifestations:
- pain during bowel movements;
- discomfort in the abdominal area;
- bloating;
- the anus itches;
- there is a feeling that there is something “inside” the anus, the sphincter;
- feces contain blood and mucus;
- disruption of intestinal function, manifested by diarrhea and constipation.
Approximately these symptoms characterize the appearance of colon adenoma; only specialists can give a more accurate diagnosis after a complete examination.
Regardless of how the type of pathology manifests itself (serrated adenoma, villous adenoma), at the first stage of its occurrence, treatment at home is possible. Tubular and tubular-villous adenoma cannot be treated at home.
Traditional methods involve the use of poisonous plants, such as celandine, meadowsweet (meadowsweet), agrimony, calendula, and St. John's wort.
Based on them, decoctions are prepared for oral administration before meals, enemas are performed, and tinctures and alcohol solutions are used.
The procedures are performed from 7 days to a month, after which they rest, and after three days the treatment is repeated again, even if the symptoms cease to appear.
In order not to miss the time of occurrence and development of colon adenoma, you should carefully monitor the general condition of the digestive system. Engage in the prevention of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, and promptly eliminate any pathologies associated with the work of these organs.
In addition, you should not abuse the use of medications without the knowledge of a specialist, overeat, periodically overloading the stomach, and often eat junk food - carbonated, smoked, salty, spicy, sour.
It is useful to spend a lot of time in the fresh air, harden yourself, adhere to a healthy diet, a nutritious, proper daily routine and rest!
Intestinal adenoma is a dangerous type of neoplasm. These are polyps that are localized in different parts of the digestive organ. The pathology needs to be treated as it often causes cancer. Rectal carcinoma transforms from benign mucous membranes and can quickly lead to patient decline.
Development mechanism
A benign lump looks like a polyp and is a growth on the tissues of the mucous membranes. It consists of epithelial cells and often has a thin stalk that is attached to the intestine.
Typically, this type of thickening slowly increases in size and rarely exceeds 1 cm in diameter.
If this happens, the probability of transformation of benign cells into malignant ones increases several times.
Polyps are constantly injured when digested food remains pass through the digestive tract. Therefore, they worsen a person’s condition and reduce immunity. If the neoplasm reaches a large size, it also makes it difficult for the passage of feces, which provokes constipation.
Causes
Doctors have not established the exact reasons why papillary adenoma of the colon or small intestine occurs. Risk factors have been identified that increase the likelihood of developing pathology:
- hereditary factor. If one of the parents has developed polyps at least once, the risk that they will appear in the child is several times higher. If there were many tumors (polyposis), then in most cases the children will be given the same diagnosis;
- unhealthy diet, which is dominated by fatty foods and lacks vegetables and fruits;
Localization and danger
Neoplasms appear in different parts of the digestive organ. An adenoma of the colon, small intestine, and rectum often forms.
Small intestine
This section of the digestive organ is the longest. Polyps rarely form here. In total, they make up no more than 3–4 percent of all cases. The compaction does not bother the patient until it increases to 1.5 - 2 cm in diameter. When this happens, it becomes very painful.
Rectum
Adenoma in the rectum is a more dangerous type of formation. Its tissues often transform into malignant ones. This happens even when the thickening has increased slightly. A cystic formation with a diameter of 1 cm or more provokes unpleasant symptoms. Intestinal obstruction occurs and a focus of inflammation develops.
Colon adenoma - what is it?
An adenoma in the large intestine appears in one of its three sections, for example, in the blind (although less often). This type of neoplasm also has a tendency to transform benign cells into malignant ones.
Therefore, it is important to diagnose the pathology in a timely manner. Unfortunately, patients often ignore the problem and go to the hospital at a later stage. If done earlier, there is a chance of preventing the development of colon carcinoma.
In 10–15% of all cases, the tumor degenerates into malignant. It depends on its type. In this case, size does not matter. Even small polyps pose a serious threat.
Symptoms
Adenoma of the sigmoid colon or other parts of the digestive organ rarely manifests itself. In the early stages it reaches several millimeters, so it does not interfere with the patient. Thickenings that increase to 1 - 1.5 cm may manifest themselves with characteristic symptoms:
Source: https://zhivizdravo.ru/info/adenoma-kishechnika-lechenie-narodnymi-sredstvami/
Symptoms
Adenoma of the sigmoid colon or other parts of the digestive organ rarely manifests itself. In the early stages it reaches several millimeters, so it does not interfere with the patient. Thickenings that increase to 1 - 1.5 cm may manifest themselves with characteristic symptoms:

Constant bloating, flatulence.
- a person experiences pain when going to the toilet. This occurs during the process of defecation, but the sensations may persist after;
- discomfort appears in the area where the tumor is localized;
- there is constant bloating and flatulence;
- the digestive process is disrupted. This manifests itself as either constipation or diarrhea. States may alternate;
- burning and itching occurs in the anus;
- with significant tumor growth in the abdominal cavity, the presence of a foreign body is clearly felt. If the adenoma is located in the rectum, then this sensation extends to the area of the anus, sphincter;
- During bowel movements, patients note the appearance of foreign impurities in the stool. They contain blood clots and mucus. The stool may take on a black tint;
- in some cases, bleeding begins from the anus. If they are repeated frequently, the person will experience iron deficiency in the blood.
Depending on the part in which the intestinal adenoma is localized, it may have additional characteristic features and manifestations.
Clinical signs
Polypous growths in the stomach develop asymptomatically for a long time. The appearance of tubular adenomas does not affect the functioning of the organ. Primary symptoms occur when the polyp becomes twisted or reaches a large size.
The presence of tumors in the stomach is indicated by pain of low intensity. This symptom mainly occurs after eating food that irritates the mucous membrane: spicy, fatty, salty foods. Similar phenomena occur after a heavy meal on an empty stomach.
The growth of tubular adenoma provokes attacks of vomiting. The appearance of this symptom is explained by the fact that the polyp blocks the passage to the stomach, causing food to be thrown back into the esophagus.
On this topic
- Digestive system
The role of hormonal contraceptives in the development of liver hemangioma
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 6, 2020
Vomit often contains blood. In addition, patients with large tumors feel full when undernourished.
If the polyp becomes twisted and internal bleeding occurs, the sick person develops tarry stools. Due to loss of appetite caused by the growth of adenoma, body weight decreases. This leads to general exhaustion of the body, which is why the patient feels persistent weakness.
Internal bleeding provokes the development of anemia, which manifests itself in the form of pale skin. Cyanosis is usually accompanied by sharp pain in the stomach.
Sometimes tumor growth provokes disruption of the digestive system. Patients in this case experience flatulence and frequent heartburn. Belching with bad breath is also possible, appearing regardless of food intake.
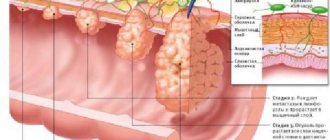
Types of adenomas
There is a classification of benign tumors based on several factors. They take into account the size of the thickening, the risk of its transformation into malignant and the degree of epithelial dysplasia. One polyp or several at once, combined into one formation, appears on the internal tissues.
Serrated
The peculiarity of this type is that the compaction combines the characteristics of an adenoma and a hyperplastic polyp. The cells have a special, irregular shape with jagged edges. Because of this, the surface of the capsule resembles small jagged divisions. Usually the stalk with which the polyp is attached to the mucosa is wide. But sometimes it can be narrowed.
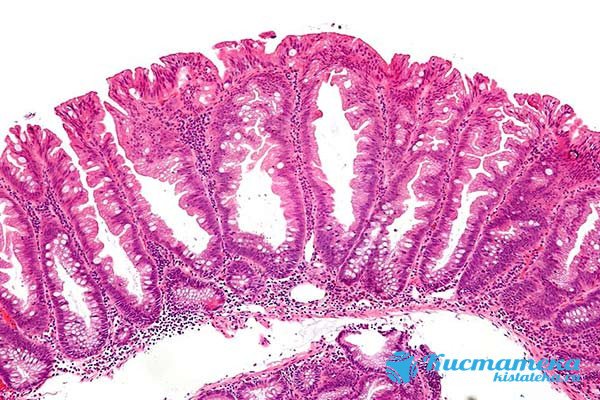
The cells are irregular in shape with jagged edges.
Serrated adenoma of the colon or other intestine rarely exceeds 1–2 cm. If this happens, the risk of its transformation into a malignant neoplasm increases several times. The more mucous membranes are affected, the higher this probability. Therefore, upon diagnosis, immediate treatment is required.
Tubular
This is the most common type of tumor. The tubular formation has a smooth surface, dense structure and clearly defined boundaries. A thickening is visualized, like glandular tissue with numerous branches. At the same time, it is limited by connective tissue.
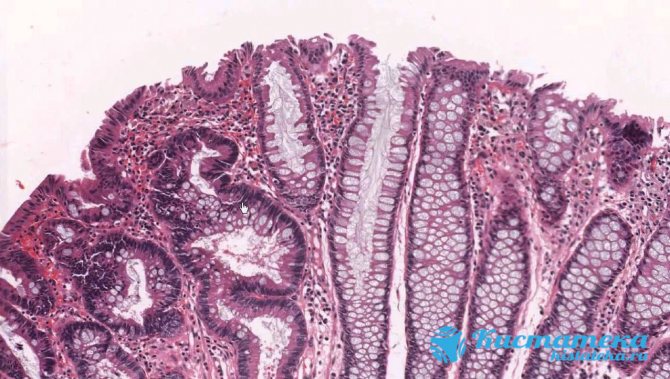
Smooth surface, dense structure and clearly defined boundaries.
Polyps usually do not grow more than 1 cm. In rare cases, they grow up to 3 cm. If this happens, the appearance changes. The capsule rises on a stalk and acquires a crimson color. Large cystic formations often degenerate into malignant ones.
Villous
This type of intestinal adenoma is a soft lump. In structure, it is a polyp, which consists of fibrous villi of the epithelial tissue of the digestive organ.
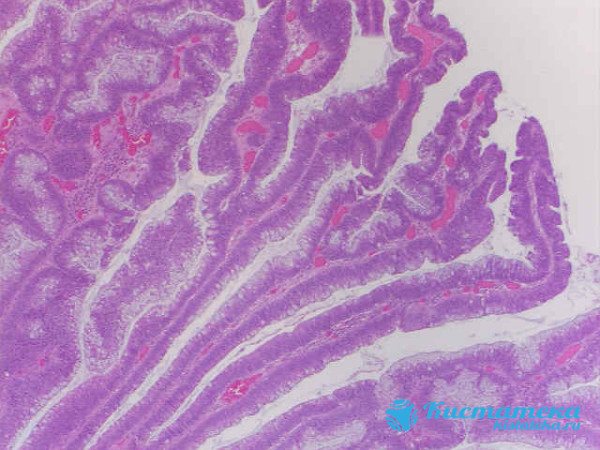
Consists of fibrous villi of epithelial tissue.
It can be attached with an entire wall to the intestinal mucosa or have a thin stalk. In the latter case, it can increase to 3 cm in diameter. But usually villous neoplasms reach 2 cm. If the capsule is of a creeping type, then it practically does not protrude above the surface.
This type of thickening has a high risk of cancerous transformation. In 40% of cases, lack of treatment leads to the appearance of a malignant tumor.
Tubular-villous
Tubulovillous adenoma combines the features of the previous types. It mainly consists of villi that line the intestinal mucosa. Tubular-villous types often reach a large size than others. They increase to 2 or more centimeters in diameter. They are mounted on a flat, extended base or have a thin leg.
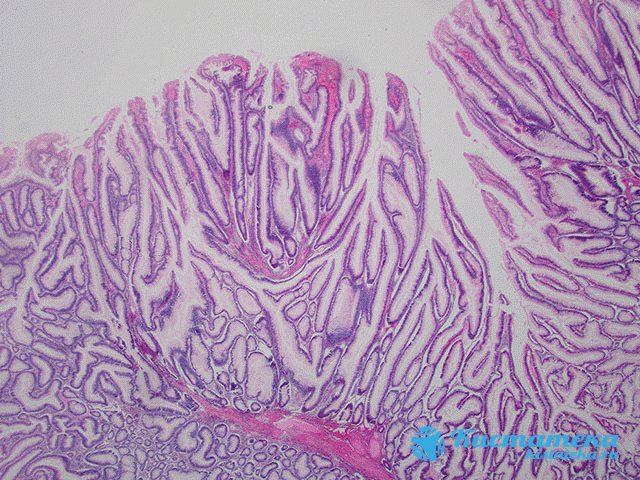
They increase to 2 or more centimeters in diameter.
The volume of villi in their tissues reaches 3/4. Like the tubular seal, there is a jagged structure of the epithelial layer. Dysplasia predominates on the tissue surface. It is used to determine how serious changes the neoplasm has provoked.
What is tubular adenoma of the sigmoid colon, how it manifests itself and is treated
Tubular adenoma of the sigmoid colon is a benign neoplasm. It is formed mainly against the background of an inflammatory process from the glandular epithelium; another concept comes down to hereditary predisposition.
Twisting of the adenoma leg is accompanied by the formation of cystic structures, hemorrhages and dysfunction of the affected intestinal segment.
Features and types of disease
Classification of adenomas:
- Tubular. Often does not exceed 1 cm. It is a combination of glandular epithelium and connective tissue. The neoplasm has a large number of processes, red and pink color and clear outlines. Tubular adenoma with a soft base is common.
- Villous. It consists of many fibrous components that resemble villi. They are almost the largest in size (the diameter of such adenomas does not exceed 2 cm), and are shaped like cauliflower.
- Tubular villous adenoma of the colon is a large tumor. The size of the pathological formation is often 2 cm. It is a combination of the two types presented above, i.e. has branches and grows like cauliflower.
- Serrated. A special form of dysplasia, characterized by the formation of notches from epithelial tissue. This type has a high risk of malignancy.
Causes and degrees of dysplasia
The appearance of small polyps on a thin stalk is associated with changes in the structure of intestinal tissue under the influence of unfavorable factors: poor nutrition, chronic gastrointestinal diseases, smoking and alcohol abuse. The causes of this pathology are:
- unfavorable environmental conditions;
- treatment with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and other potent medications;
- obesity;
- work in hazardous conditions;
- chronic colitis, gastritis and ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract;
- immunodeficiency states;
- autoimmune diseases.
Colon adenoma with dysplasia forms in the absence of treatment of the primary disease. The pathological process contributes to the transition of a benign tumor to a malignant one.
Degrees of dysplasia:
- Moderate - the basal layer becomes dense and gradually thickens.
- Medium - the contours of the tumor become blurred, the tumor grows deeper.
- Expressed - at this stage, transformation of normal epithelial cells into atypical ones occurs.
Treatment methods
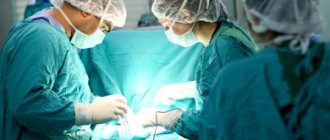
Treatment is surgical; only the changed tissue is removed. In this case, the size of the neoplasm and its structure are taken into account. Adenomas that are prone to degeneration into malignant tumors are excised along with some fragments of the intestine. Most often, laser coagulation methods are used to remove tumors.
In this case, access is carried out through a small puncture in the peritoneum or using a special rectal endoscope. The adenoma is carefully cauterized with a laser; the success of the operation is indicated by a change in color; the intestines continue to function normally after the scab has passed.
After surgery, a diet is followed, which includes pureed porridge and vegetarian soups. During the rehabilitation period, it is important to avoid constipation, which can trigger a relapse of the disease. For this purpose, laxative medications are prescribed, as well as vegetable stews and dried fruit decoctions.
Treatment with folk remedies is used only for small adenomas that are not predisposed to malignant degeneration. Anti-inflammatory infusions based on chamomile and calendula are used for therapy.
Both ingredients must be taken in the amount of 2 tbsp. l. and pour a glass of boiling water. Let it brew for 2 hours and filter. Dilute with 1 glass of boiling water and take 200 ml 2 times a day half an hour before meals.
The course of therapy is 3 months.
For a complete cure, it is important to follow a diet and normalize intestinal motility. For this purpose, doctors prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs, probiotics and medications that stimulate peristalsis.
It is important to pay attention to the treatment of chronic gastrointestinal diseases: gastritis, colitis, pancreatitis.
Prognosis and prevention
The prognosis with timely treatment is favorable. Often the tumor degenerates into a malignant one (depending on the provoking factors and the therapeutic approach). Prevention rules:
- Eat properly. Eliminate carcinogens from your diet: fried foods, palm oil, GMOs, harmful additives and preservatives. Eat fresh fruits and vegetables, consume more cereals and fish.
- Eliminate bad habits. Stop using alcohol and tobacco.
- Monitor the state of the immune system.
- Eliminate inflammatory bowel diseases in a timely manner.
- Monitor bowel movements. Go to the toilet at the first urge, don’t endure it.
- If you experience frequent constipation, take laxatives and enrich your diet with plant fiber.
It is not recommended to take any medications without a doctor's prescription.
What is tubular adenoma of the sigmoid colon, how it manifests itself and is treated Link to main publication
Source: https://ProPolip.info/gastroenterologiya/tubulyarnaya-adenoma-sigmovidnoy-kishki.html
Possible complications
The most serious consequence of the appearance of polyps is the risk of developing cancer. The predisposition to cancer with intestinal tumors is several times higher than with other types. Therefore, they tend to remove them immediately after diagnosis.
In addition to the likelihood of developing cancer, adenoma provokes serious disturbances in the functioning of the digestive tract. In some cases, intestinal obstruction develops. If the capsule tissues injure the feces, a focus of inflammation is formed, causing symptoms of intoxication and deterioration of the person’s condition.
Nutrition for gastric adenoma
The diet for adenomatous polyps in the stomach is prescribed by a gastroenterologist, taking into account the background pathology (peptic ulcer, gastritis, etc.). To prevent the growth of adenomas and their recurrence after surgery, it is recommended to adhere to the following rules:
- “Heavy”, fatty, spicy and any dishes that can injure the gastric mucosa or cause irritation are excluded from the menu. The same goes for drinks.
- The consumption of “junk” food, fast food, processed foods, etc. is minimized.
- You should not overeat, it is advisable to eat in small portions in compliance with the principles of rational nutrition.
Any error in diet can aggravate the course of the disease.
Diagnostic methods
If one of the parents has been diagnosed with an adenoma, regular examinations by a doctor are indicated with the appointment of the necessary diagnostic methods. This will allow the tumor to be identified at an early stage in order to remove it before it degenerates into a cancerous tumor.
But in most cases, the patient goes to the hospital after the first symptoms appear. In this case, the compaction has already reached a large size. The doctor interviews the person and asks what is bothering him. By palpation, he will try to determine whether a foreign body is present in the abdominal cavity.
In addition, additional studies are prescribed to clarify the diagnosis:
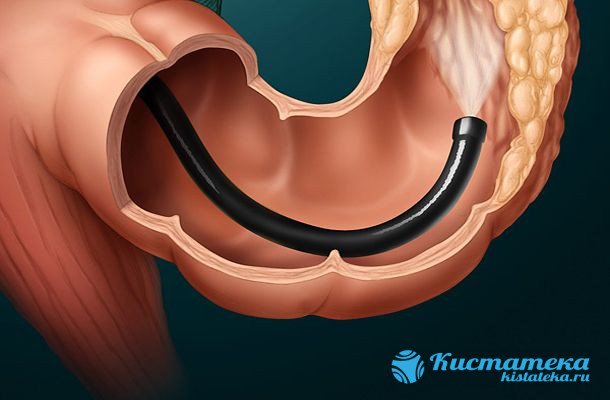
The probe penetrates inside and allows you to determine the presence of pathology.
- A stool test is done to identify blood clots in it. Sometimes it is not visible;
- perform sigmoidoscopy. This is an examination in which a probe is inserted into the anus. It penetrates 25 cm into the intestine and allows you to determine the presence of pathology;
- Colonoscopy is a similar procedure. The difference is that this method allows you to view the mucous membranes of the entire colon;
- During the examination, they can take material to send for histological examination. The test determines whether cancer cells are present in the tissue;
- Sometimes radiography or CT helps identify a tumor;
- Blood and urine tests are needed to determine the presence of a source of inflammation.
Tubular villous adenoma of the rectum
Villous adenoma of the rectum in medicine can be called by several terms. This is the same as a glandular villous polyp or papilloma. The pathology is a benign tumor, in appearance it is similar to cauliflower, soft to the touch, often grows strongly and can circularly cover the intestinal lumen. Benign tumor
Villous adenoma does not have a leg, it sits on a wide base and bleeds with a slight touch. Sometimes the tumor does not have clear boundaries; it seems to spread across the mucous membrane of the colon.
Treatment
Since an increase in the size of the adenoma leads to the development of cancerous processes, its mandatory removal is required. If medications are prescribed, they are needed to reduce pain and other unpleasant sensations. Painkillers are used during recovery in the postoperative period. In addition, the patient takes probiotics and prebiotics, vitamins, and complexes containing microelements.
If the tumor is small, it is usually removed during sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy. During the operation, the pedicle that attaches the polyp to the mucosa is cauterized and removed. If the tumor spreads along the surface, then the intervention is carried out in several steps.
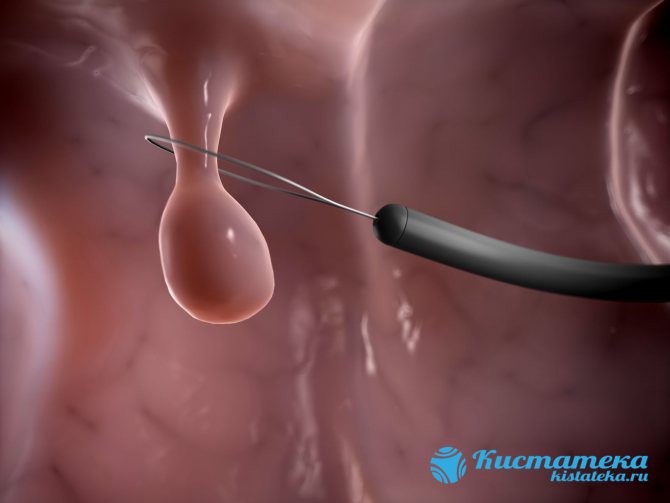
During the operation, the leg is cauterized and the polyp is removed.
In addition to standard methods, the following types of operations can be prescribed:
- laparoscopy. This method involves making pinpoint punctures in the abdominal cavity, through which the seal is removed. Intervention is prescribed if the diameter of the polyp exceeds 2 cm. Recovery occurs quickly;
- laparotomy involves excision of the abdominal wall and is used for large adenomas. In some cases, it is necessary to bring the damaged area outside;
- resection of the intestine is a complex method that is used in serious cases. It involves removing not only the polyp, but also the part of the intestine on which it is attached. The ends are sewn together. Typically, this method is used when benign cells have degenerated into cancer.

After any type of intervention, the patient needs to stay in the hospital for some time under the supervision of doctors. Rehabilitation takes from one to several months. Recovery time depends on the type of surgery. During the entire period, the patient needs to take medications prescribed by the attending physician.
Experts warn that you should not self-medicate with this type of cystic formation.
Traditional methods will not help reduce the adenoma and will not slow down its growth. In most cases, such treatment is even harmful. If the doctor agrees on folk remedies, then they can be used in the early stages of tumor development or during the recovery period after surgery. Typically, herbs are used to reduce inflammation.
Tubular adenoma of the sigmoid colon treatment with folk remedies
A benign polypous formation that appears on the walls of the intestine is called intestinal adenoma. The pathology occurs independently and becomes a consequence of other diseases of the digestive system - ulcers, gastritis.
Very often the disease takes on a more dangerous form and turns into cancer (carcinoma).
Any type of intestinal adenoma is equally dangerous and disease prevention measures must be taken throughout life, and in cases of occurrence, treatment must be started immediately.
It is believed that a small formation measuring up to 10 mm does not pose a major health risk. A polyp larger than 10 mm in size becomes cancerous in 10% of cases. The severity of the pathology and symptoms depend on the form the tumor has taken. Most often, the disease manifests itself after fifty years.
Kinds
Types of pathologies
The following types of pathology are distinguished:
- tubular;
- villous;
- tubular-villous;
- serrated
Any of these types of polyps can occur in different sections of the large intestine. Most often, the site of localization is the rectum and sigmoid colon; less often, polyps grow in the area of the cecum. The rest of the region accounts for 11% to 18%.
At the same time, a large number of papillomas may appear in one area, and gradually with age and the development of the disease, the number of neoplasms increases.
This phenomenon becomes a precursor to colon polyp and cancer, which is why doctors recommend not delaying treatment.
Intestinal adenoma treatment with folk remedies
Intestinal adenoma treatment with folk remedies
Regardless of how the type of pathology manifests itself (serrated adenoma, villous adenoma), at the first stage of its occurrence, treatment at home is possible. Tubular and tubular-villous adenoma cannot be treated at home.
Traditional methods involve the use of poisonous plants, such as celandine, meadowsweet (meadowsweet), agrimony, calendula, and St. John's wort.
Based on them, decoctions are prepared for oral administration before meals, enemas are performed, and tinctures and alcohol solutions are used.
The procedures are performed from 7 days to a month, after which they rest, and after three days the treatment is repeated again, even if the symptoms cease to appear.
In order not to miss the time of occurrence and development of colon adenoma, you should carefully monitor the general condition of the digestive system. Engage in the prevention of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, and promptly eliminate any pathologies associated with the work of these organs.
In addition, you should not abuse the use of medications without the knowledge of a specialist, overeat, periodically overloading the stomach, and often eat junk food - carbonated, smoked, salty, spicy, sour.
It is useful to spend a lot of time in the fresh air, harden yourself, adhere to a healthy diet, a nutritious, proper daily routine and rest!
Tubular adenoma of the colon, as well as villous tumor of the rectum, are quite dangerous neoplasms that are polyps.
Any such papillary tumor, although considered benign, can sometimes degenerate into malignant. The size of the adenoma is about 1 cm in diameter.
The prognosis of the disease depends on the timeliness of the diagnosis and the correctness of the prescribed therapy.
Types of adenomas that can occur in the intestines
Intestinal adenomas often cause colorectal cancer.
Based on the nature of germination and external signs, polyps are divided into:
- villous formations;
- tubular tumors;
- serrated adenomas;
- mixed neoplasms.
Villous.
It is the villous tumor of the colon that doctors call the most dangerous. This is due to the fact that in 40% of cases it degenerates into cancer.
Its features include:
- softness of structure;
- numerous formations that spread over the entire surface of the intestine;
- can grow up to 10 cm in diameter;
- velvety surface with villi, looks like a cauliflower inflorescence;
- has a wide base that can rise 30 mm above the surface of the mucous membrane.
This adenoma is also called villous and consists of fibrous villi, which look like a wide rod and are covered with columnar epithelium.
Tubular.
Tubular adenoma of the large intestine is called the most common.
Its signs:
- wide base;
- structure density;
- has clearly defined boundaries;
- smoothness of the tumor surface;
- has a red tint.
Basically, the identified tubular adenomas do not exceed 1 cm. Very rarely, specimens with a diameter of 3 cm or more are found. The larger the formation, the softer it is and the lobular structure it has.
This formation basically has a tubular, glandular structure, which is surrounded on different sides by loose tissue. This tumor has the most favorable prognosis for recovery.
SENSATION! Follow the link:
Serrated.
This type of adenoma is characterized by abnormal cell division (dysplasia). The surface of the epithelium is jagged. Another name for adenoma is papillary.
Tubulo villous adenoma.
This is a mixed type of neoplasm. Tubular villous adenoma also has a name - pseudotumor. It incorporates all the characteristics that villous and tubular tumors have. They are capable of growing more than 3 cm and are very rarely small.
Causes
Doctors have not yet been able to find out the exact reasons why colon adenomas appear. It is generally accepted that this can be caused by somatic diseases associated with exposure to unfavorable external factors on the body. It is also noted that there is a hereditary predisposition to the appearance of neoplasms.
The following factors can provoke the appearance of a tubular or villous polyp of the rectum:
- Poor nutrition. Food with a high content of carcinogenic substances and a small amount of fiber can cause enormous harm to the body. This diet leads to disruption of intestinal motility and microflora.
- Environmental pollution, prolonged exposure to toxins on the body, or employment in hazardous work.
- Having bad habits.
- Frequent stress.
- Sedentary lifestyle and lack of necessary physical activity.
- Excess weight.
- Pathologies of the digestive organs.
- Heredity.
Classification of pathology
The classification of the disease is associated with the severity of dysplasia (the possibility of reversibility of the process in tissues).
There are 3 degrees of tumor:
- Tubular adenoma of the colon with grade 1 dysplasia, when cell division occurs without significant structural changes.
- Tubular adenoma of the colon with moderate dysplasia with grade 2 disorders. At this stage of pathology development, changes in cell structure are characterized as moderately pronounced. Cells divide quite quickly, but the boundaries between layers are poorly distinguished.
- A stage 3 colon tumor (called intraepithelial neoplasia) is considered practically irreversible and requires observation by an oncologist.
Symptoms
At the very beginning of the development of pathology, adenomas have no symptoms, and they can be identified completely by chance when an examination is carried out regarding another disease.
Over time, when the size of the tumor reaches 2 cm, the patient begins to experience the following tumor symptoms:
- painful bowel movements;
- itching in the anus;
- frequent bloating and abdominal pain;
- mucus and streaks of blood in stool;
- sensation of a foreign body in the intestines;
- unstable stool (diarrhea is often replaced by constipation and vice versa).
A growing tumor leads to the fact that the lumen in the intestine decreases and obstruction appears. In addition, other pathological processes are possible.
Diagnosis and treatment
The main diagnostic measures include:
SENSATION! Follow the link:
- palpation;
- endoscopy;
- sigmoidoscopy;
- irrigoscopy;
- colonoscopy;
- radiography;
- histology to identify a malignant tumor.
Multiple small adenomas (about 5 mm in diameter) located in the mucous tissue of the colon often go unnoticed.
Tubular and villous adenoma of the rectum requires mandatory surgery, because conservative therapy is not able to affect the tumor.
The surgical technique is chosen based on the size and location of the adenoma:
- A tumor of the sigmoid colon, as well as a neoplasm of the rectosigmoid intestine, can be removed through the anus.
- Highly localized adenomas are removed using an endoscope.
As a rule, they are cauterized, which is the treatment of the affected epithelial tissue with an electrode. If there is a leg, it is grabbed first. The flat polyp is removed in parts, since it lacks a stalk.
The operation is performed under general anesthesia and requires special preliminary preparation of the intestines with mandatory cleansing.
In the postoperative period, the patient needs drug therapy.
After removal of the polyp, the risk of developing cancer is minimal, but there is a risk of relapse of the tumor. Therefore, the patient regularly needs to undergo sigmoidoscopy.
In the case of rectal adenoma, treatment with folk remedies is not recommended, because mainly for their preparation it is recommended to use plants such as belladonna or celandine, which have poisonous properties.
Any adenoma, including villous adenoma of the colon and intestine, has a favorable prognosis if it can be identified at the initial stage of development. To prevent it from developing into a malignant formation, the patient must undergo regular preventive examinations with a doctor and, if any disturbances in the intestines occur, seek medical help.
Prevention
Since the exact causes of adenoma of the duodenum and other parts have not been studied, there are no specific preventive measures. Doctors recommend following general rules that will help reduce the risk of developing a tumor.

You need to get rid of bad habits.
First of all, you need to get rid of bad habits. We are talking about alcohol abuse and smoking. It is important to lead an active lifestyle with moderate physical activity. Activity is needed if you have a sedentary job or are constantly in the same position. Take frequent breaks with short stretches.
Eat right, limit the presence of harmful, fatty, spicy foods in your diet. Eat more fiber-rich vegetables and fruits. Make sure that the weight is within acceptable limits. Don't get too cold and visit your doctor regularly, even if nothing bothers you.
Adenoma of the digestive organs is one of the most dangerous types of benign tumors. It very often transforms into malignant, and therefore requires mandatory removal.
Pumpkin in the treatment of male problems
When thinking about how to treat prostate adenoma, men never ignore folk remedies using pumpkin.
It is rich in sucrose and glucose, and bright varieties (orange) are rich in carotene, so they surpass even carrots in quantity.
Among the useful vitamins, it has the following: D, PP, A, E, B1, C, B2. They help the body digest food well, select useful substances and significantly increase a person’s defenses.
This disease can be a harbinger of cancer. Pumpkin, rich in minerals and iron, helps prevent the development of anemia. In addition, the vegetable removes dangerous toxins and waste, as well as cholesterol. Pumpkin is of particular value in the treatment of various ailments or their prevention due to the body’s good response to fiber.
Treatment of prostate adenoma in men can be carried out using the following traditional medicine: the patient should eat 3 glasses of seeds daily and drink 3 tbsp of juice. l. It is useful to include a variety of pumpkin porridges in the menu. There is real evidence that an elderly man was relieved of such a problem after taking the seeds. But there is a strict warning here, because it is forbidden to fry them. In this form they will lose their medicinal properties.

An interesting way to treat male problems is the pumpkin ball. To prepare it, you need to grind 0.5 kg of seeds in a meat grinder, after peeling them. Add honey (200 mg) to the mixture and mix thoroughly. Now from this mass you can roll small balls the size of a nut. The product is stored in the refrigerator, removing it only before immediate consumption.
Course of administration: 1 ball 30 minutes before meals in the morning and evening for 3 weeks. The product should not be swallowed; to increase effectiveness, the ball should be sucked or chewed slowly for 3 minutes. This is a strong medicine, so one course per year will be enough.