Liver cirrhosis is a condition that affects not only the liver itself, but also all organs and systems.
The fact is that the liver performs many different functions, and when it is destroyed and the ability to perform these functions is reduced, many other processes in the body are also disrupted.
If we talk about laboratory tests, changes are found in general blood and urine tests and, of course, in biochemical blood tests. But due to liver cirrhosis, the characteristics of feces also change.
Primarily, cirrhosis of the liver can affect the frequency and shape of stools. Often one of the symptoms of this disease is diarrhea or, conversely, constipation.
In addition, cirrhosis of the liver leads to the development of hemorrhoids, which also affects stool: as a rule, it becomes difficult.
Stool color in liver cirrhosis
With liver cirrhosis in the sub- and decompensation stages, feces often become white, or the color of clay.
This is due to the fact that the pigment that turns the stool brown does not enter the intestines. Let's take a closer look at this process.
With a normally functioning liver, the following occurs. Hemoglobin, with the help of enzymes, breaks down into several substances with the formation of an intermediate product - biliverdin.
Next, biliverdin is converted into bilirubin, which exists in the bloodstream in free form for a short time. This bilirubin is called free, or direct, and is toxic.
Normally, its content in the blood is insignificant and does not pose a danger. Free bilirubin undergoes a complex of reactions and is neutralized in the liver, turning into bound, or indirect bilirubin.
Then it enters the intestines with the bile flow, where it is converted into urobilin, which again enters the bloodstream and is excreted by the kidneys, causing the yellow color of urine.
In addition, the formation of stercobilin, a pigment that gives feces its characteristic color, occurs in the intestines.
What happens with liver cirrhosis? Hepatocytes are destroyed, their functional ability also decreases.
Therefore, the binding of bilirubin and its neutralization slows down, the main part of the bilirubin remains in free form and circulates in the blood, excreted by the kidneys.
This is why bilirubin does not enter the intestines and stercobilin is not formed. The color of feces changes with cirrhosis of the liver: it becomes light, and then completely white.
The appearance of white or just light-colored feces is a bad sign. It indicates a rather serious dysfunction of the liver and biliary tract. If you notice this symptom repeatedly, you should consult a doctor.
What in the coprogram indicates hepatitis
A coprogram is a comprehensive study of stool that allows you to assess the functioning of various organs. The analysis is included in the list of free ones, and can be taken at any clinic under the compulsory medical insurance policy. Usually it is taken by referral, and the results come back to the doctor who sent you for examination. Normally, feces should be dark brown in color and have a persistent, characteristic odor. The presence of liver pathology is indicated not only by the tone, but also by a number of other indicators:
- Color from light yellow to white indicates destructive processes in the pancreas and liver.
- Ointment-like consistency is a lack or excess of bile produced by the liver. Loose stools may be a consequence of inflammatory processes.
- Acidity 8-8.5 pH – dysfunction of the small intestine and the hollow organ of the digestive tract (stomach).
- Mild or no odor – disorders of the pancreas and liver.
- A stercobilin level below 75 means blockage of the bile ducts, malfunction of the exocrine gland located in the abdominal cavity.
- The presence of leukocytes is an inflammatory process in the abdominal cavity.
- Fatty acids are found when there is a lack of bile produced by the liver.
- Triglycerides are a disruption of the process of synthesis and transportation of bile.
We do not provide photos with the color of stool for hepatitis in adults and children for aesthetic reasons.
With this disease, excrement changes not only its color. Only comprehensive diagnostics allows us to draw a conclusion.
Other changes in stool color in liver cirrhosis
In addition to lightening, feces with cirrhosis may undergo other changes. First of all, bloody discharge may appear along with feces.
They are most often associated with the presence of hemorrhoids: cirrhosis of the liver leads to dilation of hemorrhoidal veins, which subsequently become inflamed. Bleeding from hemorrhoids has the following characteristics:
- Blood is scarlet
- Little bloody discharge
- Blood appears immediately after defecation
- Characteristic signs of hemorrhoids are present (pain, burning, constipation)
In any case, if bloody discharge from the rectum or scarlet blood appears in the stool, you should consult a doctor.
A much more dangerous situation is a change in the color of stool, such as blackening. Black stool is called “melena” and is a very dangerous condition that requires emergency medical attention.
Black stool in liver cirrhosis occurs when internal bleeding develops. In this case, the feces will be unformed, almost liquid.
Internal bleeding is often accompanied by vomit that is “coffee grounds”—dark in color. The dark color of stool and vomit is due to the fact that the blood spent some time in the stomach and was digested.
Bleeding develops due to varicose veins in liver cirrhosis.
Urine color depending on the stage of cirrhosis
The progression of cirrhosis leads to an increase in free bilirubin in the blood and urine. The higher the stage, the darker the liquid.
| Urine color | Symptoms | Stage of cirrhosis |
| Deep yellow | Constant fatigue (even in the morning), absent-mindedness. Poor appetite. | Stage 1 |
| Dark beer, strong tea | Sudden weight loss, digestive problems, dizziness, feeling of aversion to food. | Stage 2 |
| Brown with yellow, bubbly foam that disappears quickly. | Ascites (water in the abdomen), frequent vomiting, sometimes with blood, and jaundice develop. Stool becomes discolored or black (due to internal bleeding) | Stage 3 |
| A red color appears with opacities and flakes. | Bloody urine, pain when going to the toilet, progression of complications. | Stage 4 |
Red impurities in urine indicate the presence of blood in it. It is not always liver disease. But if you did not eat beets (a natural dye) the day before, consult a doctor immediately. This color is a cry from the human body for help. In men, it may appear after an injury or blow to the genital organ. In women - erosion, inflammation of the uterus and ovaries.
Stool analysis for liver cirrhosis
A coprogram (general stool analysis) greatly helps to suspect liver cirrhosis. The color of the stool will change to white, clayey. The amount of stercobilin in feces decreases, in which case the feces are called acholic.
The normal content of stercobilin in feces: 75-350 mg/day. Blood may also be detected in a general stool test for liver cirrhosis. The detection of scarlet blood most likely indicates hemorrhoids or a rectal fissure.
Black stool is a sign of internal bleeding. Also a sign of bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract is the detection of insoluble protein in the stool.
A stool occult blood test helps determine the presence of bleeding if there are no obvious signs of it.
A positive stool reaction to occult blood can indicate not only hemorrhoids, anal fissure, but also hidden internal bleeding.
This situation requires immediate further diagnosis and treatment.
gemor.su
How to return normal stool color?
In case of liver cirrhosis, no matter what stage of development the disease is at, it is necessary to strictly follow a number of rules:
- rest more often;
- avoid crowded places, do not contact sick people;
- do not lift heavy objects;
- take diuretics (the dosage is calculated by the attending physician);
- follow a diet;
- take medications prescribed by your doctor.
To restore intestinal function and maintain the balance of intestinal microflora, you should take Duphalac. This drug is a synthetic sugar that provides nutrition for beneficial bacteria. Duphalac helps normalize stool up to 2 times a day, has no side effects and is suitable for newborns.
The role of the liver in the body
The function of the liver in the human body is to protect other organs from toxic influences and break down incoming substances necessary for normal life. Failure of an organ in cirrhosis has a serious impact on the normal functioning of other parts of the body. Therefore, the changed color of urine and feces should alert a person, especially if the stool is disrupted, constipation or diarrhea alternates.
It is necessary to immediately undergo diagnostics of the body, donate blood for a biochemical analysis, which will make it completely clear why the stool becomes discolored and the urine darkens. It should be remembered: a dangerous disease can be cured only at the initial stage.
In 40% of cases of liver cirrhosis, the cause is chronic alcoholism. Damage to the organ occurs without symptoms for a long time, especially since a frequent state of intoxication prevents the manifestation of signs of the disease.
Therapeutic measures
Treatment is prescribed depending on the stage of cirrhosis and the extent of liver damage, the presence and nature of complications. As a rule, intensive drug therapy is indicated together with diet No. 5. It is possible to perform surgery through anastomosis and ligation of the hepatic artery. Self-medication is strongly discouraged due to the severity of the disease. Cirrhosis of the liver is incurable.
When deciphering analyzes of excrement or biological fluid, one of the first indicators is color. It indicates a malfunction of an organ or an entire system. With hepatitis, the color of stool often changes, as does the consistency. To understand why this happens and what the changes indicate, you must first have an understanding of the disease itself.
How the disease develops
There are 3 stages of the disease:
Compensated cirrhosis has very few symptoms that only a person who values his health can notice:
- Changed color of urine to the color of dark beer;
- Blood escaping from the gums when brushing teeth, bleeding from the nose are signs of a blood cell clotting disorder;
- Discoloration or black stool, blood, alternating diarrhea and constipation are a consequence of insufficient production of bile enzymes involved in the digestion of food;
- Fatigue, drowsiness, decreased performance.
With subcompensatory cirrhosis, you can still return to normal life if you consult a doctor in time and notice the following signs:
- Nausea, loss of appetite, indigestion, alternating constipation and loose stools;
- Loss of strength, severe weight loss;
- Aching pain on the right, abdominal enlargement is associated with stretching of the liver due to the inflammatory process.
Decompensated cirrhosis of the liver is characterized by symptoms:
- Itching of the skin, which manifests itself mainly at night, dry skin;
- Accumulation of fluid in the peritoneum;
- Decreased libido, in men the figure becomes effeminate;
- Thin blood provokes subcutaneous hemorrhages with the slightest pressure on the body;
- The palms and feet change color - they become covered with red spots;
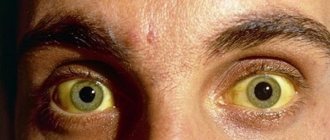
- The skin of the body and the whites of the eyes turn yellow.
What else affects the change in color of excrement?
Feces are waste products from the body. Nutrition is a necessity to maintain life. A varied diet is essential for health. Some foods do not break down completely, and the excrement turns into a color characteristic of a particular food:
- Citrus fruits and sorrel contain a large amount of acid. Increased pH in the stomach promotes the production of bilirubin. Stool after abuse of such products is usually abnormally dark in color.
- Greenish stool indicates that a person has consumed food rich in chlorophyll: broccoli, lettuce.
- Beets contain several coloring components: vitamin B9 and betaine. After eating the vegetable, the excrement is often red.
- Alcohol destroys the intestinal microflora. After drinking alcohol, the stool is loose and light.
The color of stool with hepatitis also depends on the patient’s diet and lifestyle. It often happens that even with chronic inactive forms of pathology, excrement has a normal tone and consistency.
Consequences
Having heard the diagnosis of cirrhosis, the patient is concerned about what awaits him and whether there are any chances of recovery.
How long do people live with cirrhosis?
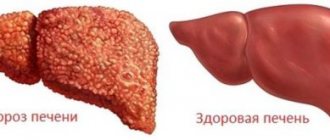
At the third stage of the disease, irreversible consequences occur in the liver: the organ tissue is replaced by connective and scar tissue, and the liver cannot perform its functions. Scars affecting the organ are clearly visible in the photo.
Life expectancy at stages 1-2 is 5-7 years, provided that you abstain from alcohol, follow a diet, and follow all the recommendations of your doctor. Only 10-35% of patients with stage 3 liver disease can live for more than three years. The main causes of death are bleeding, hepatic coma, and cancer.
Complications
With alcoholic cirrhosis of the third stage, complications of other organs develop, aggravating the general condition of the body:
- Bleeding: hemorrhoidal, gastric, intestinal bleeding occurs due to increased permeability of varicose vessels. Black stool indicates internal bleeding;
- Inflammation of the abdominal wall, peritonitis is provoked by abdominal dropsy;
- Impaired brain function caused by liver failure;
- Problems in the cardiovascular system;
- Malignant degeneration of the liver;
- Kidney failure;
- Hemorrhoids, constipation or loose stools , quite often blood is released in the stool;
- Bone fragility.
Most complications of cirrhosis are fatal if the disease is left to chance.
What type of hepatitis causes stool to change color?
The main functionally active cells of the liver are hepatocytes. They make up up to 80% of the mass of the gland. They perform many functions, including bile formation. Hepatocytes have a limited number of divisions and, unlike epidermal cells, a lower ability to regenerate. Liver damage involves destruction of hepatocytes. Hence the name of the disease.
The change in the color of stool most likely depends not on the type or form of hepatitis, but on the degree of liver damage. Thus, destruction of the gland caused by long-term alcohol intake, and against this background the development of pathology, can be treated. In this case, the excrement quickly acquires a normal color (provided one abstains from alcohol), although the liver is affected by a viral anthropogenic disease.
In most cases, the tone of biological waste changes. Similar changes in the color of urine and feces in hepatitis A and fetal. The latter is congenital, formed in the fetus in the womb at the sixteenth week of development. The causative agent of this form of hepatitis is a virus. The clinical picture is the same as for jaundice: the urine is dark, the stool is light, and bilirubin is detected.

How to determine cirrhosis
To diagnose the development of the disease, you should undergo a full examination and tests. The blood tested shows the amount of hemoglobin, which is significantly reduced in cirrhosis. Blood clotting also decreases, which promotes bleeding from various organs: stomach, esophagus, intestines. Blood often flows from the nose and gums. Testing for hepatitis, viral and sexually transmitted diseases is required.
It is also recommended to take a stool test to determine the exact reason for the loss of color.
If the diagnosis is confirmed, it is recommended to stop drinking alcohol and switch to a special salt-free diet, which is a prerequisite for treatment. The patient must remember that his life expectancy directly depends on following the doctor’s recommendations. Treatment is prescribed on a strictly individual basis.
Should be considered:
- The age of the patient - the older the person, the more ancient his illness. Older people have a worse prognosis for cirrhosis than younger people;
- Gender – women become drunk faster, and the damage to the female body is more severe with cirrhosis;
- Concomitant diseases - hepatitis, AIDS - greatly complicate the unfavorable prognosis of treatment.
At the third stage of the disease, a liver transplant is recommended, however, the transplant will not be successful unless you stop drinking alcohol.
A person with cirrhosis must understand that the disease poses a mortal threat. To maximize your life, you should inform your doctor about all changes in your body. It is necessary to protect yourself from infections that affect the respiratory organs - influenza, ARVI, pneumonia, which weaken the body.
In severe cases of the disease, characterized by bleeding, hospital treatment and bed rest are recommended.
Quitting drinking alcohol reduces the risk of developing cirrhosis of the liver.
alcoholism.com
Today you can easily find descriptions of liver diseases, and fatigue and decreased performance are often considered the first signs. However, you will agree that they are unlikely to serve as criteria for differential diagnosis, and certainly not a single patient will go to an infectious disease specialist with complaints of decreased performance. Therefore, we will look at the specific symptoms of liver disease using the example of viral hepatitis and talk about those signs that can really identify the pathology of the main filter of our body.
1. We start with icteric syndrome , since it is the most reliable marker of liver pathology. Viral hepatitis and other liver diseases are usually accompanied by this syndrome, although there are cases where the disease occurs without it. The icteric coloration of the mucous membranes and skin is caused by an increase in the concentration of bilirubin pigment in the blood and its accumulation in all tissues of our body.
In acute hepatitis, jaundice does not appear from the first day of the disease, because it takes some time for bilirubin to accumulate in the tissues in sufficient concentration. However, there is an early sign of developing jaundice - a change in the color of the urine. It is almost impossible to go wrong with this symptom - the urine becomes bright yellow or dark, and this is sure to attract attention. Some clinicians compare the color of urine in liver pathology with the color of dark beer, but even a lesser degree of severity of the symptom unmistakably indicates liver damage.
After three to five days, signs of liver disease appear on the skin - yellowness of the skin and mucous membranes becomes noticeable. The easiest way to detect this symptom is by the conjunctiva of the eyes, which takes on the color of lemon peel, the mucous membrane of the oral cavity and tongue turn yellow, and a little later the skin also becomes colored.
2. Intoxication syndrome. It is expressed from the first day of the disease, and often intoxication and fever are the first signs of liver disease. Often viral hepatitis begins like the flu - the body temperature rises, the head begins to hurt, and other accompanying signs of intoxication appear. At the same time, there are no catarrhal manifestations (runny nose, cough), but changes in the gastrointestinal tract are expressed, to which we will devote the next paragraph of the material.
3. Dyspeptic syndrome. Appetite sharply worsens, the patient feels nauseous, and vomiting is possible even after drinking or eating a small amount of food. Diarrhea appears at the same time or a little later. These symptoms of liver disease in humans persist throughout the entire acute period of the disease.
4. Smoothly move on to the next symptom associated with stool - any liver pathology is characterized by discoloration of it . This symptom, like jaundice, like the dark coloring of urine, is almost impossible to miss, however, it develops a little later, and is clearly expressed only at the end of the first week of the disease. The color of the stool may become almost white, in which case clinicians speak of acholic stool.
5. Pain syndrome. The liver does not hurt, because it does not have the corresponding nerve endings, but minor pain may be present, and often the patient describes it as a feeling of discomfort in the right hypochondrium, nagging and aching pain of low intensity. As a rule, these symptoms are caused by an increase in the size of the liver, but sharp pain will indicate the addition of biliary tract pathology.
Using hepatitis as an example, we looked at the classic signs of liver disease, now let’s try to figure out how the symptom complex will change with other diseases (cholecystitis, cirrhosis, gallstones, etc.).
Let's start with cholecystitis. The chronic form of the disease is not characterized by jaundice, but the pain syndrome is more pronounced - the patient complains of aching pain in the right side, and the pain is provoked by eating fatty, salty or fried foods. Dyspeptic syndrome is present, but its main symptoms are bitterness, metallic taste in the mouth, nausea and bloating. There is no intoxication, but there is weakness, insomnia and fatigue, which we mentioned at the beginning of the material. The color of the stool is not changed, although discoloration is possible in case of impaired bile secretion and obstruction of the biliary tract (calculous cholecystitis). Another characteristic symptom may be itching of the skin.
With chronic hepatitis, external signs of liver disease are most often present - jaundice, changes in the color of urine and feces, but the absence of these symptoms does not mean that the disease has gone into remission. As a rule, dyspeptic syndrome is moderately expressed, there may be pain, but intoxication and fever are not typical.
A special liver disease is cirrhosis . It can develop both against the background of hepatitis and for other reasons, among which alcoholism comes first. With cirrhosis, all organ functions are grossly impaired, icteric syndrome is pronounced, vascular changes are noticeable (spider veins are a characteristic sign of liver cirrhosis), the brain is affected and encephalopathy develops.
Further diagnosis of liver pathology should be entrusted to professionals - a biochemical blood test, urine test, liver tests, markers of viral hepatitis and other examinations are vital if there is even the slightest suspicion of liver pathology.
Tweet
healthport.ru
What does black stool tell us, or accurate diagnosis of diseases?
The normal color of human stool should range from light brown to dark brown. In general, a certain color is considered natural for every person, so if there are any violations, he should immediately notice changes and consult a doctor.
Stool acquires a brown color because it contains bile processed in the intestines and those food particles that remain undigested.
But black stool is, as a rule, a deviation from the norm. The presence of such coloring indicates a malfunction of any organs of the digestive system or more serious disorders. Our task is to explain to you what to do if you notice that your or your child’s stool has acquired this color.
So, first of all, you should make a list of the foods and drinks that you have consumed over the past three days. Very often, black stools occur as a result of consuming certain medications (activated carbon, vitamin complexes, bismuth preparations) or foods (for example, beets, prunes, grapes). There are a number of other medications that can give a similar side effect. However, it is very difficult to list them all, therefore, when purchasing any medicine, be sure to read the instructions for its use and the side effects column.
If black stool appears as a result of taking the above medications or foods, then it is not dangerous and does not require specific treatment. It is very important to remember that those medications that contain acetylsalicylic acid, anti-inflammatory medications and those that reduce blood clotting do not color the stool in a similar color, but can cause internal bleeding, which leads to a similar effect. This is very dangerous and requires immediate medical attention.
If the stool becomes a normal color within a few days, as a rule, such changes were not the result of serious illnesses. However, if black stool continues for two to three days (especially in the form of diarrhea), you should immediately consult a doctor.
As a rule, black specks in stool are undigested food particles or elements of medications. Remember that many foods can become dark as they pass through the intestines, even if they were not that shade.
Black stools, the causes of which can only be reliably determined by a doctor, sometimes occur along with some accompanying symptoms. It can also be a consequence of the development of acute or chronic diseases. Therefore, it is necessary to seek medical help if dark stool appears:
- Simultaneously with vomiting, nausea and fever.
- A patient has an ulcer (duodenal or stomach).
- In a patient with liver cirrhosis or chronic hepatitis.
- In the event that a person has intestinal cancer.
- After severe vomiting the day before.
- That patient whose blood test results are often diagnosed with anemia.
Sometimes black stool may appear along with blood. As a rule, the causes of this condition are serious intestinal diseases. If this happens after surgery, the patient may have internal bleeding.
General signs of cirrhosis
The symptoms of this disease are quite varied. The main signs that will help recognize cirrhosis of the liver are:
- attacks of nausea and vomiting. There may be blood in the vomit;
- pain in the right hypochondrium, pain can also be felt in the epigastric region. At the same time, it will become more intense after eating and physical activity;
- rapid weight loss;
- dry mouth and a feeling of bitterness;
- itching of the skin;
- increased fatigue;
- frequent stools, while they are liquid and discolored, urine darkens;
- decreased libido in men and disrupted menstrual cycle in women.
Painful sensations with cirrhosis appear due to the fact that the organ significantly enlarges and the parenchyma stretches. It is also important that at this stage there are already concomitant diseases, for example, gastritis and chronic pancreatitis, cholecystitis, and damage to the biliary tract. It is with dyskinesia that colic or mild nagging pain may occur in the right side. The patient is also bothered by a feeling of heaviness in the liver area. Due to dysfunction of the gallbladder, a large amount of fatty acids is released and this provokes itching. Sometimes a person scratches the skin so much that an infection gets into the affected areas and pustules appear. This condition in cirrhosis requires treatment. Yellowness of the skin is one of the main symptoms. It is due to the fact that the concentration of bilirubin (bile pigment) in the blood gradually increases. Since the blood clotting function is impaired when the liver is damaged, blood may be present during vomiting. This blood appears due to dilation of the veins of the gastrointestinal tract. A person who suffers from cirrhosis always loses weight rapidly. This occurs because fats, carbohydrates and proteins are not absorbed. Secondary intestinal enzyme deficiency also occurs.
What is hepatitis: etiology and clinical picture
Chronic and acute diseases of the exocrine gland, located in the abdominal cavity, of an inflammatory nature of various origins are called hepatitis.
Considering the duration of the disease, clinical symptoms, morphological features, hepatitis can be acute or chronic. The fundamental conditions in the formation of the acute form are infections and toxins. Most often, acute hepatitis, in addition to Botkin's disease, is caused by the following microorganisms:
- enteroviruses;
- Epstein-Barr virus;
- Leptospira;
- shigella;
- Escherichia Collie;
- butolotoxin.
Stages of the disease
In order to understand how to determine liver cirrhosis, you need to know its stages. It occurs in 3 stages:
- compensation;
- subcompensation;
- decompensation.
- Stage I - compensation Compensation (class A) is the initial stage of liver cirrhosis, in which there are no pronounced symptoms. The onset of the disease can only be diagnosed using laboratory tests. During the compensatory stage, a person may feel the following first signs of liver cirrhosis: weakness, loss of appetite, and concentration is impaired; the person may become irritable. But such symptoms can be attributed to fatigue at work. It is important to recognize the disease at an early stage, as treatment will bring positive results.
- Stage II - subcompensation With subcompensation (class B), signs of cirrhosis gradually begin to appear. To begin with, a person may notice the appearance of spider veins on the body and darkening of the urine. There is also a general deterioration in well-being and increased fatigue. Then jaundice, frequent attacks of nausea and vomiting, itching, and reddening of the skin on the palms and soles appear. As a rule, during the period of subcompensation a person eats a small amount of food. After this, he feels a heaviness in his stomach and nausea. As subcompensation develops, the temperature may rise. All this is explained by the fact that the liver already has areas affected by connective tissue and healthy hepatocytes cannot cope. One of the common manifestations of liver cirrhosis at the subcompensation stage is ascites, that is, the accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity. In this case, the patient’s abdomen is enlarged.
- Stage III - decompensation Decompensation is the last stage of cirrhosis, in which the liver can no longer perform its tasks of cleansing the body of toxins, since most of the hepatocytes are affected. Symptoms of liver cirrhosis at the stage of decompensation are pronounced. In this case, a person has constant intestinal upset, frequent vomiting, high body temperature, atrophy of muscles localized in the intercostal zone and in the upper shoulder girdle occurs. At this stage, the patient's exhaustion will already be visible, since he has already lost many kilograms. The only effective treatment at the stage of decompensation is a liver transplant. Expensive drug treatment will only slightly delay the irreversible process.
Asymptomatic course
Sometimes there may be no signs of liver cirrhosis at an early stage, or the disease may occur with the predominance of a single symptom, for example, spider veins, a dense, rough liver and an enlarged spleen may be the reason for further in-depth examination of the patient for liver cirrhosis.
It also happens that the disease manifests itself as a periodic increase in temperature, decreased performance, after which bleeding gums and signs of dyspepsia occur. However, the increase in bilirubin in liver cirrhosis with asymptomatic course will be insignificant in the initial stage and pronounced in the stage of advanced clinical manifestations.
Liver pathology is so multifaceted that independent diagnostic assumptions and taking medications are categorically unacceptable without a specialist doctor. If you notice any symptom that may indicate liver disease, you should consult a doctor. Further prognosis and success of treatment depend on early detection of the disease.
Liver cirrhosis is a progressive liver disease characterized by a restructuring of the normal structure of the liver, resulting in impaired liver function, and the subsequent development of liver failure and portal hypertension.
What is cirrhosis of the liver?
Due to the death of liver cells under the influence of various damaging factors, normal liver tissue is replaced by fibrous tissue with the formation of nodes and restructuring of the entire structure of the liver. Violation of the liver structure leads to disruption of all its functions.
In economically developed countries, cirrhosis is one of the six main causes of death in patients aged 35 to 60 years, accounting for 14-30 cases per 100 thousand population. About 300 thousand people die from liver cirrhosis every year in the world, and over the past 10 years the frequency has increased by 12%. Asymptomatic cirrhosis occurs in 12% of patients suffering from chronic alcoholism.
It is more often observed in men: the ratio of men to women is on average 3:1. The disease can develop in all age groups, but more often after 40 years.
Causes of liver cirrhosis
— Viral hepatitis (B, C, delta, G). The most cirrhotic viruses are C and delta, and the hepatitis C virus is called the “gentle killer”, because it leads to liver cirrhosis in 97% of cases, while the disease does not have any clinical manifestations for a long time;
— Autoimmune hepatitis (when the body perceives its own cells as foreign);
— Alcohol abuse, the disease develops 10-15 years from the start of consumption (60 grams/day for men, 20 g/day for women);
— Metabolic disorders (hemochromatosis, Wilson's disease, alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency, etc.);
— Chemical toxic substances and medications;
Types of cirrhosis
There are 3 more types of liver cirrhosis, which are classified according to their clinical course, since not everyone has the same course of this disease. There are portal, biliary hypertrophic and mixed types of cirrhosis. Treatment is also different. The portal type is characterized by increased pressure in the hepatic venous system. Signs of this type of liver cirrhosis:
- bleeding from the nose and during bowel movements;
- blood impurities in vomit;
- loose stools;
- bloating;
- abdominal enlargement due to ascites. Also because of this, a venous network appears around the navel;
- weight loss resulting in complete cachexia;
- loose skin;
- low blood pressure.
It is characteristic that in the portal stage of cirrhosis the patient does not have jaundice. This cirrhosis can last from 6 months to 2 years. As a result of this type of disease, hepatic coma often occurs, and death can occur from acute bleeding.
Biliary hypertrophic cirrhosis is longer lasting, so it is considered favorable. It lasts from 5 to 8 years. Symptoms of biliary type liver cirrhosis:
- yellowness of the skin;
- xanthelasmas (yellowish growths), which are localized on the eyelids, chest, face;
- severe itching.
These symptoms are caused by stagnation of bile and a high concentration of bile pigments in the blood. Death in biliary cirrhosis occurs from bleeding.
The mixed type is the most severe form of cirrhosis, since it occurs with complications and symptoms are present from both portal and biliary cirrhosis.
Appearance of the abdomen with cirrhosis at the last stage
Big belly and prominent veins
During the first stage, notes Prokishechnik.Ru, it is problematic to detect obvious symptoms and respond in a timely manner. With the development of liver cirrhosis to the last stages, external signs become clearly visible. You can see them in photos of people with this diagnosis.
Patients with liver cirrhosis begin to experience stomach problems, discomfort, possible nausea, and loss of appetite. Ulcers may bleed and intestinal spasms may appear. In this case, a change in the structure and color of the stool is observed, and an unpleasant odor comes from the mouth.
Fluid accumulates in the stomach, the volume of which can reach 26 liters. The skin acquires a yellowish tint and becomes rough. In the final stages, the stomach looks like a swollen ball. These symptoms are called ascites, which appear in the last stages of the disease.
Minor signs of cirrhosis
When examining a patient, the doctor pays special attention to minor signs of the disease:
- angiomas, which are located near the edge of the nose and corners of the eyes. Such formations may bleed;
- "varnished" tongue. At the same time, it is swollen, bright red and shiny. And also the red mucous membrane of the mouth;
- “liver palms” is an erythema that appears as red skin on the palms;
- spider veins located on the body above the navel. They look like spiders and during the period of exacerbation they are more pronounced, and during the period of remission they are less;
- atrophy of the genital organs;
- gynecomastia in men (female-type breast development);
- secondary sexual characteristics are less pronounced (hair growth in the axillary area, pubis).
Most of these symptoms occur due to hyperestrogenemia. At the same time, the liver affected by cirrhosis is not able to participate in the metabolism of the hormone estrogen. And also in the body there is an accelerated peripheral conversion from androgens to estrogens.
Also, patients with cirrhosis can be recognized by their appearance, but not at an early stage. They are characterized by a thin face with pronounced cheekbones, erythema in the cheekbone area, and a subicteric and unhealthy complexion. Lips are red and bright. Also a sign are dilated capillaries on the face. With cirrhosis, the limbs atrophy and become thin, but the lower limbs are often swollen.
Symptoms of diseases based on the color of stool
Perhaps modern young people do not know, but people did not always determine diseases based on test results. Until now, in eastern countries there are diagnostic practices based on external signs of a person - by the condition, color and size of the tongue, nails, hair, by the iris of the eye and even by urine and feces. The color of stool can be a symptom and tell a lot. Let's consider what diseases can be identified by the color of stool.
Symptoms of what diseases can be determined by the color of stool?
Green stool can occur in those who have been taking antibiotics or medications containing iron for a long time. Green stool may appear due to an overdose of a laxative. If the person himself looks pale with a greenish tint to his skin, then he may have gastroenterological infections.
Orange stool may make a person think there are blood particles in the stool. But most likely, the day before he ate a lot of foods that contain beta-carotene - for example, carrots, apricots, pumpkin, sweet potatoes, mangoes. The same effect occurs from consuming vitamin A in large quantities.
Diagnostic signs of cirrhosis
How to determine liver cirrhosis using diagnostic methods? Already during the examination, the doctor can suspect cirrhosis by palpation. Namely, if the liver and spleen are enlarged. The liver is compacted, tuberous, with pointed edges and is palpable slightly below the costal arch, and the left lobe reaches the left hypochondrium. Felt below the xiphoid process. With large-nodular liver disease, the doctor may feel some nodes during palpation. After the examination, the specialist will send the person for laboratory tests. These are general and biochemical blood tests.
Signs:
- AST and ALT levels may increase;
- increased bilirubin levels;
- decrease in albumin, total protein, urea and cholesterol;
- decreased prothrombin index;
- increased gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase;
- reduced polypoprotein A1;
- elevated leukocytes and ESR during exacerbation of the disease and/or if an infection is activated in the body against the background of cirrhosis;
- the blood contains creatine phosphokinases, fibrin and active aminotransphenases.
In the results of serological tests, you can see signs of the disease in the form of the presence of various antibodies. Namely, anti-smooth muscle, anti-mitochondrial, hepatitis antibodies and antinuclear. A general urine examination will reveal elevated red blood cells, protein, and casts in the patient.
When examining stool, characteristic signs of cirrhosis are discoloration, undigested parts of food, the presence of fats and fibers are visible. And also quite often there are eggs of pinworms, roundworms, amoebas or lamblia.
An ultrasound will show fibrous foci, organ size, and enlarged veins. CT or MRI provide a complete picture of the organ. Its sections and all signs of cirrhosis will be visible in the picture.
Complications
Due to cirrhosis of the liver, disorders develop in other organs. Hepatorenal syndrome. This syndrome appears when the kidneys are damaged. Quite often, kidney failure begins to develop. At the same time, bleeding from the esophagus and stomach only intensifies. And:
- high blood pressure;
- rapid development of oliguria;
- azotemia. It indicates severe liver damage and possible imminent death. In this condition, the concentration of nitrogenous products in the blood is increased due to protein metabolism.
Why is it so important to monitor the color of your urine?
Abnormal bowel movements and urination should alert patients. Be sure to monitor the frequency of trips to the toilet, the characteristics of the urge, pain during urination, the color of urine, and the presence of foreign impurities in it.
Doctors recommend that people over 30 years of age undergo monitoring once a month. To do this, you need to urinate in a transparent container and evaluate the appearance of the liquid. If something worries you, you can safely go to the doctor. Do not think that a specialist will laugh at you if you complain about a non-standard shade of urine.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UjyA8zIZQj0
If everyone is responsible and attentive to their own health, then the number of identified cases of liver cirrhosis will noticeably decrease. Sometimes the unusual color of urine is the only symptom by which it is generally possible to determine the presence of disturbances in the functioning of the organ.
Disorders of the digestive system
In cirrhosis, concomitant reflux is often diagnosed - esophigitis. In this case, the person is bothered by frequent belching of both air and stomach contents, heartburn, and a localized burning sensation behind the sternum. In this case, the mucous membrane of the esophagus and the cardiac part of the stomach may be affected.
Gastritis is a very common occurrence in cirrhosis. In this case, dull pain in the epigastrium appears, which is activated after eating, attacks of nausea, heaviness in the pit of the stomach, frequent belching and loss of appetite.
Damage to the endocrine system
Half of the patients experience an increase in insulin in the blood. Since carbohydrate metabolism is disrupted, tolerance to carbohydrates decreases. Some patients develop diabetes mellitus after 5 years of cirrhosis. In this case, the treatment of this disease is very difficult.
With cirrhosis of the liver, the body's production of testosterone in men decreases, and the production of estrogens, prolaetin and globulin also increases. Signs of this violation may include:
- atrophic processes in the testicles and penis;
- reduction in the manifestation of secondary sexual characteristics;
- decreased libido and sexual weakness;
- gynecomastia.
Women may have menstrual irregularities, breast atrophy, and decreased libido.
Peritonitis
Spontaneous bactericidal peritonitis can occur in the decompensated stage of cirrhosis, the treatment of which is complicated and does not give positive results. It develops against the background of ascites. Characteristic symptoms:
- fever, chills;
- sharp abdominal pain;
- weakened bowel sounds;
- low blood pressure;
- tense anterior abdominal wall.
This complication develops in only 2-4% of patients, and with this disease the mortality rate is almost 90%.
alkogolu.net
Manifestations of cirrhosis in the early stages
At the onset of the disease or the compensation stage, signs of liver cirrhosis often go unnoticed. At this time, the destruction of blood vessels, parenchyma and inflammatory-necrotic processes are not yet so strong.
Outwardly, this may resemble a condition that doctors usually call asthenic syndrome:
- general malaise;
- rapid fatigue and weakness;
- difficulty concentrating;
- decreased appetite.
Unfortunately, at this stage people are in no hurry to see specialists, although biochemical tests would not be difficult to establish the presence of cirrhosis.
Is it possible to get rid of cirrhosis?
Nowadays, not one, but several options for effective treatment of cirrhosis have been invented. You should know that the treatment process can take quite a long period. All methods must be used comprehensively, and not separately from each other. It is with this approach that experts make favorable predictions for a positive result.
Possible treatments for cirrhosis:
- Diet No. 5. A popular type of diet, the actions of which are aimed at restoring liver function and normalizing urination. The main thing in it is considered to be 5 meals a day and the complete exclusion of fatty, fried foods, and refusal to drink alcoholic beverages. It is important to observe the required amount of liquid consumption, but not less than one and a half liters. When fluid forms in the stomach, salt consumption is excluded.
- Treatment with drugs. In addition to a strict diet, drugs are prescribed that have the function of restoring liver cells. These include medications based on phospholipids and milk thistle extract. For viral hepatitis, antiviral drugs are prescribed.
- Surgical intervention. This procedure is carried out in case of inaction of other treatment methods, already at the last stage of the disease, when the liver becomes unable to perform its direct functions. The main purpose of the operation is transplantation of liver cells.
- Traditional methods. They are not always effective, but still the majority is inclined to use them in the treatment of cirrhosis. These include: cleansing the liver with a decoction of oats, using infusions based on honey, lemon and garlic, drinking natural vegetable juices from beets, carrots, potatoes, cucumbers, tomatoes and sauerkraut. Also popular methods are: jam from dandelion flowers, decoction of corn silk, treatment with black radish juice, adding horseradish and boiled or raw pumpkin to food. Infusions based on the herbs cornflower, St. John's wort, yarrow and willow bark are considered effective.
We suggest you read: Least harmful alcohol for the liver
Unfortunately, it is not possible to completely get rid of the disease. It will have an impact one way or another, affecting the health of not only the liver, but also other important functions of the body.
In order not to one day be “pinned to the wall” by cirrhosis of the liver, it is important to monitor the changes occurring in the body. Preventive measures must be followed, such as:
- ensuring water balance;
- annual testing to exclude hepatitis B and C infection;
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle;
- giving up alcohol and smoking;
- following a diet, maintaining normal lipid metabolism;
- reducing the amount of medications used, especially antibiotics;
- taking vitamins and healthy foods that improve liver function;
- choosing an active and healthy lifestyle.
It is very important not to ignore the first signs of liver cirrhosis, because it is in the initial stages that the disease can be treated, without further negative consequences.
Further development of the disease
At the next stage of development of cirrhosis (subcompensation), an inevitable increase in destructive processes occurs, but a considerable part of the liver functions is still preserved.
The initial signs of liver cirrhosis are accompanied by new symptoms, which in themselves can often be considered as a secondary disease.
Namely:
- severe weight loss;
- discomfort, pain in the right hypochondrium, bitter taste in the mouth;
- periodic mild nausea, flatulence, belching of air or eaten food, alternating diarrhea and constipation;
- heaviness in the upper abdomen, a feeling of fullness even after eating a small amount of food;
- memory loss, impaired concentration;
- in women - deviations in the menstrual cycle, in men - erectile dysfunction;
- dryness and decreased elasticity of the skin;
- baldness (including legs and groin areas);
- sometimes pain in the back, ribs
Fatigue becomes excessive, a person feels drowsy even after a long sleep, and performance decreases. Often, patients leave themselves without treatment, attributing the first signs of liver cirrhosis to habitual gastritis or a stone in the bile ducts.
Further, the disease receives more and more distinct signs. And although it is generally accepted that there are no specific symptoms that are characteristic only of cirrhosis, there are those that most likely indicate liver damage.
Specific symptoms:
- jaundiced skin tone; The whites of the eyes and mucous membranes also turn yellow. Sometimes jaundice appears brightly, but it can also be mild;
- skin itching; the symptom develops due to the entry of bile acids into small vessels under the skin. (Normally, bile acids are constantly produced and processed by the liver; if the organ is damaged, their amount becomes excessive);
- redness of the palmar surface (the so-called “liver palms”), hands or some fingertips (palmar erythema); this is caused by an increased level of bilirubin in the blood;
- small, red interlacing of vessels (“stars”). Their typical location is in the shoulder girdle due to expansion (hypertension) of the superior vena cava;
- bruises of varying sizes, often for no apparent reason (both due to blood clotting disorders and weak blood vessels); minor spontaneous hemorrhages and nosebleeds may occur;
- periodic fevers, despite the absence of colds, elevated temperature (up to 38°C);
- the patient feels that the liver is “interfering” with him; by touch one can determine its enlargement and thickening, lumpiness; a sharp, protruding leading edge is noticeable (40% of cases);
- a person easily catches infectious diseases;
- a blue vascular pattern appears on the abdomen, reminiscent of intertwined branches (“jellyfish head”);
- hemorrhoids with bleeding and varicose veins;
- bright pink and even crimson color of the tongue; the tongue itself is smooth and shiny, as if varnished;
- cloudy and brown urine and light-colored feces;
- In men, the mammary glands become noticeably enlarged (gynecomastia).
Often, a patient with cirrhosis can also be recognized by the bright color of the skin, the unnaturally smooth border of the lips - they look like “varnished”. Their bright red color and the appearance of “stars” are associated with an excess of estrogen and serotonin in the blood.
The abdomen may bulge due to the accumulation of water in the abdominal cavity. Against the backdrop of severe weight loss, this becomes especially noticeable. The skin of a typical patient with cirrhosis is dry, pigmented, and traces of scratching are visible. A person may notice intolerance to fatty foods and alcoholic drinks.
As for such a common symptom as jaundice, it must be said that for patients with alcoholic cirrhosis at the very beginning it manifests itself only in 12% of cases, becoming noticeable in the terminal stage.
Thus, knowing how liver cirrhosis manifests itself, in the presence of a complex of similar symptoms, it can be distinguished from other diseases.
Light feces
Every person knows what color of stool is normal for him, and notices when the excrement takes on an unusual color. Light-colored feces, both in a child and an adult, may indicate diseases that cannot be ignored in order to avoid serious consequences. It is important to pay attention to the symptoms that accompany changes in stool color.
Why is stool light in color: possible reasons
The stool of a healthy person consists of the remains of food consumed over the last 2-3 days. In normal condition, the color of feces varies from light brown to dark brown, the consistency is dense, there is no specific odor or foreign impurities. If you notice the appearance of unusually light-colored stools, you should not make hasty conclusions and panic. We need to identify possible causes. Changes in stool color are caused by:
In an adult
Lightening of excrement in an adult may be associated with eating large amounts of fatty foods. For example, sour cream or butter. At the same time, a change in the color of stool does not cause discomfort to a person. Review your diet, eliminate fatty foods and stick to a healthy diet. After a few days, the stool returns to normal.
The lightening of feces is affected by taking medications. For example, antibiotics, antifungals, oral contraceptives. You should stop taking medications and contact your doctor to prescribe therapeutic measures. A great danger is a change in the color of the stool, accompanied by an increase in body temperature and pain of varying intensity in the abdominal area.
During pregnancy

The color of stool indicates the functioning of the liver and pancreas. During pregnancy, a woman's organs work under increased stress. Lightening of feces is associated with a pathological condition accompanied by a failure of the digestive process. The source of light-colored stool in pregnant women is dysbacteriosis or excessive use of multivitamin complexes. You should contact your doctor to prescribe the necessary treatment.
What disease can light-colored stool be a sign of?
Lightening of feces is caused by diseases that disrupt the normal functioning of the liver, pancreas and gastrointestinal tract. Try to evaluate how you feel. How has your health changed in recent days, weeks, months? Remember what illnesses you suffered in the recent past. If light-colored stool is associated with diseases, the following symptoms are often observed:
- general weakness;
- increased body temperature;
- stomach ache;
- yellow color of the skin and eye sclera;
- dark urine;
- nausea, vomiting;
- flatulence;
- loss of appetite and weight loss;
- unexplained increase in abdominal volume;
- skin rash.
If you notice an unusual change in the color of your feces, accompanied by a sharp deterioration in your health, immediately consult your doctor. He will give you a referral for tests, on the basis of which he will identify the cause of lightening of the stool and prescribe appropriate therapy. Ignoring your unsatisfactory condition is extremely dangerous; it can be a sign of serious diseases:
- Hepatitis A. The development of inflammatory liver disease caused by toxic, infectious or alcohol poisoning is indicated by nagging pain in the right side. upset stomach, yellow skin tone. Without treatment, the disease leads to cirrhosis of the liver.
- Cholecystitis. Inflammation of the gallbladder is accompanied by acute abdominal pain, decreased appetite, increased body temperature, and nausea. Feces with cholecystitis have a liquid consistency, sometimes with remnants of undigested food.
- Pancreatitis. Inflammation of the pancreas occurs as a result of poor diet, alcohol abuse, infectious diseases of internal organs and taking medications. The acute phase of pancreatitis is accompanied by cutting pain in the abdomen, vomiting, and diarrhea.
- Crohn's disease. A chronic disorder of the digestive system, caused by allergic reactions, psychosomatic and infectious diseases, is manifested by lightening of stools, vomiting, increased body temperature, and the frequent appearance of blood in the feces.
- Oncological diseases of the digestive tract. The development of malignant neoplasms on internal organs is asymptomatic. The first signs appear when the tumor reaches a certain size. Among the symptoms, doctors identify: pain in the abdominal cavity, constipation or diarrhea, vomiting, lack of appetite, and sudden weight loss.
Light brown stool
Human consumption of predominantly plant foods leads to lightening of feces. This is not a pathology and does not pose a risk to your health. With the accelerated passage of digestive masses through the colon, the stool becomes light brown in color. The introduction of protein products into the diet and fractional meals normalize the functioning of the digestive tract.
Light green
Human feces acquire an unnatural hue due to excessive consumption of food dyes, which are found in large quantities in sweet water, alcoholic drinks, and sweets. Addiction to herbal preparations and dietary supplements leads to stools turning greenish. After giving up foods, the color of stool is restored within 3-5 days. In other cases, green feces are a symptom of diseases:
- Dysbacteriosis. Violation of the intestinal microflora is accompanied by liquid feces with a specific putrefactive odor.
- Acute enterocolitis. Inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract in acute form is accompanied by discomfort and sharp pain in the abdomen. diarrhea, vomiting. The stool has a green tint with traces of pus.
- Infectious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract are manifested by general weakness of a person, nausea, and increased body temperature. The stool turns light green and contains blood, pus, or mucus.
Light yellow
The color of feces is affected by bilirubin, secreted along with bile by the liver. From a medical point of view, yellow stool in a healthy person is normal. You should be concerned about beige stool. This may mean that the liver is not producing bilirubin unstably or that the bile ducts are narrowed. To identify the causes, contact your doctor, who will conduct an examination and prescribe appropriate therapy.
Dark urine and white stool
Gray color of stool in combination with urine the color of strong tea is an alarming sign of the acute phase of hepatitis. Inflammation of the liver leads to disruption of the function of bile formation, which causes whitening of stool. With hepatitis, the bilirubin produced by the body is excreted through the kidneys and skin, so the urine becomes dark and the skin turns yellow.
What to do and what treatment to take
Complications and further addition of symptoms
At the last, terminal stage of cirrhosis, the liver experiences almost complete degeneration and loses its functions.
Manifestations of the disease take on not just the character of individual external symptoms, but represent quite severe conditions.
Hepatic encephalopathy (brain damage)
The cause of brain dysfunction in cirrhosis is the powerful effect of toxins that the patient’s liver is not able to neutralize.
Signs of brain damage:
- deterioration of memory and speed of thinking
- disturbances of consciousness and intelligence, changes in behavior
- nerve and muscle disorders
Patients may sleep for days and stay awake all night. Irritability and inability to concentrate turns them off from the normal rhythm of life.
Hepatic encephalopathy is sometimes impossible to determine by yourself, and it is detected by a doctor using special tests. At extreme levels of development, it can cause coma (unconsciousness).
Edema
With cirrhosis, excess salt and water accumulate in the body. At first, only the legs and then the entire abdominal area swell.
Swelling, which often appears in the evening, is called spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Their reason is the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria in the abdominal part.
This complication is life-threatening, although in half of the cases it occurs without symptoms. The general condition may worsen: fever with chills, abdominal pain, problems with appetite and diarrhea may appear.
Water in the abdominal cavity (ascites)
In later stages, numerous scars and tissue compression lead to a significant accumulation of free fluid in the abdominal cavity. The load on the kidneys becomes enormous, which is noticeable by urinary retention and dark, brownish urine.
Dilated saphenous veins
This syndrome is called portal hypertension and is extremely dangerous, leading not only to a specific “pattern” on the chest and abdomen, but to serious bleeding and ascites.
Vomiting blood
As a result of bleeding, vomiting occurs, which looks like coffee grounds mixed with blood. Accompanying symptoms are dizziness, fainting or loss of consciousness. Bleeding may occur around the liver, esophagus, or stomach.
Fever
An increase in temperature and a febrile state in the terminal stage can be caused by two reasons:
- necrosis of liver cells and intoxication (self-poisoning);
- concomitant infection of the biliary tract or enteritis.
In the final stage of cirrhosis, signs of dystrophy develop - weight loss, hypovitaminosis. The liver decreases in size.
.
muzhzdorov.ru
It is important to know! Hepatitis can be treated with a simple folk remedy, just in the morning on an empty stomach... Read more » Source: pechen5.ru
White diarrhea in liver diseases
Diarrhea is loose, unformed stool in an adult. If the small intestine is affected, then diarrhea repeats up to six times a day with food particles, with lumps, and with changes in the large intestine, stools up to 12 times a day, and sometimes more. With diarrhea, there is pain in the lower abdomen, like colic, and there may be a false urge to defecate (tenesmus).
There are acute diarrhea, which lasts two weeks, and chronic diarrhea, which lasts more than three weeks. If defecation occurs involuntarily and false urges appear, this indicates a severe course of the disease.
In this case, dehydration develops, electrolyte imbalance develops, and if vomiting occurs, the patient may die. When an adult has loose stool more than 20 times, it is necessary not only to eliminate it, but also to begin to replenish lost fluid.
If an adult is conscious and can drink, then give him saline solutions, and if he cannot drink, then the drugs are administered intravenously.
When diarrhea begins, fermentation processes develop in the intestines. This causes the color and smell of stool to change. If the color turns green, then carbohydrates are fermenting; when diarrhea is white, lipids are poorly digested.
All liver diseases appear with changes in its structures, which do not go beyond the anatomical structure of the organ. Hepatocytes, liver lobules, arterial and venous vessels, as well as bile ducts may be affected. The most common liver diseases in adults include:
- Inflammation of an organ for the first time or a functional change in liver cells (hepatitis, unclear hepatomegaly, fatty hepatosis, tuberculosis or syphilitic damage to the organ, abscess, alcoholic steatohepatosis).
- Damage due to trauma (rupture, stab wound).
- From the affected vessels (venous thrombosis, purulent inflammation of the portal vein, portal hypertension, pathological changes in blood vessels).
- Disruption of the intrahepatic bile ducts.
- Neoplasms, cysts, sarcomas.
- Damage by parasites.
- Hereditary anomalies.
- Diseases that cause the destruction of a parenchymal organ using one’s own immunity.
- Structural and functional rearrangements and their complications (cirrhosis, liver failure, coma, parenchymal jaundice).
Almost all pathological processes in the liver (the largest digestive gland) end in cirrhosis.
Cirrhosis of the liver
This is a chronic, rapidly developing change in the structure of the liver tissue and blood vessels. There is a decrease in the function of hepatocytes and their number, and the connective tissue, on the contrary, grows.
Regeneration nodes form, which lead to liver failure. This disease is one of the most common causes of death in adults.
There cannot be one reason for the development of such a pathology, and it is possible to find out why it all started only after a full examination.
At first, there may not be any clinical manifestations; they occur in only 10% of patients.
Over time, pain appears in the right hypochondrium, which intensifies in an adult after physical activity, or when taking fatty and spicy foods, or alcohol. Nausea and vomiting with blood often develop due to dilation of the esophageal veins, and the temperature rises. When eating fatty foods, light diarrhea appears. There is general malaise, weakness, the patient is losing weight, the stomach is distended, skin itching, and in women the menstrual cycle is disrupted. The skin becomes dry, flaky, and a jaundiced discoloration of the skin gradually develops. The gland itself is enlarged, dense to the touch, lumpy, with a sharp edge. The joints suffer, limiting the patient’s movements.
Stool color in cirrhosis
During the decompensation stage, diarrhea is often white. This happens because the coloring pigment does not enter the intestines. When the liver is working properly, hemoglobin is separated into substances by enzymes and forms the intermediate product biliverdin. It is converted into bilirubin, which is free at first, it is harmful, but there is little of it in the blood.
It is transformed in the largest digestive gland and becomes bound and enters the intestines with bile and becomes urobilin, it enters the blood and is excreted from the body by the kidneys, while coloring the urine yellow. And stercobilin is formed in the intestines, which provides stool with a certain color.
And with cirrhosis, bilirubin remains free in the blood for a long time and is excreted through the kidneys, that is, it does not enter the intestines and does not color the stool, it remains light. White diarrhea indicates functional impairment. Also, from cirrhosis, there may be blood clots in white feces; they occur when hemorrhoidal veins dilate.
Blood in the stool will turn black due to internal bleeding, and the vomit will be the color of “coffee grounds.” Such changes occur with varicose veins due to disease.
When stool becomes light-colored
- Hepatitis is a chronic and inflammatory disease. Hepatitis manifests itself as pain in the right hypochondrium, the pain is aching, the skin becomes yellow, and the stool becomes light yellow. If adequate treatment is not applied, cirrhosis develops.
- Cholecystitis is an inflammation of the gallbladder that often becomes a complication of hepatitis.
There is pain in the abdomen, namely the pain is localized in the right hypochondrium. There is no appetite, nausea, diarrhea appears, and body temperature rises. Diarrhea occurs with pieces of undigested food and even white mucus. With cholecystitis, gallstones often develop. - Pancreatitis is an inflammatory disease of the pancreas that occurs due to poor nutrition, alcohol abuse, medications and infections of other organs. The acute process is accompanied by severe girdling pain in the abdomen, nausea, fever, frequent, light-colored stools.
- Crohn's disease is an inflammation of the entire digestive system, characterized by various manifestations. The stool will be white or bloody. The same can be true for oncology.
Diagnosis and treatment
The doctor conducts a survey of the patient, finds out when the white stool began, after which, how many times a day, whether there was nausea, abdominal pain, in what place. Palpates the abdomen to determine the location of pain, and also listens and taps it.
Laboratory testing is required. A stool coprogram is prescribed, it is examined under a microscope, its appearance, structure, and composition are determined. A bacteriological analysis of stool is also done.
And, as usual, general and biochemical blood tests are prescribed, which allow us to find out what is causing the diarrhea.
Liver cirrhosis can only be treated in a hospital under the constant supervision of medical professionals. To improve the functioning of hepatocytes, hepatoprotectors are prescribed, and it is also necessary to eliminate provoking factors (for example, stop drinking alcohol or taking medications).
The daily routine must be scheduled, a gentle diet and bed rest must be prescribed. They use agents that improve metabolism in the gland cells; for bleeding - blood-substituting solutions, hormonal drugs, detoxification therapy. When the temperature rises - antipyretics.
Liver transplantation for cirrhosis is done as a last resort.
Treating diarrhea at home
At home, diarrhea is treated only in adults when there are no complications or dehydration. It is necessary to replenish the volume of lost fluid and essential microelements. To do this, use water with added minerals, you can take rigedron or ringer solution, but you cannot use carbonated drinks, juices, or sweet compotes.
The liquid should be drunk in a volume of 300 ml after each act of defecation; if nausea suddenly occurs after drinking the solutions, you should go to the hospital. The diet includes foods that strengthen (boiled rice, crackers, etc.).
Natural jelly is also good, the starch in which not only contains a large amount of useful vitamins and acids, but also easily improves intestinal function.
Source: https://ponosa.net/lechenie-diarei/belyy-ponos-pri-zabolevaniyah-pecheni.html