Conducting research
When the patient takes a comfortable position on the couch, the sonologist will set up the equipment, take the sensor-generator in his hand, treat its main part with a colorless conductive gel and carefully begin to move the device over the surface of the abdomen. During an ultrasound examination, dosed compression will be performed - that is, gentle pressure on certain areas of the abdominal cavity, designed to improve visualization of the intestinal tract.
Sometimes a woman needs transvaginal diagnosis, for example, if she is overweight. In this case, an ultrasound is performed using a special narrowed sensor, which is inserted into the vagina. If during the procedure the lady experiences severe discomfort or pain, it is necessary to immediately notify the specialist about the unpleasant sensations. If obvious, most acute signs of appendicitis are detected, medical personnel may immediately send the patient to the operating room.
Features of the procedure in childhood
When diagnosing appendicitis in children, ultrasound of the abdominal cavity is used most often, since in childhood the disease is atypical, and the child cannot always explain what is bothering him or where the pain is localized. The vermiform appendix is involved in the formation of immunity, so removal of appendicitis in children should be carried out only after the diagnosis has been clarified using ultrasound.
Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity in most cases shows a disease such as appendicitis, so it is used for primary and differential diagnosis. No special preparation is required to conduct the examination. It is performed transabdominally, less often transvaginally. Ultrasound is a simple, inexpensive and informative technique used in the diagnosis of appendicitis.
Indications
Since an extremely advanced disease will soon lead to peritonitis, in no case should you ignore signs that may indicate appendicitis. Indicative physiological symptoms include:
- increased body temperature (up to 38.5 °C);
- prolonged pain in the abdominal area (often on the right);
- diarrhea;
- vomit;
- frequent urge to go to the toilet;
- abdominal wall tension;
- nausea;
- dry tongue.
Laboratory methods for diagnosing appendicitis
If inflammatory processes are present, then during palpation the patient feels sharp pain.
Among the methods by which the disease is diagnosed is palpation of the abdomen, when the doctor presses on the area where appendicitis is located, and the person feels a sharp pain. When the pressure is removed, the pain goes away. It happens that only this method is enough to make a diagnosis. If necessary, an adult or child is sent for a general blood test, in which laboratory diagnostics will show an increased number of leukocytes in the blood, this will indicate that an inflammatory process is developing in the body.
A number of advantages and disadvantages
Diagnosis of appendicitis is characterized by multiple positive qualities. So, among the most significant advantages, doctors highlight:
- High level of information content (about 90–92%).
- Obtaining reliable results about the patient’s condition.
- There is no need for any surgical intervention.
- Accessibility for citizens with an average level of income.
- Low cost.
- Speed of procedure (from 15 to 30 minutes).
- Possibility of making a diagnosis even with an unusual location of the appendix.
- Lack of special preparation.
It should also be noted that ultrasound shows the true cause of physiological discomfort, which, at first glance, resembles appendicitis. If other organs are affected, sonography will most likely reveal this.
Since official medicine does not have accurate data regarding the effects of ultrasonic vibrations on humans, it is impossible to declare with absolute certainty that there is no danger to health. However, inflammation of the appendage of the cecum is exactly the case that requires urgent diagnosis using an echography device: only it, at the stage of exacerbation, is able to detect appendicitis on ultrasound in time.
If we talk about obvious shortcomings, then we can focus on two significant flaws:
- Not every doctor has the opportunity to identify a dangerous disease, so there is a practice of so-called linking to the appropriate specialist.
- It is practically impossible to carry out the study through the abdominal wall of a patient if he has significant excess body weight.
Preparation requirements
The radiation procedure requires virtually no preparation. The only thing worth paying attention to is the diet: you need to remove gas-forming foods (milk, cabbage, baked goods, etc.) from it 2-3 days before the examination.
In addition, a predisposition to flatulence suggests the use of a more suitable antispasmodic on the eve of the session. It is also advisable to cleanse the intestines with an enema or laxative medications. To combat bloating, you can brew mint tea with cinnamon and drink it throughout the day instead of your usual drinks.
Can a doctor make a mistake?
In medical practice, there are cases of incorrect interpretation of the results of ultrasound of the appendix, associated with several reasons: the incompetence of the specialist, the physiological characteristics of the patients. If a person doubts the professionalism of a sonologist, if possible, he has the right to undergo diagnostics again from another specialist.
The second case requires special clarification. Sometimes incorrect or “blurred” elements are displayed on the monitor if a patient is being examined who has, for example, increased gas formation in the gastrointestinal tract, pregnancy or obesity. A similar situation is visible in the case of children and women - in these categories of people it is often difficult to identify the location of the appendix due to the peculiarities of their anatomical structure.
In order to accurately diagnose the disease, a qualified specialist refers the patient to additional procedures - repeated examination, blood and urine tests. The uncertain health status of the female population may be a reason to contact a gynecologist.
Is it possible to detect other abnormalities instead of appendicitis during an ultrasound?
Quite often, the main symptoms of inflammation of the vermiform appendage indicate completely different diseases of the abdominal organs. When performing an ultrasound, doctors can diagnose the following ailments:
- Ketoacidosis.
- Hernia.
- Pyelonephritis.
- Intestinal obstruction.
- Ectopic pregnancy.
- Gastroenteritis.
- Urolithiasis disease.
- Mesadenitis.
- Liver abscess.
- Porphyria.
- Inflammation of the ovaries.
- Renal colic.
- Lower lobe pneumonia.
- Acute cholecystitis.
- Pancreatitis.
- Intussusception.
- Salpingoophoritis (inflammation of the fallopian tubes).
- Diverticulitis.
Encyclopedia of Ultrasound and MRI
Appendicitis is a common disease of the abdominal cavity. It occurs at any age and requires immediate surgical intervention. The main symptom is a constant aching pain that occurs in the epigastric region and then covers the entire abdomen. After some time it is felt in the right iliac region. In some cases, vomiting or diarrhea occurs. To make a diagnosis, an ultrasound of the appendix is performed.
Dangerous disguise: how to recognize the enemy
Appendicitis very skillfully disguises itself as many other diseases, so it is completely impossible to recognize it on your own. There is no point in scouring the Internet, looking for symptoms and comparing them with the described clinical picture. If you have a stomach ache, have suspicions or become paranoid about this (this happens too), then you can simply do a tomography for your own peace of mind. The price of an abdominal MRI is not that high (from 4,000 rubles). But you will get rid of all fears and obsessions, and as a bonus, you will learn whether you have gallstones, whether your spleen is in order, whether your stomach and other organs are functioning normally.
What is appendicitis?
In humans, the intestine consists of the small intestine and large intestine. Between them is the cecum. It has a vermiform appendix. Doctors also call it the appendix. It is a tubular formation.
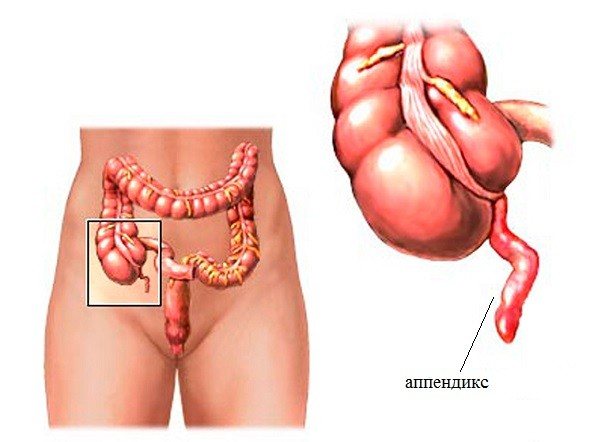
The lumen of the appendix, connecting to the lumen of the cecum, sometimes becomes blocked by fecal stones, a tumor, a foreign body or a parasite. Because of this, mucus accumulates in the appendix. Such an environment is favorable for the reproduction and growth of microorganisms. As a result, the appendix becomes inflamed, that is, appendicitis occurs.
Peculiarities
Inflammatory processes that appear in the gastrointestinal tract have various causes. These include poor nutrition, abuse of bad habits, and untimely treatment of chronic diseases. The cause of inflammatory processes in the appendix is also pathogenic microorganisms, such as E. coli, staphylococcus, streptococcus, and enterococcus. As soon as the immune system declines and fails, these bacteria begin to multiply rapidly and cause inflammatory processes in the body of a child or adult.
This picture is often observed in women who are pregnant. Their immunity is reduced, and this is a favorable environment for the proliferation of pathogenic microflora, so appendicitis in pregnant women is a common problem that requires urgent medical attention. In adults, the disease manifests itself against the background of deterioration of intestinal motility, when feces are not removed from the body in a timely manner, resulting in the formation of pathogenic microflora that causes inflammation.
Diagnostic methods
A computed tomography (CT) scan may be performed to detect inflammation. This research method makes it possible to detect appendicitis with a high probability. However, CT has a number of disadvantages. The following negative aspects can be identified:
- the presence of ionizing radiation that negatively affects the body;
- the use of contrast agents (intravenous or rectal), which sometimes lead to serious complications;
- high cost of research.
Computed tomography can be performed if there is a suspicion of a through defect (hole) in the appendix or an abscess. It is generally undesirable for pregnant women and children. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a more suitable method for diagnosing appendicitis. It has the same high accuracy as CT. Another advantage is the absence of ionizing radiation. However, computed tomography is extremely rarely prescribed. It has a higher cost.
Ultrasound diagnostics is the more preferable research method. It does not contain ionizing radiation, therefore it is absolutely safe for children and pregnant women. The following advantages of this research method can also be highlighted:
- low cost;
- non-invasive;
- speed of obtaining results;
- possibility of conducting repeated studies.
The main disadvantage is low sensitivity in the diagnosis of acute appendicitis.
How tomography works
X-rays hit the matrix, which transmits all the necessary information to the computer. All received data is instantly processed and displayed on the screen. Doctors will be able to evaluate them in detail, noting all fragments with changes in the absorption of rays.
This technique allows you to see appendicitis in much more detail and better than with a conventional x-ray examination. This helps to study the problem comprehensively. And such a detailed study is extremely important in order to capture the problem when it has not yet reached critical stages and dimensions.
Also, during a computed tomography scan of appendicitis, contrast agents may well be injected into the body. Such substances are specially used to highlight all difficult places. Appendicitis in this case will be presented in all its glory.
Ultrasound: can a specialist see appendicitis?
There is no consensus on the effectiveness of ultrasound diagnostics in detecting inflammation of the appendix. Some doctors recommend using ultrasound in unclear cases and not prescribing it to patients who have a clear clinical picture of appendicitis. It is generally accepted that this research method has a low percentage of visualization of the normal appendix. For patients with obvious symptoms, it is best to undergo immediate surgical treatment, since the specialist may not see appendicitis at all on an ultrasound.
Other doctors believe that ultrasound can be performed on all patients without exception (both if appendicitis is suspected and if there are obvious symptoms). The accuracy of the diagnosis depends on the specialist performing the ultrasound. A person with extensive experience can notice echo signs of inflammation. A lot depends on technology. Modern high-resolution ultrasound scanners can detect appendicitis.
Carrying out an ultrasound
First, a sonologist (radiologist) performs a screening abdominal ultrasound. It gives an overview of the pelvic organs. Such a diagnosis is necessary in order to exclude the presence of other pathologies (for example, acute cholecystitis). After this, the specialist begins to examine the appendix.
Ultrasound of the appendix is performed with a high-frequency sensor. The first step is to search for the vermiform appendix. Then signs of inflammation are detected in the detected appendix. Experts evaluate:
- width of the appendix;
- wall thickness;
- the amount and nature of the contents of the appendix;
- condition of surrounding tissues.
Ultrasound diagnostics takes from several minutes to half an hour. The duration of the study will be quite short if the sonologist or radiologist can quickly locate the appendix. If difficulties arise in visualization, the ultrasound is delayed.
Ultrasound signs of inflammation
If an ultrasound shows an enlarged appendix, this means that it is engulfed in an inflammatory process. This is the main symptom of appendicitis. The measurement is made using a transverse scan. The vermiform appendix is considered expanded when its external anteroposterior dimension under the influence of compression is more than 6 mm. If the diameter is less than this value, then acute appendicitis is excluded.
The contents of the lumen of the appendix are also assessed. Normally it is filled with gas. During the pathological process, only hypoechoic fluid (pus) is visible in the appendix. Rarely, gas released by microorganisms is present in the inflamed appendix. An appendix with similar contents causes diagnostic difficulties.
Ultrasound diagnostics also includes measuring the thickness of the wall of the appendix. As a rule, during the inflammatory process the value increases. The wall becomes thickened (more than 2 mm). However, it is quite difficult to measure. Often the inflamed wall cannot be distinguished from the hypoechoic fluid that has filled the lumen of the appendix.
The vermiform appendix must be checked for compressibility. During the study, compression is applied. A normal appendix moves and changes shape. When inflamed, it cannot be compressed. There is no peristalsis.
A fecal stone can be found in the lumen of the appendix. Its size is most often about 1 cm. A fecal stone appears as an echogenic or hyperechoic focus with an acoustic shadow. Its detection indicates an inflammatory process.
The above ultrasonic signs are the main ones. Additional criteria for appendicitis can be identified:
- enlarged lymph nodes in the lower right quadrant;
- the presence of fluid around the appendix (it is detected not only with perforation of the appendix, but also with other pathologies);
- inflammation and increase in the volume of adipose tissue surrounding the appendix (it becomes more echogenic).
What can appendicitis be confused with?
Mesenteric lymphadenitis
— Enlarged lymph nodes
— Slight thickening of the wall of the terminal jejunum and cecum
Crohn's disease
- Longer medical history
— Marked thickening of the wall of the terminal ileum
— Suppression of peristalsis in the terminal ileum
- Thickened intestinal wall accumulates contrast
Oophoritis
— Normal appendix size
— The area above the gonads is painful when pressed with a sensor
— Tumor of the appendix
— Chronic symptoms
- Uneven thickening of the intestinal wall extending into the cecum
Appendix tumor
— Chronic symptoms
- Uneven thickening of the intestinal wall extending into the cecum
Cecal diverticulitis
— Diverticula in the ascending colon
– Peridiverticulitis in adipose tissue
— Circular thickening of the wall of the cecum
Inflammation of the omental processes of the large intestine
— Fatty nodules with an inflammatory rim surrounding the colon
Ultrasound results
If the appendix is visualized with signs of inflammation, then this result is considered positive. Acute appendicitis is diagnosed. The result is negative in cases where the appendix is not detected during the study, and signs of inflammation in the lower right quadrant are not detected.
The vermiform appendix can be visualized without signs of inflammation. This is a true negative result. If the appendix is detected, but the criteria for inflammation are inconclusive or an insufficient number of them is detected, then the result is considered doubtful.
Ultrasound diagnostics is a simple and quick way to detect appendicitis. This method is successfully used in diagnostic practice, despite the low percentage of visualization of the normal appendix. If the result is positive, immediate surgical treatment is performed, and if the result is doubtful, additional studies are prescribed (for example, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging).
Severe abdominal pain can occur for various reasons. When the appendix becomes inflamed, a person feels acute pain in the right side of the abdomen. This inflammatory process is called appendicitis, and the appendix itself is called the appendix. It is sometimes difficult to determine such a condition. Only an experienced doctor can understand the cause of such pain. Ultrasound of appendicitis is a simple and accessible way to determine inflammation of the appendix. An ultrasound examination gives doctors the opportunity to assess the condition of internal organs, examine the pathological focus and find out the cause of abdominal pain.
When is it necessary to make an accurate diagnosis?
Experts know that the pain experienced by the patient has a 50% probability of appendicitis. The other 50% say that this may be another inflammatory process in the peritoneum, masquerading as that disease. Accurate diagnosis is important.
In the West, experts argue whether to do an ultrasound only for those who clearly have signs of an appendix or for everyone with similar pain symptoms? After all, if they are diagnosed incorrectly, the appendix may burst, and peritonitis already poses a threat to the patient’s life. There are also patients who often have atypical symptoms. These are children who cannot accurately describe their feelings, people weakened by some illness, or elderly, pregnant women.
If the doctor, after examining the patient, suspects that the condition is critical, he decides to urgently perform surgery without ultrasound and other additional studies. Otherwise, complications may begin in the near future in the form of:
- perforations;
- sepsis;
- peritonitis;
- gangrenization, etc.
The doctor will most likely prescribe an ultrasound of appendicitis in the case when the patient feels pain both at the location of the appendix and somewhere in the navel area, which is not very typical. Diagnostics will help to determine exactly where the problem area is and prescribe surgery.
Appendicitis is also diagnosed using a barium x-ray. The first ultrasound scans of patients with this diagnosis began in the 80s. This technique has been described in detail and scanning has been successful in diagnosing this disease to this day.
Benefits of Ultrasound
Ultrasound examinations are well received by people and do not cause fear or mistrust. Ultrasound of the appendix has advantages over other diagnostic methods:
- the procedure takes 10-30 minutes. The data obtained during the survey is processed quickly and the conclusion is issued immediately;
- the examination is non-invasive and painless. For acute pain in children, this is a big plus;
- absence of irradiating moment;
- the method is able to identify other disorders in the body;
- scanning can be performed several times as necessary.
Symptoms
Where the pain comes from is difficult to understand at first. Its localization is not determined; it seems to move throughout the abdominal cavity. A painful sensation may appear in the navel area on the right, in the stomach area at the top, and then move down. The person has difficulty moving, as the pain increases sharply when moving. It can be dull and barely aching, then it becomes cutting and unbearable.

After several hours, the pain becomes so unbearable that the person assumes the fetal position and curls up. Movement becomes impossible. Digestive upset is added to everything. At this point, the localization of the pain becomes clear - it is clearly recorded in the abdomen on the right. The onset of the disease is characterized by an increase in temperature to 38 degrees, as well as nausea and vomiting. The temperature may drop to normal, but then rise again to 40 degrees, which precedes the breakthrough of pus, and this is very dangerous. This is the standard picture of the progression of appendicitis.
How to diagnose at home
If you suspect appendicitis in a loved one, do not panic. Before doctors arrive, you can try to determine the signs of appendicitis by the type of manifestations. To do this, you need to do several manipulations:
- a person can calmly lie on his right side with his legs bent; in this “childish” position the pain stops. If you put the patient on his left side and ask him to straighten his legs, it will return, this indicates inflammation of the appendix;
- there is no way to cough without increasing pain;
- when tapping on the right side of the abdomen, pain is felt from below;
- If you put a little pressure on the painful area and then let go, a sharp pain occurs - another sign of appendicitis.
Determining the disease in yourself or in your loved ones is, of course, possible, but often a person’s life depends on the provision of immediate assistance. This means that there is no need to waste precious minutes on independent manipulations; you need to urgently call doctors.
In what cases is it not performed?
When the manifestations of the disease as a result of the examination are obvious, patients are prescribed an ultrasound scan, since the consequences of inaction are dangerous. Today, doctors are arguing whether ultrasound scanning should be prescribed to all patients with a clinical picture of appendicitis or only to those groups of citizens who have a non-standard picture of inflammation. The position of the appendix varies from person to person, so symptoms are difficult. Patients belonging to risk groups (children, pregnant women, the elderly) usually have non-standard symptoms. Untimely diagnosis of inflammation of the appendix is fraught with serious complications, in which a person’s right to existence becomes dependent on the timely intervention of doctors without unnecessary research. In these circumstances, ultrasound is not performed because the patient urgently needs a surgical solution to the problem. If sepsis, peritonitis or perforation of the appendix occurs due to inflammation, emergency surgery is performed immediately.
Is it possible to see appendicitis on an ultrasound and determine inflammation?
Ultrasound diagnostics is an informative method for quickly determining acute inflammation of the appendix and is of particular importance in differential diagnosis.
Ultrasound is prescribed for an atypical course of appendicitis, for example, with chronic inflammation, abnormal location of the appendix, if there is a suspected exacerbation of diseases of the peritoneal and genitourinary system in women.
Due to the accessibility and speed of the procedure, the issue of surgical treatment of acute appendicitis is promptly and quickly resolved.
Causes of appendicitis
As a rule, appendicitis develops due to the influence of polymicrobial flora, which is represented by staphylococci, Escherichia coli, anaerobes, strepto-, staphylo- and enterococci. Pathogens penetrate the wall of the appendix from the lumen, that is, in an enterogenous manner.
Also, conditions for the occurrence of appendicitis are created during stagnation of intestinal contents in the appendix due to its bending, as well as the presence of hyperplasia of lymphoid tissue, fecal stones and foreign bodies in the lumen.
A certain role is played by dietary habits and the location of the appendix, excessive consumption of meat and a tendency to constipation, as a result of which a large amount of protein breakdown products accumulates in the intestinal contents, and this creates a favorable environment for the proliferation of various pathogenic microorganisms. Many people are interested in whether an ultrasound will show appendicitis.
In addition to mechanical causes, appendicitis can be caused by parasitic and infectious diseases, for example, typhoid fever, intestinal tuberculosis, amoebiasis and yersiniosis.
In pregnant women, the risk of appendicitis increases due to an increase in the size of the uterus and changes in the position of the appendix and cecum. They also have factors predisposing to appendicitis, such as changes in the immune system, constipation and changes in the blood supply to the pelvic organs.
Technique for performing ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity
Figure 3. Fecal calculus deposits.
Usually, ultrasound is performed without prior preparation of the patient (enema or waiting for the food taken to be absorbed). The patient lies on his back, points or independently places the sensor on the place where the pain is felt most strongly. Then the doctor slowly begins dosed compression.
He gradually presses harder and harder, and the distance between the sensor and the appendix decreases to 0.5-3 cm. The cecum is emptied and reduced. In this case, the sensor visualizes the appendix, and the structure of the organ is visible on the screen. Women are sometimes examined transvaginally.
In controversial cases, the examination is repeated. Before this, empty the bladder or perform the procedure after a half-hour break.
If the patient is unable to independently determine the most painful point (the pain is mild or the appendix is located abnormally), they search for the location of the appendix. He can be:
- Near the sacrum.
- Behind the rectum.
- In the pelvis near the rectum, uterus and bladder.
- Near the liver and gall bladder.
- If the cecum is underdeveloped and is in an abnormal position, the appendix may be located in front of the stomach.
- On the left, if the internal organs occupy a mirror position.
The most difficult thing to find is the process behind the cecum. If it has decreased during the preliminary examination, then the results are much easier to obtain. The location of the appendix determines the path of spread of purulent contents during an acute inflammatory process in the event of perforation. This can be seen in the figure (Fig. 2).
In what cases is ultrasound required?
Appendicitis is an acute inflammation of the appendix that requires surgical therapy. Although this vermiform appendix is a vestigial organ, it still performs three main functions:
— collects and grows colonies of beneficial intestinal microflora;
- produces a number of hormones;
- acts as a barrier that blocks the movement of various types of infections.
Although a number of experts consider this organ useful (although it was previously argued that it is useless and harmful), when it becomes inflamed, it is necessary to get rid of it surgically. The best way to help identify appendicitis in the absence of a pronounced clinical picture is ultrasound. The doctor may order an examination of the abdominal organs in the following cases:
- if the patient complains of pain of any intensity, concentrated in various places of the abdomen (most often appendicitis is characterized by pain in the lower abdomen or iliac region on the right side);
- the doctor has preliminary examination and medical history information that allows one to suspect appendicitis;
— a blood test, along with the growth of leukocytes, reflects a shift in the formula to the left: in this case, it is necessary to exclude the presence of inflammation of the appendix of the cecum or non-specific symptoms in the patient.
Atypical situations
Ultrasound for appendicitis is also performed in atypical situations, especially for pregnant women, children and the elderly, as well as for patients who are weakened by other diseases. They may feel pain in places other than those that are more common with appendicitis.
Thanks to ultrasound, you can no longer doubt the origin of pain in people with an abnormal location of the appendix. This rudimentary organ may be located in different people differently than shown in anatomical manuals.
Since this part of the cecum is mobile, it is able to change its direction in the abdominal cavity. That is why pain may occur in places other than those typical for classic type appendicitis. In this situation, methods such as ultrasound and computed tomography are most often used.
Ultrasound for appendicitis is more widely used because it is accessible, less expensive, and faster. In addition, not all hospitals are equipped with CT scanners.
Source: https://AptekaTamara.ru/zhkt-zabolevaniya/pokazhet-li-uzi-appendicit.html
Will an ultrasound show appendicitis or not, and how is the diagnosis carried out?
If the appendix is found through examination, but the signs characteristic of appendicitis are not visible, the doctor casts doubt on the preliminary diagnosis (appendicitis). It is impossible to diagnose appendicitis without detecting signs of inflammation. In these circumstances, the result is determined to be negative. If the appendix has ruptured, the following indicators of rupture may be detected:
- the structure is layered and uneven;
- the density and echogenicity of the omentum are increased due to the resulting inflammation;
- intestinal loops are inflamed (abscess).
Ultrasound may show ambiguous results if the signs are non-standard, and to confirm the diagnosis, the doctor prescribes additional examinations:
- X-ray;
- blood and urine tests;
- tomography;
- laparoscopy.
To conduct this type of ultrasound, there is no need to go on a diet, cleanse the body, or drink a lot of water. If appendicitis is suspected, the sensor moves across the patient's abdomen, emitting high-frequency waves that are reflected from his organs and display the overall picture on the monitor. When identifying the nature of inflammation in adults and children, doctors use a compression method with dosed load. The doctor applies gentle pressure to the anatomical location of the appendix. When a process is detected, doctors pay attention to its appearance, walls, size and nearby organs. The diagnosis of “appendicitis” is made when the test gives a picture of the changes:
- the walls are thicker than normal. The norm is less than 3 mm;
- increased diameter (norm – up to 6 mm);
- increased echogenicity.
How is the procedure performed?
For mild pain, an ultrasound of the abdomen is performed according to a specific algorithm:
- The upper part of the rectum is examined.
- The iliac vessels located slightly higher are examined.
- Examination of the space behind the ileum and cecum.
- The pelvic organs are studied.
- In female patients, the doctor must examine the right ovary and the surrounding area.
Important! Ultrasound is not the end result! In addition to such diagnostic measures, laboratory tests, MRI, laparoscopy, and CT are prescribed.
After receiving all the data, the doctor makes a final diagnosis. An ultrasound after removal of appendicitis is done in situations where the patient has become worse after the operation.
In addition to ultrasound, it is recommended to take a blood test for appendicitis.
Norms and interpretation of results
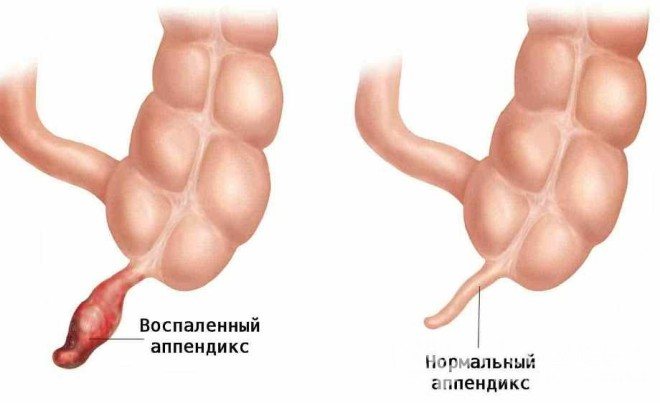
During an ultrasound scan for painful symptoms, the monitor shows an unambiguous picture: an increase in the inflamed appendage surrounded by exudate. The doctor compares the data obtained with established standards. A healthy appendix looks like this:
- curved, consistency – tubular;
- cross section – round;
- ending - blind;
- wall thickness – up to 3 mm;
- diameter – up to 6 mm (maximum – 7 mm);
- There are no contractions of the walls.
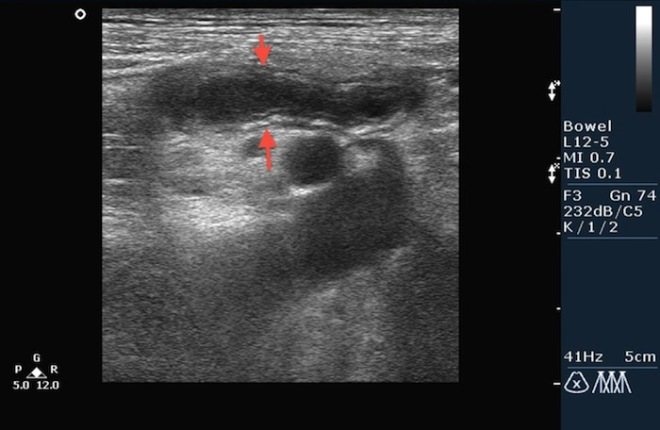
An inflamed appendix has signs:
- tubular structure. The ending is blind;
- the cross section resembles a target;
- wall thickness and diameter increased;
- there may be a fecal stone in the lumen (1 cm).
There are cases when the appendix has established normative indicators, but pain is present, then doctors look for their cause in defects of other organs.
Perforated and inflamed appendix
The perforated type appendix has a discontinuous structure in the form of layers. Its walls are thickened unevenly. The echogenicity of the fluid around it is increased. It is surrounded by an inflamed omentum. Abscesses are observed in intestinal loops.
The inflamed appendix in cross section resembles a target. It is filled with air, which does not escape when pressed. Tubularity is inherent. Ends blindly. The wall thickness is more than 3 mm, and the diameter exceeds 6 mm. Making a diagnosis of “appendicitis” can be complicated by the presence of gases in the intestines, therefore, if the patient’s examination is planned, he should take this into account and not consume foods that cause gas formation the day before.