What's happened
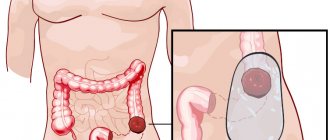
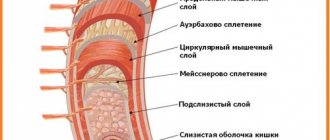
Malignant and benign tumors of the rectum are a heterogeneous group of non-epithelial and epithelial formations that have certain differences in growth, course, and histological structure.
One of the most serious pathological processes is cancer, which is characterized by a high mortality rate.
Recently, rectal tumors have become increasingly diagnosed. According to statistics, rectal disease accounts for approximately 40 percent of all intestinal tumors.
In most cases, the disease is detected in the adult population.
Classification
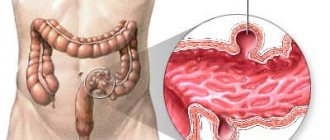
All neoplasms diagnosed in the rectum are divided into two large groups.
Benign
The localization site can be any layer of the organ. They can be of several varieties.
Epithelial
This group includes the following types of neoplasms.
Polyps
The structure of tumors is made up of epithelial tissue lining the intestinal mucosa. The location is any area of the organ. At the beginning of the development of the pathological process, there are no signs, which creates certain difficulties in early diagnosis.
As the disease progresses, the patient begins to experience pain in the anal area. The appearance of bleeding is also noted.
Polyps can come in various shapes and sizes. This type of neoplasm has a predisposition to rapid malignancy and acts as a provoking factor in the development of intestinal obstruction.
Villous
Villous tumors are also difficult to diagnose. In addition, they can quickly degenerate into cancerous tumors. The shape of the cone is round or slightly elongated. It has a red-pinkish tint. Small papillae can be observed on the surface.
Diffuse
The main reason for the development of this form of pathology is hereditary predisposition. Often detected in children and adolescents. The site of localization is the rectal mucosa. With this condition, fever, diarrhea mixed with blood, and intoxication appear.
Fibroids
Fibromatous tumors have a fairly dense structure. Connective tissue takes part in the formation. At the beginning of the onset of the disease, inclusions practically do not manifest themselves at all.
Fibroids, as a rule, do not reach large sizes. Predisposing factors for its occurrence are heredity and inflammatory processes.
In addition, benign neoplasms are often predisposed to malignancy. This is possible in the absence or incorrectly carried out therapeutic measures.
Myomatous
Rarely affects the rectum. Outwardly they are similar to polypous formations, but have a more solid structure. They are formed from submucosal or longitudinal tissues. In this condition, there is frequent false urge to defecate and blood in the stool.
Nonepithelial
This type of tumor forms in the connective and muscle tissue of the organ, lymph nodes and blood vessels. According to the classification, nonepithelial formations can take the form of:
- lipomas;
- neurofibromas;
- adenoma;
- angiomas;
- fibroids
Despite the benign nature of the tumors and the absence of a risk to life, it is not recommended to delay the treatment of such tumors.
Carcinoids
These are neuroendocrine neoplasms, due to which certain hormones are produced - serotonin, histamine and others.
The clinical picture largely depends on the type and amount of hormonal substance produced. In any situation, prompt surgical intervention is necessary.
Malignant
They can also be of epithelial and non-epithelial origin. The first category includes melanoblastoma, adenocarcinoma, and squamous cell. Solid, mixed, signet ring cell carcinoma, melanoma, scirrhus.
The second group consists of lymphomas, leiomyosarcomas, angiosarcomas, rhabdomyomas, neurilemmomas, and unclassified malignant neoplasms.
If we consider the growth pattern of tumors, they are divided into diffuse, exophytic and endophytic types.
Stages
Malignant neoplasms go through several stages in their development.
Zero
The tumor is small in diameter and does not grow in the cavity of the epithelial inner layer. In 95 percent of cases, it is possible to achieve complete cure and survival of patients for five years.
First
The tumor does not grow, but it is noted that it extends beyond the boundaries of the internal layers of the intestine. At this stage, the 5-year survival rate will be about 90% of cases.
Second
The tumor reaches a large size. In addition, it begins to spread to the outer and inner layers of the affected organ.
Third
In addition to the intestines, all layers of its walls, as well as lymph nodes, are involved in the oncological process.
Fourth
The last stage of the disease is characterized by metastasis to nearby organs. The liver, lungs and ovaries are often affected. Life expectancy over 5 years in this situation is one percent.
Clinical signs
Intestinal blastoma affects patients of all ages. If an infant falls ill, the likelihood of insufficient development of the connection of the bone structures of the cranial vault increases significantly.
Benign pathology initially occurs without any manifestations, which is why it is discovered by chance. As it progresses, a person begins to suffer from pain, discomfort in the abdominal cavity, and bloody or mucous discharge. Such symptoms often cause anemia, disturbances in water balance and protein composition in the plasma.
Large formations can lead to intestinal obstruction, requiring urgent surgical intervention. The first sign of a malignant tumor is the presence of bleeding and anemia. In this case, by the color of the blood you can understand which part of the intestine is affected.
In addition, cancerous blastoma is manifested by abdominal pain and stool disorders. In advanced cases, the patient often experiences constipation, the body becomes exhausted, general weakness, fatigue, loss of appetite and sudden weight loss appear. The patient is also unable to contain gases in the affected organ and discovers changes in skin tone.
Causes
Despite the fact that rectal tumor is a common disease, to date it has not been possible to establish the exact predisposing factors of its origin. However, experts have identified a number of reasons that may serve as prerequisites for the onset of the disease and the degeneration of healthy cells into pathological ones.
Nutrition
According to statistics, the risk of developing a tumor process increases significantly in people whose diet contains harmful foods.
If there are no fresh vegetables and fruits on the menu, then intestinal motility is disrupted. In addition, conditions are created in which pathogenic microorganisms can multiply.
Vitamin deficiency
With a lack of certain vitamins in the human body, a large amount of carcinogenic substances begins to accumulate in the intestines. As a result, healthy cells begin to mutate, which creates certain preconditions for tumor processes.
Overweight
There is a negative impact of obesity on the normal functioning of the intestinal tract. With excess body weight, blood circulation and intestinal motility are impaired. Against the background of this condition, a person experiences constipation, which creates favorable conditions for the development of the disease in the rectum.
Heredity
Chromosomes usually contain genes that are passed on to the child during conception. In the case where the parents’ history has recorded cases of cell mutations at the genetic level that control the division of cellular structures, then altered genes can be passed on to the children.
When exposed to unfavorable factors, malignant neoplasms begin to form.
Bad habits
Smoking and excessive consumption of alcohol can also have a detrimental effect on human health and, in particular, the intestines.
As a rule, nicotine and alcohol contribute to poor circulation and irritation of the intestinal mucosa. As a result, the development of benign tumors, which can subsequently degenerate into malignant ones, cannot be ruled out.
Working conditions
Sometimes the development of an oncological process can occur in people whose professional activities involve working in hazardous industries.
Precancerous conditions can also contribute to the appearance of cancerous tumors.
Polyps
They are specific growths that are localized on the walls of the intestine. As a rule, such tumors are benign and not life-threatening. However, if intensive growth of neoplasms is observed, then they must be constantly monitored.
Diffuse polyposis
As a rule, this disease can be transmitted at the genetic level. It is characterized by the formation of multiple lesions in the area of the straight and thick parts of the organ.
Anal HPV
The human papillomavirus can also be the reason why healthy cells begin to degenerate into pathological ones. As a result, their malignancy and the development of a cancer process cannot be ruled out.
Symptoms
If the tumor does not exceed 5 millimeters in size, then in most cases it does not manifest itself in any way. If it is injured, for example, during bowel movements, bleeding cannot be ruled out.
On this topic
- Oncogastroenterology
Feces for stomach cancer
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 6, 2020
With a significant loss of blood fluid, the following clinical picture occurs:
- the appearance of general weakness;
- lack of appetite;
- slight loss weight ;
- insomnia;
- lack of sexual desire in the male half of the population;
- headache ;
- menstrual irregularities in women.
As the tumor grows, the intensity of bleeding will also increase. Impurities of blood, pus or mucus are often found in the stool.
The malignant form of the pathological process also has certain symptoms.
Soreness
As the tumor grows, the patient will experience increasingly severe pain. In more advanced cases, pain may be present even in a calm state.
Discharge
When the seal is injured by feces, infection penetrates into it. In this condition, there will be blood or purulent admixture in the stool.
Intestinal obstruction
When the neoplasm reaches a large size in diameter, it becomes the cause of the development of intestinal obstruction.
Digestive disorders
At the beginning of the disease, diarrhea often alternates with constipation. Flatulence also increases. In later stages, the patient may experience uncontrollable bowel movements.
Closing the lumen
When the anus narrows, the stool changes its shape. The stool takes on a ribbon-like shape.
Foreign body
The patient is constantly bothered by the feeling that there is a foreign object in the anus. This condition is also accompanied by a frequent urge to defecate.
Treatment of inflammation of the lower colon
Treatment for inflammation depends on the specific diagnosis and severity. If a slight inflammation is caused by poisoning, then gastric lavage, taking various sorbents, drinking plenty of fluids and diet will help get rid of the problem in a few days
.
More serious diseases require a thorough examination and a professional approach to the treatment of the large intestine. Lack of proper balanced treatment can lead to dangerous consequences, including peritonitis.
For any form of colitis, it is necessary to follow a strict therapeutic diet, and especially if this is observed in pregnant women or in a newborn child. In this case, the doctor prescribes Diet No. 4
, which excludes from the diet foods that promote fermentation and rotting in the large intestine, irritating its mucous membranes: hot, salty, fatty, sweet, sour, fatty, spicy and dairy.
You should also temporarily avoid eating vegetables, fruits and berries. All food should be consumed only in liquid or thoroughly pureed form at a comfortable room temperature. This regimen must be followed throughout the entire treatment period and even after it. At the very beginning of the course of treatment (the first 1-2 days), it is better not to eat anything, and limit yourself only to drinking liquid in large quantities.
Therapeutic cleansing enemas
In case of inflammation of the large intestine, enemas are done only as prescribed by a gastroenterologist if it is necessary to cleanse the intestine of infectious components and its contents for direct delivery of therapeutic agents to the mucous membrane of the walls.
- Antiseptic enemas are made with infusions of chamomile, collargol and calendula. They help relieve swelling and soothe the intestinal mucosa, as well as remove pathological microflora locally.
- Enemas with sea buckthorn oil help rapid healing and restoration of the tissues of the mucous membrane of the large intestine.

Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis, specialists conduct a diagnostic examination, which includes several activities:
- palpation;
- fibrocolonoscopy – the condition of the entire rectum is assessed;
- irrigoscopy – makes it possible to determine multiple lesions;
- sigmoidoscopy – to visualize the internal state of the mucous membrane up to 50 centimeters in length;
- Ultrasound examination - reveals the spread of the tumor to the ureter and bladder;
- laparoscopy.
If there is a suspicion of the development of an exophytic oncological process, then computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging is additionally prescribed.
Treatment
The choice of therapeutic tactics is based on certain indicators, which include the patient’s age, the stage of the pathology, the type of tumor, and the degree of its prevalence.
If benign neoplasms are detected, surgical intervention is performed.
If rectal cancer is diagnosed, surgery, radiation and chemotherapy are used. The essence of the surgical method is to remove the tumor formation and affected lymph nodes.
On this topic
- Oncogastroenterology
First signs of rectal cancer recurrence
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 3, 2020
If it is noted that the tumor has begun to grow into neighboring organs, then combined treatment is used.
Radiation therapy is indicated both before and after surgery. Cancer cells are exposed to high-frequency radioactive irradiation, which makes it possible to destroy pathological cellular structures and stop the further spread of metastases.
Chemotherapy is also indicated to consolidate the results of surgery and destroy remaining metastases that could not be removed during surgery. This technique can also significantly reduce the re-formation of tumors.
Forecast
With timely excision of benign tumors, the prognosis is quite favorable.
On this topic
- Oncogastroenterology
Stool color for bowel cancer
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 3, 2020
When it comes to cancer, survival rates need to be predicted based on certain factors. It is important to take into account the type of tumor, the stage of the oncological process and the results of treatment.
When the disease is diagnosed at the beginning of its development, a 5-year life expectancy is observed in almost 100 percent of patients, subject to treatment.
If cancer is detected at later stages, the survival rate is significantly reduced.
When the last degree of pathology is diagnosed, the patient on average can live no more than a year, since this stage can no longer be treated.
Complications
The most common consequences of benign formations is the high risk of their degeneration into malignant forms.
When cancer is detected, a complication may be metastasis to nearby and distant anatomical structures. Also, against the background of blocking the intestinal lumen, intestinal obstruction often occurs.
Prolonged lack of treatment leads to the development of a more advanced stage of the disease, which significantly reduces life expectancy and leads to death.
Conclusion
A tumor of the small intestine can be benign or malignant, but in either case it requires medical attention. Many symptoms are attributed to the affected small intestine, which directly depend on the type of disease.
To diagnose these two types, approximately the same methods are used, but in the case of a malignant form, a study for tumor markers is carried out. In any case, no matter what type of tumor the most effective treatment is surgery.